
How to Use 3.7V Rechargeable Li-ion Nokia Battery: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 3.7V Rechargeable Li-ion Nokia Battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with 3.7V Rechargeable Li-ion Nokia Battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Nokia BL-5C 1020mAh 3.7V 3.8Wh is a compact, rechargeable lithium-ion battery designed for use in portable electronic devices. Manufactured by Nokia, this battery is known for its high energy density, long cycle life, and reliable performance. It provides a nominal voltage of 3.7V and a capacity of 1020mAh, making it suitable for applications requiring lightweight and efficient power sources.
Explore Projects Built with 3.7V Rechargeable Li-ion Nokia Battery
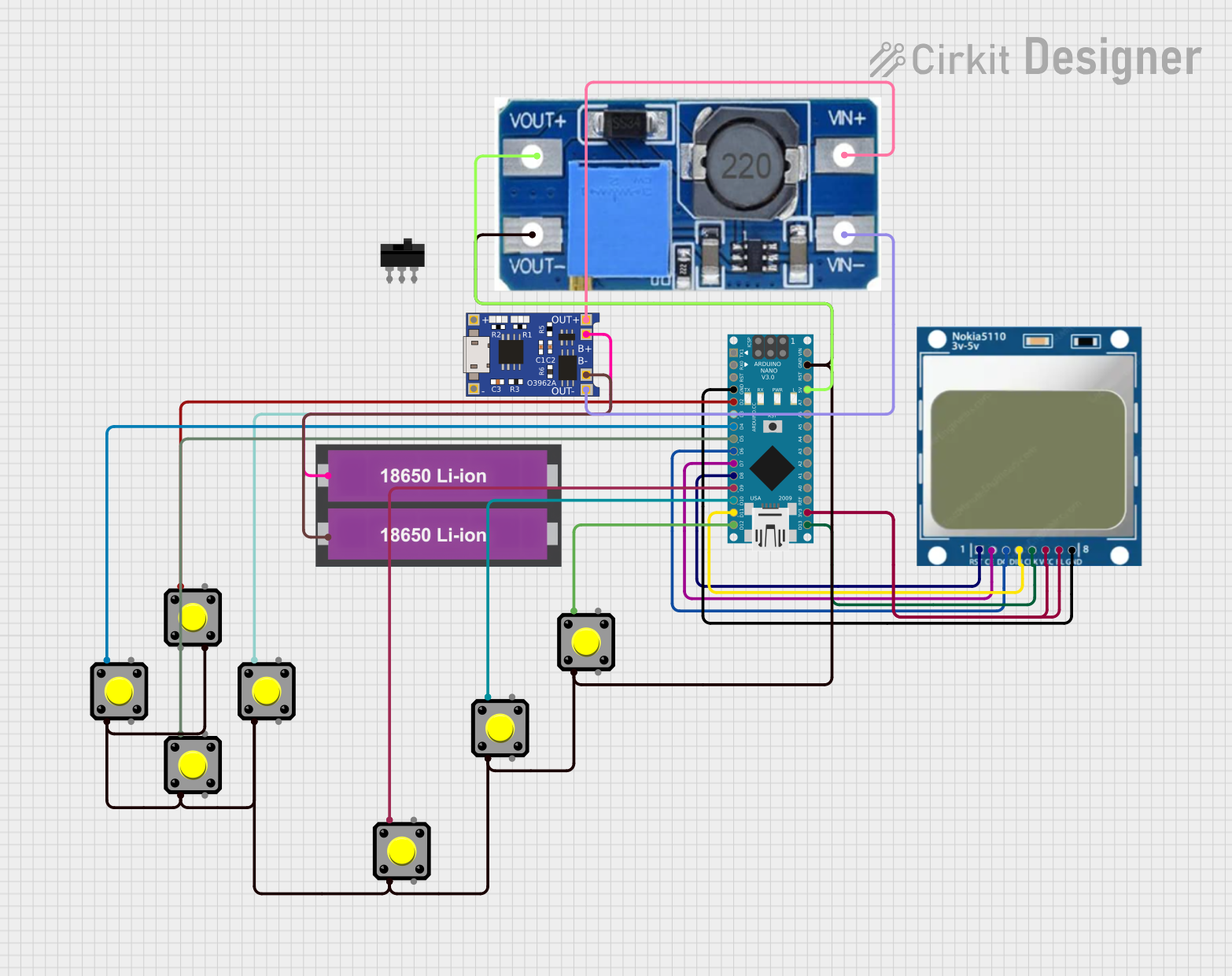
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer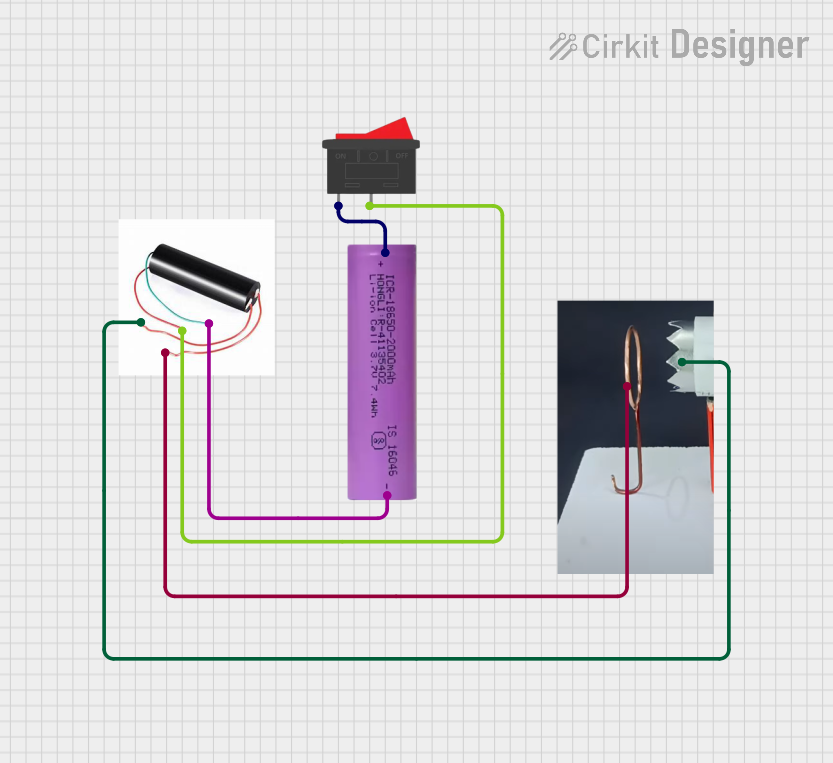
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer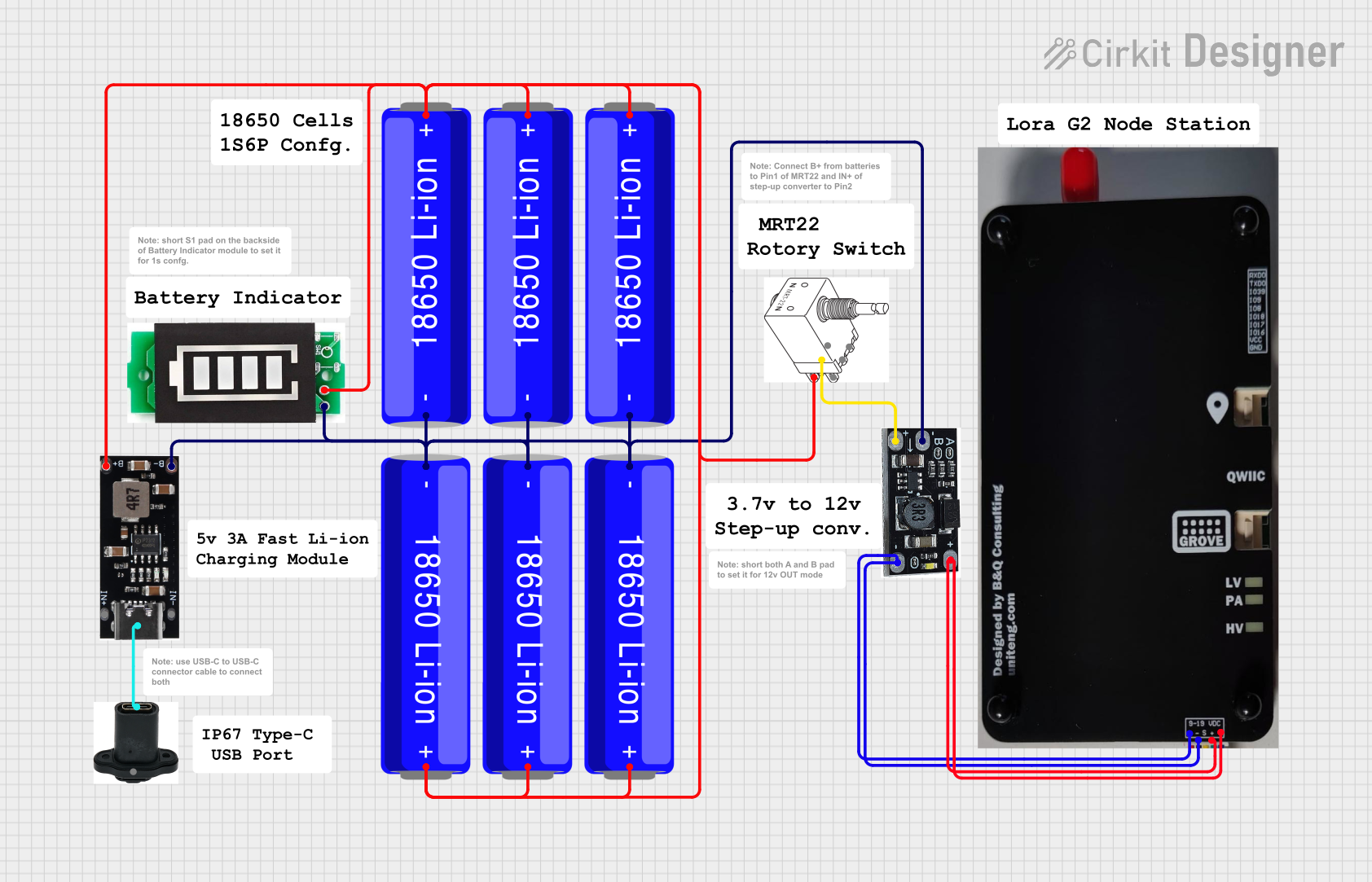
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 3.7V Rechargeable Li-ion Nokia Battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Mobile phones and smartphones
- Portable media players
- DIY electronics projects
- Backup power for small devices
- Robotics and IoT applications
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Nokia BL-5C battery:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Nokia |
| Part ID | BL-5C |
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7V |
| Capacity | 1020mAh |
| Energy | 3.8Wh |
| Chemistry | Lithium-ion (Li-ion) |
| Dimensions (L x W x H) | 53mm x 34mm x 5.5mm |
| Weight | ~22g |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2V (maximum) |
| Discharge Cutoff | 3.0V (minimum) |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to 45°C (charge) |
| -20°C to 60°C (discharge) | |
| Cycle Life | ~500 charge/discharge cycles |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The BL-5C battery has three terminals, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | B+ | Positive terminal for power output |
| 2 | B- | Negative terminal for power output |
| 3 | T | Temperature sensing pin (used for safety monitoring) |
Note: The temperature sensing pin (T) is optional and may not be used in all applications.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connection: Connect the positive terminal (B+) to the positive rail of your circuit and the negative terminal (B-) to the ground rail. If your application supports temperature monitoring, connect the T pin to the appropriate input on your circuit.
- Charging: Use a Li-ion battery charger with a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile. Ensure the charging voltage does not exceed 4.2V.
- Discharging: Avoid discharging the battery below 3.0V to prevent damage and reduce cycle life.
- Protection Circuit: For safety, use a battery management system (BMS) or protection circuit module (PCM) to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overcharging: Overcharging the battery beyond 4.2V can lead to overheating and potential safety hazards.
- Temperature Range: Operate the battery within the specified temperature range to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Storage: Store the battery in a cool, dry place at ~40% charge for long-term storage.
- Recycling: Dispose of the battery responsibly at an authorized recycling facility.
Example: Using the BL-5C with an Arduino UNO
The BL-5C can be used to power an Arduino UNO via its VIN pin. Below is an example of how to monitor the battery voltage using the Arduino's analog input:
// Example: Monitor BL-5C battery voltage with Arduino UNO
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to battery voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0; // Adjust based on your resistor values
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino UNO's reference voltage
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int analogValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read analog value from pin
float batteryVoltage = (analogValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to step down the battery voltage to a safe level for the Arduino's analog input (0-5V). For example, use two resistors in a 1:1 ratio to divide the voltage by 2.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Faulty charger or incorrect charging voltage.
- Solution: Verify the charger output is 4.2V and compatible with Li-ion batteries.
Battery Drains Quickly
- Cause: High current draw or aging battery.
- Solution: Check the load current and replace the battery if it has reached the end of its cycle life.
Overheating During Use
- Cause: Overcharging, short circuit, or excessive current draw.
- Solution: Use a BMS or PCM to protect the battery and ensure proper ventilation.
Arduino Reads Incorrect Voltage
- Cause: Incorrect voltage divider ratio or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the resistor values in the voltage divider and ensure secure connections.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use the BL-5C battery without a protection circuit?
A1: While it is possible, it is not recommended. A protection circuit ensures safety by preventing overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Q2: How long does the BL-5C battery last on a single charge?
A2: The runtime depends on the load current. For example, a 100mA load will last approximately 10 hours (1020mAh ÷ 100mA).
Q3: Can I charge the BL-5C with a USB charger?
A3: Yes, if the USB charger outputs 4.2V and is designed for Li-ion batteries. Avoid using chargers with higher voltages.
Q4: Is the BL-5C battery safe for DIY projects?
A4: Yes, as long as you follow proper safety guidelines, including using a protection circuit and avoiding overcharging or over-discharging.
Q5: How do I know if the battery is fully charged?
A5: The battery is fully charged when the charging voltage reaches 4.2V and the current drops to a minimal level (typically <50mA).