
How to Use GND: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with GND in Cirkit Designer
Design with GND in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
- The ground (GND) is a fundamental component in electrical and electronic circuits. It serves as a reference point for measuring voltages and provides a common return path for electric current. In most circuits, GND is considered the zero-voltage reference level.
- Common applications include power supply systems, signal grounding in communication circuits, and as a safety measure to prevent electrical shock in devices.
Explore Projects Built with GND
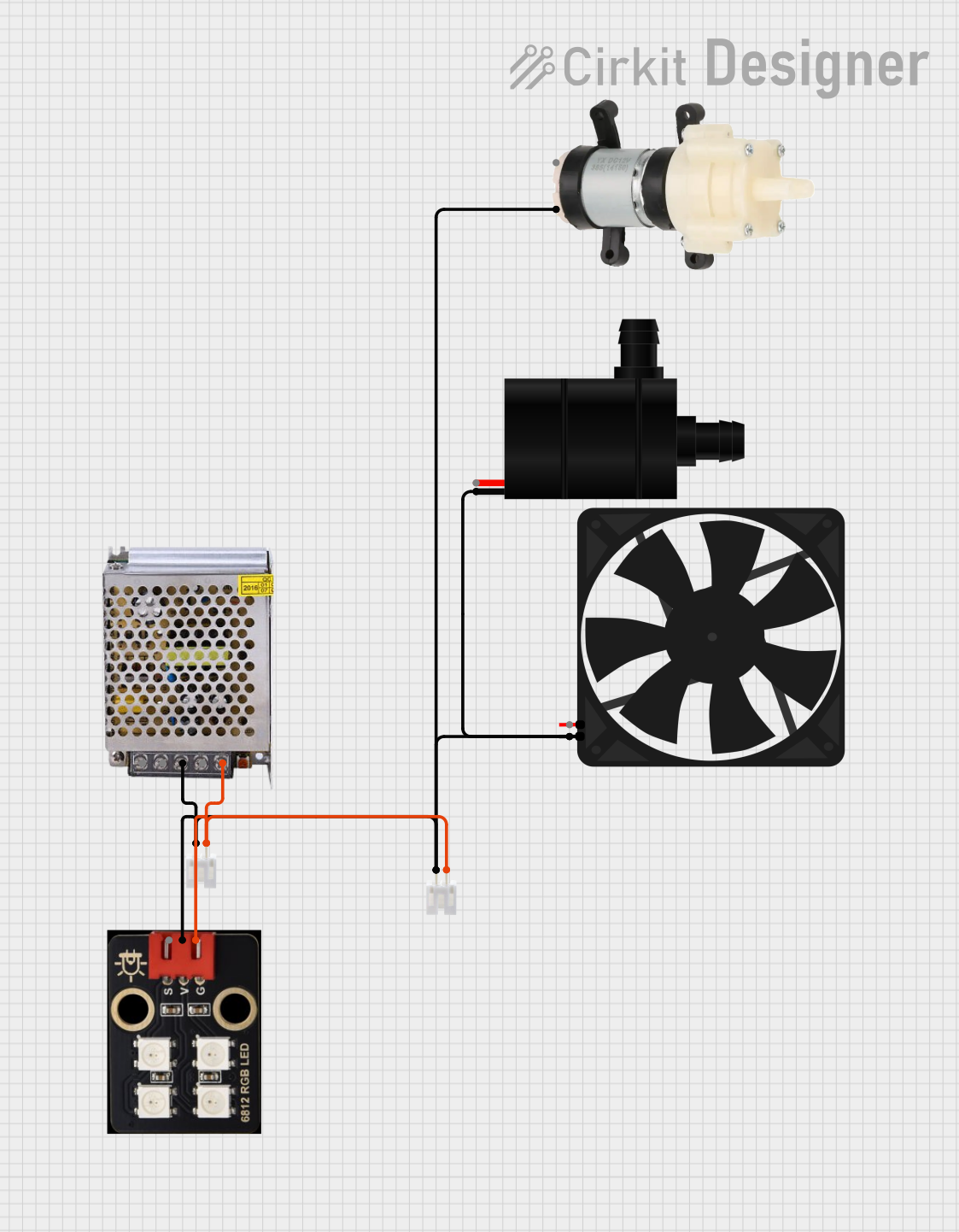
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer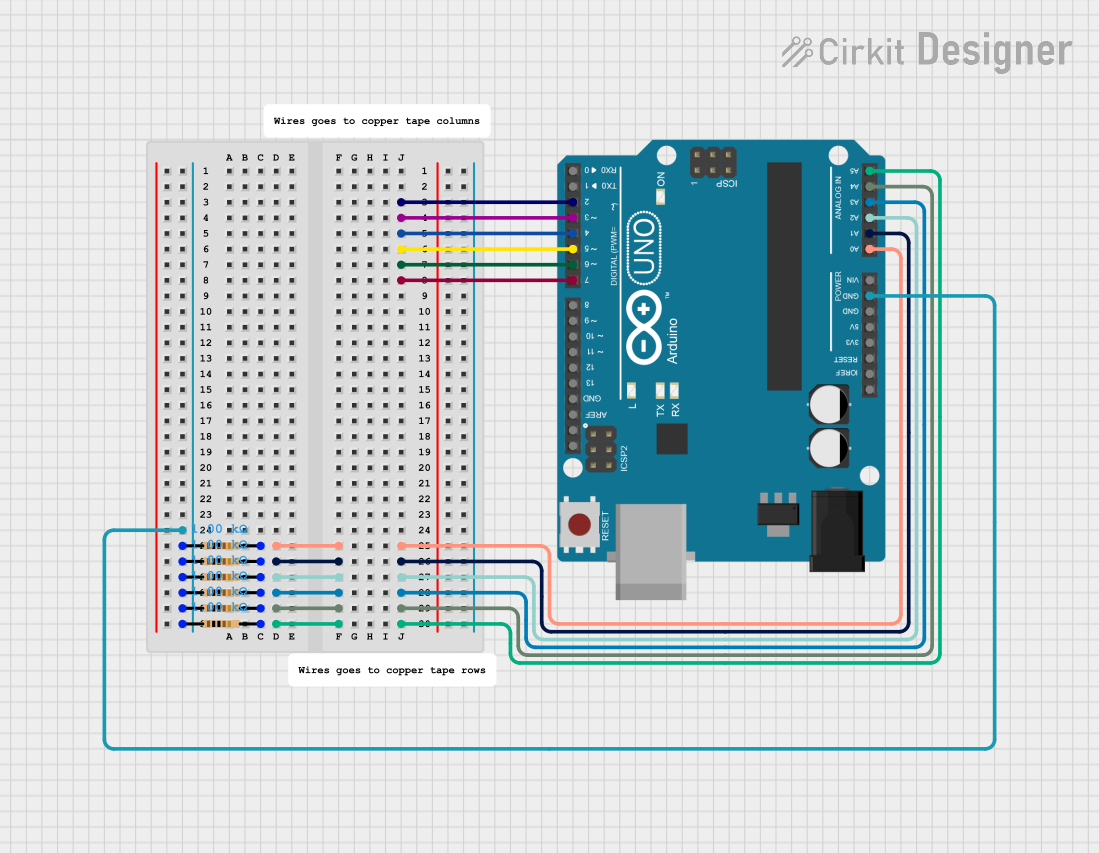
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with GND

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Type: Electrical reference point
- Voltage: 0V (reference level)
- Current Handling: Dependent on the circuit design and PCB trace width
- Polarity: Neutral (neither positive nor negative)
- Connection: Typically connected to the negative terminal of a power supply or to earth ground in some systems
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
While GND itself is not a physical component with pins, it is often represented in circuits as a connection point. Below is an example of how GND is typically used in common components:
| Component | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Regulator | GND | Ground connection for the regulator, serves as a reference for input and output |
| Microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) | GND | Ground pin to connect the circuit's common ground |
| Power Supply | GND | Negative terminal or reference point for the power supply |
Usage Instructions
How to Use GND in a Circuit:
- Identify the GND pin or terminal on your components (e.g., microcontroller, sensors, power supply).
- Connect all GND points in the circuit to establish a common reference level.
- Ensure that the GND connection is robust and has low resistance to avoid voltage drops.
Important Considerations:
- Always connect GND before powering the circuit to prevent floating voltages.
- Use a ground plane in PCB designs to minimize noise and improve signal integrity.
- Avoid creating ground loops, which can introduce noise and interference in the circuit.
Example: Connecting GND to an Arduino UNO: Below is an example of how to connect a sensor to an Arduino UNO, ensuring the GND is properly connected.
// Example: Reading a sensor value with proper GND connection
// Connect the sensor's GND pin to the Arduino's GND pin
// Connect the sensor's VCC pin to the Arduino's 5V pin
// Connect the sensor's signal pin to an analog input pin (e.g., A0)
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor's signal output
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the sensor reading
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the sensor value
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue); // Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues:
- Floating Voltages: If GND is not properly connected, components may behave erratically due to undefined voltage levels.
- Solution: Ensure all GND points are securely connected in the circuit.
- Noise in Signals: Poor grounding can introduce noise, especially in high-frequency circuits.
- Solution: Use a ground plane or thicker traces for GND connections.
- Ground Loops: Multiple GND paths can create loops, leading to interference.
- Solution: Design the circuit to have a single, unified GND path.
- Floating Voltages: If GND is not properly connected, components may behave erratically due to undefined voltage levels.
FAQs:
Q: Can I connect multiple components to the same GND point?
A: Yes, all components in a circuit should share a common GND to ensure proper operation.Q: What happens if GND is disconnected?
A: The circuit may not function correctly, and components could be damaged due to undefined voltage levels.Q: Is GND always 0V?
A: GND is considered the 0V reference point, but in some systems, it may not be directly connected to earth ground.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure proper use of GND in your circuits and avoid common pitfalls.