
How to Use 5V supply: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 5V supply in Cirkit Designer
Design with 5V supply in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The 5V supply is a power source that provides a constant voltage of 5 volts. It is one of the most commonly used voltage levels in electronics, powering a wide range of devices, including microcontrollers, sensors, and communication modules. Its reliability and compatibility make it a staple in both hobbyist and professional electronic projects.
Explore Projects Built with 5V supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer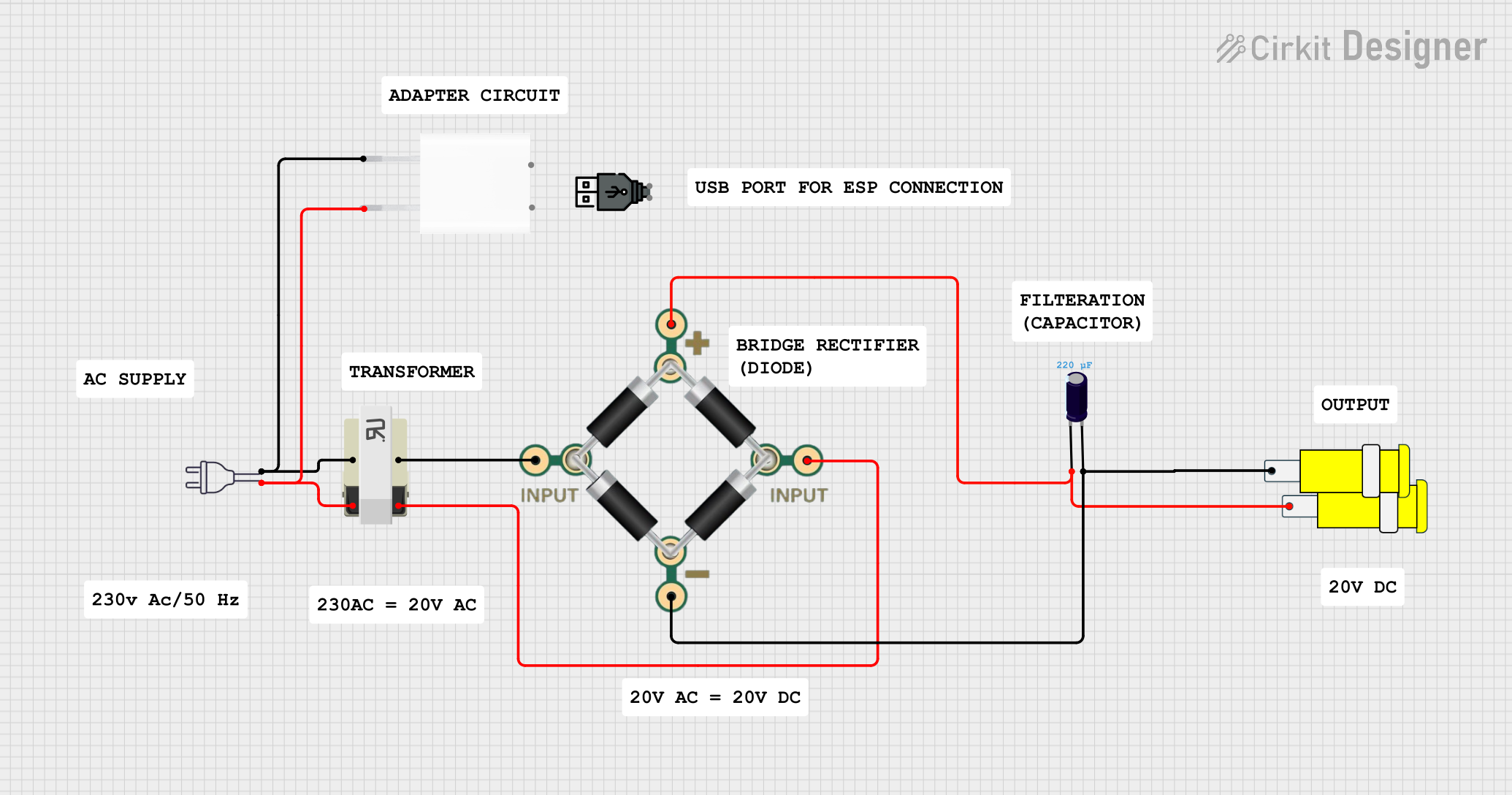
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 5V supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering microcontrollers such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and ESP32.
- Supplying voltage to sensors, actuators, and communication modules.
- Used in breadboard prototyping and small-scale electronic circuits.
- Providing power to USB-powered devices.
Technical Specifications
The 5V supply is available in various forms, such as regulated power adapters, USB ports, and voltage regulators. Below are the general specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Output Voltage | 5V DC |
| Input Voltage Range | Varies (e.g., 110-240V AC for adapters, or 7-12V DC for regulators) |
| Maximum Output Current | Depends on the specific supply (e.g., 500mA, 1A, 2A, etc.) |
| Regulation Type | Linear or Switching |
| Connector Type | USB, barrel jack, or pin headers |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
For a typical 5V supply module with pin headers:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VIN | Input voltage (e.g., 7-12V DC) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | VOUT | Regulated 5V output |
For USB-based 5V supplies:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | 5V output |
| 2 | D- | Data line (not used for power) |
| 3 | D+ | Data line (not used for power) |
| 4 | GND | Ground connection |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 5V Supply in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage (if applicable):
For modules requiring an input voltage (e.g., voltage regulators), connect a DC power source to the VIN and GND pins. Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (e.g., 7-12V DC).Connect the Output Voltage:
Use the VOUT and GND pins to power your circuit. Ensure the connected devices do not exceed the maximum current rating of the supply.Verify Connections:
Double-check all connections to avoid short circuits or overloading the supply.Power On:
Turn on the power source or connect the supply to a USB port to activate the 5V output.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overloading: Ensure the total current draw of connected devices does not exceed the supply's maximum current rating.
- Use Proper Heat Dissipation: For linear regulators, use a heatsink if the input voltage is significantly higher than 5V to prevent overheating.
- Check Polarity: Always connect the positive and ground terminals correctly to avoid damaging the supply or connected devices.
- Use Decoupling Capacitors: Add capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF and 10µF) near the power pins of sensitive devices to reduce noise and voltage fluctuations.
Example: Using a 5V Supply with Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO can be powered using a 5V supply through its 5V and GND pins. Below is an example of controlling an LED using a 5V supply:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the 5V supply's VOUT to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- Connect the supply's GND to the Arduino's GND pin.
- Connect an LED to pin 13 of the Arduino with a 220-ohm resistor in series.
Arduino Code
// Simple LED Blink Example
// This code blinks an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Input voltage is not connected or is out of range.
- Solution: Verify the input voltage and ensure it is within the specified range.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or high input voltage (for linear regulators).
- Solution: Reduce the load or use a heatsink for better heat dissipation.
Voltage Drops Under Load:
- Cause: The supply is overloaded or has insufficient current capacity.
- Solution: Use a supply with a higher current rating or reduce the load.
Noise or Voltage Fluctuations:
- Cause: Insufficient filtering or noisy input power.
- Solution: Add decoupling capacitors near the load and ensure a stable input voltage.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 5V supply to power a 3.3V device?
A: No, a 5V supply will damage most 3.3V devices. Use a voltage regulator or level shifter to step down the voltage.
Q: How do I know the current rating of my 5V supply?
A: Check the label or datasheet of the supply. It is usually specified in amperes (e.g., 1A, 2A).
Q: Can I connect multiple devices to a single 5V supply?
A: Yes, as long as the total current draw of all devices does not exceed the supply's maximum current rating.