
How to Use Mini560: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Mini560 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Mini560 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Mini560 is a compact, high-performance microcontroller designed for embedded applications. It features low power consumption, making it ideal for battery-powered devices, and integrates a variety of peripherals to support efficient processing and control. Its small form factor and versatile functionality make it a popular choice for IoT devices, robotics, and other embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with Mini560

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer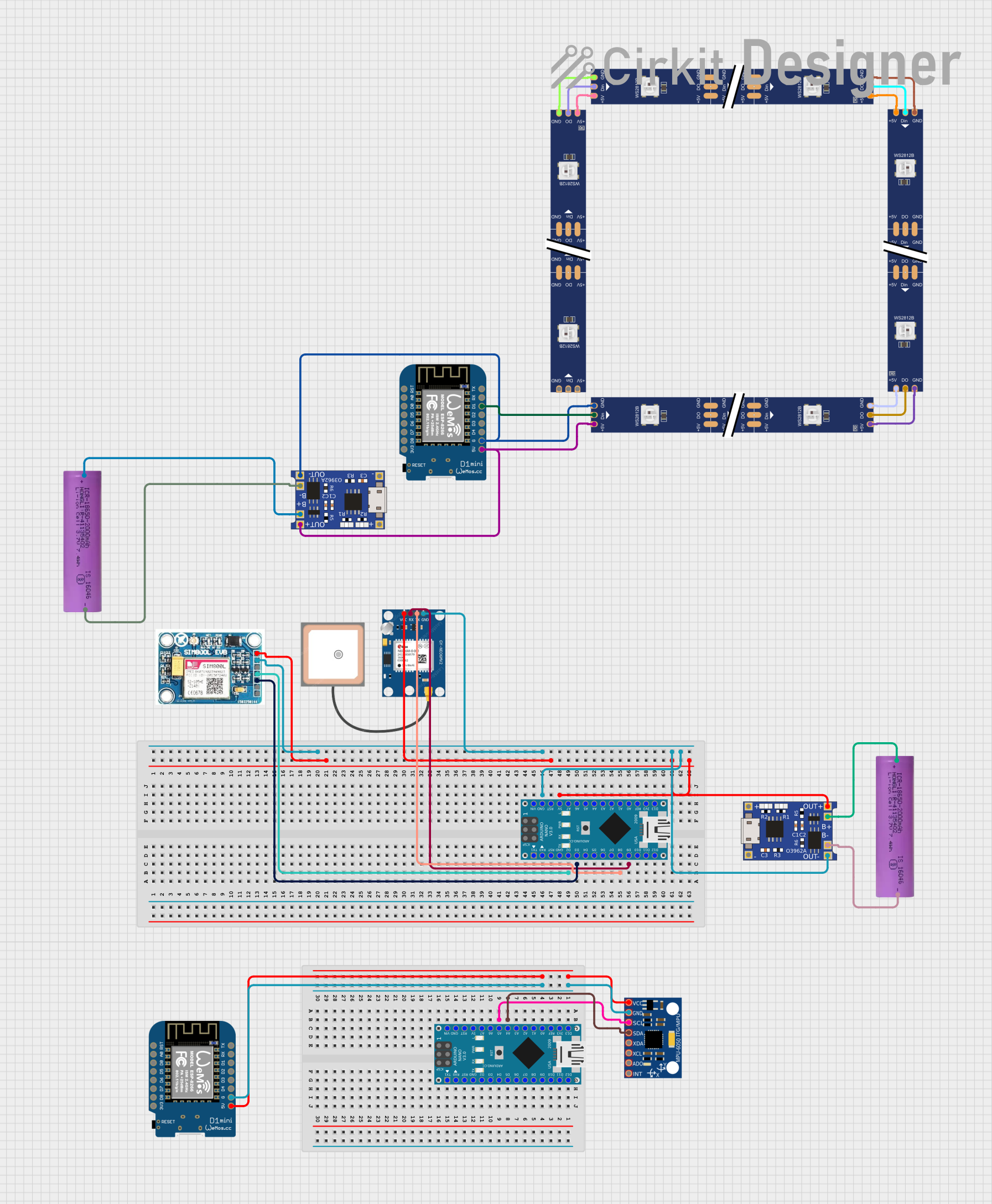
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer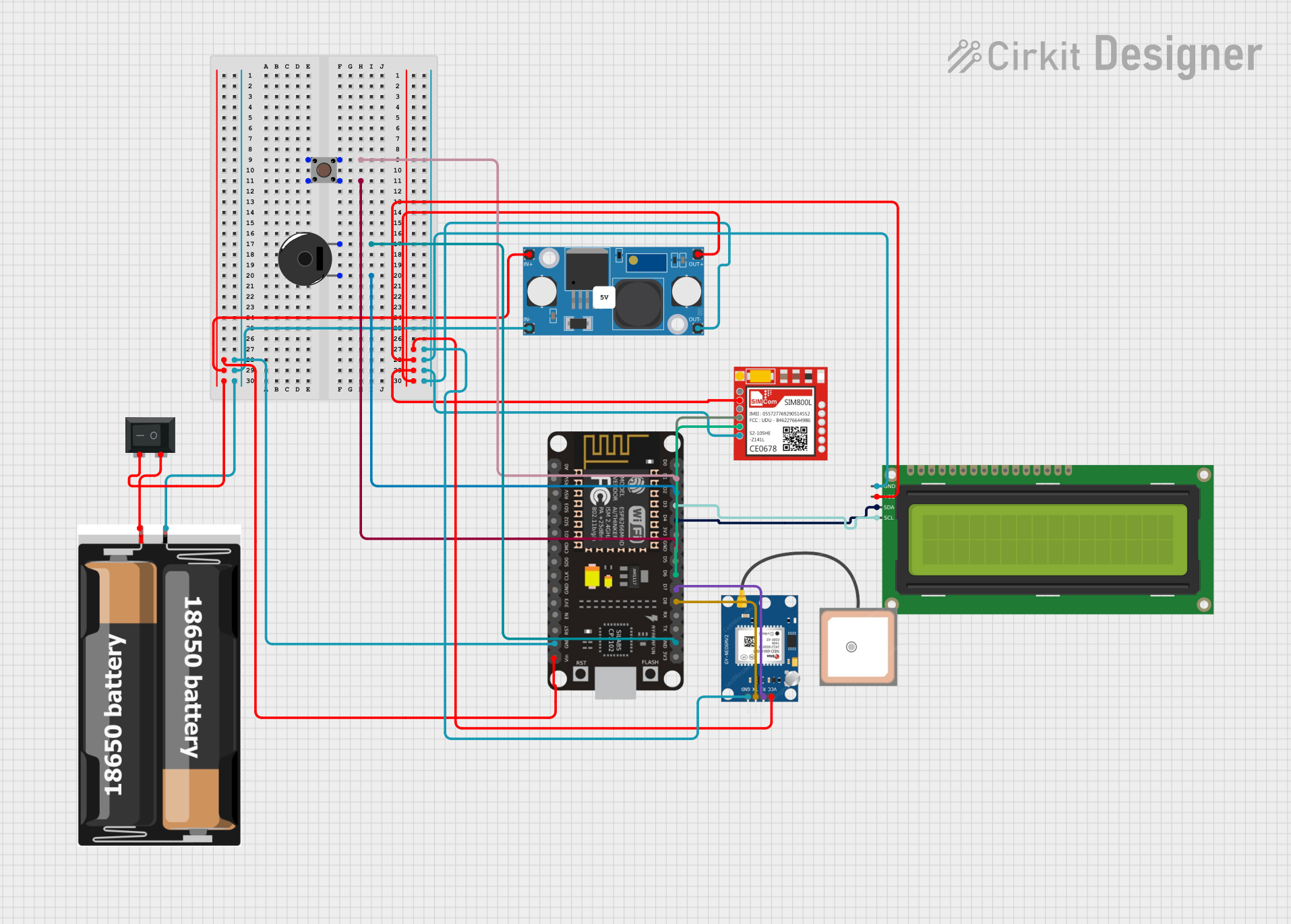
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer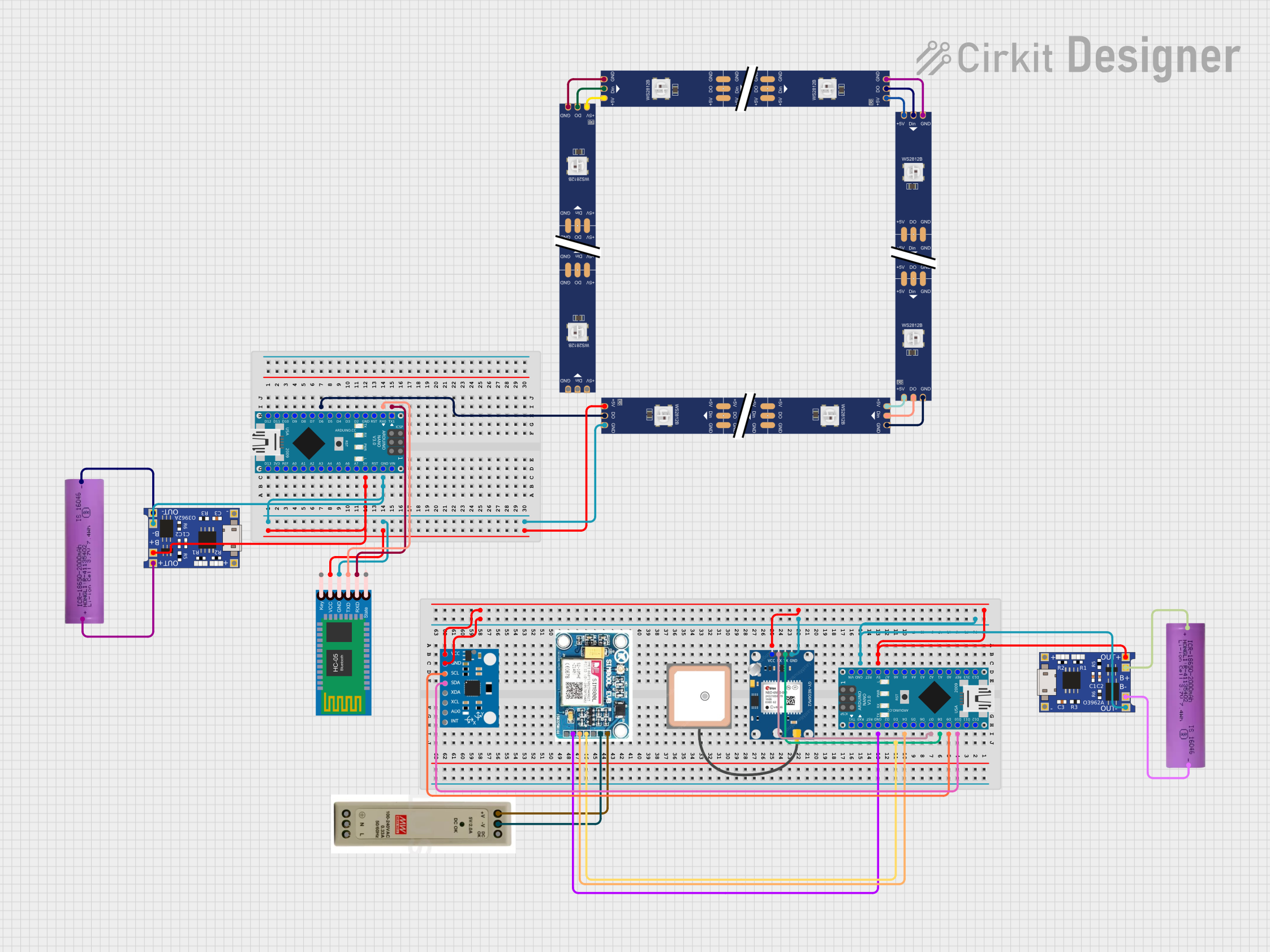
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Mini560

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
- Wearable technology
- Robotics and automation
- Home automation systems
- Portable medical devices
- Industrial control systems
Technical Specifications
The Mini560 microcontroller is designed to deliver robust performance while maintaining energy efficiency. Below are its key technical specifications:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Core Architecture | ARM Cortex-M0+ |
| Operating Voltage | 1.8V to 3.6V |
| Clock Speed | Up to 48 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 64 KB |
| SRAM | 8 KB |
| GPIO Pins | 20 |
| Communication Interfaces | I2C, SPI, UART |
| ADC Resolution | 12-bit |
| Timers | 3 (16-bit) |
| Power Consumption | < 1 µA in sleep mode |
| Package Type | QFN-32 |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Mini560 comes in a 32-pin QFN package. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VDD | Power Supply | Positive power supply (1.8V–3.6V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground | Ground connection |
| 3 | PA0 | GPIO/ADC Input | General-purpose I/O or ADC channel 0 |
| 4 | PA1 | GPIO/ADC Input | General-purpose I/O or ADC channel 1 |
| 5 | PA2 | UART_TX | UART Transmit |
| 6 | PA3 | UART_RX | UART Receive |
| 7 | PB0 | GPIO/SPI_MOSI | General-purpose I/O or SPI MOSI |
| 8 | PB1 | GPIO/SPI_MISO | General-purpose I/O or SPI MISO |
| 9 | PB2 | GPIO/SPI_SCK | General-purpose I/O or SPI Clock |
| 10 | PB3 | GPIO/SPI_CS | General-purpose I/O or SPI Chip Select |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 32 | RESET | Reset Input | Active-low reset pin |
For a complete pinout, refer to the Mini560 datasheet.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Mini560 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VDD pin to a stable power source (1.8V–3.6V) and the GND pin to ground.
- GPIO Configuration: Configure the GPIO pins as input or output based on your application. Use pull-up or pull-down resistors if necessary.
- Communication Interfaces:
- For UART communication, connect the TX and RX pins to the corresponding pins on your device.
- For SPI, connect MOSI, MISO, SCK, and CS to the appropriate pins on the SPI device.
- For I2C, connect the SDA and SCL pins to the I2C bus with pull-up resistors.
- Programming: Use an appropriate programmer or development board to upload firmware to the Mini560.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure a clean and stable power supply to avoid erratic behavior.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place a 0.1 µF ceramic capacitor close to the VDD pin for noise filtering.
- Reset Pin: Connect the RESET pin to a pull-up resistor (e.g., 10 kΩ) to prevent accidental resets.
- Clock Source: If using an external clock, connect it to the appropriate pins and configure the clock settings in the firmware.
- Programming Interface: Use SWD (Serial Wire Debug) for programming and debugging.
Example: Using Mini560 with Arduino UNO
The Mini560 can be interfaced with an Arduino UNO for communication via UART. Below is an example Arduino sketch:
// Example: Communicating with Mini560 via UART
// This code sends a message to the Mini560 and reads its response.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize UART communication at 9600 baud
while (!Serial) {
// Wait for the Serial port to initialize
}
Serial.println("Mini560 Communication Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Send a message to the Mini560
Serial.println("Hello, Mini560!");
// Wait for a response from the Mini560
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
String response = Serial.readString();
Serial.print("Response from Mini560: ");
Serial.println(response);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before sending the next message
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The Mini560 does not power on.
- Check the power supply voltage and ensure it is within the 1.8V–3.6V range.
- Verify the connections to the VDD and GND pins.
GPIO pins are not functioning as expected.
- Ensure the pins are correctly configured as input or output in the firmware.
- Check for any short circuits or incorrect wiring.
Communication interfaces are not working.
- Verify the baud rate and other communication settings (e.g., parity, stop bits).
- Check the wiring and ensure pull-up resistors are used for I2C.
The microcontroller resets unexpectedly.
- Ensure the RESET pin is connected to a pull-up resistor.
- Check for power supply fluctuations or noise.
FAQs
Q: Can the Mini560 operate at 5V?
A: No, the Mini560 operates within a voltage range of 1.8V to 3.6V. Exceeding this range may damage the component.
Q: Does the Mini560 support PWM?
A: Yes, the Mini560 supports PWM on select GPIO pins. Refer to the datasheet for details.
Q: How do I program the Mini560?
A: The Mini560 can be programmed using an SWD programmer or a compatible development board.
Q: Can I use the Mini560 for battery-powered applications?
A: Yes, the Mini560's low power consumption makes it ideal for battery-powered devices. Use sleep modes to further reduce power usage.