
How to Use 5v UPS : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
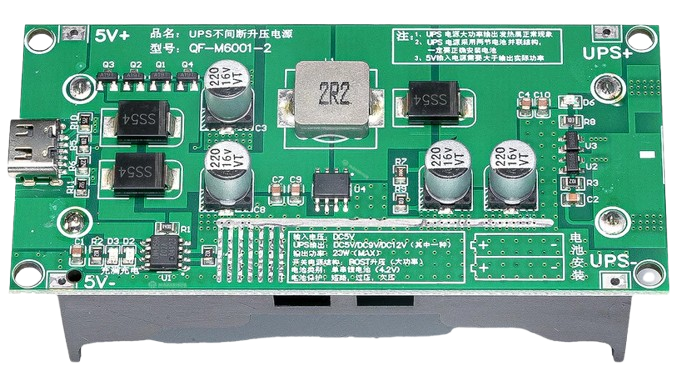
 Design with 5v UPS in Cirkit Designer
Design with 5v UPS in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 5V Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a compact power management device designed to provide a stable 5V output to electronic devices during power outages or voltage fluctuations. It ensures uninterrupted operation of critical systems, such as microcontrollers, IoT devices, routers, and other low-power electronics. The 5V UPS typically integrates a rechargeable battery, charging circuitry, and voltage regulation to maintain consistent power delivery.
Explore Projects Built with 5v UPS
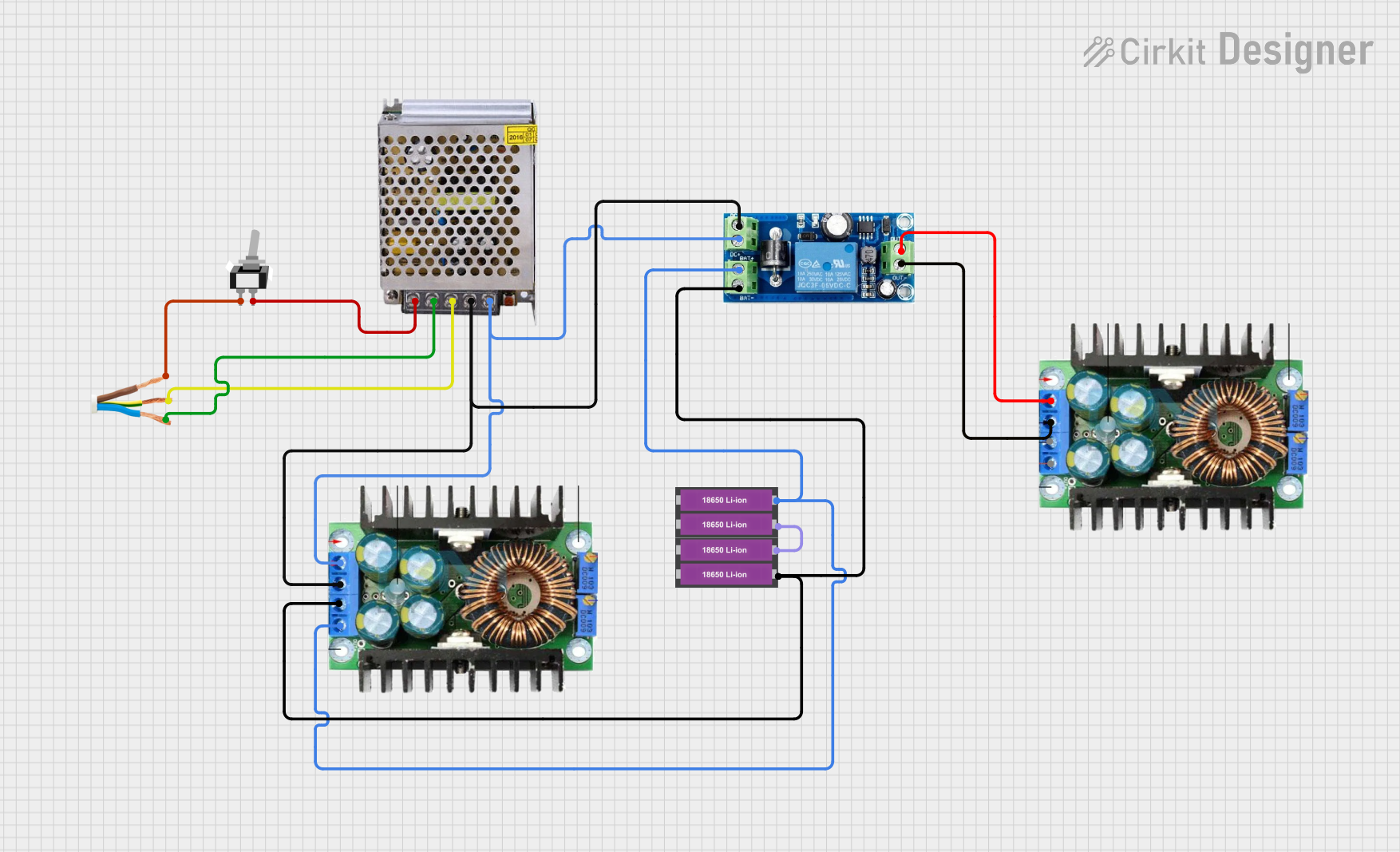
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer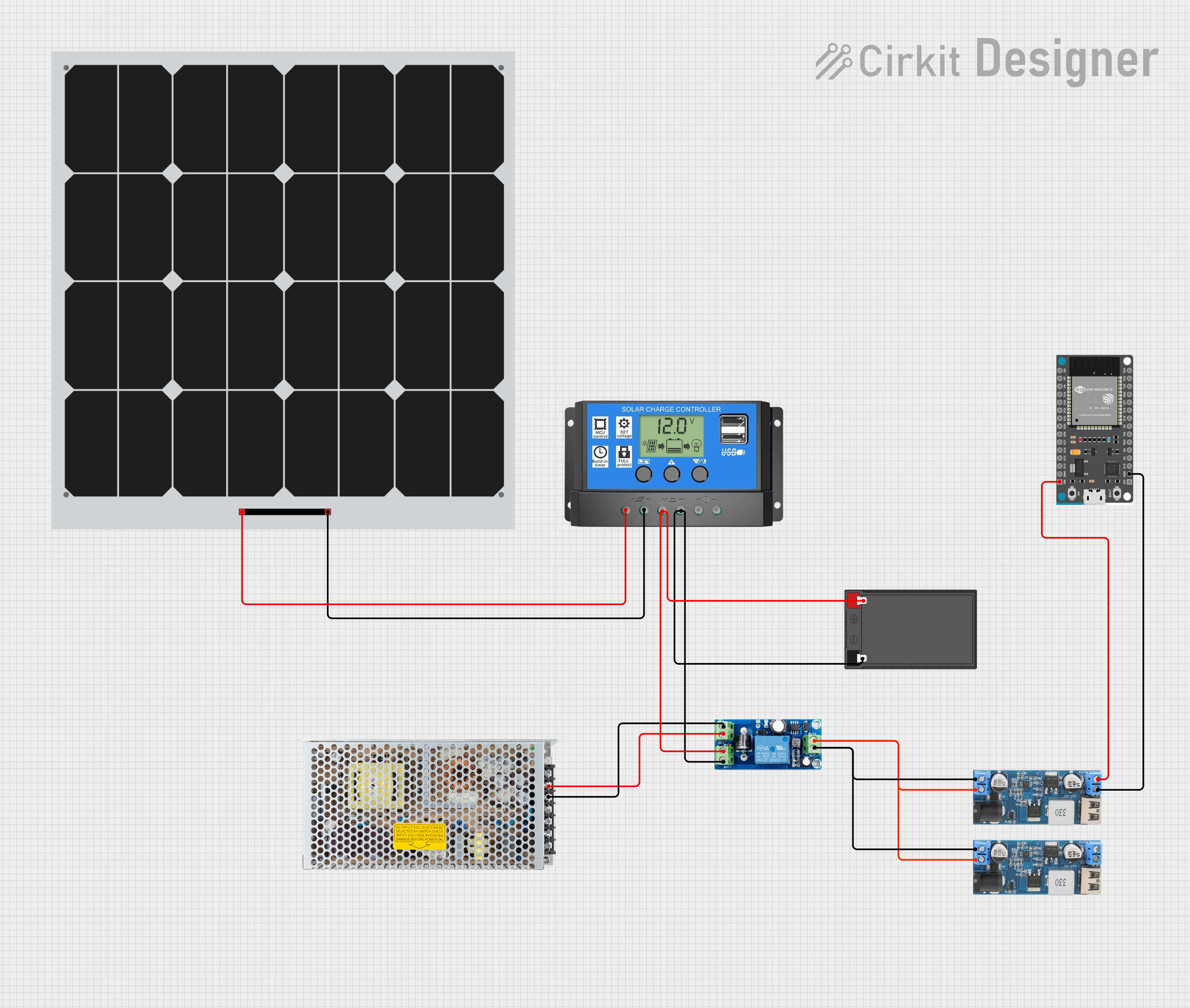
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer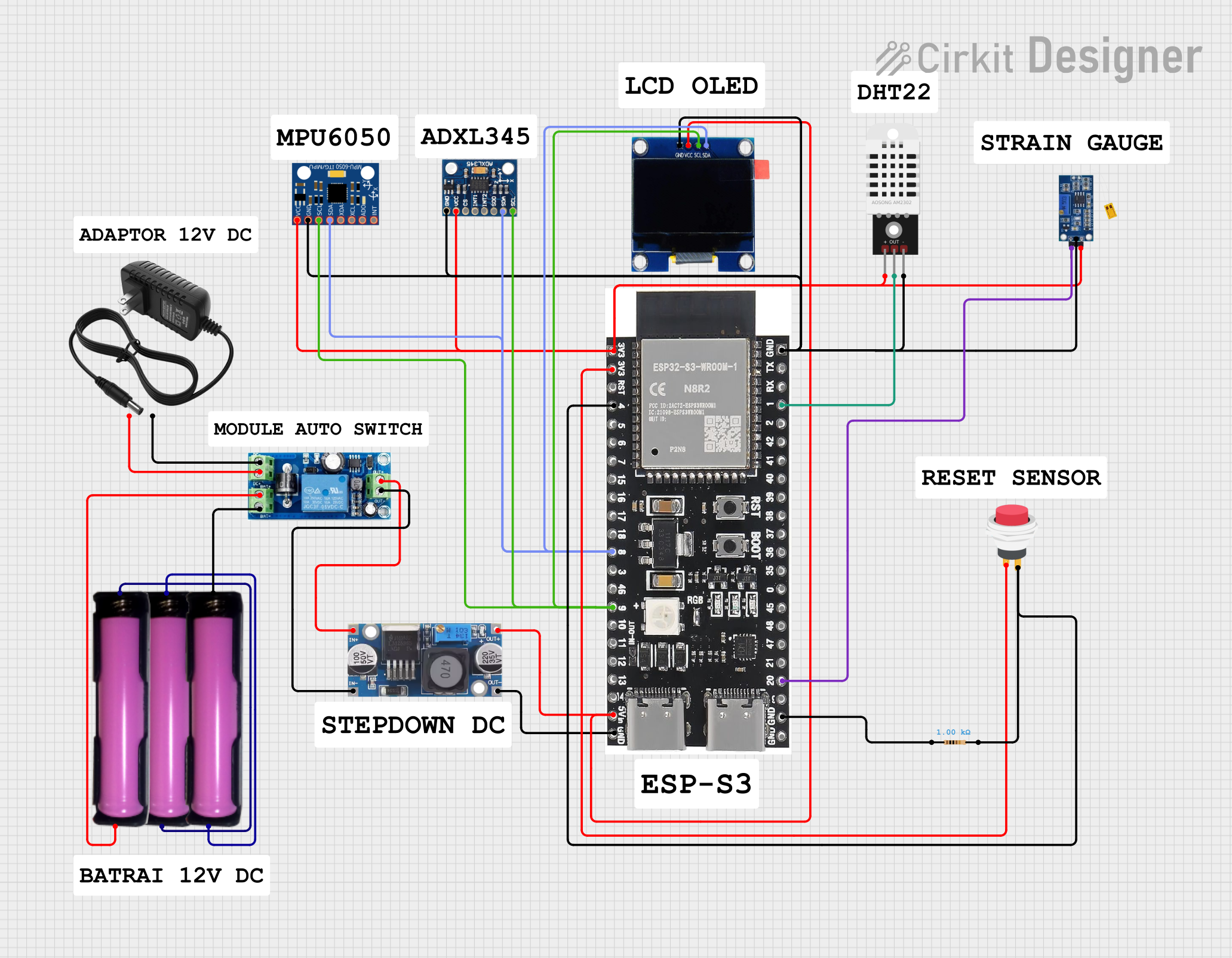
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 5v UPS

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Backup power for Raspberry Pi, Arduino, and other microcontrollers.
- Ensuring uninterrupted operation of IoT devices during power outages.
- Powering small routers, modems, or network devices.
- Providing stable power to sensors and data loggers in remote locations.
- Preventing data loss or corruption in embedded systems.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of a typical 5V UPS:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage | 5V DC |
| Output Voltage | 5V DC (regulated) |
| Output Current | Up to 2A (varies by model) |
| Battery Type | Lithium-ion or Lithium-polymer |
| Battery Capacity | 1000mAh to 5000mAh (varies by model) |
| Charging Current | 500mA to 1A |
| Protection Features | Overcharge, over-discharge, short-circuit |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 60mm x 40mm x 20mm) |
| Operating Temperature | 0°C to 50°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 5V UPS typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin (5V DC) for charging the UPS battery. |
| GND | Ground connection for both input and output. |
| VOUT | Regulated 5V output pin to power connected devices. |
| BAT+ | Positive terminal of the internal battery (not typically user-accessible). |
| BAT- | Negative terminal of the internal battery (not typically user-accessible). |
| CHG LED | LED indicator for charging status (e.g., ON when charging, OFF when charged). |
| PWR LED | LED indicator for power output status (e.g., ON when output is active). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 5V UPS in a Circuit
Connect the Input Power Source:
- Connect a 5V DC power source (e.g., USB adapter) to the
VINandGNDpins. - Ensure the input voltage is stable and within the specified range.
- Connect a 5V DC power source (e.g., USB adapter) to the
Connect the Load Device:
- Connect the device you want to power to the
VOUTandGNDpins. - Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum output current rating of the UPS.
- Connect the device you want to power to the
Monitor the LEDs:
- The
CHG LEDwill indicate the charging status of the internal battery. - The
PWR LEDwill indicate whether the UPS is supplying power to the load.
- The
Battery Backup Operation:
- During a power outage, the UPS will automatically switch to battery mode, maintaining a stable 5V output.
- When power is restored, the UPS will recharge the battery while continuing to power the load.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Capacity: Choose a 5V UPS with sufficient battery capacity to meet the runtime requirements of your application.
- Load Current: Ensure the connected device's current draw does not exceed the UPS's maximum output current.
- Heat Dissipation: Avoid placing the UPS in enclosed spaces without proper ventilation, as heat may build up during operation.
- Battery Maintenance: Periodically check the battery health and replace it if the capacity significantly degrades over time.
- Polarity: Double-check all connections to avoid reverse polarity, which may damage the UPS or connected devices.
Example: Using a 5V UPS with an Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to connect a 5V UPS to an Arduino UNO for uninterrupted operation:
Circuit Connection
- Connect the
VOUTpin of the 5V UPS to the5Vpin of the Arduino UNO. - Connect the
GNDpin of the 5V UPS to theGNDpin of the Arduino UNO. - Connect a 5V DC power source to the
VINandGNDpins of the UPS.
Sample Arduino Code
// Example code to demonstrate uninterrupted operation of an Arduino UNO
// powered by a 5V UPS. The Arduino will blink an LED continuously.
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: The UPS does not power the connected device.
- Solution: Check the input power source and ensure it is providing 5V DC. Verify that the load current does not exceed the UPS's maximum output current.
Issue: The battery does not charge.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is stable and within the specified range. Check the
CHG LEDfor charging status. If the battery is old or damaged, consider replacing it.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is stable and within the specified range. Check the
Issue: The UPS overheats during operation.
- Solution: Ensure proper ventilation around the UPS. Avoid overloading the UPS by connecting devices that draw more current than its rated capacity.
Issue: The output voltage drops below 5V during battery mode.
- Solution: Verify the battery's charge level. If the battery is nearly depleted, recharge it before use. Ensure the load is within the UPS's capacity.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the 5V UPS to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, as long as the Raspberry Pi's power requirements (voltage and current) are within the UPS's specifications.Q: How long will the UPS provide backup power?
A: The runtime depends on the battery capacity and the power consumption of the connected device. For example, a 2000mAh battery can power a 500mA load for approximately 4 hours.Q: Can I replace the internal battery?
A: Some models allow battery replacement, but it is recommended to consult the manufacturer's documentation before attempting to replace the battery.Q: Is the UPS safe to use with sensitive electronics?
A: Yes, most 5V UPS devices include protection features such as overcharge, over-discharge, and short-circuit protection to ensure safe operation.