
How to Use TP4056 Type-C: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
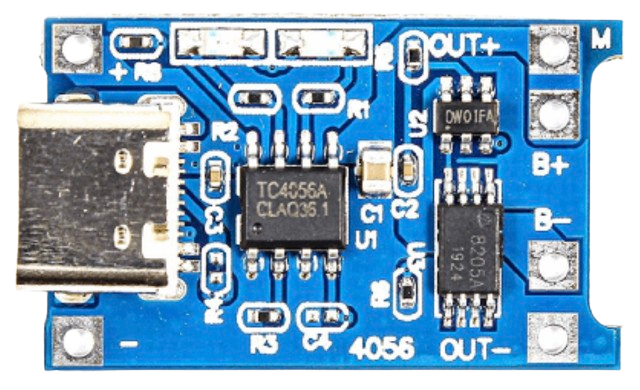
 Design with TP4056 Type-C in Cirkit Designer
Design with TP4056 Type-C in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TP4056 Type-C is a lithium battery charger IC designed for charging single-cell lithium-ion batteries. It provides a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile, ensuring safe and efficient charging. The inclusion of a Type-C interface allows for modern connectivity and reliable power delivery, making it a popular choice for portable electronics, DIY projects, and battery-powered devices.
Explore Projects Built with TP4056 Type-C

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer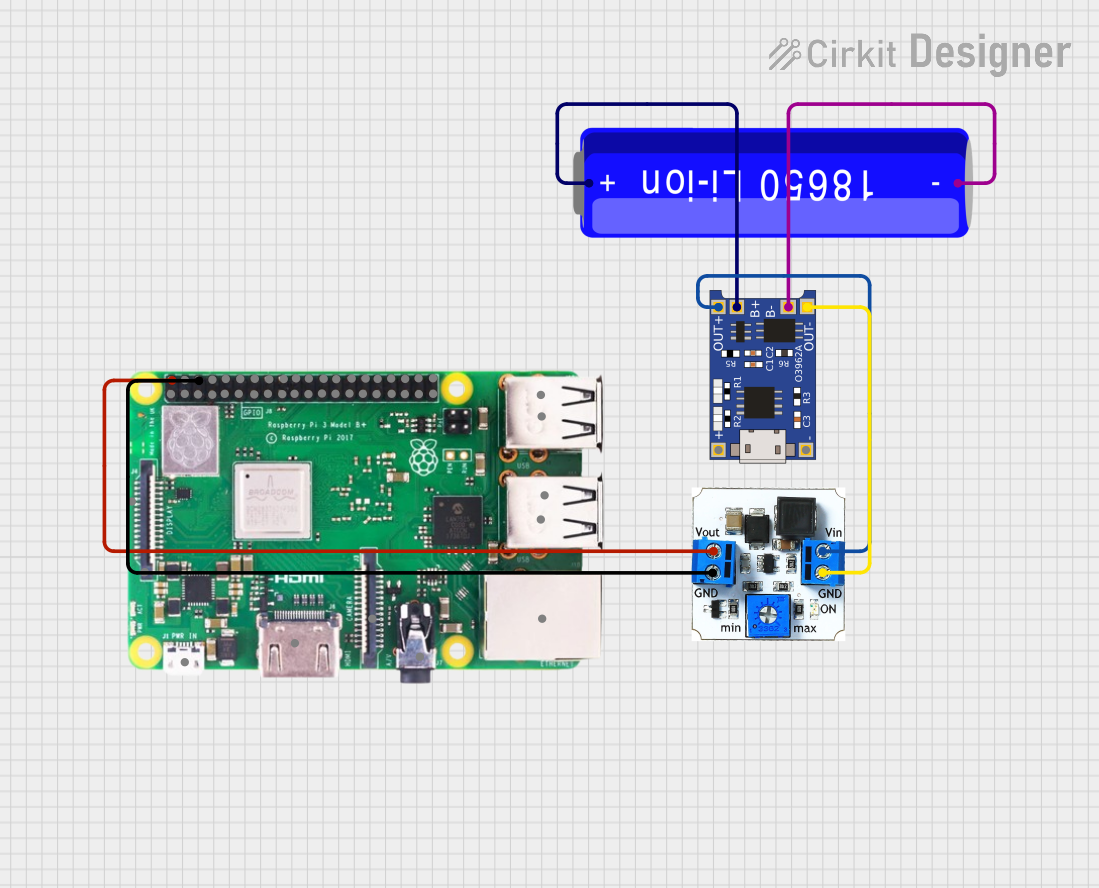
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TP4056 Type-C

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries
- Power banks and portable chargers
- DIY electronics projects
- Wearable devices and IoT gadgets
- Battery-powered tools and toys
Technical Specifications
The TP4056 Type-C module is compact and highly efficient. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.5V to 5.5V |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2V ± 1% |
| Maximum Charging Current | 1A (adjustable via resistor) |
| Charging Method | Constant Current / Constant Voltage (CC/CV) |
| Interface Type | USB Type-C |
| Battery Type Supported | Single-cell lithium-ion/lithium-polymer |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | ~25mm x 19mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TP4056 Type-C module has several pins and solder pads for connectivity. Below is a detailed description:
| Pin/Pad | Description |
|---|---|
| IN+ | Positive input voltage (4.5V to 5.5V). Connect to the positive terminal of the power source. |
| IN- | Negative input voltage (GND). Connect to the ground of the power source. |
| BAT+ | Positive terminal for the lithium battery. Connect to the positive terminal of the battery. |
| BAT- | Negative terminal for the lithium battery. Connect to the negative terminal of the battery. |
| OUT+ | Positive output voltage. Can be used to power a load directly from the battery. |
| OUT- | Negative output voltage (GND). |
| PROG | Used to set the charging current by connecting a resistor to GND. |
| STAT1 | Charging status indicator (active low). Connect to an LED for visual feedback. |
| STAT2 | Charging complete indicator (active low). Connect to an LED for visual feedback. |
| CE | Chip enable pin. Pull low to disable the module, or leave floating for normal operation. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TP4056 Type-C in a Circuit
- Power Input: Connect a 5V power source (e.g., USB Type-C adapter) to the
IN+andIN-pins. Ensure the input voltage is within the 4.5V to 5.5V range. - Battery Connection: Connect the lithium-ion battery to the
BAT+andBAT-pins. Ensure correct polarity to avoid damage. - Load Connection (Optional): If you want to power a load directly, connect it to the
OUT+andOUT-pins. Note that the load should not exceed the module's current rating. - Set Charging Current: Use a resistor on the
PROGpin to set the desired charging current. The formula is: [ I_{CHARGE} = \frac{1200}{R_{PROG}} ] For example, a 1.2kΩ resistor sets the charging current to 1A. - Status LEDs: Connect LEDs to the
STAT1andSTAT2pins for visual feedback:STAT1: Lights up during charging.STAT2: Lights up when charging is complete.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Protection: Use a lithium battery with a built-in protection circuit to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
- Heat Dissipation: The module may heat up during operation. Ensure proper ventilation or add a heatsink if necessary.
- Avoid Reverse Polarity: Double-check all connections to avoid damaging the module or the battery.
- Charging Current: Do not exceed the recommended charging current for your battery to ensure safety and longevity.
Example: Using TP4056 Type-C with Arduino UNO
The TP4056 Type-C can be used to charge a battery that powers an Arduino UNO. Below is an example of how to monitor the charging status using Arduino:
// TP4056 Status Monitoring with Arduino UNO
// Connect STAT1 to Arduino pin 2 and STAT2 to pin 3
const int stat1Pin = 2; // STAT1 pin connected to Arduino pin 2
const int stat2Pin = 3; // STAT2 pin connected to Arduino pin 3
void setup() {
pinMode(stat1Pin, INPUT); // Set STAT1 as input
pinMode(stat2Pin, INPUT); // Set STAT2 as input
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int stat1 = digitalRead(stat1Pin); // Read STAT1 pin
int stat2 = digitalRead(stat2Pin); // Read STAT2 pin
if (stat1 == LOW) {
Serial.println("Charging in progress...");
} else if (stat2 == LOW) {
Serial.println("Charging complete!");
} else {
Serial.println("No battery connected or idle state.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before checking again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Module Overheating
- Cause: High charging current or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the charging current by increasing the
PROGresistor value. Ensure proper airflow around the module.
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or damaged battery.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the battery is functional. Check the input voltage.
LEDs Not Lighting Up
- Cause: Faulty LEDs or incorrect connections.
- Solution: Test the LEDs separately and ensure they are connected to the correct pins with appropriate resistors.
Output Voltage Too Low
- Cause: Battery is deeply discharged or damaged.
- Solution: Allow the battery to charge for some time. If the issue persists, replace the battery.
FAQs
Can I use the TP4056 Type-C to charge multiple batteries in series?
- No, the TP4056 is designed for single-cell lithium-ion batteries only. Charging multiple cells in series requires a specialized balance charger.
What happens if I exceed the input voltage range?
- Exceeding the 5.5V input voltage can damage the module. Always use a regulated 5V power source.
Can I adjust the charging voltage?
- No, the charging voltage is fixed at 4.2V ± 1% and cannot be adjusted.
Is it safe to leave the battery connected after charging is complete?
- Yes, the TP4056 automatically stops charging when the battery is full, preventing overcharging.
This concludes the documentation for the TP4056 Type-C module. Follow the guidelines above for safe and efficient operation!