
How to Use Stepper Motor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Stepper Motor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Stepper Motor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A stepper motor is a type of electric motor that divides a full rotation into a large number of discrete steps. This allows for precise control of angular position, speed, and acceleration without requiring feedback systems. Stepper motors are widely used in applications where accurate positioning is critical, such as 3D printers, CNC machines, robotics, and camera platforms.
Stepper Online is a leading manufacturer of high-quality stepper motors, offering reliable and efficient solutions for various industrial and hobbyist applications.
Explore Projects Built with Stepper Motor
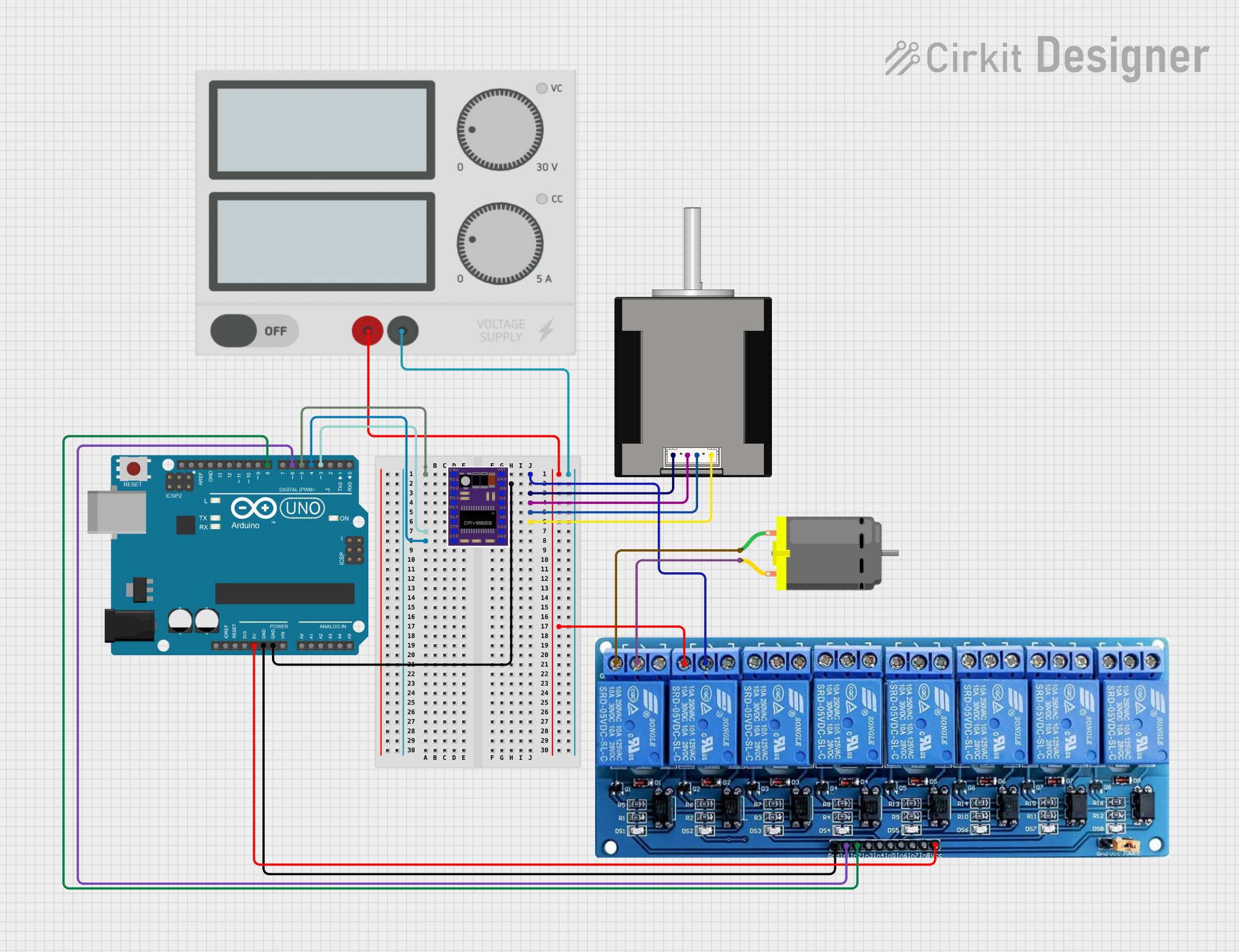
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer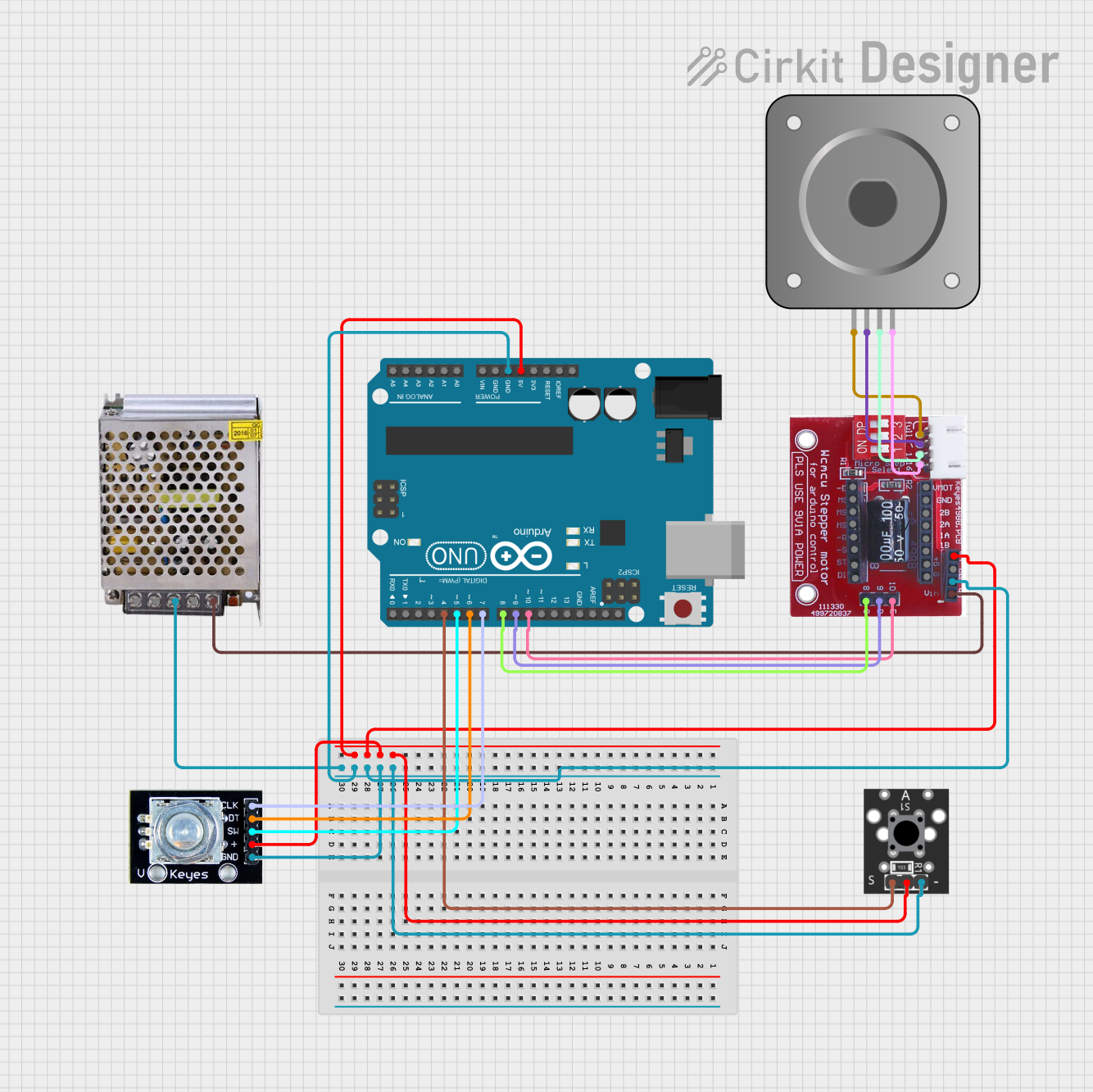
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer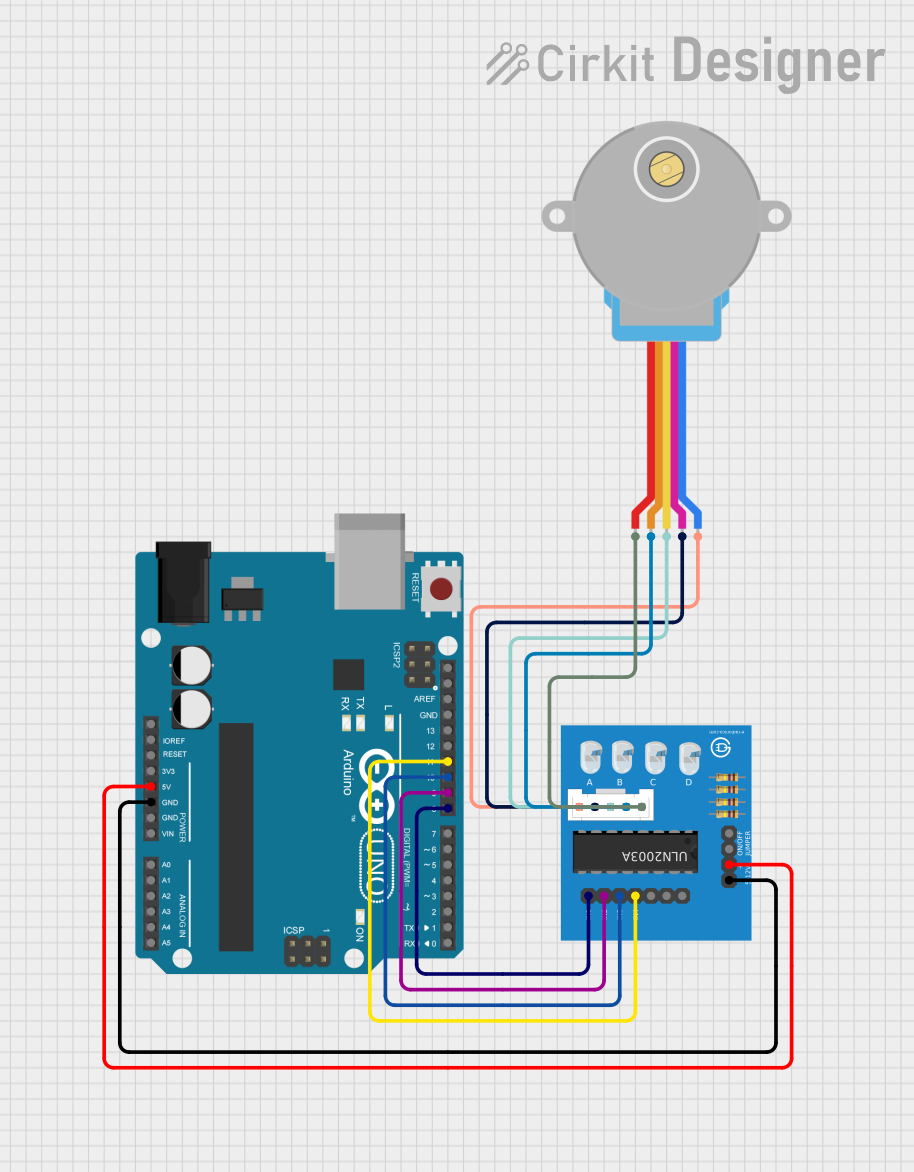
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer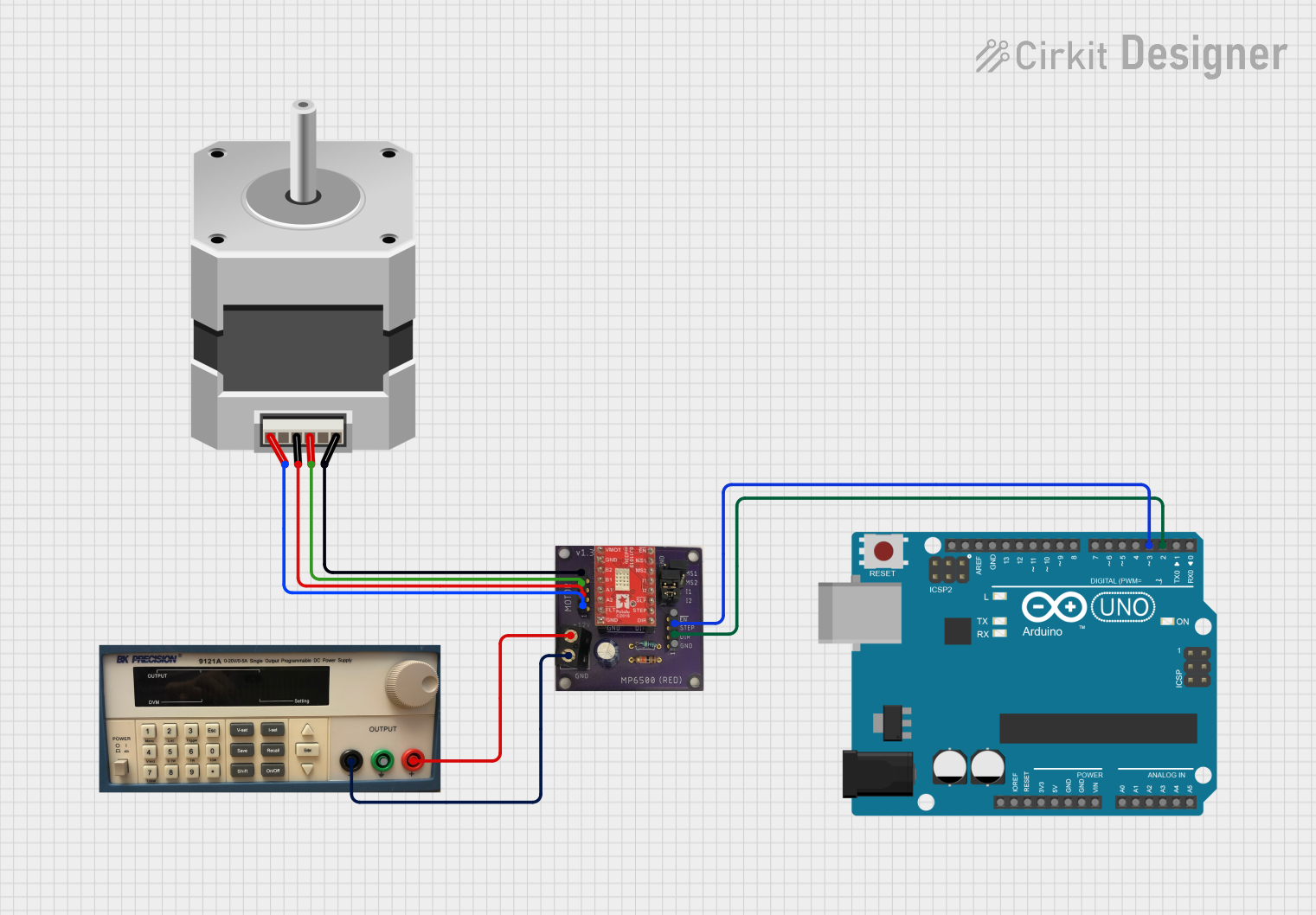
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Stepper Motor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical stepper motor from Stepper Online. Always refer to the datasheet of your specific model for exact details.
General Specifications
- Type: Bipolar or Unipolar Stepper Motor
- Step Angle: 1.8° (200 steps per revolution) or 0.9° (400 steps per revolution)
- Voltage Rating: 2.8V to 12V (varies by model)
- Current Rating: 1A to 4.2A per phase
- Holding Torque: 0.2 Nm to 3.0 Nm
- Number of Phases: 2 (Bipolar) or 4 (Unipolar)
- Inductance: 1 mH to 10 mH per phase
- Shaft Diameter: 5 mm to 8 mm (varies by model)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration depends on whether the stepper motor is bipolar or unipolar. Below are the typical pinouts:
Bipolar Stepper Motor
| Pin Number | Wire Color (Typical) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | Coil A+ |
| 2 | Blue | Coil A- |
| 3 | Green | Coil B+ |
| 4 | Black | Coil B- |
Unipolar Stepper Motor
| Pin Number | Wire Color (Typical) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Red | Coil A+ |
| 2 | Blue | Coil A- |
| 3 | Green | Coil B+ |
| 4 | Black | Coil B- |
| 5 | Yellow | Common (Center Tap) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Stepper Motor in a Circuit
- Identify the Motor Type: Determine whether your stepper motor is bipolar or unipolar. This will affect how you connect it to a driver.
- Choose a Stepper Motor Driver: Use a compatible driver such as the A4988 or DRV8825 for bipolar motors. For unipolar motors, you can use a ULN2003 driver.
- Connect the Wires: Match the motor wires to the driver pins based on the pin configuration table above. Ensure proper connections to avoid damage.
- Power Supply: Provide a power supply that matches the voltage and current requirements of your motor and driver.
- Control Signals: Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) to send step and direction signals to the driver.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Set the current limit on your driver to match the motor's rated current to prevent overheating.
- Microstepping: Enable microstepping on the driver for smoother motion and higher resolution.
- Cooling: Use a heatsink or fan for the driver if operating at high currents.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the motor's torque rating to prevent stalling or damage.
Example: Controlling a Bipolar Stepper Motor with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a bipolar stepper motor using an A4988 driver and Arduino UNO.
// Include the Stepper library
#include <Stepper.h>
// Define the number of steps per revolution for your motor
#define STEPS_PER_REV 200
// Initialize the Stepper library with the motor's step pin connections
Stepper stepper(STEPS_PER_REV, 8, 9, 10, 11);
void setup() {
// Set the motor speed (in RPM)
stepper.setSpeed(60); // 60 RPM
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Stepper Motor Test");
}
void loop() {
// Rotate the motor one full revolution clockwise
Serial.println("Rotating clockwise...");
stepper.step(STEPS_PER_REV);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Rotate the motor one full revolution counterclockwise
Serial.println("Rotating counterclockwise...");
stepper.step(-STEPS_PER_REV);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure all connections are secure.
Motor Vibrates but Doesn't Rotate:
- Cause: Incorrect step sequence or insufficient current.
- Solution: Verify the step sequence and adjust the driver's current limit.
Overheating:
- Cause: Current limit set too high or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Reduce the current limit and add a heatsink or fan to the driver.
Skipping Steps:
- Cause: Exceeding the motor's torque rating.
- Solution: Reduce the load or increase the motor's torque by using a higher current (within limits).
FAQs
Q1: Can I run a stepper motor without a driver?
A1: No, a stepper motor requires a driver to control the current and step sequence. Directly connecting it to a power source will not work.
Q2: How do I determine the step angle of my motor?
A2: Check the motor's datasheet or divide 360° by the number of steps per revolution (e.g., 360° ÷ 200 = 1.8°).
Q3: Can I use a stepper motor for continuous rotation?
A3: Yes, stepper motors can rotate continuously, but they are primarily designed for precise positioning rather than high-speed rotation.
Q4: What is microstepping?
A4: Microstepping is a technique used by drivers to divide each full step into smaller steps, resulting in smoother motion and higher resolution.