
How to Use Pushbutton: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Pushbutton in Cirkit Designer
Design with Pushbutton in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A pushbutton is a momentary switch that completes a circuit when pressed and breaks the circuit when released. It is a simple yet essential component in electronics, commonly used for user input in devices such as calculators, remote controls, and microcontroller-based projects. Pushbuttons are available in various sizes and designs, making them versatile for different applications.
Explore Projects Built with Pushbutton

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer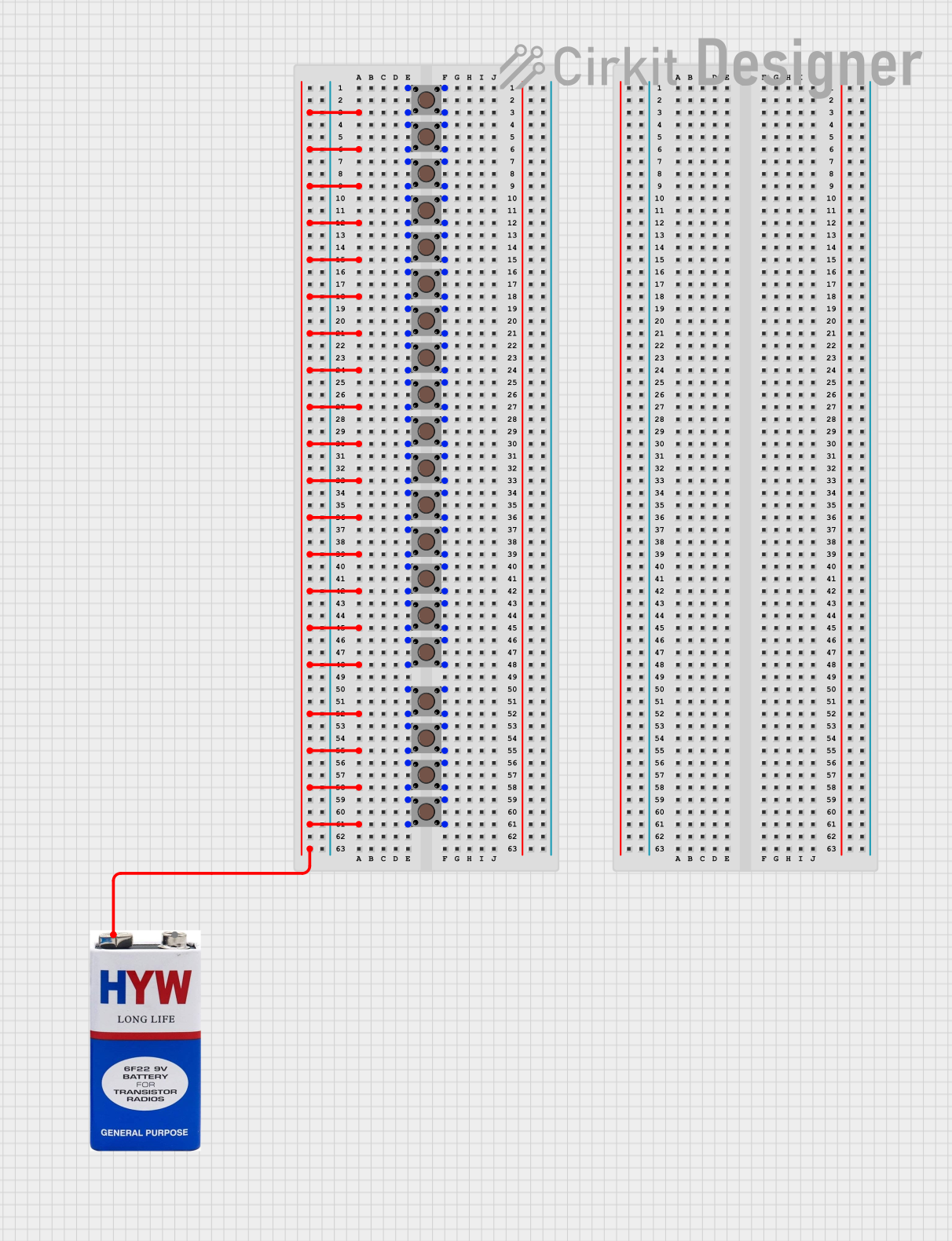
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer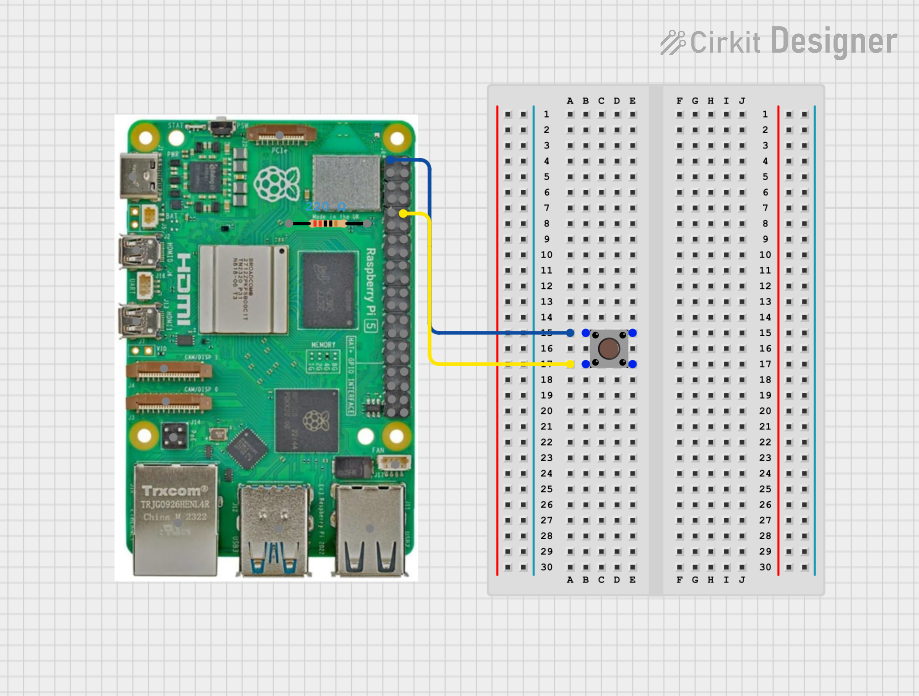
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer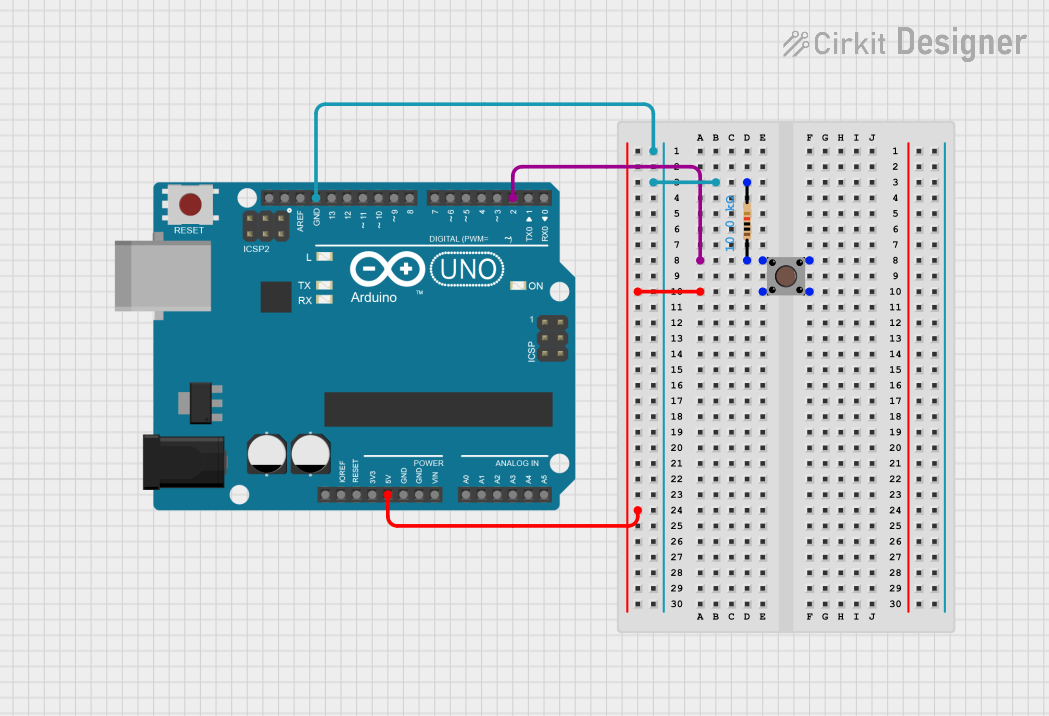
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Pushbutton

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- User input for microcontroller projects (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
- Reset or power buttons in electronic devices
- Control panels for appliances and machinery
- Prototyping and testing circuits
- Gaming controllers and interactive systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard pushbutton:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 12V (typical) |
| Maximum Current Rating | 50mA to 500mA (depending on type) |
| Contact Resistance | < 100 mΩ |
| Insulation Resistance | > 100 MΩ |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +70°C |
| Mechanical Lifespan | 100,000 to 1,000,000 presses |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
A standard 4-pin pushbutton typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|
| Pin 1 | Connected to one side of the switch |
| Pin 2 | Connected to the same side as Pin 1 |
| Pin 3 | Connected to the opposite side of the switch |
| Pin 4 | Connected to the same side as Pin 3 |
Note: Pins 1 and 2 are internally connected, as are Pins 3 and 4. When the button is pressed, the circuit between these two groups of pins is completed.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Pushbutton in a Circuit
Connect the Pushbutton:
- Identify the two groups of internally connected pins (Pins 1 & 2, and Pins 3 & 4).
- Connect one group to the power source (e.g., 5V) and the other group to the input pin of your microcontroller or circuit.
Add a Pull-Down Resistor:
- To ensure stable operation, connect a pull-down resistor (typically 10kΩ) between the input pin and ground. This prevents the input pin from floating when the button is not pressed.
Test the Circuit:
- When the button is pressed, the circuit is completed, and the input pin will read a HIGH signal. When released, the pull-down resistor ensures the input pin reads LOW.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect and use a pushbutton with an Arduino UNO:
Circuit Diagram
- Connect one side of the pushbutton to 5V.
- Connect the other side to Arduino digital pin 2.
- Add a 10kΩ pull-down resistor between digital pin 2 and ground.
Arduino Code
// Define the pin connected to the pushbutton
const int buttonPin = 2; // Pushbutton connected to digital pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED on Arduino
void setup() {
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT); // Set button pin as input
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
}
void loop() {
int buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin); // Read the button state
if (buttonState == HIGH) {
// If button is pressed, turn on the LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
} else {
// If button is not pressed, turn off the LED
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
}
}
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Debouncing: Pushbuttons can produce noise or multiple signals when pressed or released. Use hardware (capacitors) or software (debouncing code) to handle this issue.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Ensure the pushbutton's ratings match your circuit requirements to avoid damage.
- Mechanical Lifespan: Avoid excessive force or frequent use beyond the rated lifespan to maintain reliability.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Button Not Responding:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure all connections are secure.
Button Produces Erratic Behavior:
- Cause: Signal bouncing due to lack of debouncing.
- Solution: Implement software debouncing in your code or add a small capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) across the button terminals.
Input Pin Always Reads HIGH or LOW:
- Cause: Missing pull-down or pull-up resistor.
- Solution: Add a pull-down resistor (10kΩ) to ground or a pull-up resistor to the power supply.
Button Feels Stuck or Unresponsive:
- Cause: Physical damage or dirt inside the button.
- Solution: Clean the button or replace it if damaged.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a pushbutton without a pull-down resistor?
A: While it is possible, the input pin may float and produce unreliable readings. A pull-down resistor ensures stable operation.
Q: How do I debounce a pushbutton in software?
A: You can use a delay or a state-checking algorithm in your code to filter out noise. For example, wait for a stable signal for a few milliseconds before registering a press.
Q: Can I use a pushbutton with higher voltages?
A: Only if the pushbutton's voltage and current ratings support it. Otherwise, use a relay or transistor to handle higher voltages.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate a pushbutton into your electronic projects with confidence!