
How to Use fuse.: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with fuse. in Cirkit Designer
Design with fuse. in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A fuse is a safety device designed to protect electrical circuits from excessive current. When the current flowing through the circuit exceeds the fuse's rated capacity, the fuse "blows" or breaks the circuit, preventing damage to components and reducing the risk of fire or electrical hazards. Fuses are essential in a wide range of applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery and automotive systems.
Explore Projects Built with fuse.

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer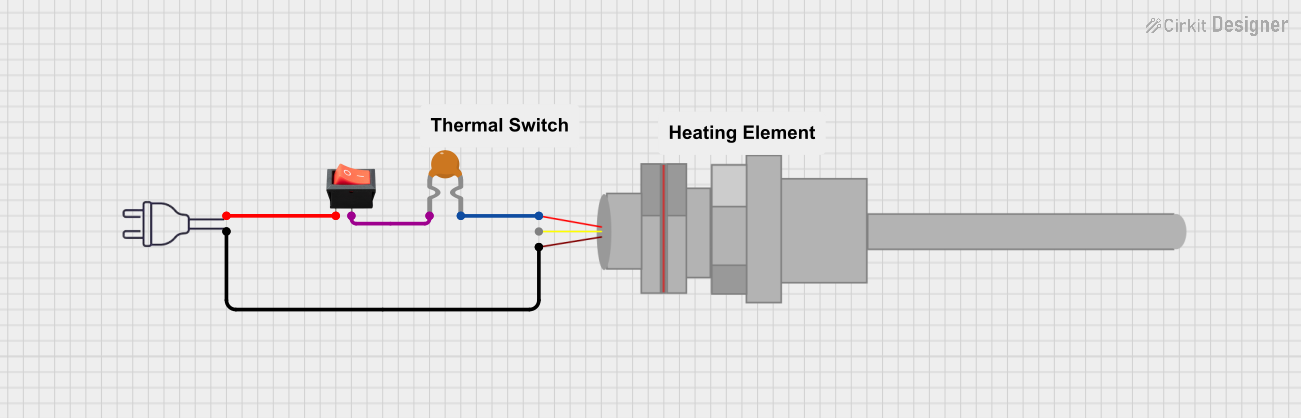
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer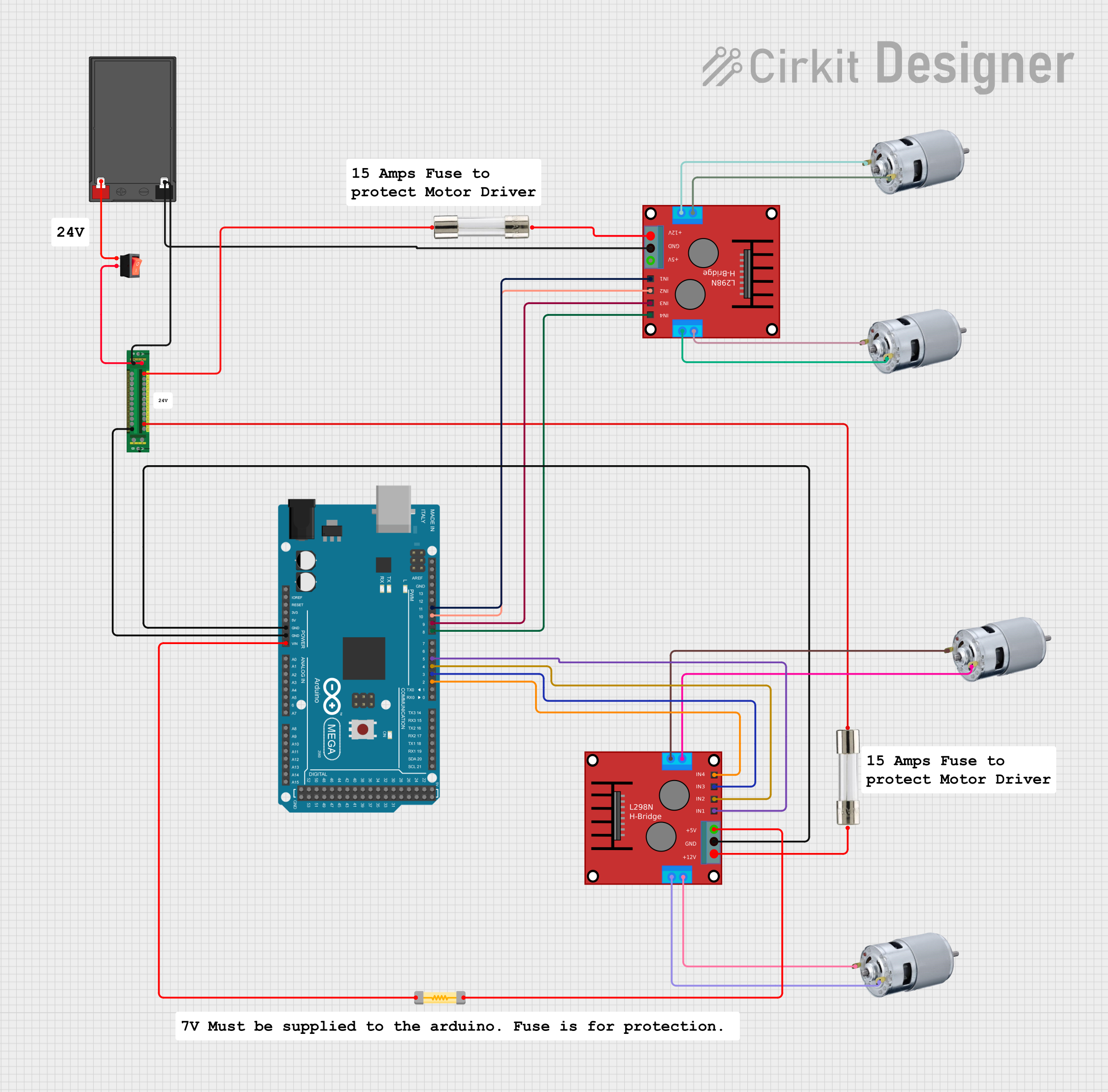
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with fuse.

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Household Electronics: Protecting devices like televisions, refrigerators, and microwaves.
- Automotive Systems: Safeguarding car electrical systems from short circuits or overloads.
- Industrial Equipment: Ensuring the safety of heavy machinery and control systems.
- Power Supplies: Preventing damage to transformers, inverters, and other power components.
- Arduino and Microcontroller Projects: Protecting sensitive components from overcurrent conditions.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the Symbol 5A fuse:
General Specifications
- Manufacturer: Symbol
- Part ID: 5A
- Type: Fast-acting fuse
- Rated Current: 5 Amperes (A)
- Rated Voltage: 250 Volts (V)
- Breaking Capacity: 1000 Amperes (A) at rated voltage
- Response Time: Fast blow (quick response to overcurrent)
- Material: Ceramic body with metal end caps
- Operating Temperature: -55°C to +125°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Fuses do not have traditional pins like ICs or transistors. Instead, they have two terminals for connection. Below is a table describing the terminals:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Input terminal for current flow |
| Terminal 2 | Output terminal for current flow |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Fuse in a Circuit
- Determine the Fuse Rating: Select a fuse with a current rating slightly higher than the normal operating current of your circuit. For example, if your circuit operates at 4A, use the Symbol 5A fuse.
- Placement in the Circuit: Place the fuse in series with the load or device you want to protect. This ensures that all current flowing to the load passes through the fuse.
- Connection: Solder or securely connect the fuse terminals to the circuit. Ensure proper insulation to avoid short circuits.
- Testing: After installation, test the circuit to ensure the fuse is functioning correctly.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Do Not Oversize the Fuse: Using a fuse with a much higher current rating than required defeats its purpose and may not protect the circuit.
- Check Voltage Rating: Ensure the fuse's voltage rating is suitable for your application.
- Use a Fuse Holder: For easy replacement, use a fuse holder instead of soldering the fuse directly to the circuit.
- Avoid Replacing with Incorrect Types: Do not replace a fast-acting fuse with a slow-blow fuse unless specified by the design.
- Inspect Regularly: Periodically check the fuse for signs of wear or damage.
Example: Using a Fuse with an Arduino UNO
When connecting an Arduino UNO to a motor or other high-current device, a fuse can protect the board from damage due to overcurrent. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Description
- Connect the Symbol 5A fuse in series with the power supply to the motor.
- Ensure the fuse is placed between the power source and the motor's positive terminal.
Arduino Code Example
// Example code for controlling a motor with an Arduino UNO
// Ensure a 5A fuse is connected in series with the motor for protection.
const int motorPin = 9; // Pin connected to motor driver input
void setup() {
pinMode(motorPin, OUTPUT); // Set motor pin as output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(motorPin, HIGH); // Turn motor ON
delay(5000); // Run motor for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(motorPin, LOW); // Turn motor OFF
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds before restarting
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Fuse Blows Frequently
- Cause: The fuse rating is too low for the circuit's operating current.
- Solution: Replace the fuse with one that has a slightly higher current rating.
Fuse Does Not Blow During Overcurrent
- Cause: The fuse rating is too high or the fuse is defective.
- Solution: Verify the circuit's current requirements and replace the fuse with the correct rating.
Fuse Heats Up During Operation
- Cause: Poor connections or excessive current near the fuse's rated limit.
- Solution: Check and secure all connections. Ensure the circuit's current is within the fuse's rating.
Fuse Holder Melts
- Cause: Loose connections or using a fuse with an incorrect rating.
- Solution: Use a high-quality fuse holder and ensure proper connections.
FAQs
Q1: Can I use a higher-rated fuse to prevent frequent blowing?
A1: No, using a higher-rated fuse may not protect your circuit effectively. Always use a fuse with the correct rating for your application.
Q2: How do I know if a fuse is blown?
A2: A blown fuse will have a visible break in the filament or show no continuity when tested with a multimeter.
Q3: Can I replace a ceramic fuse with a glass fuse?
A3: Only if the glass fuse has the same ratings and characteristics (e.g., fast-acting or slow-blow). However, ceramic fuses are more durable and better suited for high-current applications.
Q4: Is it safe to bypass a fuse temporarily?
A4: No, bypassing a fuse can lead to severe damage to your circuit and pose safety risks. Always replace a blown fuse with a new one.