
How to Use ENDSTOP: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ENDSTOP in Cirkit Designer
Design with ENDSTOP in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An endstop is a mechanical switch or sensor designed to detect the position of a moving part in a machine. It is commonly used in 3D printers, CNC machines, and other automated systems to define the limits of movement and ensure precise operation. Endstops play a critical role in preventing mechanical components from moving beyond their intended range, which could otherwise result in damage or misalignment.
Explore Projects Built with ENDSTOP
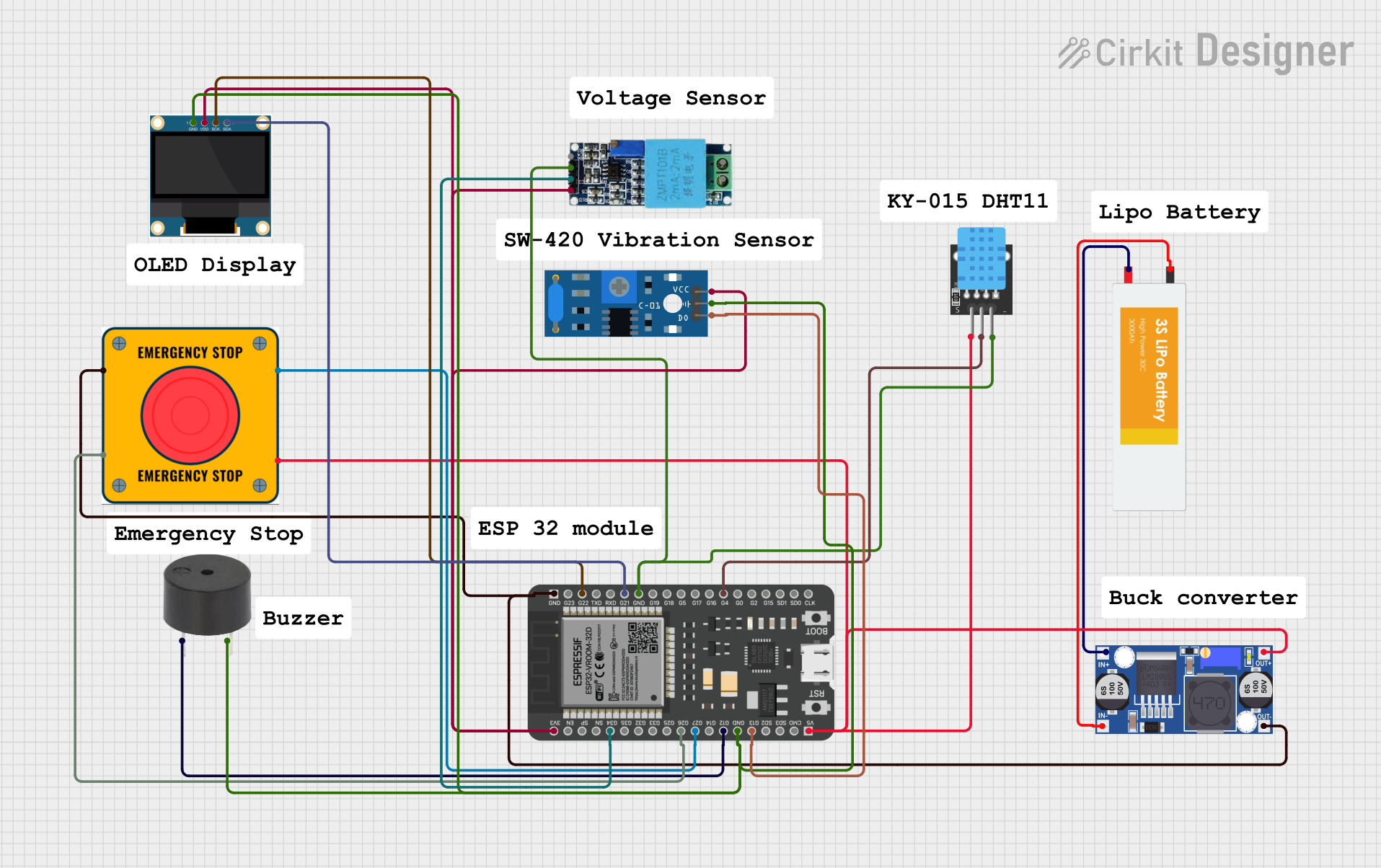
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer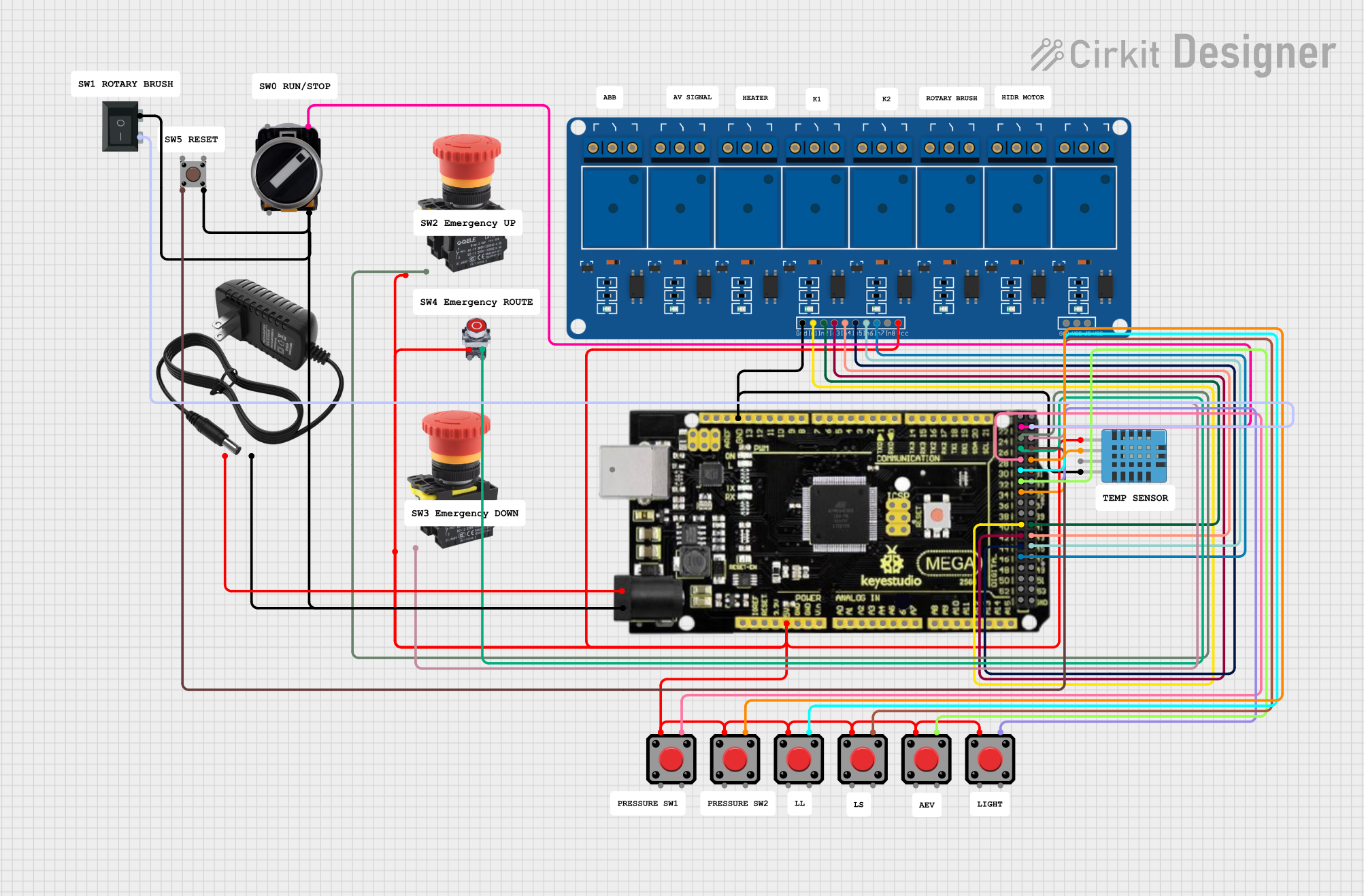
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer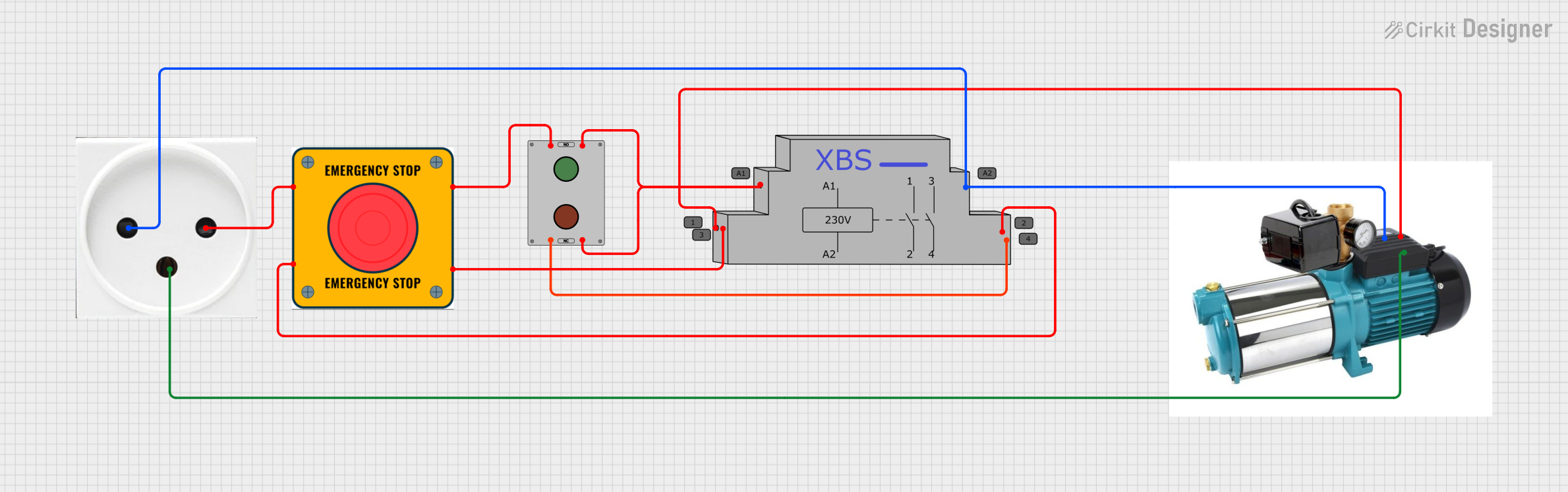
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer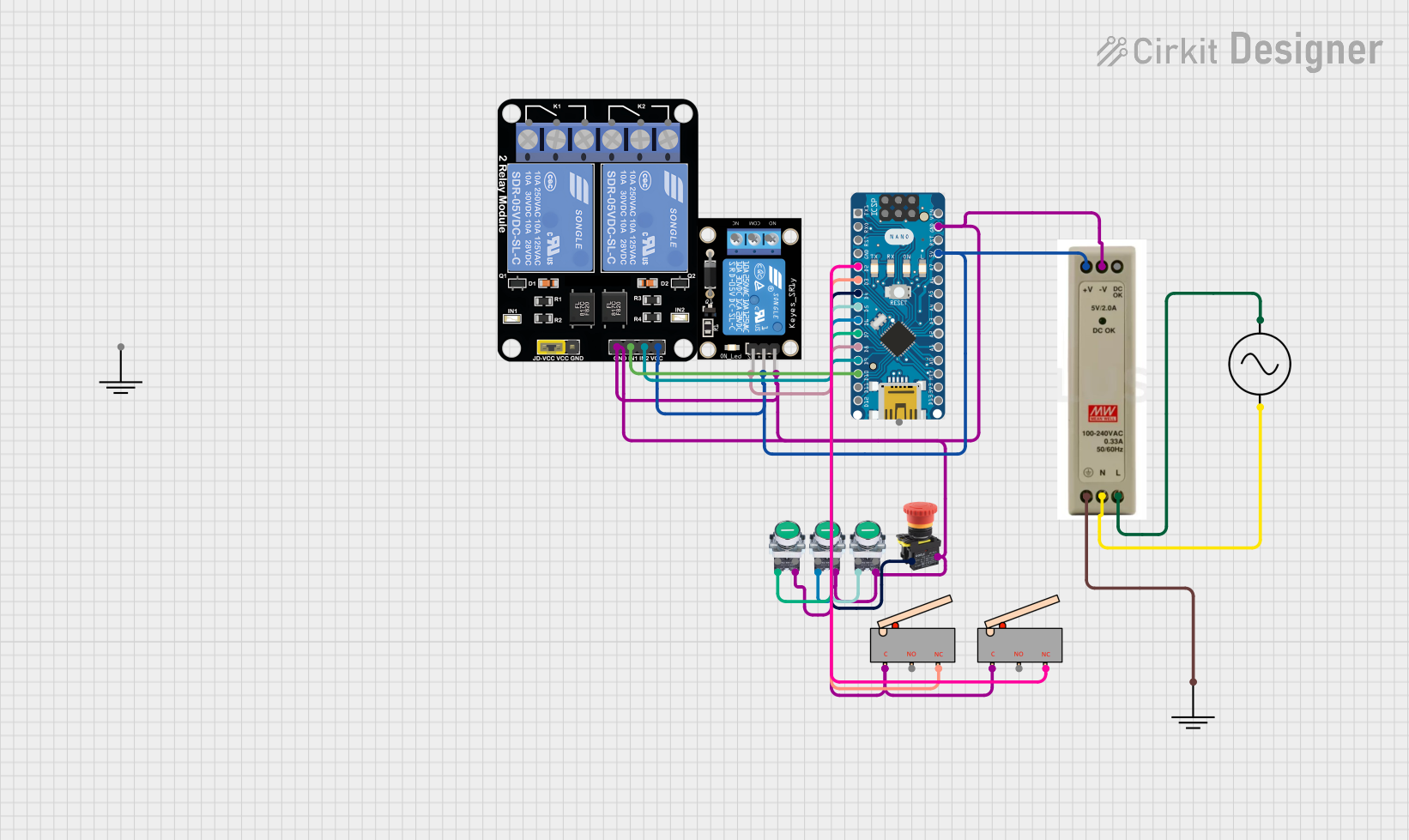
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ENDSTOP

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- 3D Printers: To home the X, Y, and Z axes and define the print bed boundaries.
- CNC Machines: To establish the working area and prevent over-travel of the tool head.
- Robotics: To detect the end of a range of motion for robotic arms or other moving parts.
- Industrial Automation: To ensure safe and accurate operation of conveyor belts, actuators, and other machinery.
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Type: Mechanical switch or optical sensor (depending on the model)
- Operating Voltage: Typically 5V (compatible with most microcontrollers)
- Current Rating: Up to 300mA (varies by model)
- Contact Type: Normally Open (NO) or Normally Closed (NC)
- Switch Life: Up to 1,000,000 cycles (for mechanical switches)
- Mounting: Screw holes or adhesive backing (varies by design)
- Connection: 3-pin interface (Signal, VCC, GND)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pinout for a typical 3-pin endstop is as follows:
| Pin Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Signal | Outputs the state of the switch | HIGH or LOW depending on state |
| VCC | Power supply for the endstop | Typically 5V |
| GND | Ground connection | Connect to system ground |
For 2-pin endstops (simpler models), the configuration is:
| Pin Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Signal | Outputs the state of the switch | HIGH or LOW depending on state |
| GND | Ground connection | Connect to system ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Wiring the Endstop:
- Connect the Signal pin to a digital input pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO).
- Connect the VCC pin to a 5V power source.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
Placement:
- Mount the endstop at the desired limit position of the moving part.
- Ensure the moving part can reliably trigger the switch or sensor without excessive force.
Testing:
- Use a multimeter or microcontroller to verify the state of the endstop when triggered and untriggered.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Debouncing: Mechanical switches may produce noise or "bouncing" when triggered. Use software debouncing or a capacitor to filter out false signals.
- Mounting: Secure the endstop firmly to prevent misalignment during operation.
- Wiring Length: Keep wiring as short as possible to reduce noise and signal degradation.
- Compatibility: Verify the voltage and current ratings of the endstop match your system requirements.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
The following code demonstrates how to use an endstop with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the pin connected to the endstop signal
const int endstopPin = 2; // Connect the Signal pin to digital pin 2
const int ledPin = 13; // Built-in LED for status indication
void setup() {
pinMode(endstopPin, INPUT_PULLUP); // Set endstop pin as input with pull-up resistor
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set LED pin as output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int endstopState = digitalRead(endstopPin); // Read the state of the endstop
if (endstopState == LOW) { // Endstop triggered (assuming active LOW)
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on LED
Serial.println("Endstop triggered!");
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off LED
Serial.println("Endstop not triggered.");
}
delay(100); // Small delay to avoid spamming the serial monitor
}
Notes:
- The
INPUT_PULLUPmode is used to simplify wiring by enabling the internal pull-up resistor. - Adjust the logic in the code if your endstop is active HIGH instead of active LOW.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Endstop Not Triggering:
- Cause: Misalignment or improper placement.
- Solution: Reposition the endstop to ensure reliable triggering.
False Triggers:
- Cause: Electrical noise or bouncing in the mechanical switch.
- Solution: Use software debouncing or add a capacitor across the signal and ground pins.
No Signal Detected:
- Cause: Faulty wiring or damaged endstop.
- Solution: Check all connections and test the endstop with a multimeter.
Microcontroller Not Responding:
- Cause: Incorrect pin configuration or code error.
- Solution: Verify the pin number in the code matches the wiring.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an endstop with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but ensure the endstop is compatible with 3.3V logic levels or use a level shifter.Q: How do I know if my endstop is Normally Open (NO) or Normally Closed (NC)?
A: Use a multimeter to test continuity. In the untriggered state, NO will show no continuity, while NC will show continuity.Q: Can I use an endstop for non-linear motion detection?
A: Yes, as long as the moving part can reliably trigger the switch or sensor.Q: What is the difference between mechanical and optical endstops?
A: Mechanical endstops use physical contact to detect motion, while optical endstops use light interruption for detection. Optical endstops are more precise and durable but may require additional circuitry.