
How to Use PCA9548: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
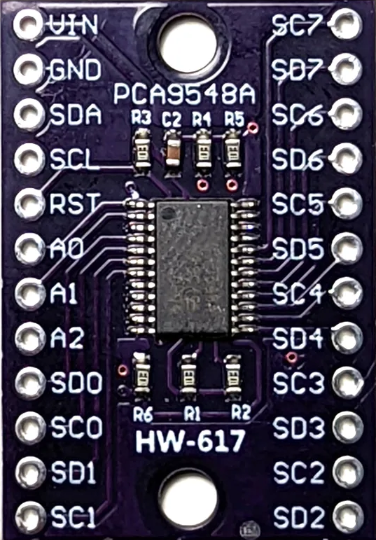
 Design with PCA9548 in Cirkit Designer
Design with PCA9548 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The PCA9548, manufactured by Texas Instruments, is an I2C multiplexer designed to expand the capabilities of a single I2C master device. It allows up to eight independent I2C buses to be connected to a single master, enabling communication with multiple I2C devices that may share the same address. This eliminates address conflicts and simplifies the design of complex I2C systems.
Explore Projects Built with PCA9548
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PCA9548

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Expanding I2C bus capacity in microcontroller-based systems
- Managing multiple I2C devices with identical addresses
- Isolating I2C devices for testing or debugging
- Applications in sensor arrays, data acquisition systems, and industrial automation
Technical Specifications
The PCA9548 is a versatile and robust component with the following key specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage Range | 2.3 V to 5.5 V |
| I2C Bus Speed | Up to 400 kHz (Fast Mode) |
| Number of Channels | 8 |
| I2C Address Range | 0x70 to 0x77 (configurable via A0, A1, A2) |
| Maximum Sink Current (IOL) | 6 mA per I/O |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Package Options | TSSOP, SOIC, QFN |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The PCA9548 is typically available in a 16-pin package. Below is the pinout and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | A0 | Address selection bit 0 |
| 2 | A1 | Address selection bit 1 |
| 3 | A2 | Address selection bit 2 |
| 4 | VSS | Ground |
| 5 | SDA | Serial Data Line (I2C) |
| 6 | SCL | Serial Clock Line (I2C) |
| 7 | RESET | Active-low reset input |
| 8 | VCC | Power supply input |
| 9–16 | SD0–SD7 | Serial Data lines for I2C channels 0 through 7 |
Usage Instructions
The PCA9548 is straightforward to use in I2C-based systems. Below are the steps and considerations for integrating it into your circuit:
Connecting the PCA9548
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a power source within the operating voltage range (2.3 V to 5.5 V) and the VSS pin to ground.
- I2C Master Connection: Connect the SDA and SCL pins to the corresponding I2C lines of the master device.
- Address Configuration: Use the A0, A1, and A2 pins to set the I2C address of the PCA9548. These pins can be tied to VCC or VSS to configure the address.
- Channel Connections: Connect the I2C devices to the SD0–SD7 pins, ensuring proper pull-up resistors are used on each channel.
Selecting an I2C Channel
To communicate with a specific I2C channel, the master device must send a control byte to the PCA9548. The control byte specifies which channel(s) to enable. Only one channel should typically be active at a time to avoid bus conflicts.
Example Control Byte Format
| Bit | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | CH7 | CH6 | CH5 | CH4 |
- Bits 0–7 correspond to channels 0–7. Setting a bit to
1enables the corresponding channel.
Example Arduino Code
Below is an example of how to use the PCA9548 with an Arduino UNO to enable channel 0 and communicate with a device on that channel:
#include <Wire.h> // Include the Wire library for I2C communication
#define PCA9548_ADDRESS 0x70 // Default I2C address of PCA9548
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Enable channel 0 on the PCA9548
Wire.beginTransmission(PCA9548_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0x01); // Control byte to enable channel 0
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("Channel 0 enabled on PCA9548");
}
void loop() {
// Example: Communicate with a device on channel 0
Wire.beginTransmission(0x50); // Address of the I2C device on channel 0
Wire.write(0x00); // Example command to the device
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Best Practices
- Use pull-up resistors on the SDA and SCL lines of both the master and each active channel.
- Avoid enabling multiple channels simultaneously to prevent bus conflicts.
- Use the RESET pin to reset the PCA9548 if communication issues occur.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
No Communication with I2C Devices
- Cause: Incorrect I2C address configuration or channel selection.
- Solution: Verify the A0, A1, and A2 pin settings and ensure the correct control byte is sent.
Bus Conflicts
- Cause: Multiple channels enabled simultaneously.
- Solution: Ensure only one channel is active at a time.
Devices Not Responding
- Cause: Missing pull-up resistors on SDA/SCL lines.
- Solution: Add appropriate pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ or 10 kΩ).
Reset Issues
- Cause: PCA9548 stuck in an unknown state.
- Solution: Use the RESET pin to perform a hardware reset.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the PCA9548 with 3.3 V and 5 V devices on different channels?
A: Yes, the PCA9548 supports level translation between 3.3 V and 5 V devices, provided the VCC voltage is compatible with the master device.
Q: How do I determine the I2C address of the PCA9548?
A: The address is determined by the A0, A1, and A2 pin settings. Refer to the datasheet for the address mapping.
Q: Can I enable multiple channels at once?
A: While technically possible, it is not recommended as it may cause bus conflicts if devices on different channels share the same address.
Q: What happens if I don't use the RESET pin?
A: The RESET pin is optional but recommended for recovering from communication errors or resetting the device to a known state.