
How to Use relay 8 pin: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with relay 8 pin in Cirkit Designer
Design with relay 8 pin in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A relay is an electromechanical switch that allows a low voltage signal to control a high voltage or high current circuit. The 8-pin relay is a versatile component commonly used in automation, home appliances, automotive systems, and industrial control applications. It enables the isolation of control and load circuits, ensuring safety and efficient operation.
Explore Projects Built with relay 8 pin
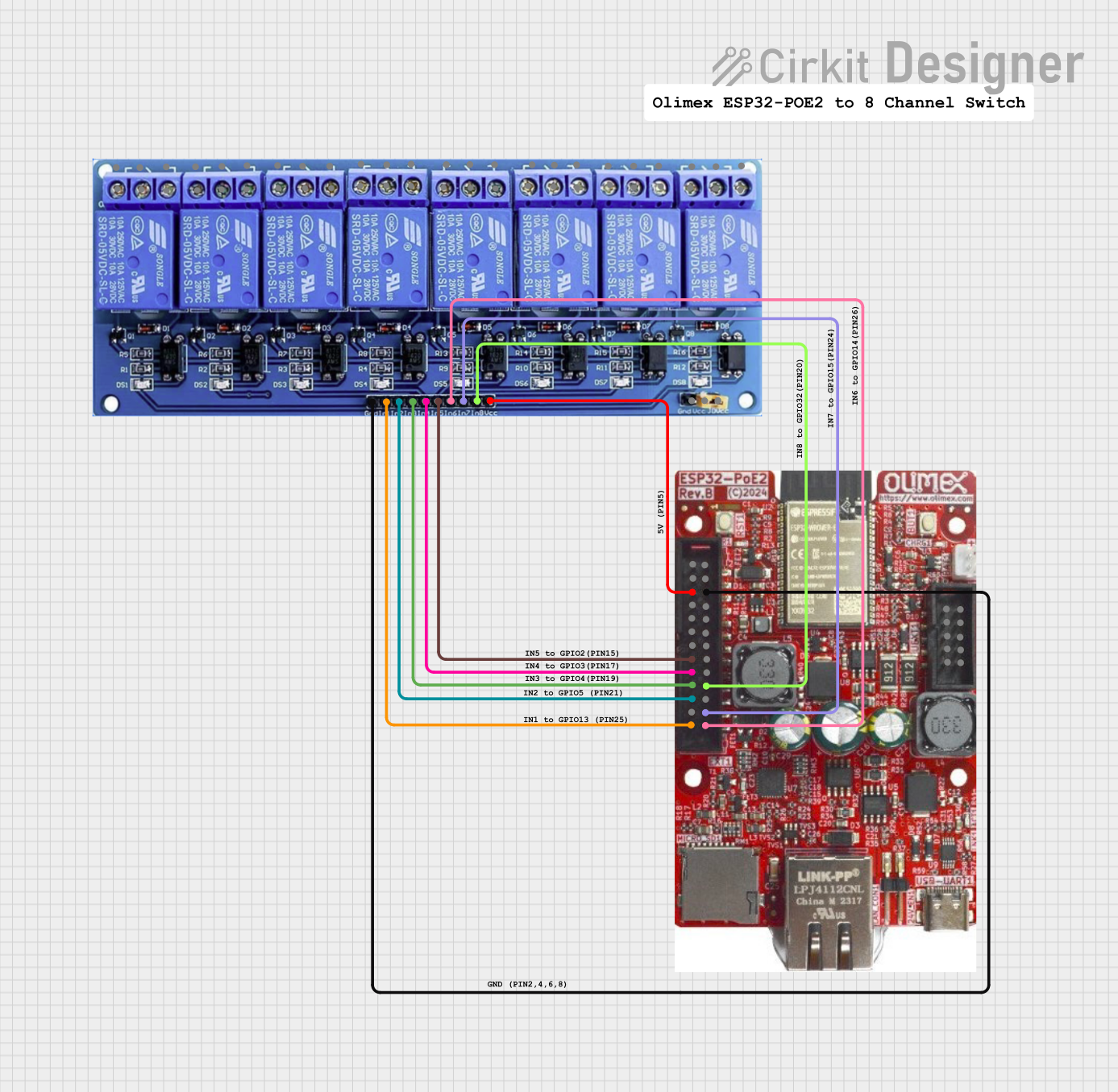
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer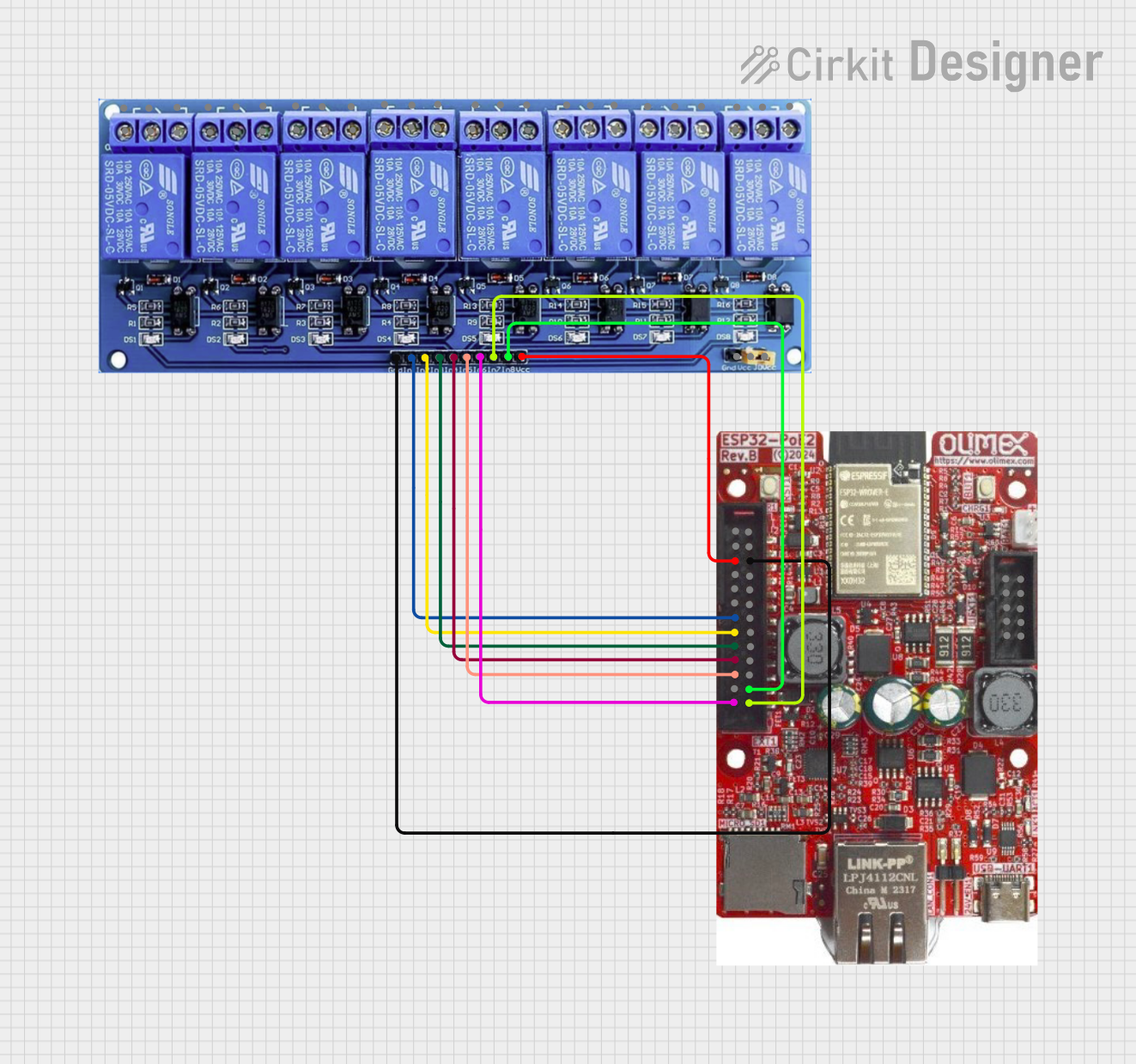
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer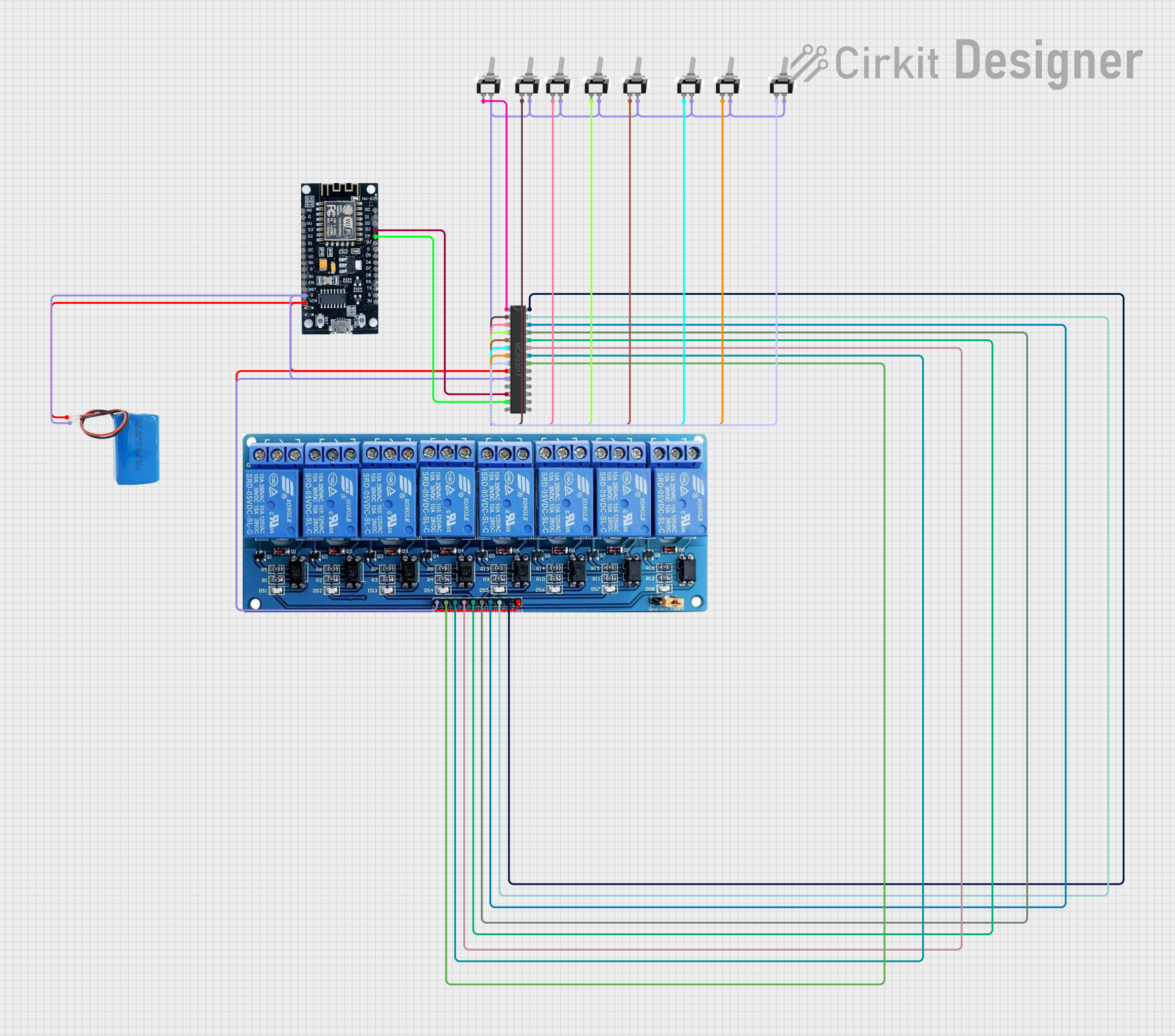
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer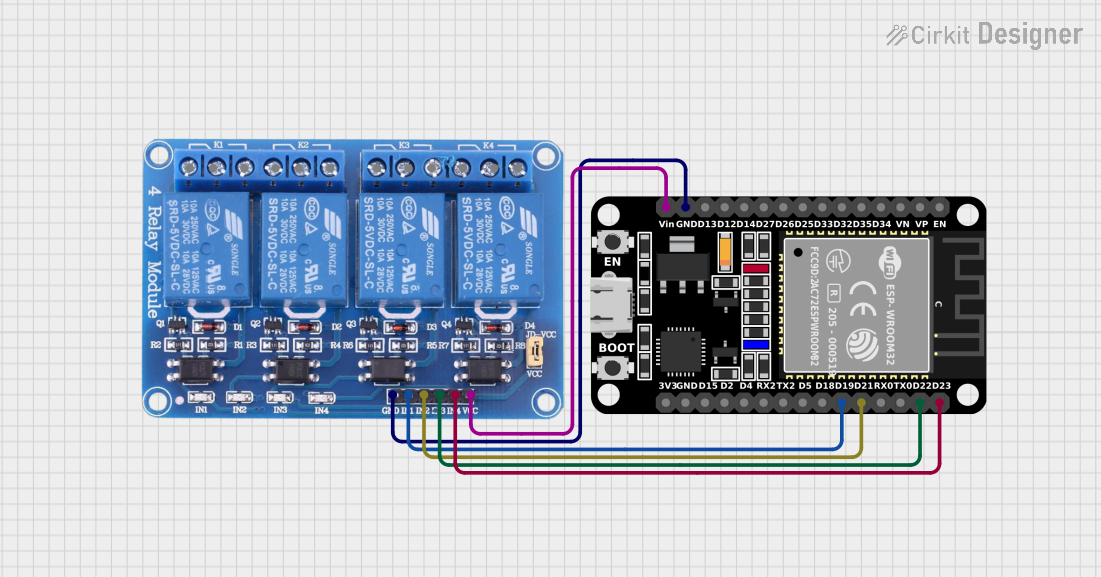
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with relay 8 pin

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Home automation systems (e.g., controlling lights or appliances)
- Automotive electronics (e.g., controlling headlights or motors)
- Industrial machinery and process control
- Microcontroller-based projects (e.g., Arduino or Raspberry Pi)
- Power distribution and switching circuits
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a standard 8-pin relay:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Coil Voltage | 5V, 12V, or 24V (depending on model) |
| Coil Resistance | Typically 70–400 Ω (varies by model) |
| Contact Configuration | SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw) or DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw) |
| Contact Rating | 10A at 250V AC or 10A at 30V DC |
| Switching Voltage (Max) | 250V AC / 30V DC |
| Switching Current (Max) | 10A |
| Insulation Resistance | ≥ 100 MΩ at 500V DC |
| Dielectric Strength | 1500V AC (coil to contacts) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | Varies by model (e.g., 28mm x 12mm x 15mm) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The 8-pin relay typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coil (+) | Positive terminal of the relay coil. Connect to the control voltage. |
| 2 | Coil (-) | Negative terminal of the relay coil. Connect to ground. |
| 3 | Common (COM1) | Common terminal for the first set of contacts. |
| 4 | Normally Open (NO1) | Normally open contact for the first set of contacts. Closed when the relay is activated. |
| 5 | Normally Closed (NC1) | Normally closed contact for the first set of contacts. Open when the relay is activated. |
| 6 | Common (COM2) | Common terminal for the second set of contacts (if DPDT relay). |
| 7 | Normally Open (NO2) | Normally open contact for the second set of contacts (if DPDT relay). |
| 8 | Normally Closed (NC2) | Normally closed contact for the second set of contacts (if DPDT relay). |
Note: For SPDT relays, only one set of contacts (pins 3, 4, and 5) is used.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Relay in a Circuit
Connect the Coil Terminals:
- Connect the positive terminal of the relay coil (Pin 1) to the control voltage (e.g., 5V or 12V).
- Connect the negative terminal of the relay coil (Pin 2) to ground.
- Use a transistor or MOSFET to drive the relay if the control signal comes from a microcontroller.
Connect the Load:
- Identify the load you want to control (e.g., a light bulb or motor).
- Connect one terminal of the load to the common terminal (COM) of the relay (Pin 3 or Pin 6).
- Connect the other terminal of the load to either the normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC) contact, depending on the desired behavior:
- Use the NO contact (Pin 4 or Pin 7) if the load should be powered only when the relay is activated.
- Use the NC contact (Pin 5 or Pin 8) if the load should be powered when the relay is not activated.
Power the Relay:
- Apply the appropriate control voltage to the relay coil to activate it. This will switch the contacts and control the load.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use a Flyback Diode: Always connect a flyback diode (e.g., 1N4007) across the relay coil terminals to protect the driving circuit from voltage spikes caused by the collapsing magnetic field when the relay is deactivated.
- Check the Contact Ratings: Ensure the relay's contact ratings (voltage and current) are suitable for the load you are controlling.
- Avoid Overheating: Do not exceed the relay's maximum switching current or voltage to prevent overheating or damage.
- Isolation: Use optocouplers or isolation circuits if the relay is controlling high voltage loads to ensure safety.
Example: Connecting an 8-Pin Relay to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control an 8-pin relay using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the relay control pin
const int relayPin = 7; // Connect this pin to the relay's coil (+) terminal
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set the relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure the relay is off at startup
}
void loop() {
// Turn the relay on
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH);
delay(5000); // Keep the relay on for 5 seconds
// Turn the relay off
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW);
delay(5000); // Keep the relay off for 5 seconds
}
Note: Use a transistor (e.g., 2N2222) or a relay driver module to interface the Arduino with the relay, as the Arduino's GPIO pins cannot directly supply enough current to drive the relay.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Relay Not Activating:
- Cause: Insufficient control voltage or current.
- Solution: Verify the control voltage matches the relay's coil voltage. Use a transistor or relay driver circuit if necessary.
Load Not Switching:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring of the load to the relay contacts.
- Solution: Double-check the connections to the COM, NO, and NC pins. Ensure the load is connected to the correct terminals.
Relay Buzzing or Chattering:
- Cause: Unstable control signal or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Use a stable power source and ensure the control signal is steady. Add a capacitor across the relay coil for noise suppression.
Overheating or Damage:
- Cause: Exceeding the relay's contact ratings.
- Solution: Ensure the load's voltage and current are within the relay's specified limits.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an 8-pin relay with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, but you will need a transistor or relay driver module to step up the control voltage to match the relay's coil voltage.Q: What is the purpose of the flyback diode?
A: The flyback diode protects the driving circuit from voltage spikes generated when the relay coil is de-energized.Q: Can I use the relay to switch both AC and DC loads?
A: Yes, as long as the load's voltage and current are within the relay's contact ratings.Q: How do I know if my relay is SPDT or DPDT?
A: Check the datasheet or pin configuration. SPDT relays have one set of contacts (COM, NO, NC), while DPDT relays have two sets.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use an 8-pin relay in your projects while ensuring safety and reliability.