
How to Use DC Power Jack: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with DC Power Jack in Cirkit Designer
Design with DC Power Jack in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A DC power jack is a connector used to supply direct current (DC) power to electronic devices. It typically features a cylindrical shape and is designed to accept a matching DC power plug, allowing for easy connection and disconnection of power. DC power jacks are commonly found in consumer electronics, such as laptops, routers, and small appliances, where they serve as the primary interface for external power supplies.
Explore Projects Built with DC Power Jack

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer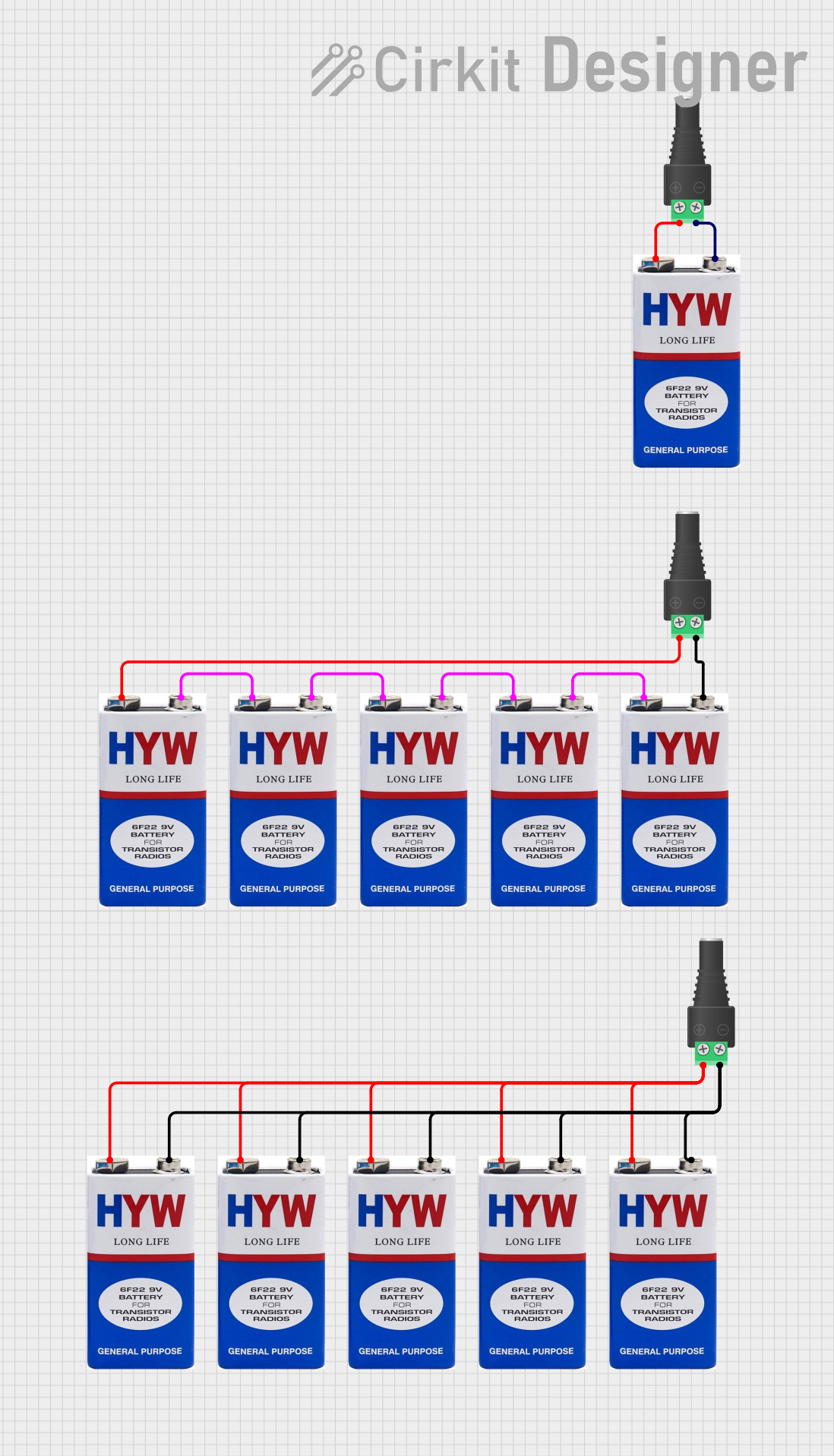
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer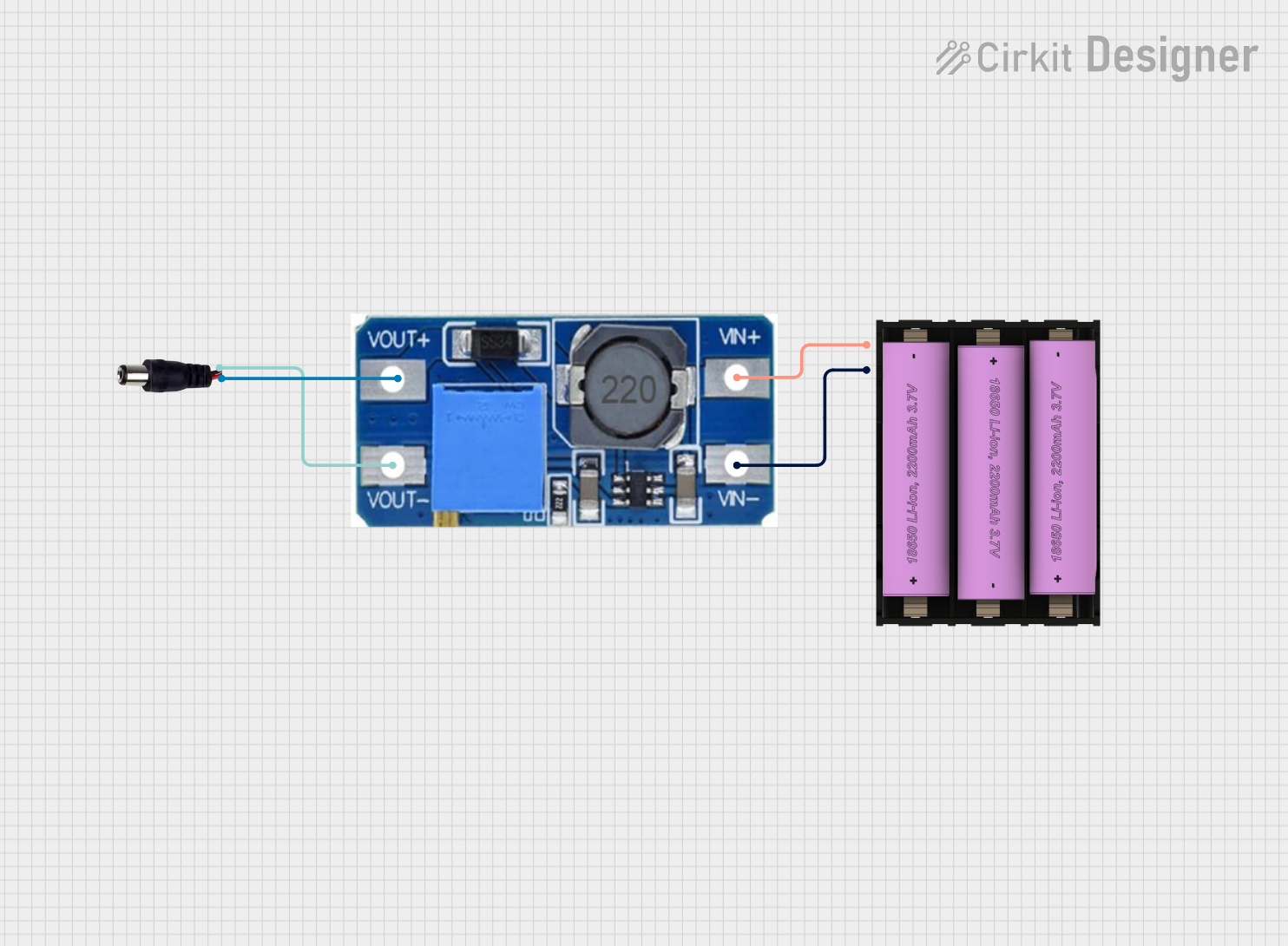
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DC Power Jack

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering small electronic devices like Arduino boards, Raspberry Pi, and other microcontrollers.
- Providing a reliable connection for external power adapters in consumer electronics.
- Used in DIY electronics projects for easy power input integration.
- Replacing damaged power connectors in devices.
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard DC power jack. Note that specific models may vary slightly, so always refer to the datasheet of the exact component you are using.
Key Technical Details
- Voltage Rating: Typically 12V to 24V (varies by model).
- Current Rating: Commonly 1A to 5A.
- Connector Type: Barrel-style connector (e.g., 5.5mm outer diameter, 2.1mm or 2.5mm inner diameter).
- Polarity: Center pin is usually positive (+), and the outer sleeve is negative (-).
- Mounting Style: Panel mount or PCB mount.
- Material: Metal contacts with plastic insulation.
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DC power jack typically has three pins:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Pin 1 (Center Pin) | Connects to the positive terminal of the power supply. |
| Pin 2 (Outer Sleeve) | Connects to the negative terminal of the power supply. |
| Pin 3 (Switch Pin) | Optional pin used to detect the presence of a plug or to disconnect internal power. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Identify the Pins: Use the pin configuration table above to identify the center pin, outer sleeve, and switch pin (if applicable).
- Connect Power Supply: Ensure the power supply matches the voltage and current requirements of your circuit. Verify the polarity of the DC power jack and plug.
- Soldering: If using a PCB mount jack, solder the pins to the appropriate pads on the PCB. For panel mount jacks, secure the jack to the panel and connect wires to the pins.
- Polarity Check: Double-check the polarity of the connections before powering the circuit to avoid damage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Polarity Matters: Always confirm the polarity of the power supply and the DC jack to prevent reverse polarity damage.
- Current Rating: Ensure the jack can handle the maximum current required by your circuit.
- Secure Mounting: For panel mount jacks, ensure the jack is securely fastened to prevent movement or disconnection.
- Switch Pin Usage: If your jack has a switch pin, you can use it to automatically disconnect an internal battery when an external power source is connected.
Example: Connecting a DC Power Jack to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use a DC power jack to power an Arduino UNO. The Arduino UNO has a built-in DC barrel jack that accepts 7-12V DC.
Arduino Code Example
// This example demonstrates powering an Arduino UNO via a DC power jack.
// No specific code is required to use the DC jack, as it directly powers
// the board. However, you can use this code to verify the board is powered
// and functioning correctly by blinking the onboard LED.
void setup() {
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); // Set the onboard LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
No Power to the Circuit:
- Cause: Incorrect polarity or loose connections.
- Solution: Verify the polarity of the power supply and ensure all connections are secure.
Overheating of the Jack:
- Cause: Exceeding the current rating of the jack.
- Solution: Use a jack with a higher current rating or reduce the load on the circuit.
Intermittent Power Loss:
- Cause: Poor solder joints or loose panel mounting.
- Solution: Re-solder the connections or tighten the mounting hardware.
Device Not Turning On:
- Cause: Faulty power supply or damaged jack.
- Solution: Test the power supply with a multimeter and inspect the jack for physical damage.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to check the voltage at the output of the DC power jack.
- Inspect the jack for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- If using a switch pin, ensure it is properly connected and functioning as intended.
- Always use a power supply that matches the voltage and current requirements of your circuit.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and troubleshoot a DC power jack in your electronic projects.