
How to Use Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
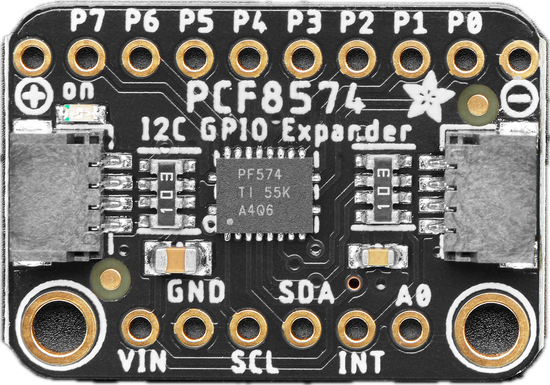
 Design with Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout in Cirkit Designer
Design with Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout (Part ID: 5545) is a versatile module designed to expand the number of digital input/output (GPIO) pins available to your microcontroller. It communicates via the I2C protocol, allowing you to control up to 8 additional GPIO pins with minimal wiring. This breakout is ideal for projects requiring more GPIOs than your microcontroller natively provides, such as controlling LEDs, reading button states, or interfacing with other digital devices.
Explore Projects Built with Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout
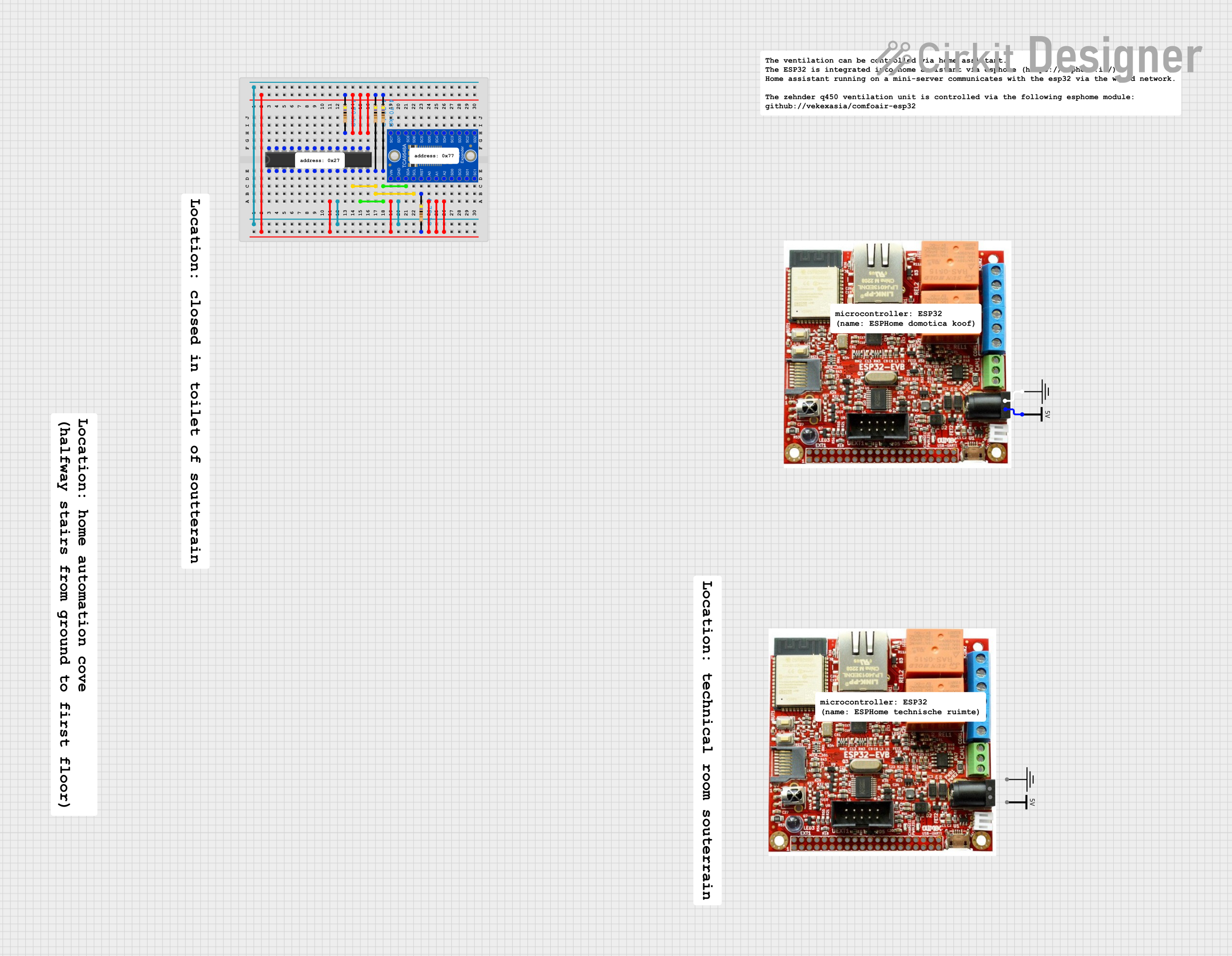
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer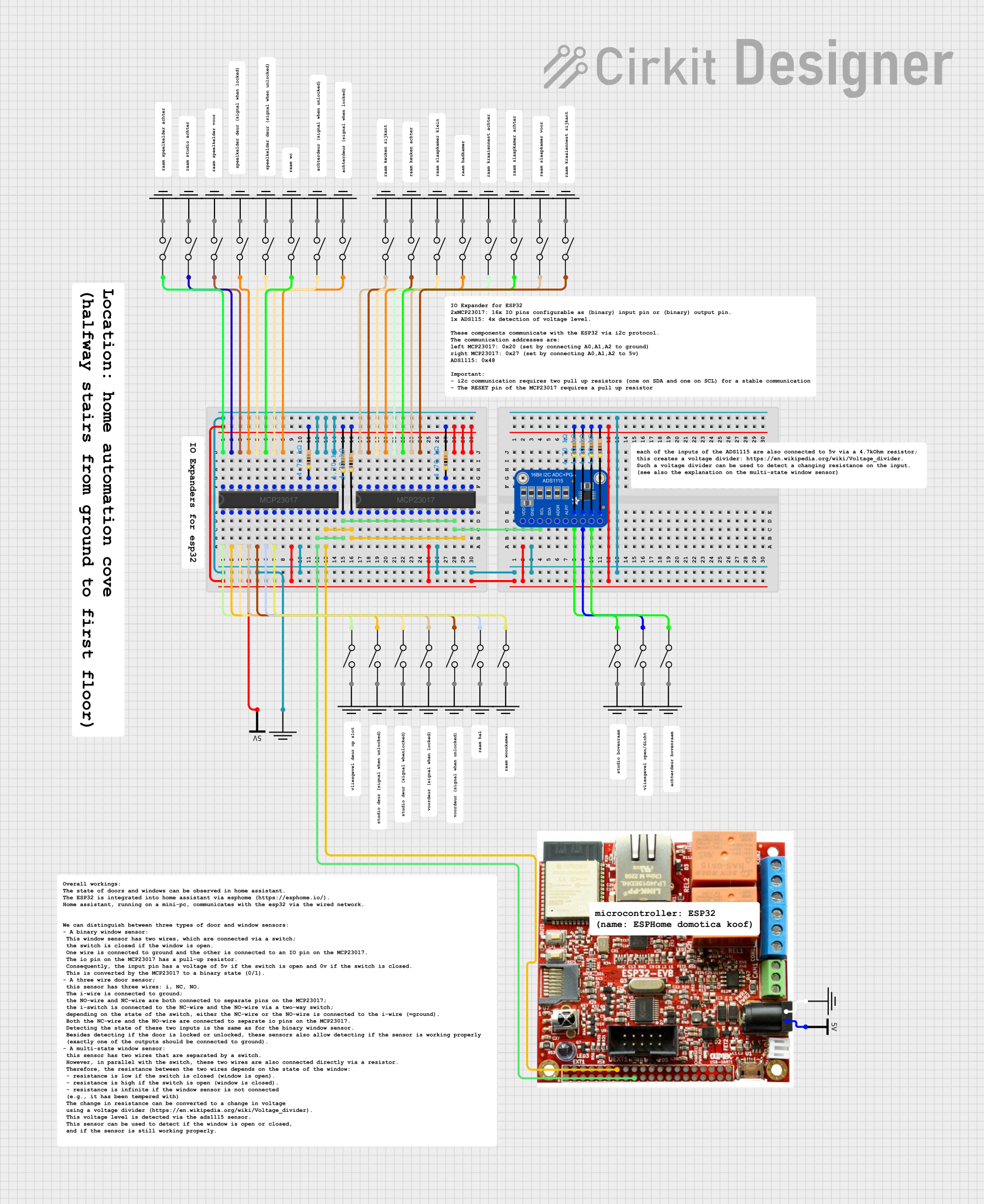
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer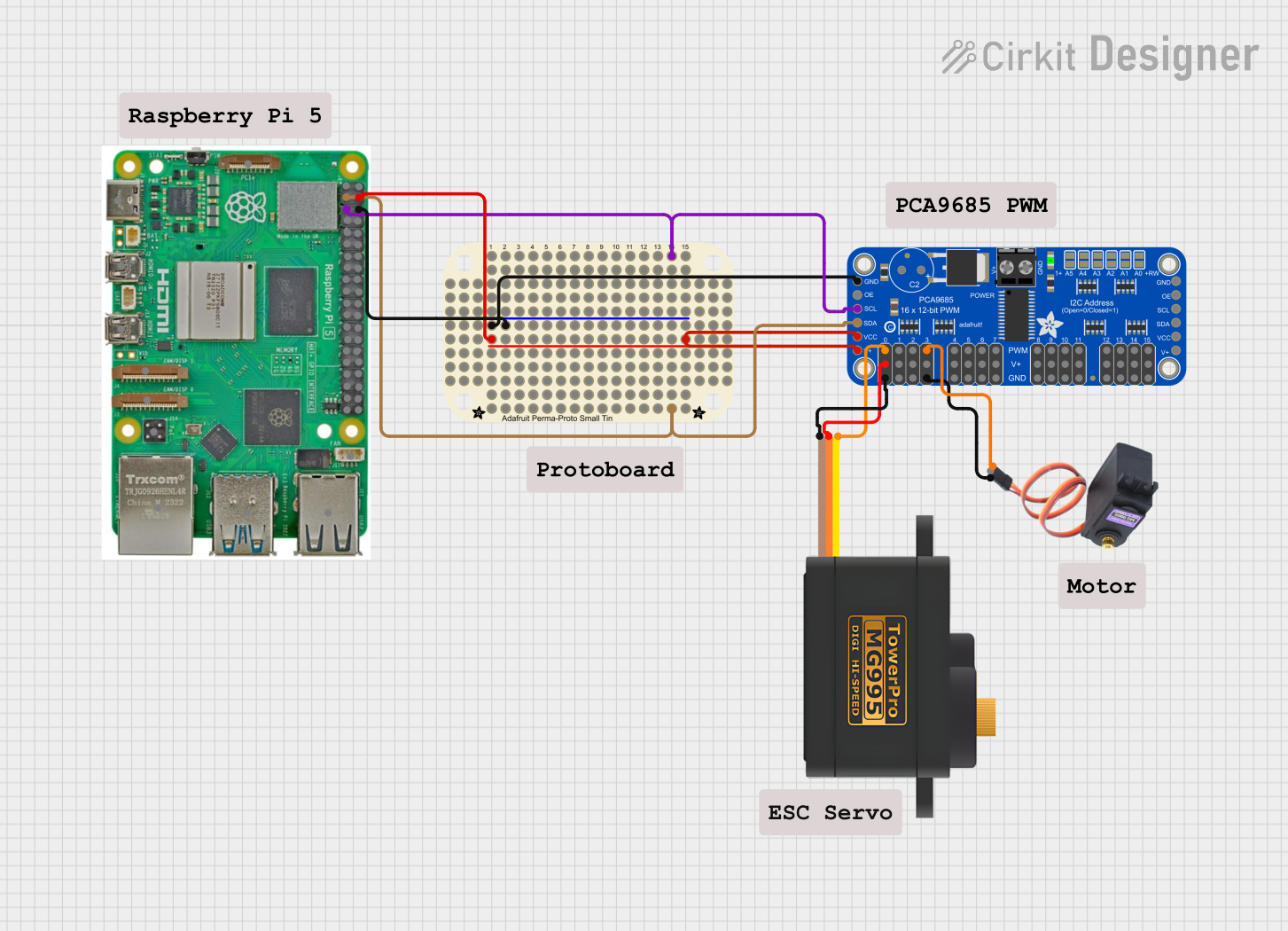
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer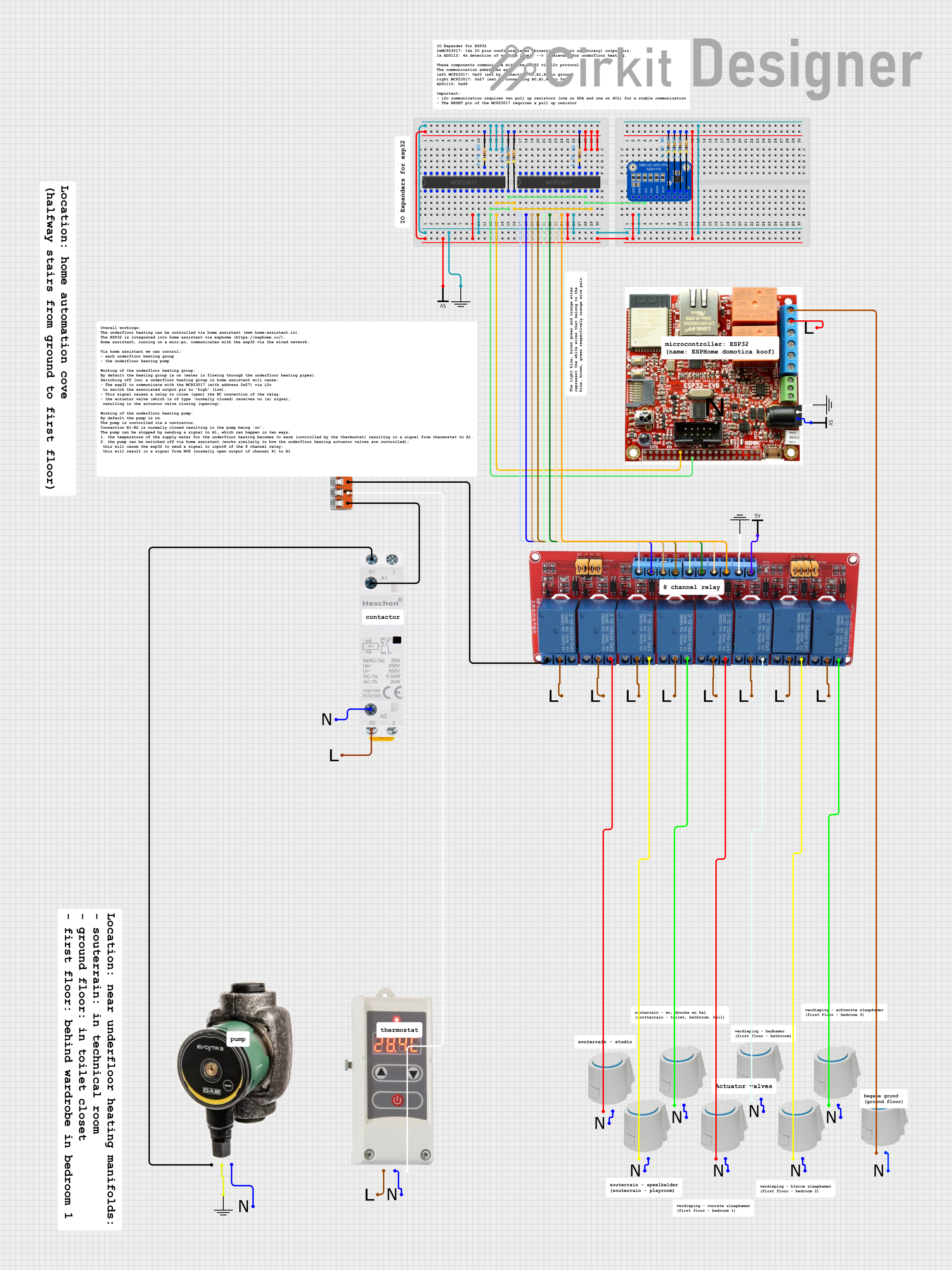
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Expanding GPIO capabilities for microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or ESP32.
- Controlling LEDs, relays, or other digital outputs.
- Reading button states or other digital inputs.
- Building I2C-based sensor hubs or control panels.
- Projects requiring multiple I2C GPIO expanders for scalable designs.
Technical Specifications
The Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout is based on the PCF8574 chip, which provides 8 configurable GPIO pins. Below are the key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 2.5V to 6V
- I2C Address Range: 0x20 to 0x27 (configurable via address jumpers)
- GPIO Pins: 8 (individually configurable as input or output)
- Maximum Sink Current (per pin): 25mA
- Maximum Source Current (per pin): 300µA
- I2C Speed: Up to 100kHz
- Dimensions: 25mm x 18mm x 2mm (excluding header pins)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The breakout board has the following pin layout:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply input (2.5V to 6V). Connect to the microcontroller's 3.3V or 5V pin. |
| GND | Ground connection. Connect to the microcontroller's ground. |
| SDA | I2C data line. Connect to the microcontroller's SDA pin. |
| SCL | I2C clock line. Connect to the microcontroller's SCL pin. |
| P0-P7 | GPIO pins. Configurable as input or output. |
| A0, A1, A2 | Address selection jumpers. Used to set the I2C address (0x20 to 0x27). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect Power and Ground:
- Connect the
VCCpin to the 3.3V or 5V power supply of your microcontroller. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your microcontroller.
- Connect the
Connect I2C Lines:
- Connect the
SDApin to the microcontroller's SDA pin. - Connect the
SCLpin to the microcontroller's SCL pin.
- Connect the
Set the I2C Address:
- Use the
A0,A1, andA2jumpers to configure the I2C address. For example:- All jumpers open: Address = 0x20 (default).
- A0 closed: Address = 0x21.
- A1 closed: Address = 0x22, and so on.
- Use the
Connect GPIO Devices:
- Use the
P0toP7pins to connect LEDs, buttons, or other digital devices. - Configure each pin as input or output in your code.
- Use the
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Pull-Up Resistors: Ensure that the I2C bus has appropriate pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SDA and SCL lines.
- Current Limitations: Avoid exceeding the maximum sink/source current ratings for the GPIO pins.
- Address Conflicts: If using multiple PCF8574 modules, ensure each has a unique I2C address.
- Debouncing Inputs: For buttons or switches connected to GPIO inputs, implement software debouncing to avoid false triggers.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the Adafruit PCF8574 I2C GPIO Expander Breakout with an Arduino UNO to toggle an LED connected to pin P0:
#include <Wire.h>
// Define the I2C address of the PCF8574 (default is 0x20)
#define PCF8574_ADDRESS 0x20
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Set all GPIO pins to HIGH (default state for outputs)
Wire.beginTransmission(PCF8574_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0xFF); // All pins HIGH
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("PCF8574 initialized.");
}
void loop() {
// Toggle the state of P0 (connected to an LED)
Wire.beginTransmission(PCF8574_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0xFE); // Set P0 LOW, others HIGH
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(500); // Wait 500ms
Wire.beginTransmission(PCF8574_ADDRESS);
Wire.write(0xFF); // Set all pins HIGH
Wire.endTransmission();
delay(500); // Wait 500ms
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
I2C Communication Not Working:
- Solution: Verify the SDA and SCL connections. Ensure pull-up resistors are present on the I2C lines.
- Tip: Use an I2C scanner sketch to confirm the module's address.
GPIO Pins Not Responding:
- Solution: Check the wiring to the GPIO pins and ensure they are configured correctly in your code.
- Tip: Use a multimeter to verify the voltage levels on the pins.
Address Conflict with Other I2C Devices:
- Solution: Change the I2C address of the PCF8574 using the
A0,A1, andA2jumpers.
- Solution: Change the I2C address of the PCF8574 using the
LEDs Not Lighting Up:
- Solution: Ensure the LED is connected with the correct polarity and that the current-limiting resistor is appropriate.
FAQs
Can I use multiple PCF8574 modules on the same I2C bus? Yes, up to 8 modules can be used by configuring unique I2C addresses using the
A0,A1, andA2jumpers.What is the maximum cable length for I2C communication? The maximum length depends on the pull-up resistor values and the I2C speed, but typically it is limited to a few meters.
Can the GPIO pins handle analog signals? No, the GPIO pins are digital-only and cannot process analog signals.
Is the PCF8574 compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers? Yes, the PCF8574 operates at 2.5V to 6V, making it compatible with both 3.3V and 5V systems.