
How to Use Teseo-LIV4F: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Teseo-LIV4F in Cirkit Designer
Design with Teseo-LIV4F in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Teseo-LIV4F, manufactured by STMicroelectronics, is a high-performance GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver module designed for precise positioning and navigation applications. It supports multiple satellite systems, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, making it a versatile solution for global navigation needs. The module incorporates advanced algorithms to enhance accuracy and reliability, even in challenging environments such as urban canyons or dense foliage.
Explore Projects Built with Teseo-LIV4F
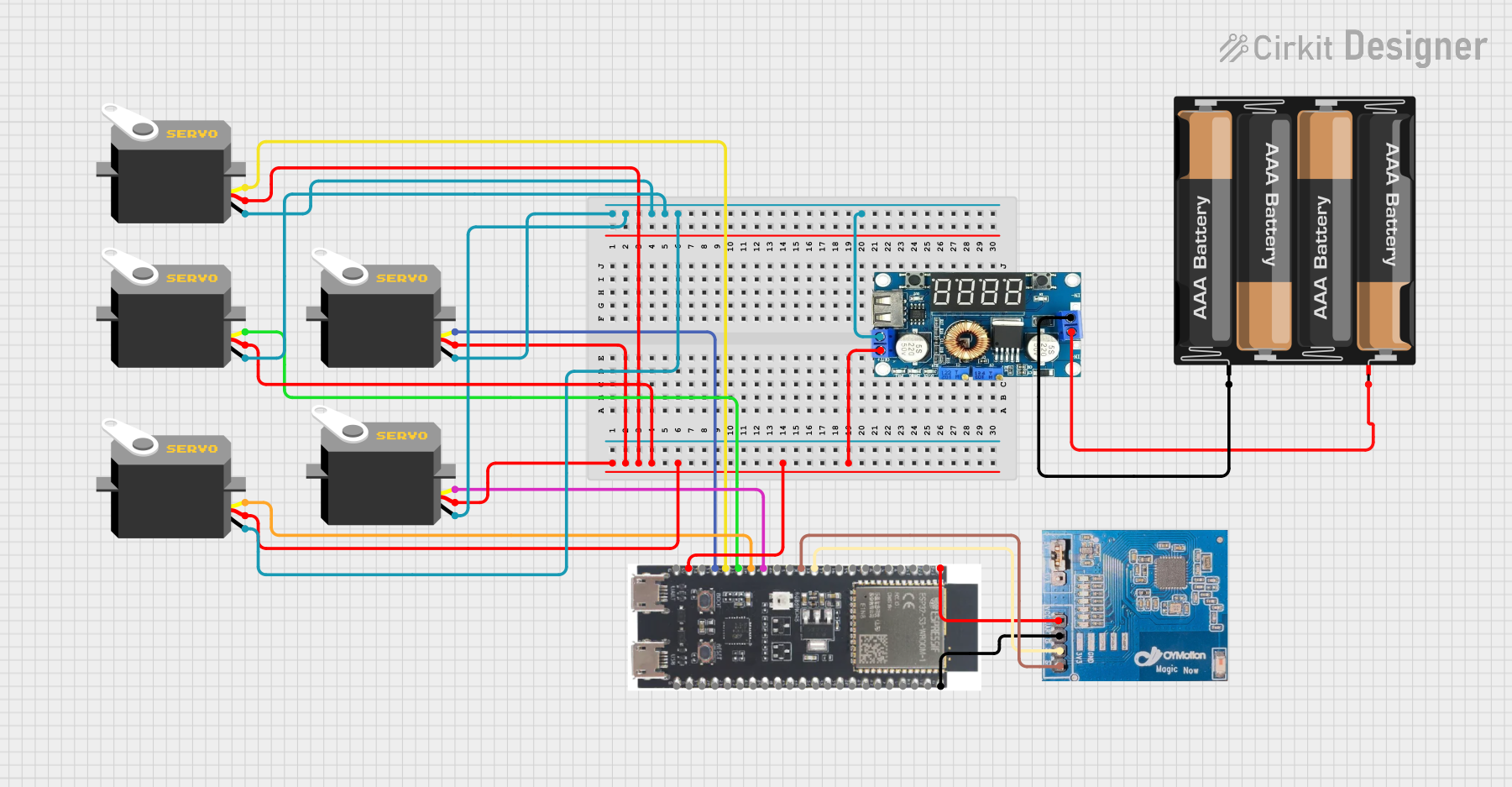
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer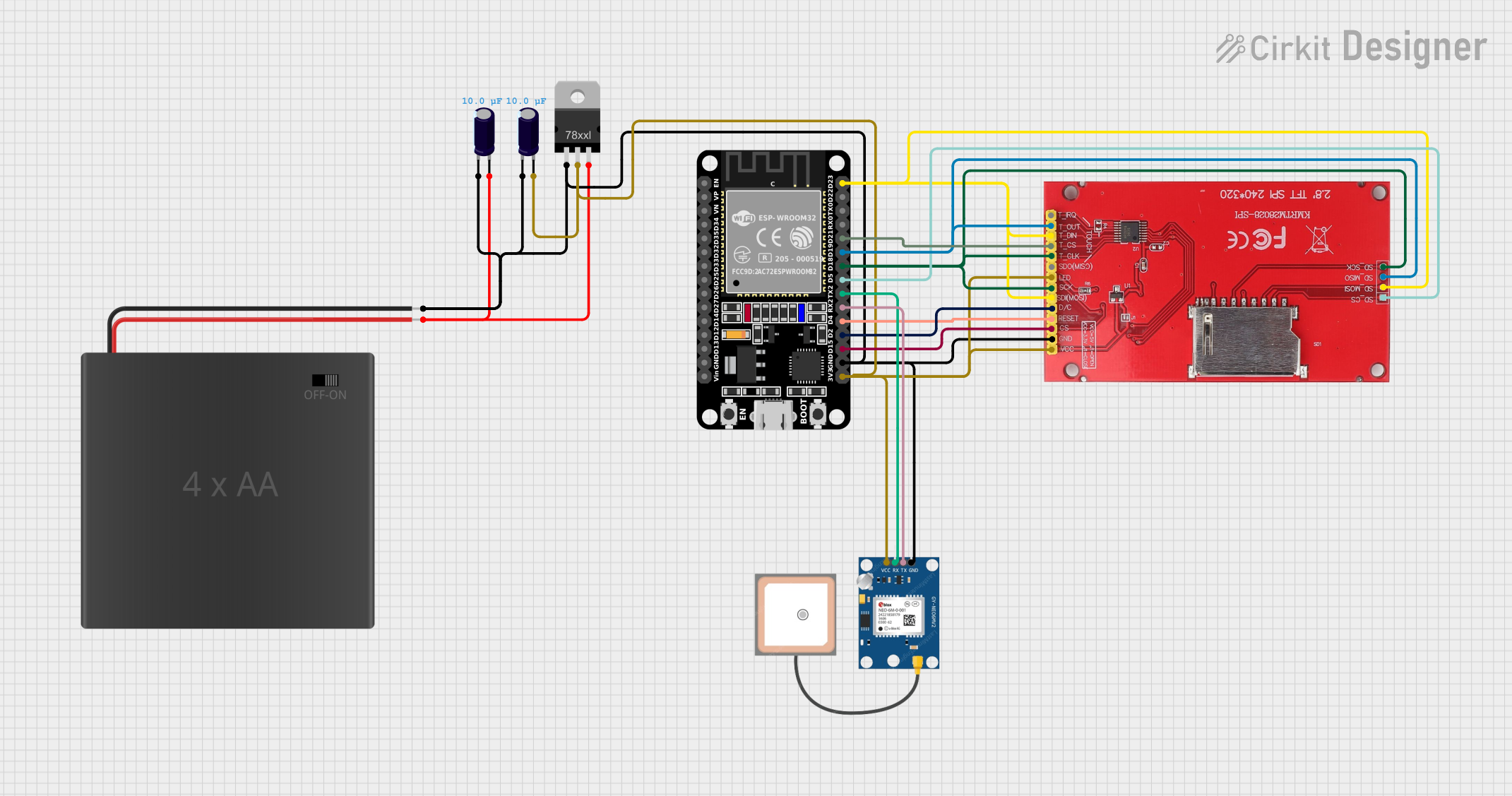
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer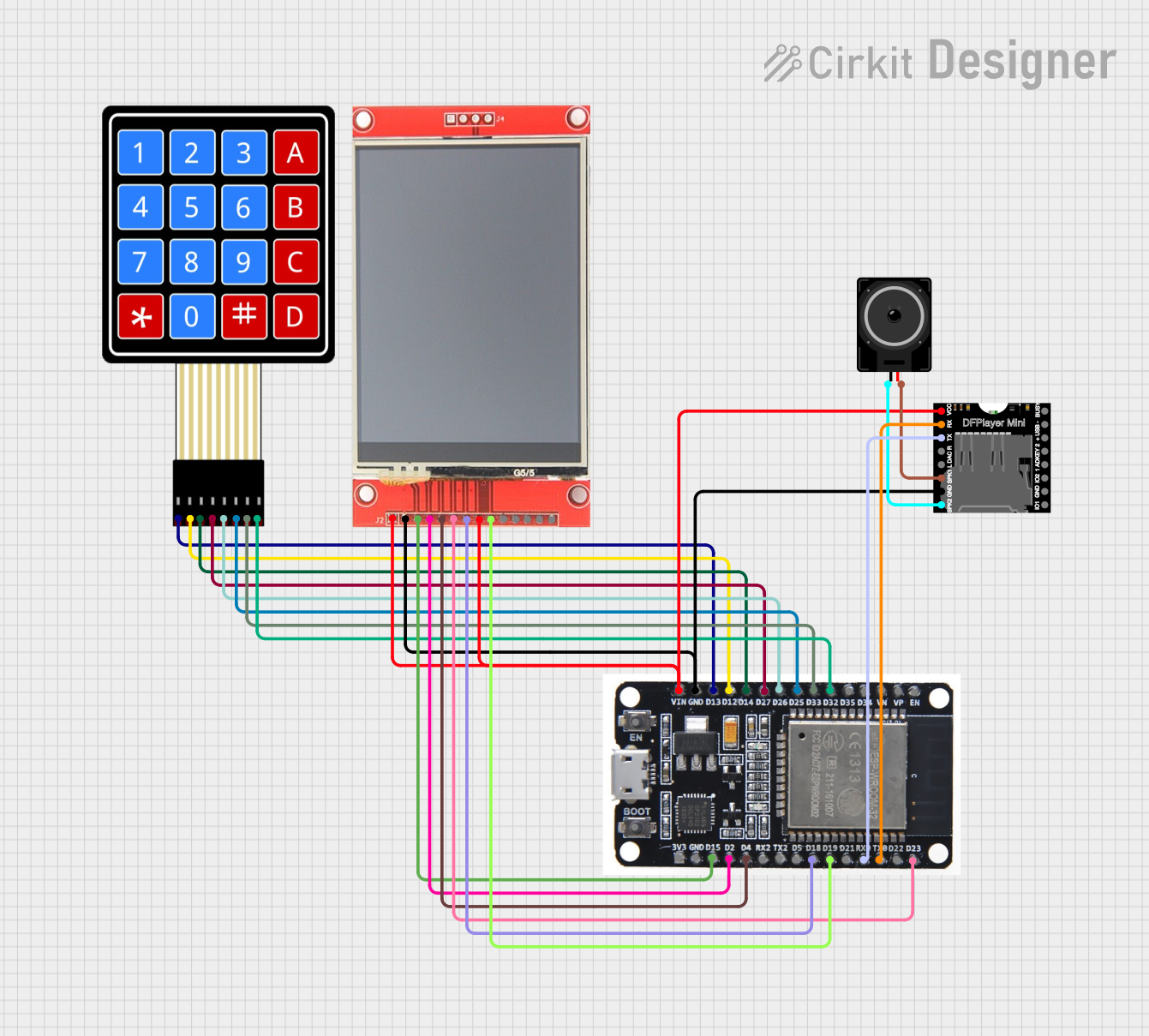
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Teseo-LIV4F

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automotive navigation systems
- Asset tracking and fleet management
- Drones and UAVs (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles)
- IoT devices requiring geolocation
- Marine and outdoor navigation
- Precision agriculture
Technical Specifications
The Teseo-LIV4F is a compact and efficient GNSS module with the following key specifications:
Key Technical Details
- Supported GNSS Systems: GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, BeiDou
- Frequency Bands: L1 (1575.42 MHz for GPS, Galileo, and BeiDou; 1602 MHz for GLONASS)
- Sensitivity:
- Acquisition: -147 dBm
- Tracking: -163 dBm
- Position Accuracy: < 1.5 meters CEP (Circular Error Probable)
- Update Rate: Up to 10 Hz
- Power Supply Voltage: 3.0V to 3.6V
- Power Consumption:
- Acquisition: ~30 mA
- Tracking: ~25 mA
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
- Communication Interfaces: UART, I2C, SPI
- Dimensions: 9.7 mm x 10.1 mm x 2.5 mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Teseo-LIV4F module has a set of pins for power, communication, and control. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description | Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.0V to 3.6V) | Input |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection | - |
| 3 | TXD | UART Transmit | Output |
| 4 | RXD | UART Receive | Input |
| 5 | PPS | Pulse Per Second output for timing | Output |
| 6 | I2C_SCL | I2C Clock | Input |
| 7 | I2C_SDA | I2C Data | Bidirectional |
| 8 | SPI_MISO | SPI Master-In-Slave-Out | Output |
| 9 | SPI_MOSI | SPI Master-Out-Slave-In | Input |
| 10 | SPI_CLK | SPI Clock | Input |
| 11 | SPI_CS | SPI Chip Select | Input |
| 12 | RESET_N | Active-low reset | Input |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Teseo-LIV4F in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a stable 3.3V power source and the GND pin to the ground.
- Communication Interface: Choose a communication protocol (UART, I2C, or SPI) based on your application. For example:
- For UART, connect the TXD and RXD pins to the corresponding UART pins on your microcontroller.
- For I2C, connect I2C_SCL and I2C_SDA to the microcontroller's I2C pins, with appropriate pull-up resistors (typically 4.7 kΩ).
- For SPI, connect SPI_MISO, SPI_MOSI, SPI_CLK, and SPI_CS to the microcontroller's SPI pins.
- Antenna Connection: Attach an external GNSS antenna to the module's antenna port for optimal signal reception.
- Reset: Use the RESET_N pin to reset the module if needed. Pull this pin low for at least 10 ms to trigger a reset.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Antenna Placement: Ensure the antenna has a clear view of the sky for optimal satellite reception. Avoid placing it near metal objects or inside enclosures that block RF signals.
- Power Supply: Use a low-noise power supply to prevent interference with the GNSS signals.
- Ground Plane: For best performance, use a ground plane under the module to improve signal quality.
- Firmware Updates: Check for firmware updates from STMicroelectronics to ensure the module operates with the latest features and bug fixes.
Example: Connecting Teseo-LIV4F to Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the Teseo-LIV4F with an Arduino UNO using UART communication:
Circuit Connections
- Connect the Teseo-LIV4F's TXD pin to the Arduino's RX (Pin 0).
- Connect the Teseo-LIV4F's RXD pin to the Arduino's TX (Pin 1).
- Connect the VCC pin to the Arduino's 3.3V pin.
- Connect the GND pin to the Arduino's GND pin.
Arduino Code
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial GNSS(10, 11); // RX = Pin 10, TX = Pin 11
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize Serial Monitor
GNSS.begin(9600); // Initialize GNSS module communication
Serial.println("Teseo-LIV4F GNSS Module Test");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the GNSS module
if (GNSS.available()) {
// Read data from GNSS and send it to Serial Monitor
while (GNSS.available()) {
char c = GNSS.read();
Serial.print(c);
}
}
// Optional: Add a small delay to avoid flooding the Serial Monitor
delay(100);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No GNSS Fix (No Position Data)
- Cause: Poor antenna placement or obstructed view of the sky.
- Solution: Ensure the antenna is placed in an open area with a clear view of the sky. Check the antenna connection.
Module Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or communication interface setup.
- Solution: Verify the power supply voltage (3.3V) and check the wiring of the communication interface.
Intermittent Signal Loss
- Cause: RF interference or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Use a low-noise power supply and ensure the module is placed away from sources of RF interference.
Data Corruption in Output
- Cause: Mismatched baud rate or noisy communication lines.
- Solution: Ensure the baud rate of the microcontroller matches the module's default baud rate (9600 bps). Use shorter wires for communication.
FAQs
Q: Can the Teseo-LIV4F operate indoors?
- A: While the module can operate indoors, signal reception may be weak or unavailable due to obstructions. Use it in open areas for best results.
Q: How do I increase the update rate?
- A: The update rate can be configured up to 10 Hz using specific commands sent via the communication interface. Refer to the module's datasheet for details.
Q: Does the module support differential GNSS (DGNSS)?
- A: Yes, the Teseo-LIV4F supports DGNSS for improved positioning accuracy.
Q: What type of antenna should I use?
- A: Use an active GNSS antenna with a gain of 15-30 dB for optimal performance.