
How to Use battery1: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with battery1 in Cirkit Designer
Design with battery1 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A battery is a device that stores electrical energy in chemical form and converts it to electrical energy when needed. It serves as a portable power source for a wide range of electronic devices, from small gadgets like remote controls and smartphones to larger systems such as electric vehicles and backup power supplies. Batteries are essential in applications where mobility, reliability, and independence from a fixed power source are required.
Common applications include:
- Powering portable electronic devices (e.g., flashlights, cameras, and toys)
- Providing backup power for critical systems (e.g., UPS systems)
- Enabling mobility in electric vehicles and robotics
- Supplying energy for renewable energy storage systems (e.g., solar panels)
Explore Projects Built with battery1
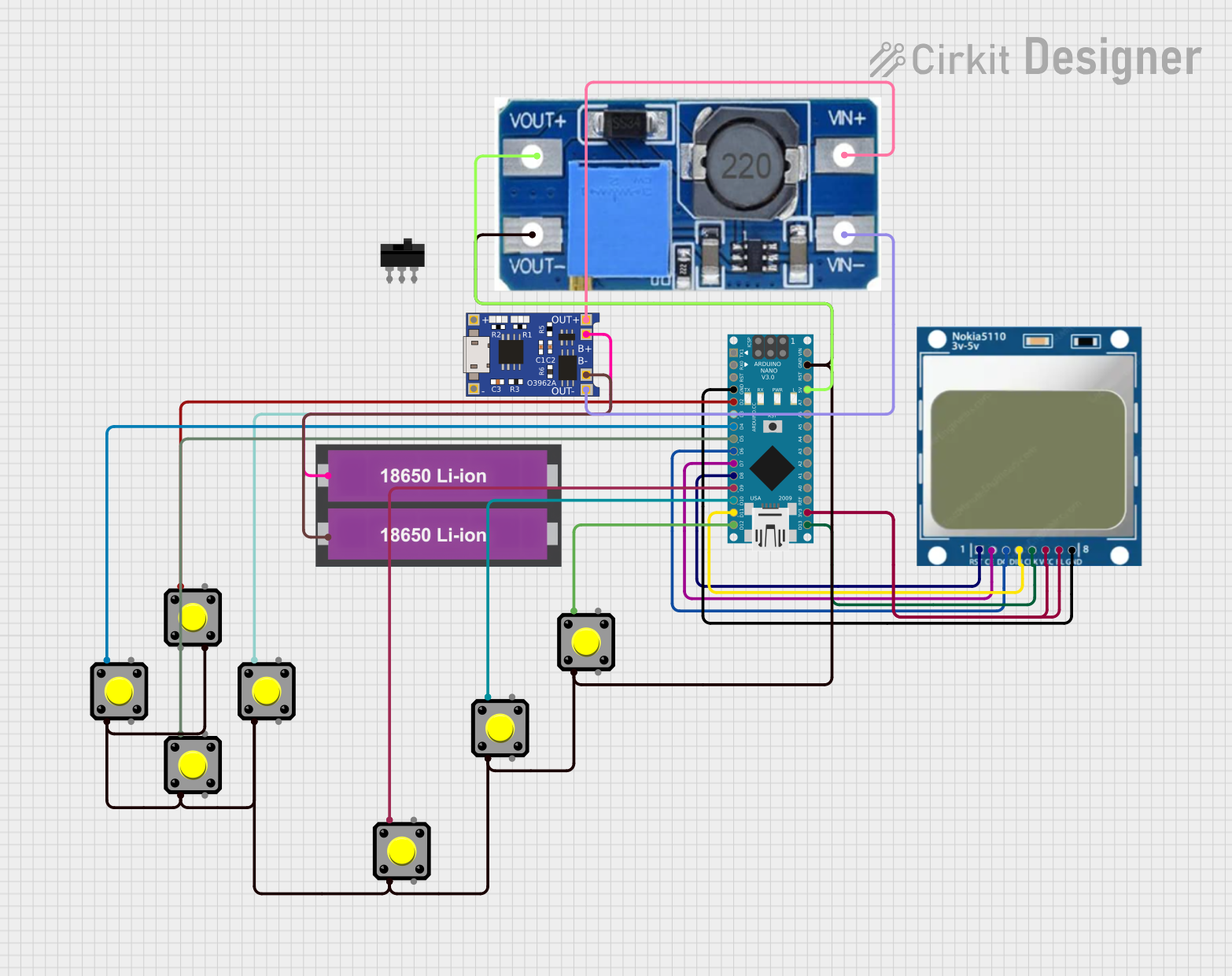
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer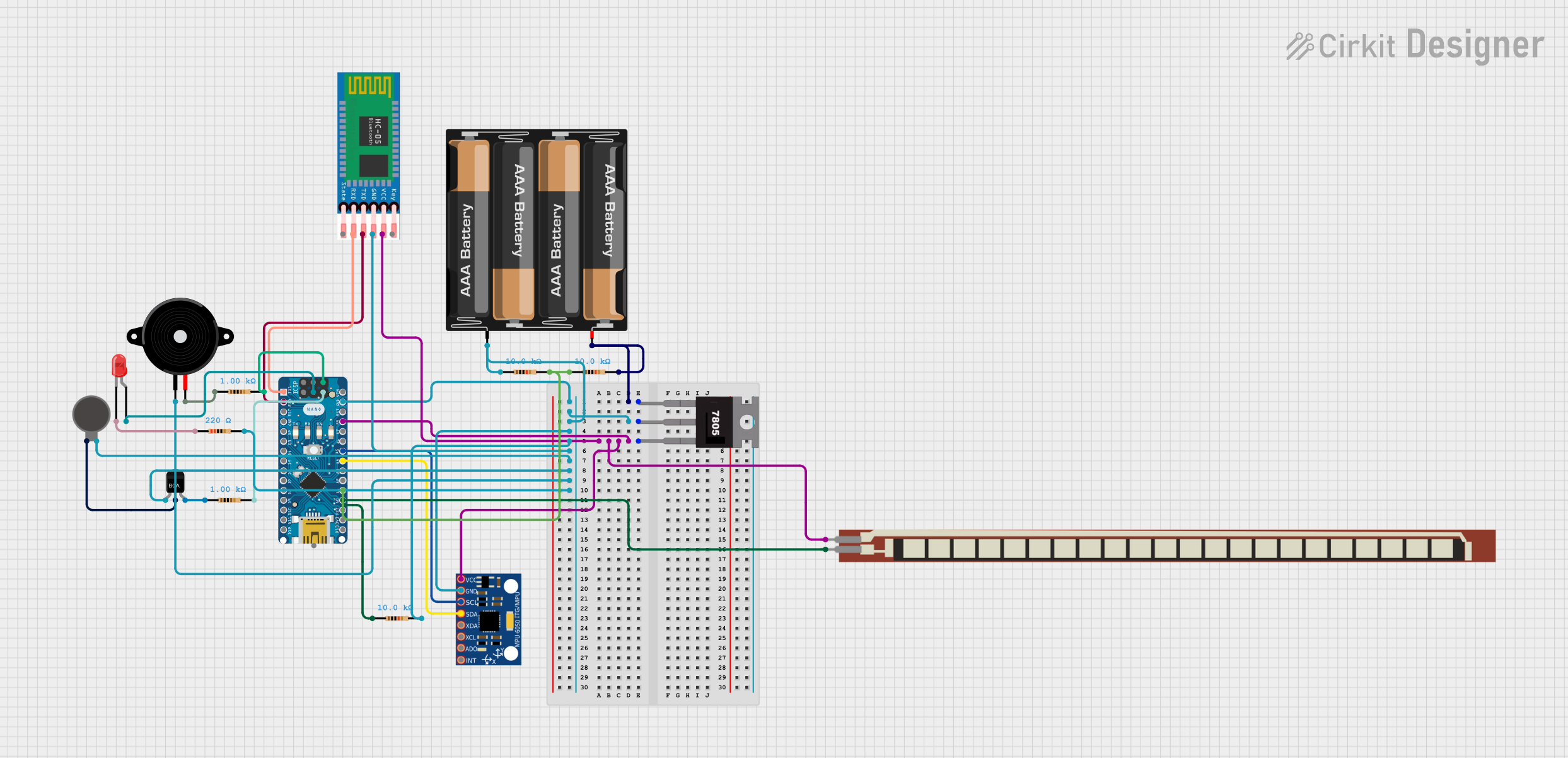
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer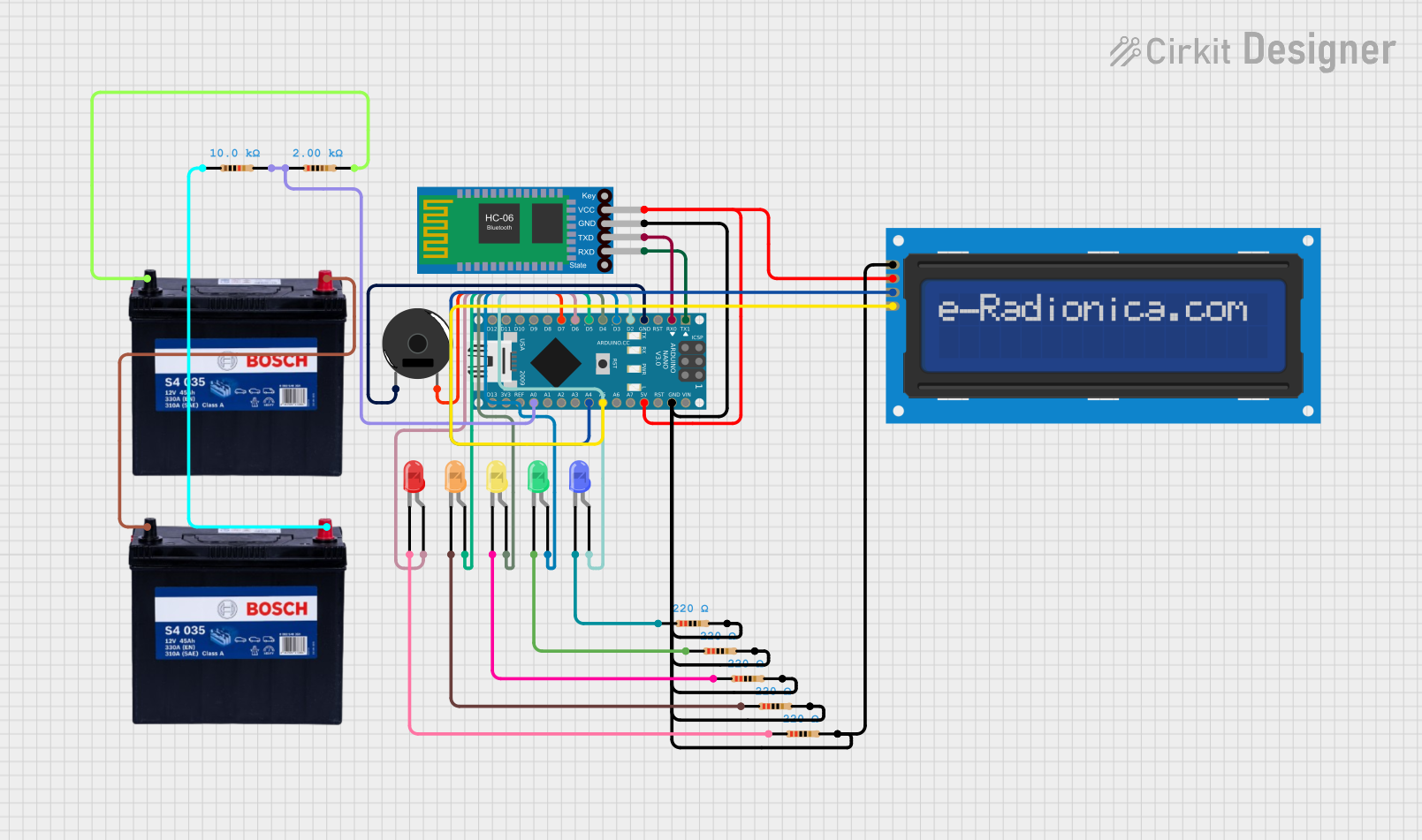
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer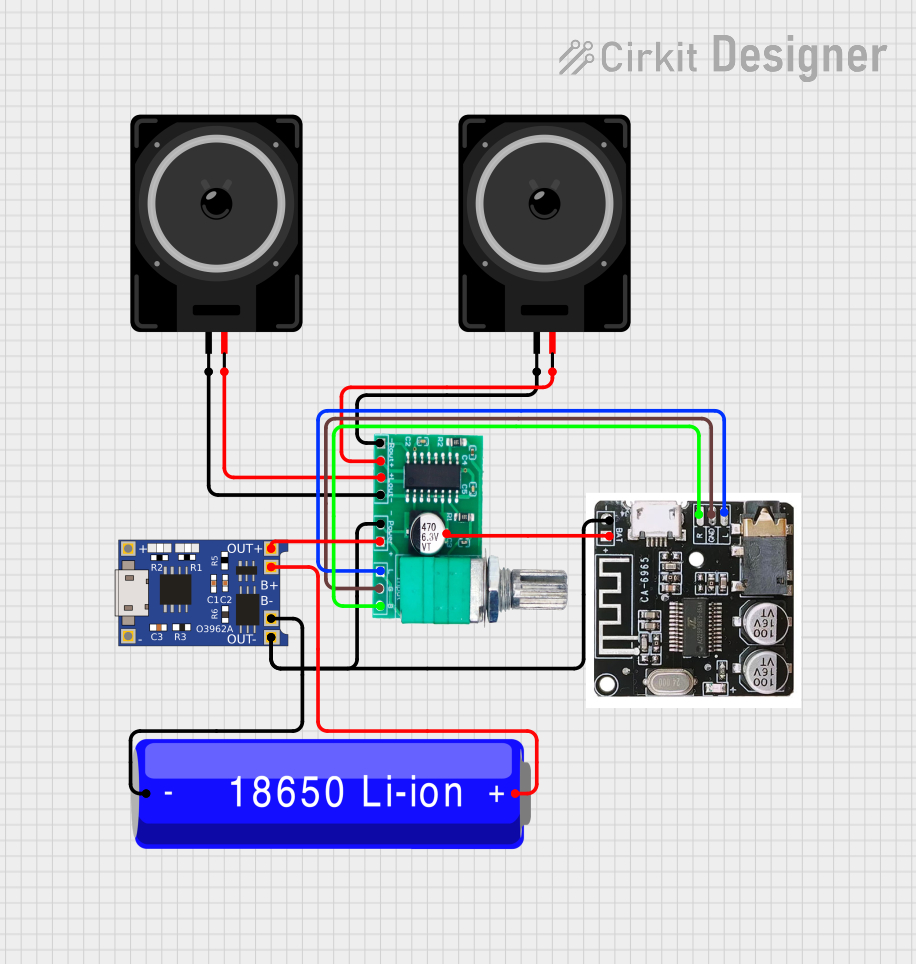
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with battery1

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The specifications of a battery vary depending on its type (e.g., alkaline, lithium-ion, lead-acid). Below is a general overview of key parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | The nominal voltage output of the battery. Common values: 1.5V, 3.7V, 9V, etc. |
| Capacity (mAh or Ah) | The amount of charge the battery can store, measured in milliampere-hours (mAh). |
| Chemistry | The chemical composition of the battery (e.g., alkaline, lithium-ion, NiMH). |
| Rechargeability | Indicates whether the battery is rechargeable (e.g., lithium-ion, NiMH). |
| Dimensions | Physical size of the battery (e.g., AA, AAA, 18650, etc.). |
| Operating Temperature | The temperature range within which the battery operates efficiently. |
Example Pin Configuration (for a 9V Battery Connector)
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive (+) | The positive terminal of the battery, typically connected to the circuit's VCC. |
| 2 | Negative (-) | The negative terminal of the battery, typically connected to the circuit's GND. |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the Battery:
- Identify the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals of the battery.
- Use appropriate connectors or holders to securely attach the battery to your circuit.
- Ensure the voltage and current ratings of the battery match the requirements of your circuit.
Important Considerations:
- Polarity: Always connect the battery with the correct polarity to avoid damaging the circuit.
- Overloading: Do not exceed the battery's maximum current rating, as this can cause overheating or damage.
- Storage: Store batteries in a cool, dry place to prevent leakage or degradation.
- Rechargeable Batteries: Use a compatible charger to recharge batteries safely. Avoid overcharging.
Using a Battery with an Arduino UNO:
- A common use case is powering an Arduino UNO with a 9V battery.
- Connect the positive terminal of the battery to the Arduino's VIN pin and the negative terminal to GND.
Example Arduino code to read battery voltage using an analog pin:
// This code reads the battery voltage using an analog pin on the Arduino UNO. const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the battery voltage divider float voltage = 0.0; // Variable to store the calculated voltage void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication } void loop() { int sensorValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog value (0-1023) voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); // Convert to voltage (assuming 5V reference) Serial.print("Battery Voltage: "); Serial.print(voltage); Serial.println(" V"); delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading }Note: Use a voltage divider circuit if the battery voltage exceeds the Arduino's input voltage range (0-5V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Battery Drains Quickly:
- Cause: High current draw from the circuit or a faulty battery.
- Solution: Check the circuit's power consumption and replace the battery if necessary.
Battery Overheats:
- Cause: Overloading or short-circuiting the battery.
- Solution: Ensure the circuit does not exceed the battery's current rating. Check for short circuits.
Device Does Not Power On:
- Cause: Incorrect polarity or insufficient battery voltage.
- Solution: Verify the battery's polarity and ensure it meets the device's voltage requirements.
Rechargeable Battery Does Not Charge:
- Cause: Faulty charger or battery degradation.
- Solution: Test the charger with another battery or replace the battery if it no longer holds a charge.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a higher voltage battery than specified for my device?
A: No, using a higher voltage battery can damage your device. Always use a battery with the recommended voltage.Q: How do I dispose of old batteries?
A: Follow local regulations for battery disposal. Many areas have recycling programs for batteries.Q: Can I mix different types of batteries in the same device?
A: No, mixing battery types (e.g., alkaline and NiMH) can cause uneven discharge and damage the device.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure safe and efficient use of batteries in your electronic projects.