
How to Use Ardupilot Mega APM 2.8: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Ardupilot Mega APM 2.8 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Ardupilot Mega APM 2.8 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Ardupilot Mega APM 2.8, manufactured by ATMEGA2560 (Part ID: APM), is a versatile open-source autopilot platform designed for controlling drones and other unmanned vehicles. It features advanced flight control algorithms and supports a wide range of sensors, making it a popular choice for hobbyists and professionals in the field of robotics and UAVs.
Explore Projects Built with Ardupilot Mega APM 2.8
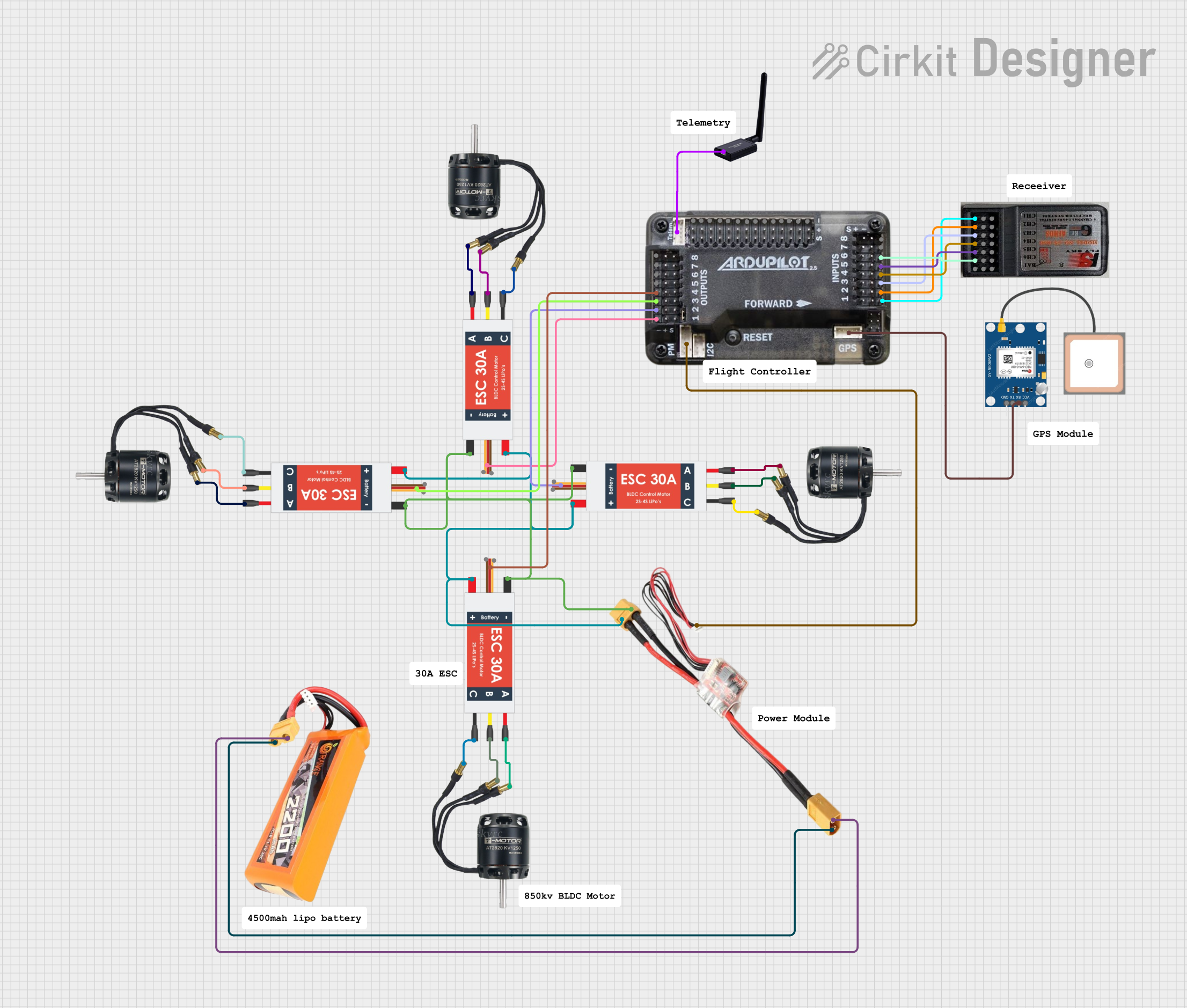
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer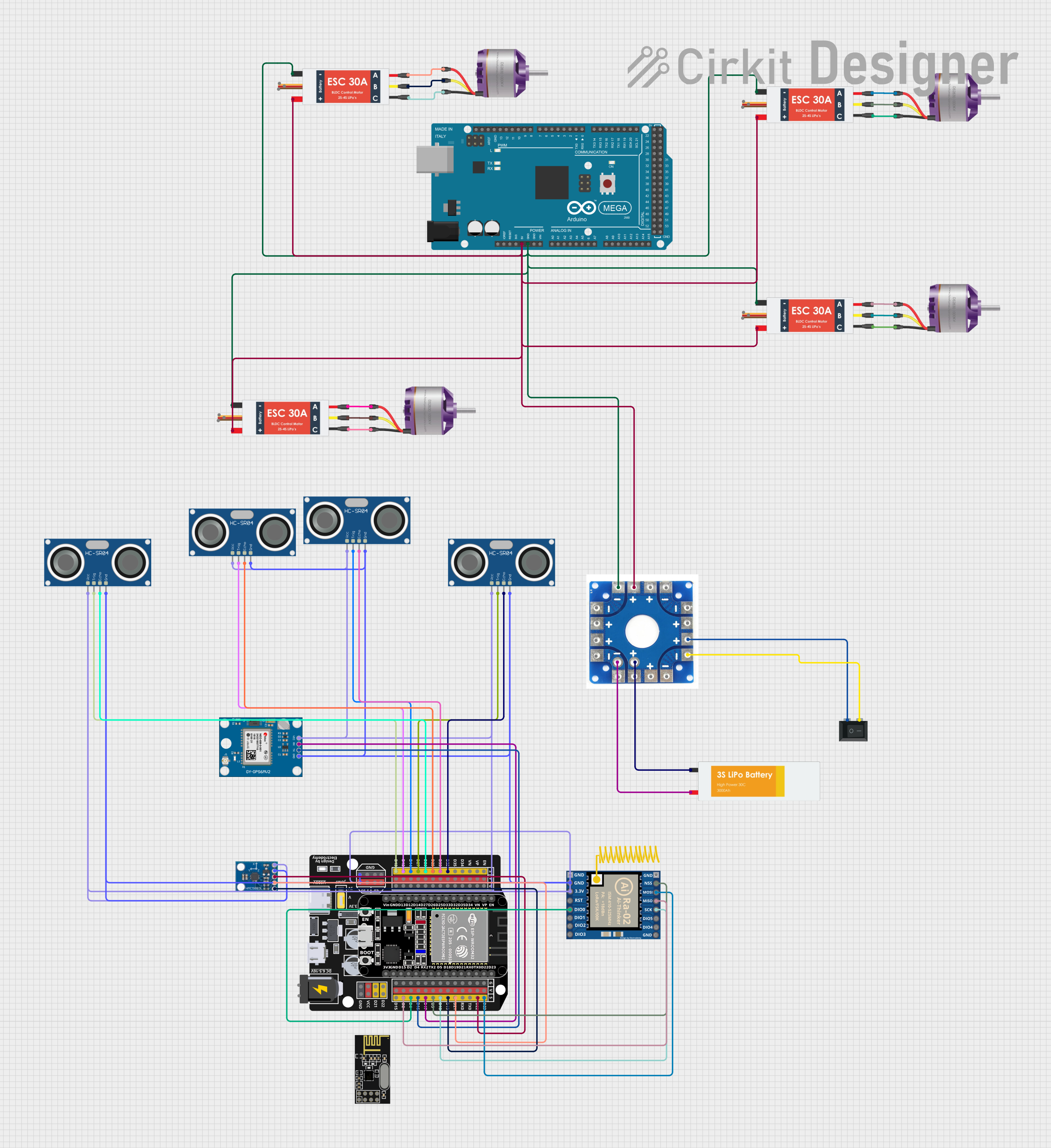
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer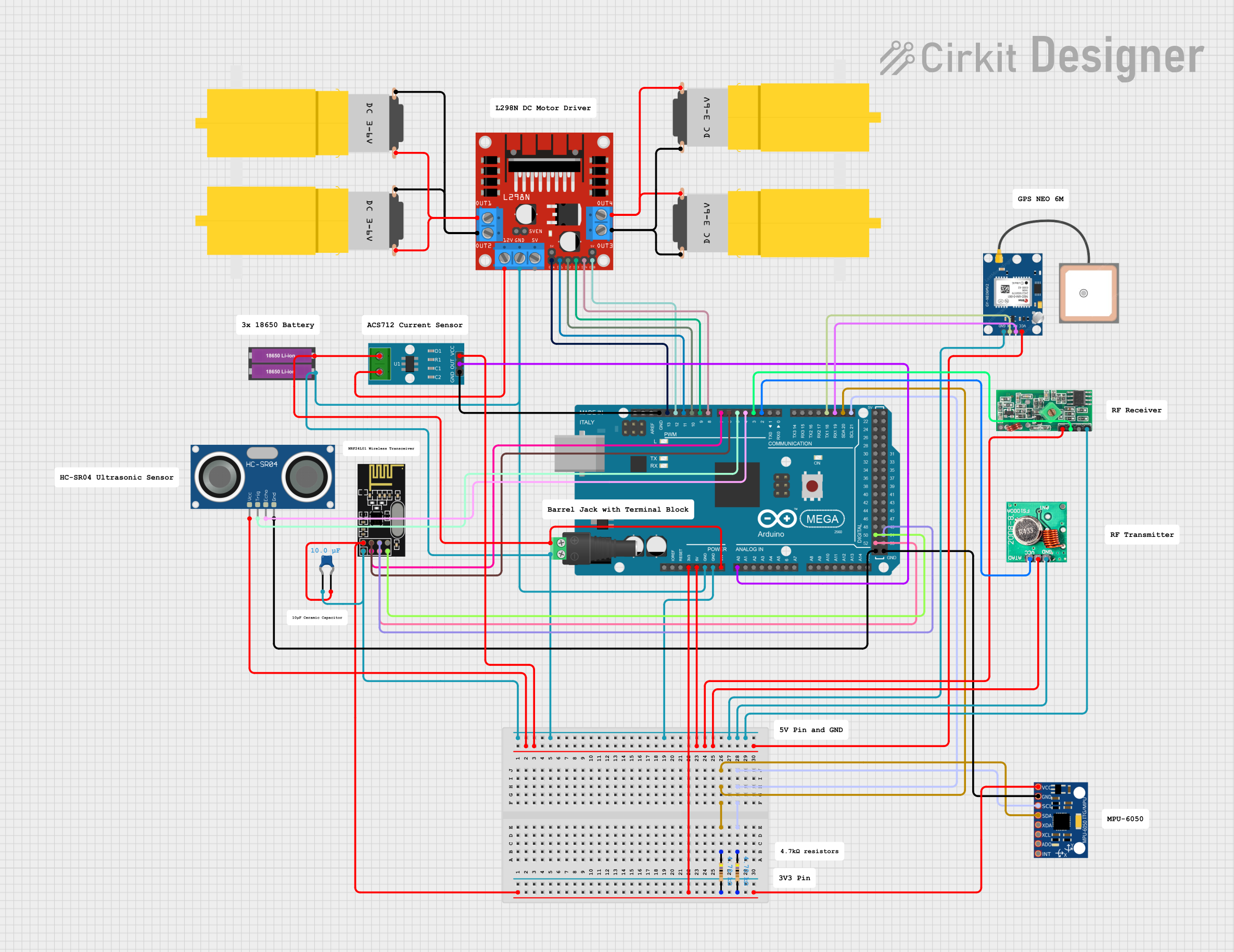
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer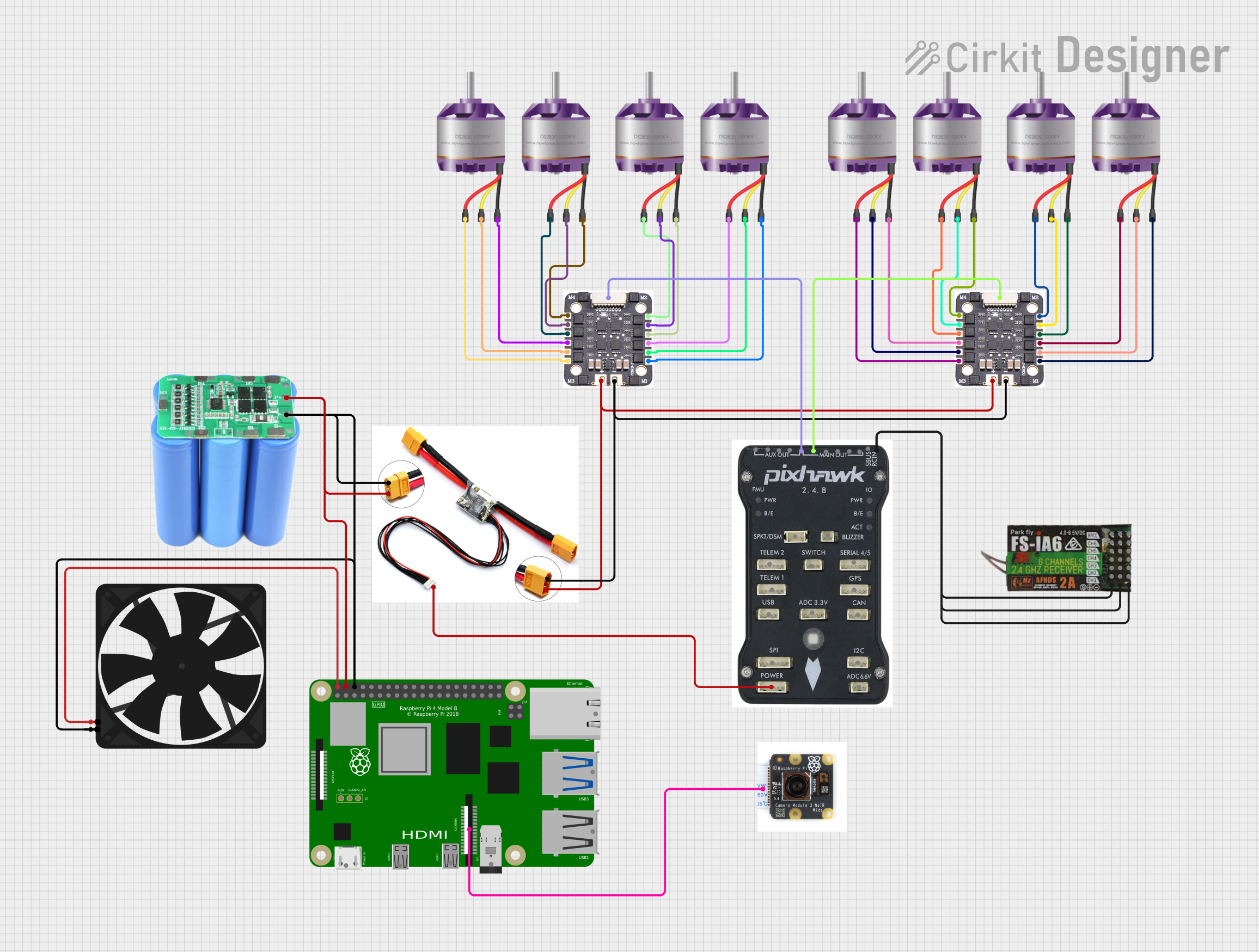
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Ardupilot Mega APM 2.8

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Autonomous drones (quadcopters, hexacopters, etc.)
- Fixed-wing aircraft
- Ground vehicles (rovers)
- Marine vehicles (boats, submarines)
- Research and development in robotics and UAV technology
- Educational projects and prototyping
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ATMEGA2560
- Input Voltage: 5V (via USB) or 7-12V (via power module)
- Processor Speed: 16 MHz
- Flash Memory: 256 KB
- RAM: 8 KB
- EEPROM: 4 KB
- IMU Sensors:
- 3-axis gyroscope
- 3-axis accelerometer
- 3-axis magnetometer
- Barometer: MS5611 high-resolution barometer
- Communication Interfaces: UART, I2C, SPI, USB
- PWM Outputs: 8 channels
- Dimensions: 70mm x 45mm
- Weight: 28g
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The APM 2.8 features multiple connectors for peripherals and sensors. Below is a summary of the key pin configurations:
Power and Input/Output Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power input (5V or 7-12V via power module) |
| GND | Ground connection |
| PWM 1-8 | PWM outputs for motor/servo control |
| A0-A11 | Analog input pins for sensors |
| UART0 | Serial communication port for telemetry or GPS |
| I2C | Interface for external sensors (e.g., compass, barometer) |
| SPI | Interface for high-speed peripherals |
Auxiliary Pins
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| GPS | Dedicated port for GPS module connection |
| Telemetry | Port for telemetry radio module |
| USB | USB port for programming and data transfer |
| RC IN | Input for RC receiver signals |
| Buzzer | Output for status buzzer |
| LED | Output for status LEDs |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the APM 2.8 in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect the power module to the APM 2.8's power input port. Ensure the input voltage is within the range of 7-12V. Alternatively, you can power the board via USB for programming or testing.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Attach the GPS module to the GPS port.
- Connect the telemetry module to the telemetry port for real-time data monitoring.
- Plug in the RC receiver to the RC IN pins for manual control.
- Connect motors or servos to the PWM output pins (PWM 1-8).
Programming the Board:
- Install the Mission Planner software on your computer.
- Connect the APM 2.8 to your computer via USB.
- Use Mission Planner to upload the desired firmware (e.g., ArduCopter, ArduPlane).
Calibrating Sensors:
- Use Mission Planner to calibrate the accelerometer, compass, and radio.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the calibration process.
Flight Testing:
- Ensure all connections are secure.
- Perform a pre-flight check using Mission Planner.
- Test the system in a controlled environment before full deployment.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always use a power module with proper voltage regulation to avoid damaging the board.
- Ensure the GPS module has a clear view of the sky for optimal performance.
- Calibrate all sensors before each flight to maintain accuracy.
- Use vibration dampening mounts to reduce noise in sensor readings.
- Regularly update the firmware to access the latest features and bug fixes.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
While the APM 2.8 is a standalone autopilot, it can communicate with an Arduino UNO for additional functionality. Below is an example of how to send data from the APM 2.8 to an Arduino UNO via UART:
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for communication with APM 2.8
SoftwareSerial apmSerial(10, 11); // RX = pin 10, TX = pin 11
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial monitor
apmSerial.begin(57600); // Initialize communication with APM 2.8
Serial.println("Arduino UNO connected to APM 2.8");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from APM 2.8
if (apmSerial.available()) {
String data = apmSerial.readString(); // Read data from APM
Serial.println("Data from APM: " + data); // Print data to serial monitor
}
// Send a test message to APM 2.8
apmSerial.println("Hello APM!");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
APM 2.8 Not Powering On:
- Ensure the power module is connected properly and providing the correct voltage.
- Check the USB cable if powering via USB.
GPS Not Locking:
- Verify the GPS module is connected to the correct port.
- Ensure the GPS has a clear view of the sky and is not obstructed.
Telemetry Not Working:
- Check the baud rate settings in Mission Planner and ensure they match the telemetry module.
- Verify the telemetry module is securely connected to the telemetry port.
Unstable Flight:
- Recalibrate the accelerometer, compass, and radio.
- Check for loose connections or excessive vibrations.
FAQs
Can I use the APM 2.8 with a Raspberry Pi?
Yes, the APM 2.8 can communicate with a Raspberry Pi via UART or USB for advanced applications.What is the maximum range of the telemetry module?
The range depends on the specific telemetry module used, typically between 500m and 2km.Does the APM 2.8 support LiDAR sensors?
Yes, LiDAR sensors can be connected via I2C or UART for obstacle detection and altitude measurement.Can I use the APM 2.8 for underwater vehicles?
Yes, with proper waterproofing and sensor selection, the APM 2.8 can control underwater vehicles.How do I update the firmware?
Use the Mission Planner software to download and upload the latest firmware to the APM 2.8 via USB.