
How to Use DC-DC Step down converter 12V output: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with DC-DC Step down converter 12V output in Cirkit Designer
Design with DC-DC Step down converter 12V output in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A DC-DC step down converter, also known as a buck converter, is a power electronics device that reduces a higher input voltage to a lower output voltage while maintaining high efficiency. This specific converter is designed to provide a stable 12V output from a higher voltage source, such as a 24V or 48V power supply.
Explore Projects Built with DC-DC Step down converter 12V output

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer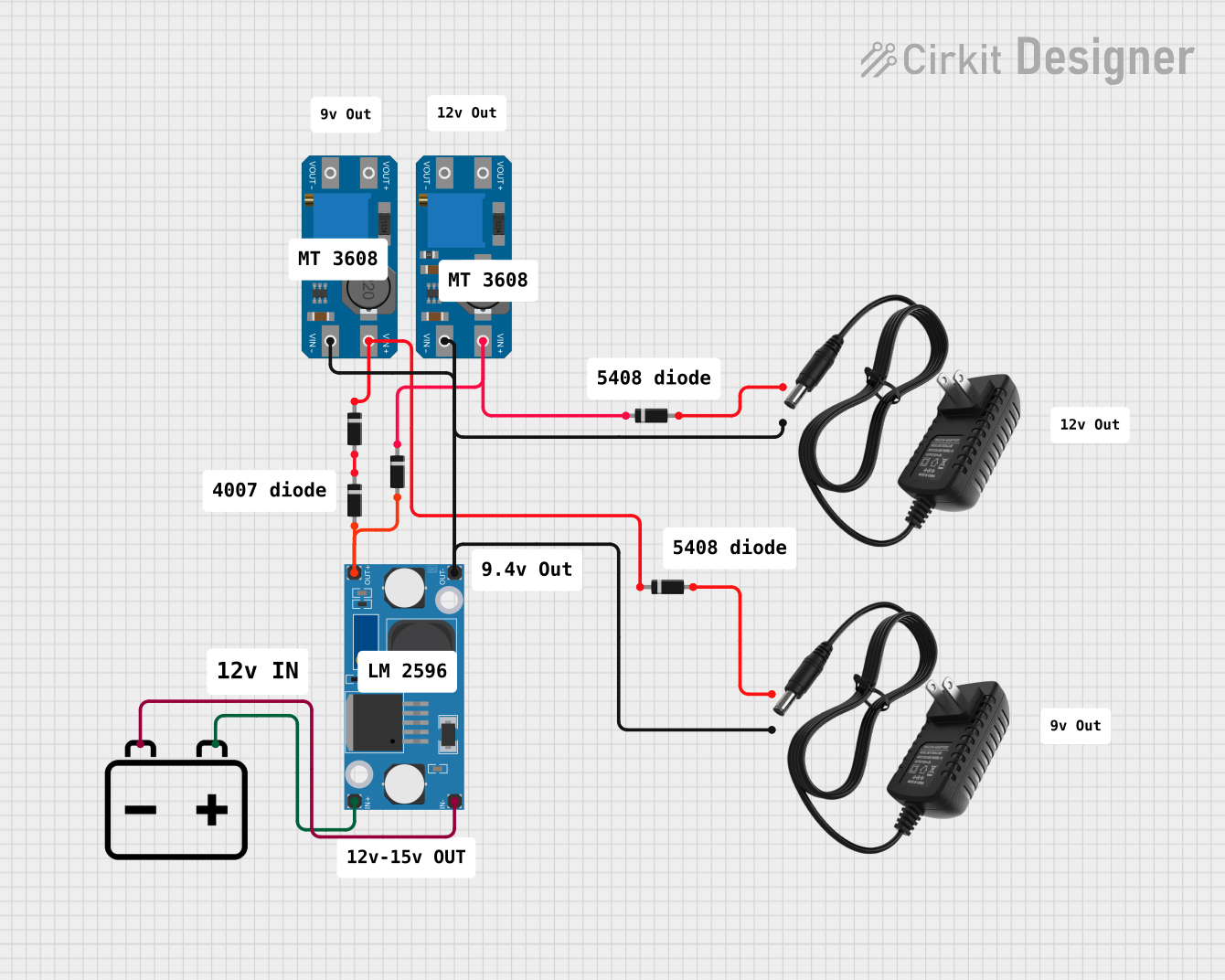
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with DC-DC Step down converter 12V output

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering 12V devices (e.g., fans, LED strips, and sensors) from higher voltage sources.
- Battery-powered systems where voltage regulation is required.
- Automotive applications to step down voltage from a car battery (e.g., 24V to 12V).
- Renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, to regulate output voltage.
- Industrial equipment requiring a stable 12V power supply.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the DC-DC step down converter with a 12V output:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 15V to 40V |
| Output Voltage | 12V (fixed) |
| Output Current | Up to 5A (depending on input) |
| Efficiency | Up to 95% |
| Switching Frequency | 150 kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Protection Features | Overcurrent, Overtemperature, and Short Circuit Protection |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DC-DC step down converter typically has the following pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN+ | Positive input voltage terminal (connect to source) |
| VIN- | Negative input voltage terminal (connect to ground) |
| VOUT+ | Positive output voltage terminal (12V output) |
| VOUT- | Negative output voltage terminal (ground) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage:
- Connect the positive terminal of the input voltage source to the
VIN+pin. - Connect the negative terminal of the input voltage source to the
VIN-pin. - Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (15V to 40V).
- Connect the positive terminal of the input voltage source to the
Connect the Output Load:
- Connect the positive terminal of the load to the
VOUT+pin. - Connect the negative terminal of the load to the
VOUT-pin.
- Connect the positive terminal of the load to the
Power On:
- Turn on the input voltage source. The converter will regulate the input voltage and provide a stable 12V output.
Verify Output:
- Use a multimeter to confirm the output voltage is 12V before connecting sensitive devices.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure the input voltage is always higher than 12V and within the specified range (15V to 40V). Exceeding the range may damage the converter.
- Heat Dissipation: For high current loads, the converter may generate heat. Use a heatsink or active cooling if necessary.
- Load Current: Do not exceed the maximum output current (5A). Overloading may trigger protection features or damage the device.
- Polarity: Double-check the polarity of the input and output connections to avoid damage.
- Filtering: For sensitive applications, consider adding input and output capacitors to reduce noise.
Example: Using the Converter with an Arduino UNO
The DC-DC step down converter can be used to power an Arduino UNO from a 24V source. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Setup
- Connect the 24V source to the
VIN+andVIN-pins of the converter. - Connect the
VOUT+pin to the Arduino'sVINpin. - Connect the
VOUT-pin to the Arduino'sGNDpin.
Arduino Code Example
// Example code to blink an LED connected to pin 13 of the Arduino UNO
// Ensure the Arduino is powered via the DC-DC step down converter.
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT); // Set pin 13 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Input voltage is below the minimum required (15V).
- Solution: Verify the input voltage and ensure it is within the specified range.
Overheating:
- Cause: High current load or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Reduce the load current or add a heatsink/active cooling.
Output Voltage Not Stable:
- Cause: Insufficient input voltage or noisy power source.
- Solution: Use a stable input power source and consider adding input/output capacitors.
Short Circuit Protection Triggered:
- Cause: Output terminals are shorted.
- Solution: Disconnect the power, fix the short circuit, and reconnect.
FAQs
Q: Can I adjust the output voltage?
A: No, this converter provides a fixed 12V output. For adjustable output, use a variable DC-DC converter.Q: Can I use this converter with a 12V input?
A: No, the input voltage must be higher than 12V for proper operation.Q: Is the converter waterproof?
A: No, ensure the converter is used in a dry environment or enclosed in a waterproof case.Q: Can I connect multiple converters in parallel for higher current?
A: It is not recommended unless the converters are specifically designed for parallel operation.
This documentation provides all the necessary details to use the DC-DC step down converter effectively and troubleshoot common issues.