
How to Use TB6600 DRIVER: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
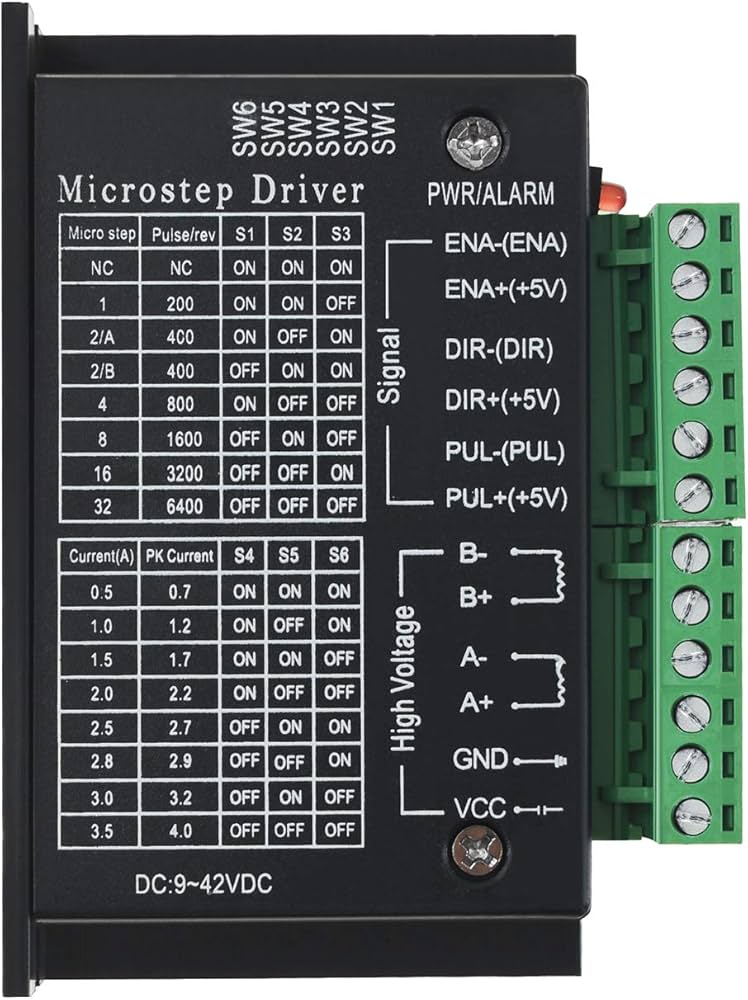
 Design with TB6600 DRIVER in Cirkit Designer
Design with TB6600 DRIVER in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TB6600 is a stepper motor driver designed to provide precise control of stepper motors. It supports a wide range of microstepping settings, enabling smooth operation and high torque output. This driver is widely used in applications such as CNC machines, 3D printers, robotics, and other motion control systems. Its robust design and versatility make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with TB6600 DRIVER
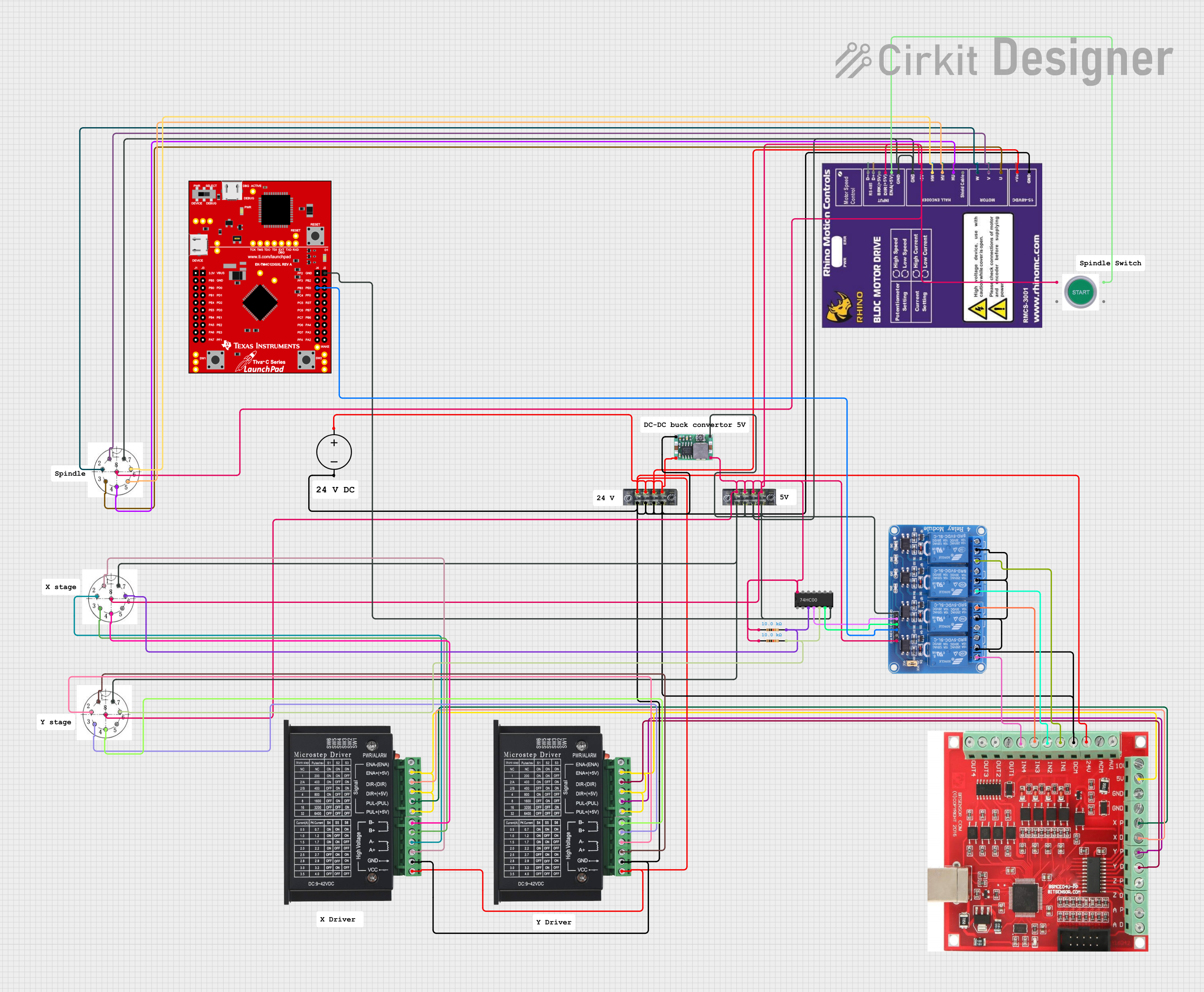
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer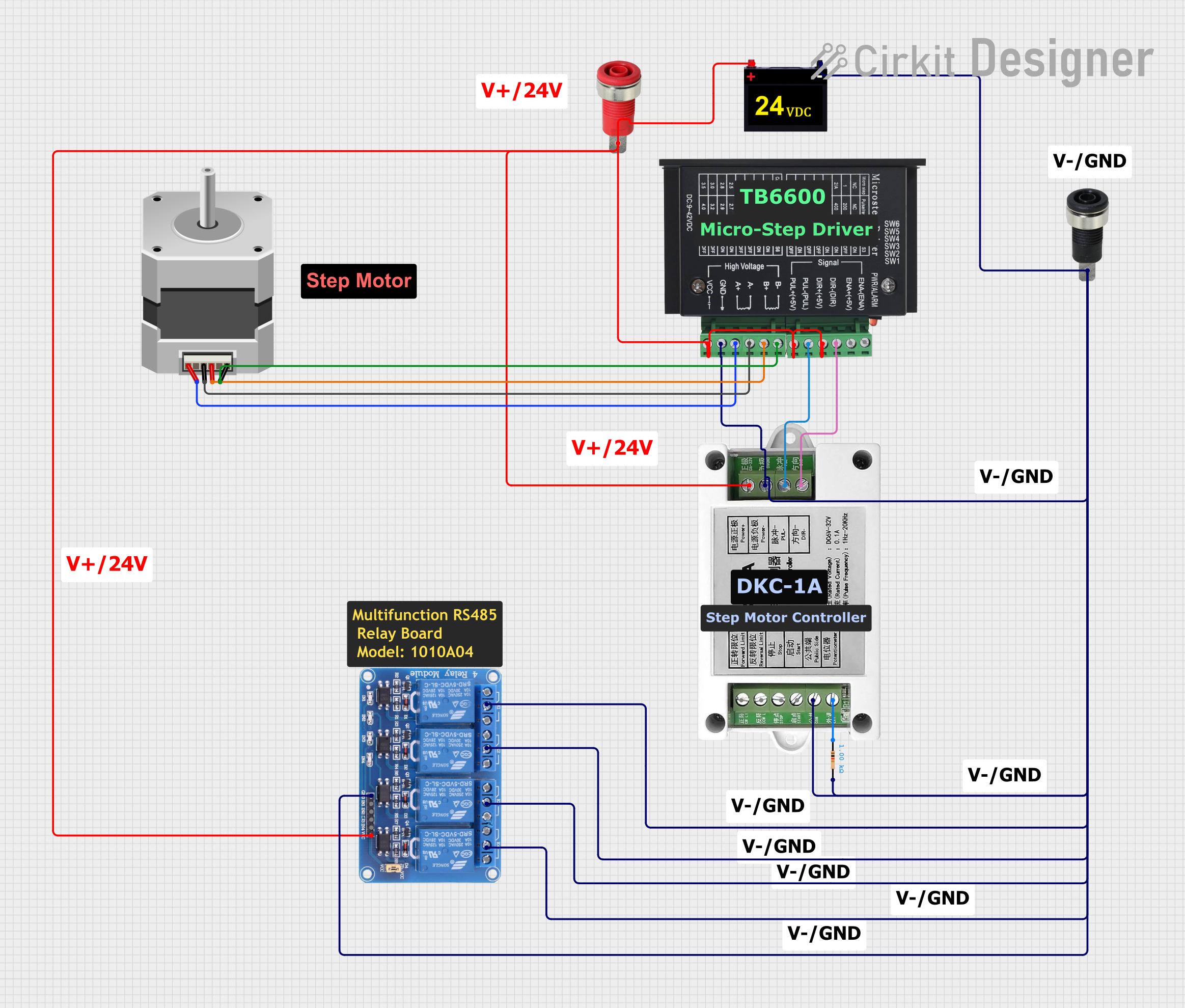
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer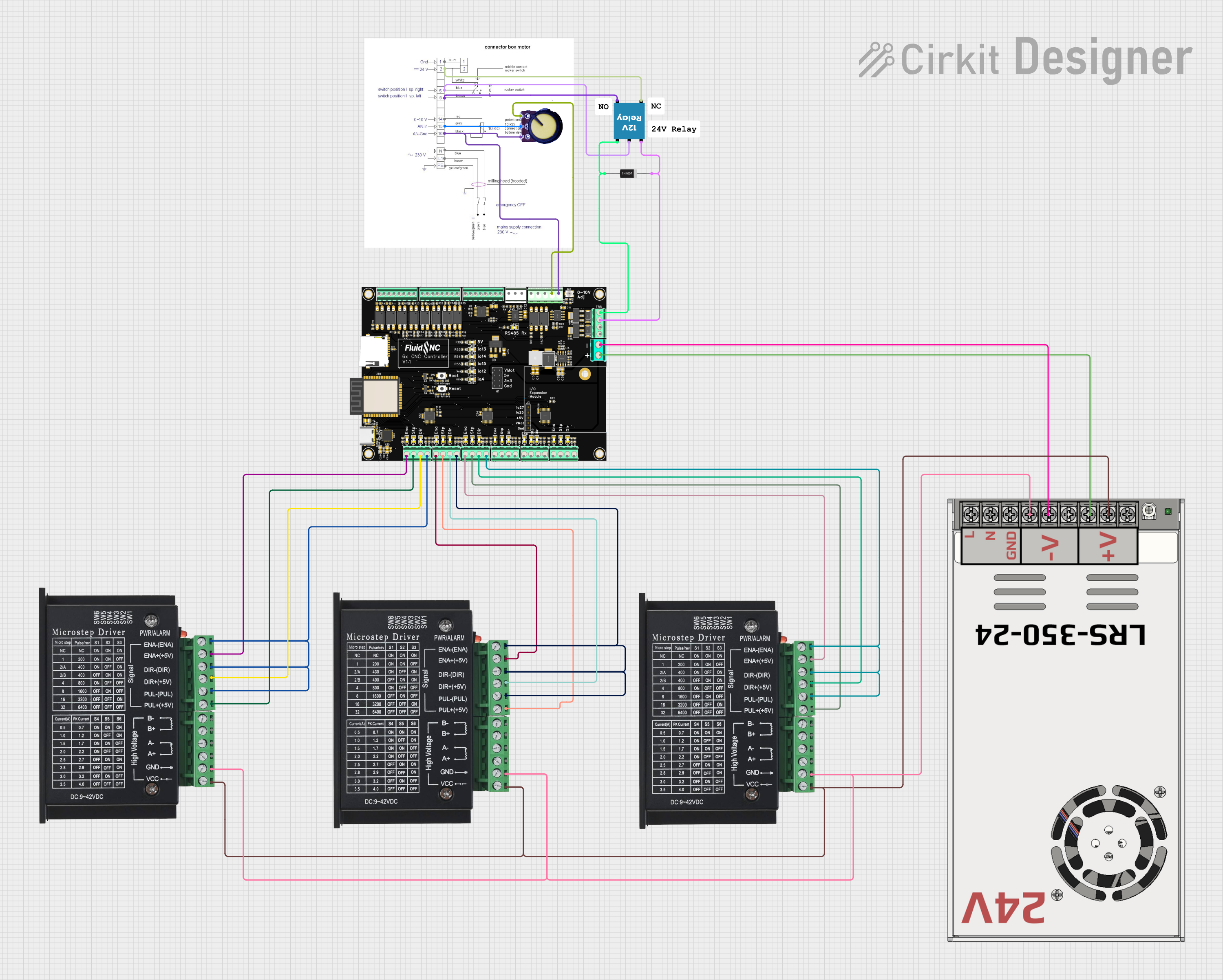
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer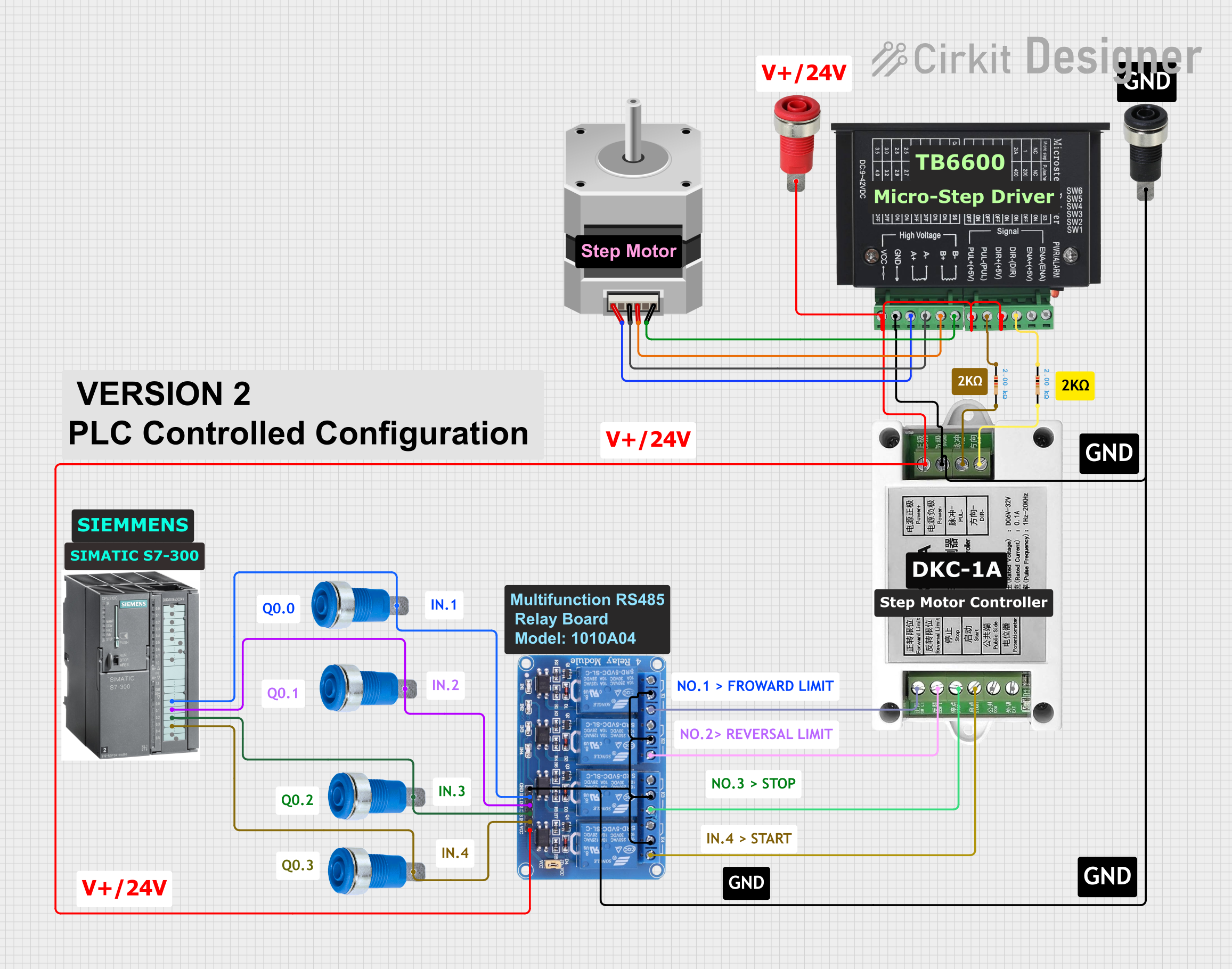
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TB6600 DRIVER

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- CNC machines for precise cutting and engraving
- 3D printers for accurate layer deposition
- Robotics for controlled motion
- Automated conveyor systems
- Any project requiring stepper motor control
Technical Specifications
The TB6600 driver is equipped with features that make it suitable for demanding applications. Below are its key technical details:
Key Specifications
- Input Voltage: 9V to 42V DC
- Output Current: Adjustable, up to 4.5A
- Microstepping Modes: Full step, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16
- Control Signal Voltage: 3.3V to 5V (compatible with most microcontrollers)
- Step Frequency: Up to 200 kHz
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to 45°C
- Protection Features: Overcurrent, overvoltage, and thermal protection
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TB6600 driver has several input and output terminals. Below is a detailed description of its pin configuration:
Input Terminals
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PUL+ | Pulse signal input (positive terminal) |
| PUL- | Pulse signal input (negative terminal) |
| DIR+ | Direction signal input (positive terminal) |
| DIR- | Direction signal input (negative terminal) |
| ENA+ | Enable signal input (positive terminal) |
| ENA- | Enable signal input (negative terminal) |
Output Terminals
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| A+ | Stepper motor coil A positive terminal |
| A- | Stepper motor coil A negative terminal |
| B+ | Stepper motor coil B positive terminal |
| B- | Stepper motor coil B negative terminal |
Power Terminals
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply positive terminal (9-42V DC) |
| GND | Power supply ground terminal |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the TB6600 Driver
- Power Supply: Connect a DC power supply (9V to 42V) to the VCC and GND terminals.
- Stepper Motor: Connect the stepper motor coils to the A+, A-, B+, and B- terminals. Ensure the wiring matches the motor's datasheet.
- Control Signals: Connect the PUL+, PUL-, DIR+, DIR-, ENA+, and ENA- pins to the corresponding pins on your microcontroller or controller board.
- PUL: Controls the step pulses.
- DIR: Determines the rotation direction.
- ENA: Enables or disables the driver (optional; can be left unconnected if not used).
- Microstepping Settings: Use the DIP switches on the driver to configure the microstepping mode and current limit according to your motor's requirements.
Example: Using TB6600 with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a stepper motor using the TB6600 driver and an Arduino UNO:
Wiring Diagram
- PUL+: Connect to Arduino pin 2
- PUL-: Connect to Arduino GND
- DIR+: Connect to Arduino pin 3
- DIR-: Connect to Arduino GND
- ENA+: Connect to Arduino pin 4 (optional)
- ENA-: Connect to Arduino GND
- VCC: Connect to a 24V DC power supply
- GND: Connect to the power supply ground
Arduino Code
// Define control pins for the TB6600 driver
#define PUL_PIN 2 // Pulse pin
#define DIR_PIN 3 // Direction pin
#define ENA_PIN 4 // Enable pin (optional)
void setup() {
// Set pin modes
pinMode(PUL_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(DIR_PIN, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENA_PIN, OUTPUT);
// Enable the driver
digitalWrite(ENA_PIN, LOW); // LOW to enable the driver
}
void loop() {
// Set direction
digitalWrite(DIR_PIN, HIGH); // HIGH for one direction, LOW for the other
// Generate step pulses
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) { // 200 steps for one revolution (1.8°/step)
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500); // Adjust for speed
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before reversing direction
// Reverse direction
digitalWrite(DIR_PIN, LOW);
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(PUL_PIN, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000); // Wait 1 second before repeating
}
Best Practices
- Ensure the power supply voltage matches the requirements of both the TB6600 driver and the stepper motor.
- Use a heat sink or cooling fan if the driver operates at high current for extended periods.
- Double-check the wiring to avoid damaging the driver or motor.
- Configure the DIP switches correctly for your motor's current and microstepping settings.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Moving
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or no pulse signal.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the microcontroller is sending pulse signals.
Motor Vibrates but Does Not Rotate
- Cause: Incorrect stepper motor wiring.
- Solution: Check the motor's datasheet and ensure the coils are connected correctly.
Driver Overheating
- Cause: Excessive current or poor ventilation.
- Solution: Reduce the current setting using the DIP switches or improve cooling.
Motor Moves Erratically
- Cause: Noise in control signals or incorrect microstepping settings.
- Solution: Use shielded cables for control signals and verify DIP switch settings.
FAQs
Can I use the TB6600 with a 12V power supply? Yes, the TB6600 supports input voltages from 9V to 42V. Ensure your stepper motor is compatible with 12V.
What microcontroller platforms are compatible with the TB6600? The TB6600 is compatible with most platforms, including Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and other 3.3V or 5V logic controllers.
Do I need to use the ENA pins? The ENA pins are optional. If not used, leave them unconnected or tied to GND.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use the TB6600 driver in your projects for precise stepper motor control.