
How to Use Logic level 3,3V-5V step-up (4 channels, SPI/UART): Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Logic level 3,3V-5V step-up (4 channels, SPI/UART) in Cirkit Designer
Design with Logic level 3,3V-5V step-up (4 channels, SPI/UART) in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
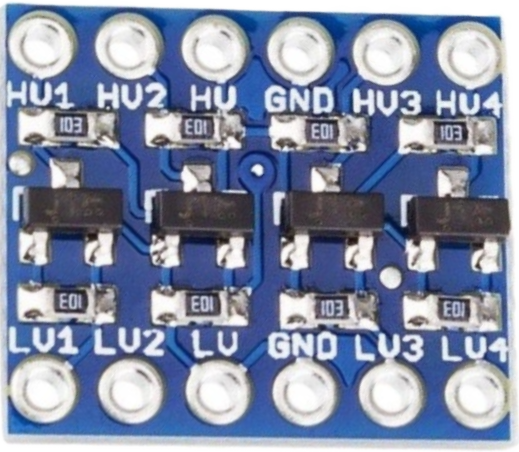
The Logic Level 3.3V-5V Step-Up (4 Channels, SPI/UART), manufactured by JH Global Trading (HK) Co., Limited, is a versatile bidirectional logic level converter. It allows seamless communication between devices operating at different voltage levels, such as 3.3V and 5V. This component is particularly useful in interfacing microcontrollers, sensors, and communication modules that require different logic levels.
Explore Projects Built with Logic level 3,3V-5V step-up (4 channels, SPI/UART)
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Logic level 3,3V-5V step-up (4 channels, SPI/UART)

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Interfacing 3.3V microcontrollers (e.g., ESP32, STM32) with 5V peripherals (e.g., Arduino, sensors).
- Bridging communication between UART or SPI devices operating at different voltage levels.
- Enabling compatibility between 3.3V and 5V I2C buses.
- General-purpose voltage level shifting in mixed-voltage systems.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the component:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | JH Global Trading (HK) Co., Limited |
| Part ID | Logic Level 3.3V-5V Step-Up (4 Channels, SPI/UART) |
| Operating Voltage (Low Side) | 1.8V to 3.6V |
| Operating Voltage (High Side) | 4.5V to 5.5V |
| Number of Channels | 4 |
| Communication Protocols | SPI, UART, I2C |
| Maximum Data Rate | 10 Mbps (SPI/UART) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 15mm x 12mm x 3mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The component has a total of 8 pins, as described in the table below:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | HV | High voltage input (4.5V to 5.5V) |
| 2 | LV | Low voltage input (1.8V to 3.6V) |
| 3 | GND | Ground connection |
| 4 | TX_H | High-side transmit (5V logic) |
| 5 | TX_L | Low-side transmit (3.3V logic) |
| 6 | RX_H | High-side receive (5V logic) |
| 7 | RX_L | Low-side receive (3.3V logic) |
| 8 | EN | Enable pin (active high, pull to LV to enable) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Power Connections:
- Connect the HV pin to the 5V power supply.
- Connect the LV pin to the 3.3V power supply.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of both power supplies.
Enable the Converter:
- Pull the EN pin to the LV voltage level to enable the converter.
Connect Logic Signals:
- For SPI or UART communication:
- Connect the 3.3V device's TX pin to TX_L and RX pin to RX_L.
- Connect the 5V device's TX pin to TX_H and RX pin to RX_H.
- For I2C communication:
- Use pull-up resistors on both the high-side and low-side data lines.
- For SPI or UART communication:
Verify Connections:
- Ensure all connections are secure and that the voltage levels match the specifications.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply Isolation: Ensure that the 3.3V and 5V power supplies share a common ground.
- Data Rate Limitations: Do not exceed the maximum data rate of 10 Mbps to avoid signal distortion.
- Enable Pin Usage: If the enable pin is left floating, the converter may not function correctly. Always pull it to the LV voltage level.
- Pull-Up Resistors for I2C: Use appropriate pull-up resistor values (e.g., 4.7kΩ) for stable I2C communication.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
The following example demonstrates how to use the logic level converter to interface a 3.3V sensor with an Arduino UNO (5V logic).
Circuit Diagram
- 3.3V Sensor:
- TX → TX_L
- RX → RX_L
- VCC → LV
- GND → GND
- Arduino UNO:
- TX → TX_H
- RX → RX_H
- 5V → HV
- GND → GND
Arduino Code Example
// Example: Reading data from a 3.3V sensor using a logic level converter
// Ensure the logic level converter is properly connected as per the circuit diagram.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define pins for the logic level converter
#define SENSOR_TX 2 // Arduino pin connected to TX_H
#define SENSOR_RX 3 // Arduino pin connected to RX_H
SoftwareSerial sensorSerial(SENSOR_RX, SENSOR_TX); // RX, TX
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize Serial Monitor
sensorSerial.begin(9600); // Initialize communication with the sensor
Serial.println("Starting communication with 3.3V sensor...");
}
void loop() {
if (sensorSerial.available()) {
// Read data from the sensor and print it to the Serial Monitor
String sensorData = sensorSerial.readString();
Serial.println("Sensor Data: " + sensorData);
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Communication Between Devices:
- Cause: The enable pin is not properly connected.
- Solution: Ensure the EN pin is pulled to the LV voltage level.
Signal Distortion or Data Loss:
- Cause: Exceeding the maximum data rate of 10 Mbps.
- Solution: Reduce the communication speed in your code or hardware setup.
I2C Communication Fails:
- Cause: Missing or incorrect pull-up resistors.
- Solution: Add pull-up resistors (e.g., 4.7kΩ) to the SDA and SCL lines on both sides.
Component Overheating:
- Cause: Incorrect voltage levels or short circuits.
- Solution: Verify all connections and ensure the voltage levels are within the specified range.
FAQs
Q1: Can this component be used for 1.8V to 5V level shifting?
A1: Yes, the component supports low-side voltages as low as 1.8V, making it suitable for 1.8V to 5V level shifting.
Q2: Is it compatible with bidirectional I2C communication?
A2: Yes, the component supports bidirectional communication, including I2C, SPI, and UART.
Q3: What happens if the enable pin is left floating?
A3: The converter may not function correctly. Always pull the EN pin to the LV voltage level to enable the device.
Q4: Can I use this for 3.3V to 12V level shifting?
A4: No, the high-side voltage must not exceed 5.5V. For higher voltage levels, use a dedicated level shifter designed for those ranges.