
How to Use TB660 Stepper Motor Driver : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with TB660 Stepper Motor Driver in Cirkit Designer
Design with TB660 Stepper Motor Driver in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TB6600 Stepper Motor Driver is an efficient and versatile driver for controlling stepper motors in various applications. It is commonly used in CNC machines, 3D printers, and other precision motion control systems. The TB6600 driver allows for precise control of the speed and direction of a stepper motor, converting digital signals from a controller into the physical movement of the motor's shaft.
Explore Projects Built with TB660 Stepper Motor Driver
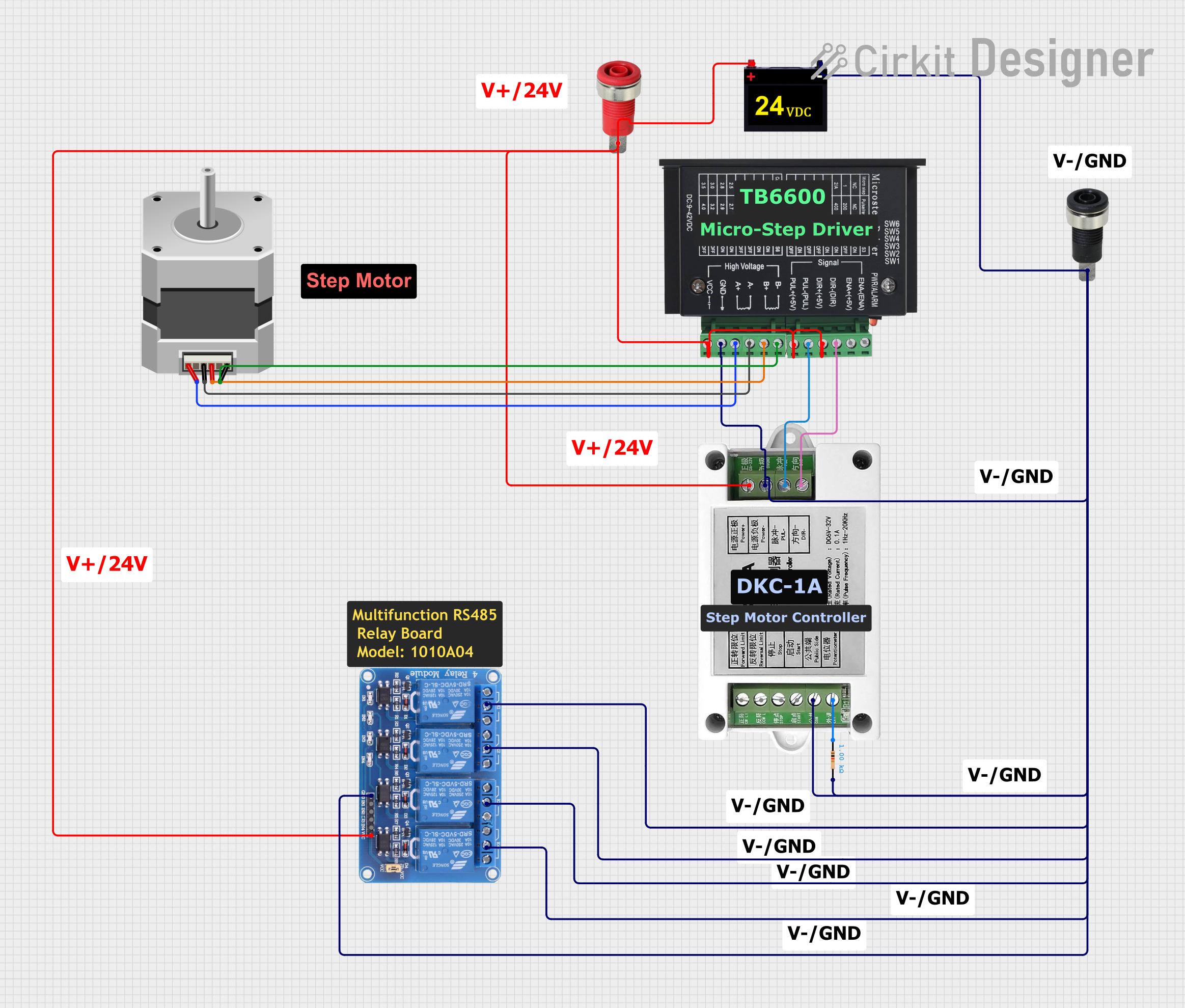
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer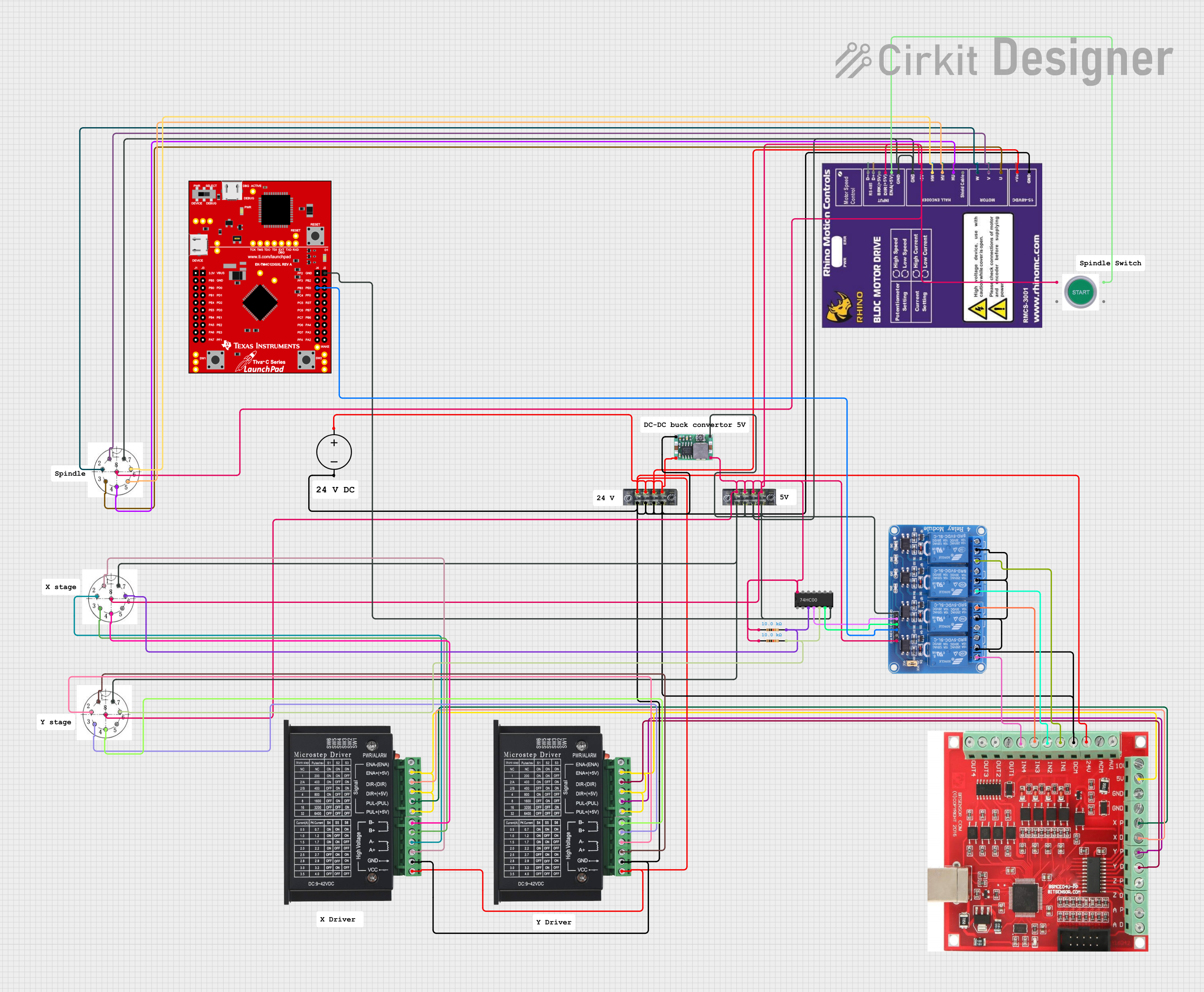
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer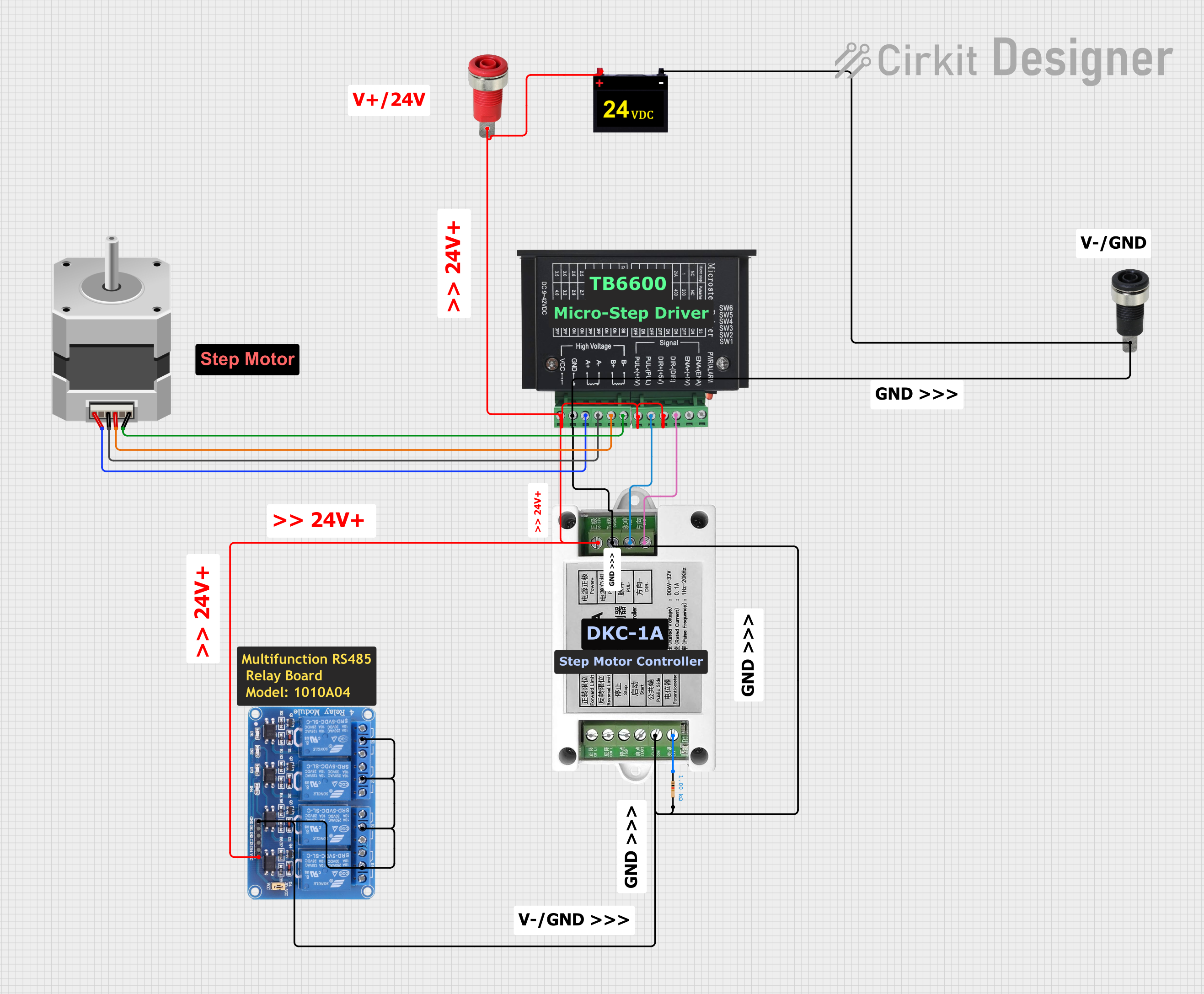
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer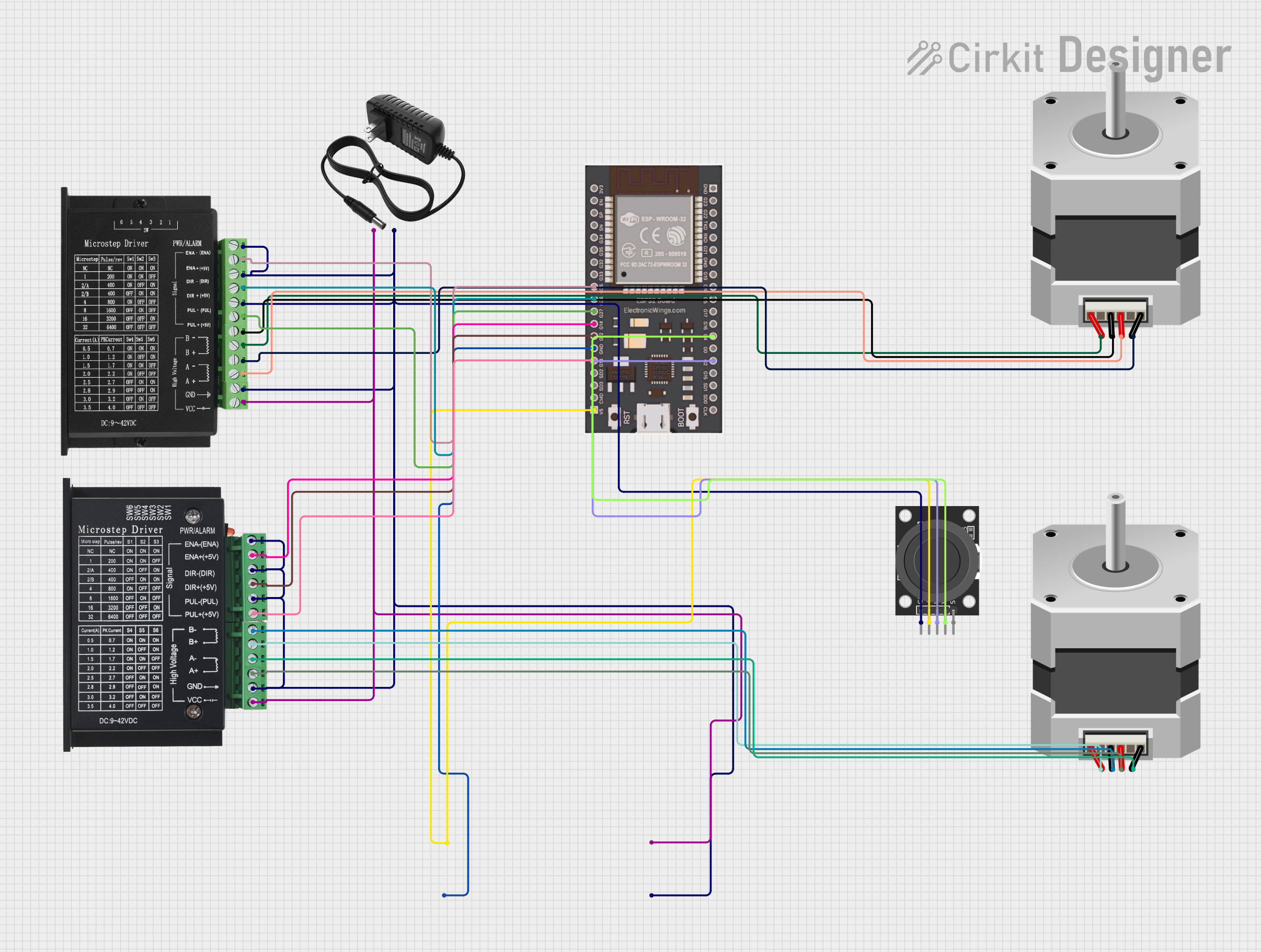
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TB660 Stepper Motor Driver

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage: 9V to 42V DC
- Output Current: Adjustable from 0.2A to 4.5A
- Input Signal Voltage: 3.3V to 24V
- Microstepping: Full, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32 selectable
- Operating Temperature: -10°C to 45°C
- Storage Temperature: -20°C to 65°C
- Dimensions: 96mm x 71mm x 28mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ENA+ | Enable signal positive |
| 2 | ENA- | Enable signal negative |
| 3 | DIR+ | Direction signal positive |
| 4 | DIR- | Direction signal negative |
| 5 | PUL+ | Pulse signal positive |
| 6 | PUL- | Pulse signal negative |
| 7 | A+ | Motor coil A+ |
| 8 | A- | Motor coil A- |
| 9 | B+ | Motor coil B+ |
| 10 | B- | Motor coil B- |
| 11 | VCC | Power supply positive |
| 12 | GND | Power supply ground |
Usage Instructions
Connecting the TB6600 to a Stepper Motor
- Power Supply Connection: Connect a DC power supply to the VCC and GND pins. Ensure the voltage is within the specified range.
- Motor Connection: Connect the motor coils to the A+ and A-, B+ and B-, ensuring that the polarity matches the motor's specifications.
- Control Signal Connection: Connect the PUL+, PUL-, DIR+, DIR-, ENA+, and ENA- to the respective outputs from the controller.
Best Practices
- Always double-check wiring before powering up to prevent damage.
- Use a suitable heatsink to dissipate heat during operation.
- Adjust the current setting according to the motor's specifications to avoid overheating.
- Ensure that the microstepping setting matches the requirements of your application for smooth operation.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
// Define the connection pins
const int dirPin = 2; // DIR pin connected to digital pin 2
const int stepPin = 3; // STEP pin connected to digital pin 3
const int enablePin = 8; // ENABLE pin connected to digital pin 8
void setup() {
// Set the pin modes
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enablePin, OUTPUT);
// Enable the driver
digitalWrite(enablePin, LOW);
}
void loop() {
// Set the direction
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH); // Set to HIGH to go in one direction
// Spin the motor
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
// These four lines result in 1 step:
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000); // Wait a second
// Change direction
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW); // Set to LOW to go in the opposite direction
// Spin the motor the other way
for(int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
// These four lines result in 1 step:
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(500);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(500);
}
delay(1000); // Wait a second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- Motor not moving: Check power supply, wiring, and ensure the enable pin is set correctly.
- Motor stalling or skipping steps: Adjust current settings, check for mechanical obstructions, or reduce the speed.
- Overheating: Ensure proper current settings and adequate cooling.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the TB6600 with a 5V stepper motor? A: Yes, as long as the motor's current and voltage requirements are within the TB6600's specifications.
Q: How do I set the microstepping resolution? A: Microstepping is set using the DIP switches on the TB6600. Refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for the correct switch positions for your desired microstepping resolution.
Q: What is the maximum pulse frequency for the TB6600? A: The TB6600 can handle a maximum pulse frequency of up to 200kHz, but it is recommended to stay well below this limit for most applications.
For further assistance, consult the manufacturer's datasheet or contact technical support.