
How to Use ESC 40A: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with ESC 40A in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESC 40A in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An Electronic Speed Controller (ESC) rated for 40 Amperes is a critical component used to control the speed, direction, and braking of brushless motors. The ESC 40A is specifically designed for high-performance applications such as remote-controlled (RC) vehicles, drones, boats, and other robotics projects. It provides precise throttle control, smooth motor operation, and efficient power delivery, making it ideal for demanding environments.
Explore Projects Built with ESC 40A
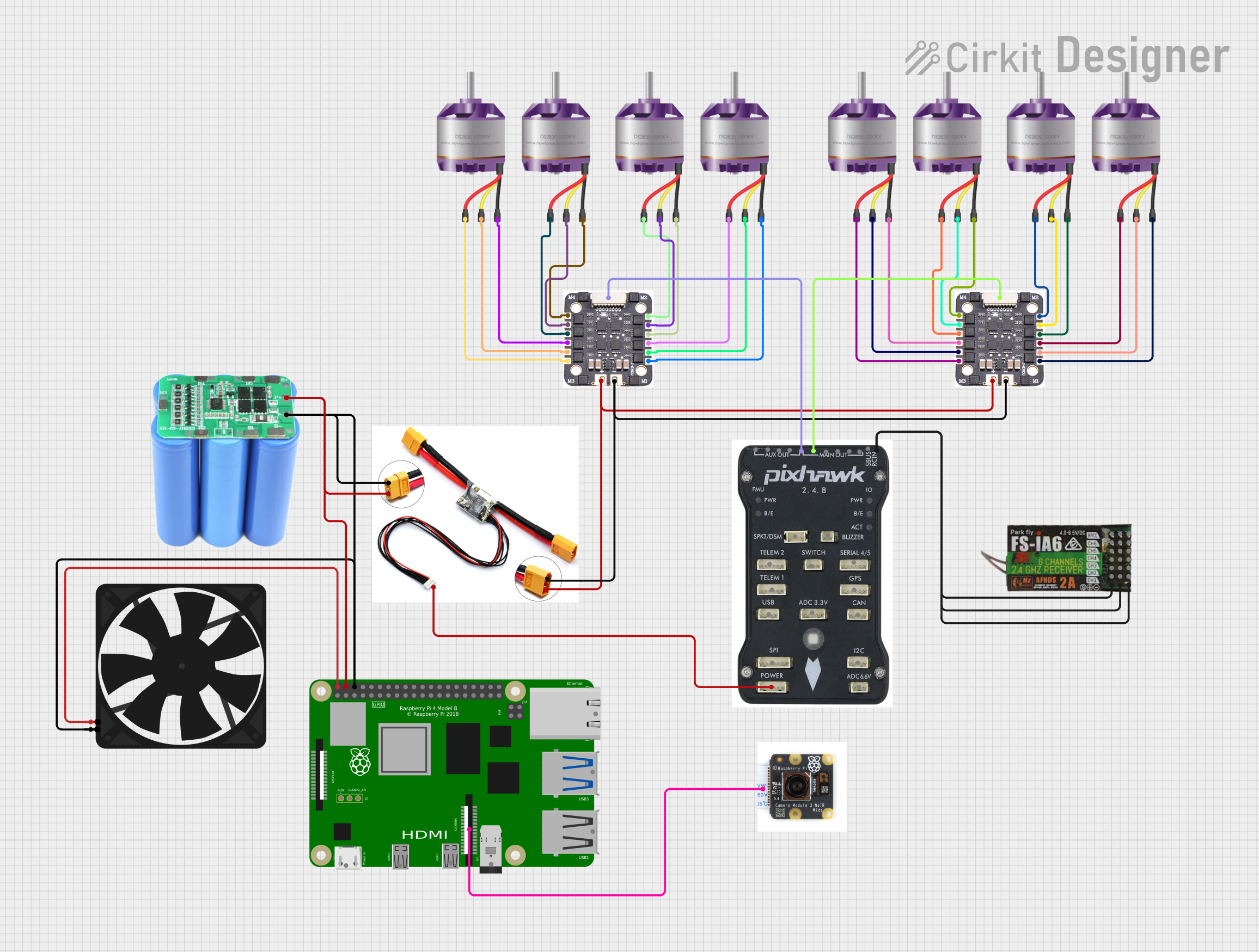
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer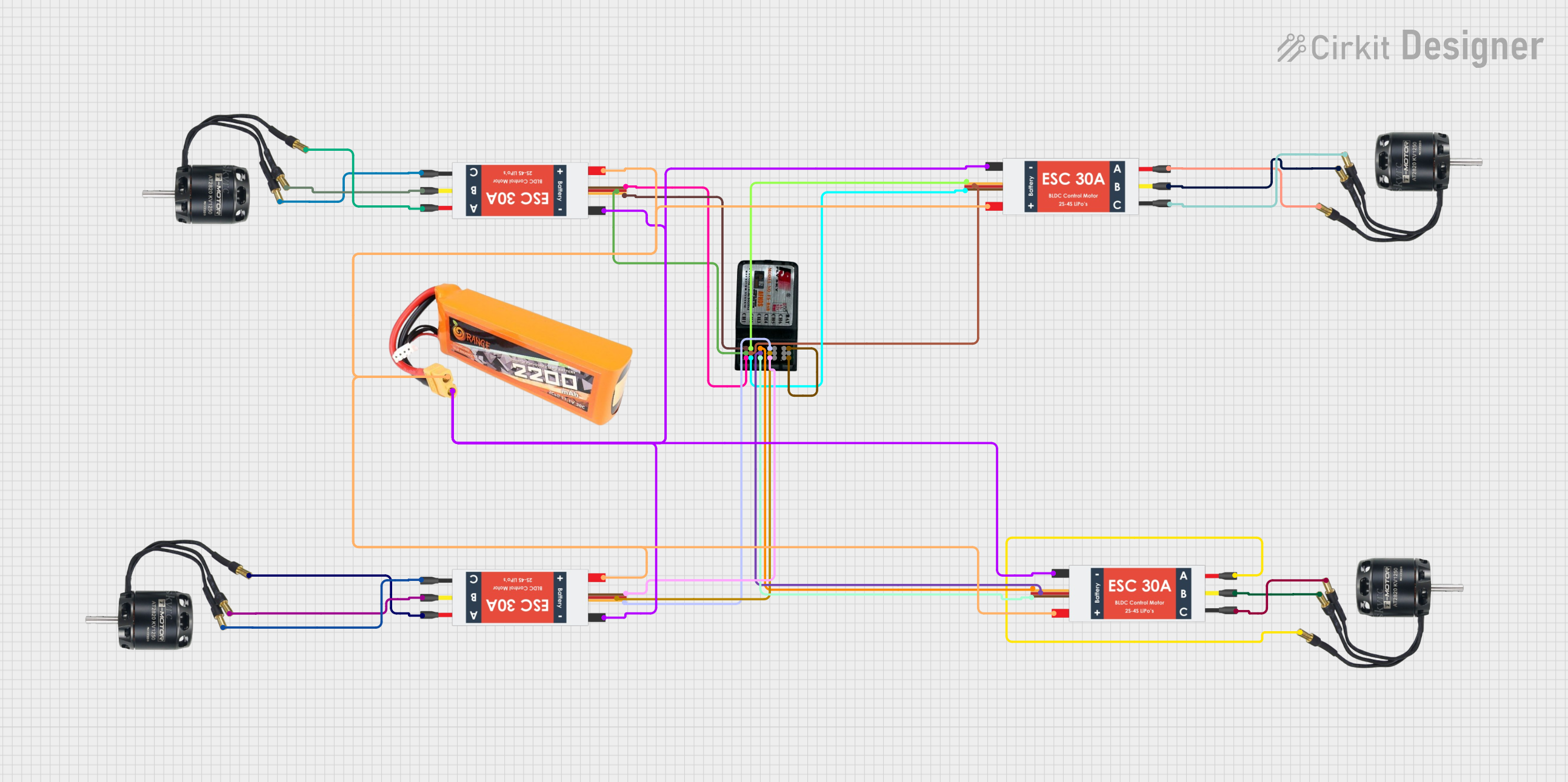
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer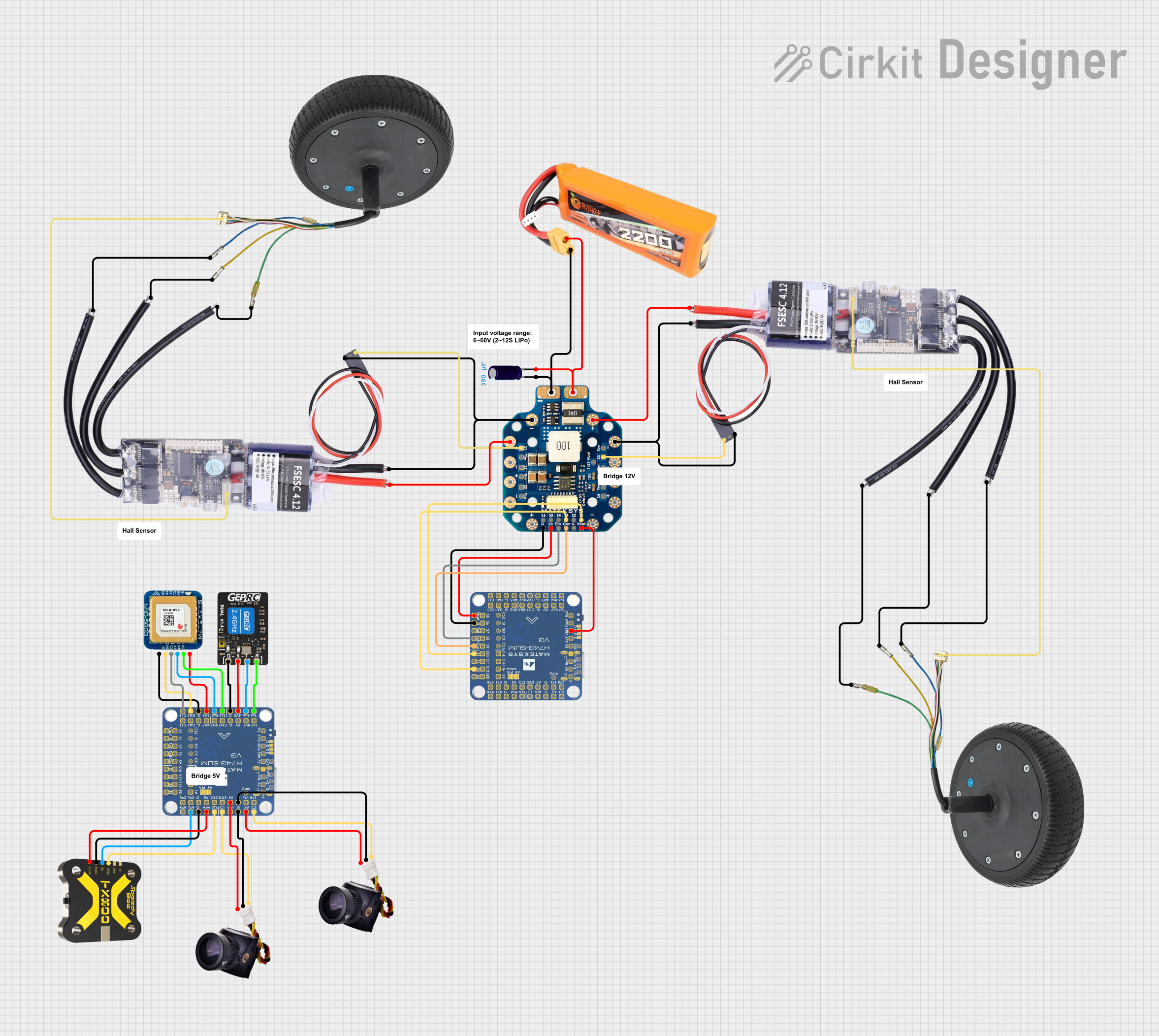
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer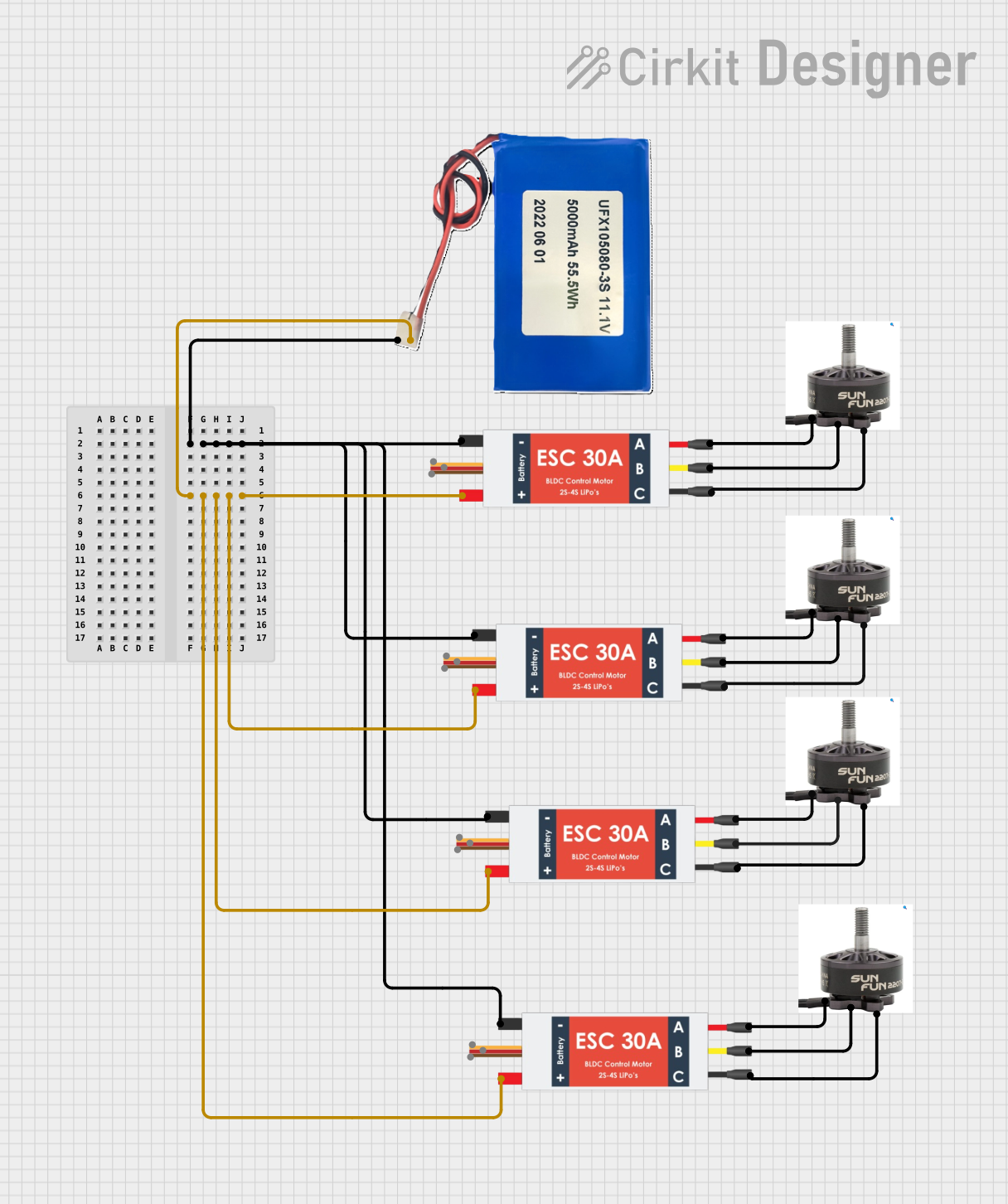
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESC 40A

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- RC drones and quadcopters for stable flight and motor control
- RC cars and boats for speed and direction management
- Robotics projects requiring brushless motor control
- Electric skateboards and other personal mobility devices
Technical Specifications
The ESC 40A is designed to handle high currents and provide reliable performance. Below are its key technical details:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Continuous Current | 40A |
| Peak Current | 50A (for 10 seconds) |
| Input Voltage Range | 2S–6S LiPo (7.4V–22.2V) |
| Motor Compatibility | Brushless motors (sensorless) |
| BEC Output | 5V/3A (Battery Eliminator Circuit) |
| PWM Input Signal Range | 1000–2000 µs |
| Weight | ~30g |
| Dimensions | 45mm x 25mm x 10mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESC 40A typically has the following connections:
| Pin/Connector Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Input (+) | Connects to the positive terminal of the battery (e.g., LiPo battery). |
| Power Input (-) | Connects to the negative terminal of the battery. |
| Motor Phase A | Connects to one of the three wires of the brushless motor. |
| Motor Phase B | Connects to the second wire of the brushless motor. |
| Motor Phase C | Connects to the third wire of the brushless motor. |
| Signal Input | Receives the PWM signal from the flight controller or RC receiver. |
| Ground (Signal) | Ground connection for the signal input. |
| BEC Output (+) | Provides regulated 5V power to the flight controller or receiver. |
| BEC Output (-) | Ground connection for the BEC output. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESC 40A in a Circuit
- Connect the Power Supply: Attach the positive and negative terminals of a compatible LiPo battery (2S–6S) to the ESC's power input connectors.
- Connect the Motor: Attach the three motor phase wires (A, B, C) to the corresponding wires of the brushless motor. The order of connection determines the motor's rotation direction.
- Connect the Signal Input: Connect the signal input pin to the PWM output of your flight controller, RC receiver, or microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
- Connect the BEC Output: Use the BEC output to power your flight controller or receiver if needed.
- Calibrate the ESC: Follow the ESC calibration procedure to ensure proper throttle range detection (see your ESC's manual for specific steps).
- Test the Setup: Power on the system and test the motor's response to throttle input.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Compatibility: Ensure the battery voltage is within the ESC's supported range (7.4V–22.2V).
- Cooling: Avoid overheating by providing adequate airflow or heat dissipation, especially during high-current operation.
- Signal Quality: Use a clean and stable PWM signal to avoid erratic motor behavior.
- Motor Rotation Direction: If the motor spins in the wrong direction, swap any two of the motor phase wires.
- Safety: Always disconnect the battery when making wiring changes to prevent accidental short circuits.
Example: Using ESC 40A with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of controlling the ESC 40A with an Arduino UNO using the Servo library:
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library for generating PWM signals
Servo esc; // Create a Servo object to control the ESC
void setup() {
esc.attach(9); // Attach the ESC signal wire to pin 9 on the Arduino
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Send minimum throttle (1000 µs) to arm the ESC
delay(2000); // Wait for 2 seconds to allow the ESC to initialize
}
void loop() {
esc.writeMicroseconds(1500); // Set throttle to 50% (1500 µs)
delay(5000); // Run the motor at 50% throttle for 5 seconds
esc.writeMicroseconds(1000); // Set throttle to 0% (1000 µs)
delay(5000); // Stop the motor for 5 seconds
}
Note: Always follow the ESC's arming procedure as specified in its manual. Failure to do so may result in the motor not responding to throttle inputs.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Spinning
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or uncalibrated ESC.
- Solution: Verify all connections and perform the ESC calibration procedure.
Motor Spins in the Wrong Direction
- Cause: Incorrect motor phase wire connections.
- Solution: Swap any two of the motor phase wires to reverse the direction.
ESC Overheating
- Cause: Prolonged high-current operation or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Ensure proper airflow or add a heatsink to the ESC.
No Response from ESC
- Cause: Incorrect PWM signal or ESC not armed.
- Solution: Check the signal connection and ensure the ESC is armed correctly.
Receiver or Flight Controller Not Powering On
- Cause: BEC output not connected or overloaded.
- Solution: Verify the BEC connections and ensure the load does not exceed 3A.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the ESC 40A with a brushed motor?
A: No, the ESC 40A is designed specifically for brushless motors.Q: How do I know if my ESC is calibrated?
A: The ESC will typically emit a series of beeps during calibration to indicate throttle range detection.Q: Can I use a 7.4V (2S) battery with this ESC?
A: Yes, the ESC supports 2S–6S LiPo batteries.Q: What happens if I exceed the 40A current rating?
A: Exceeding the current rating may cause the ESC to overheat, shut down, or become permanently damaged.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the ESC 40A into your projects and troubleshoot common issues with ease.