
How to Use PS2 Joystick: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with PS2 Joystick in Cirkit Designer
Design with PS2 Joystick in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Keyes PS2 Joystick with Button is an input device designed for precise control in video games, robotics, and other interactive applications. It features two analog potentiometers for X and Y directional movement and a tactile push-button for additional functionality. The joystick is compact, easy to use, and compatible with microcontrollers like Arduino, making it a popular choice for hobbyists and developers.
Explore Projects Built with PS2 Joystick
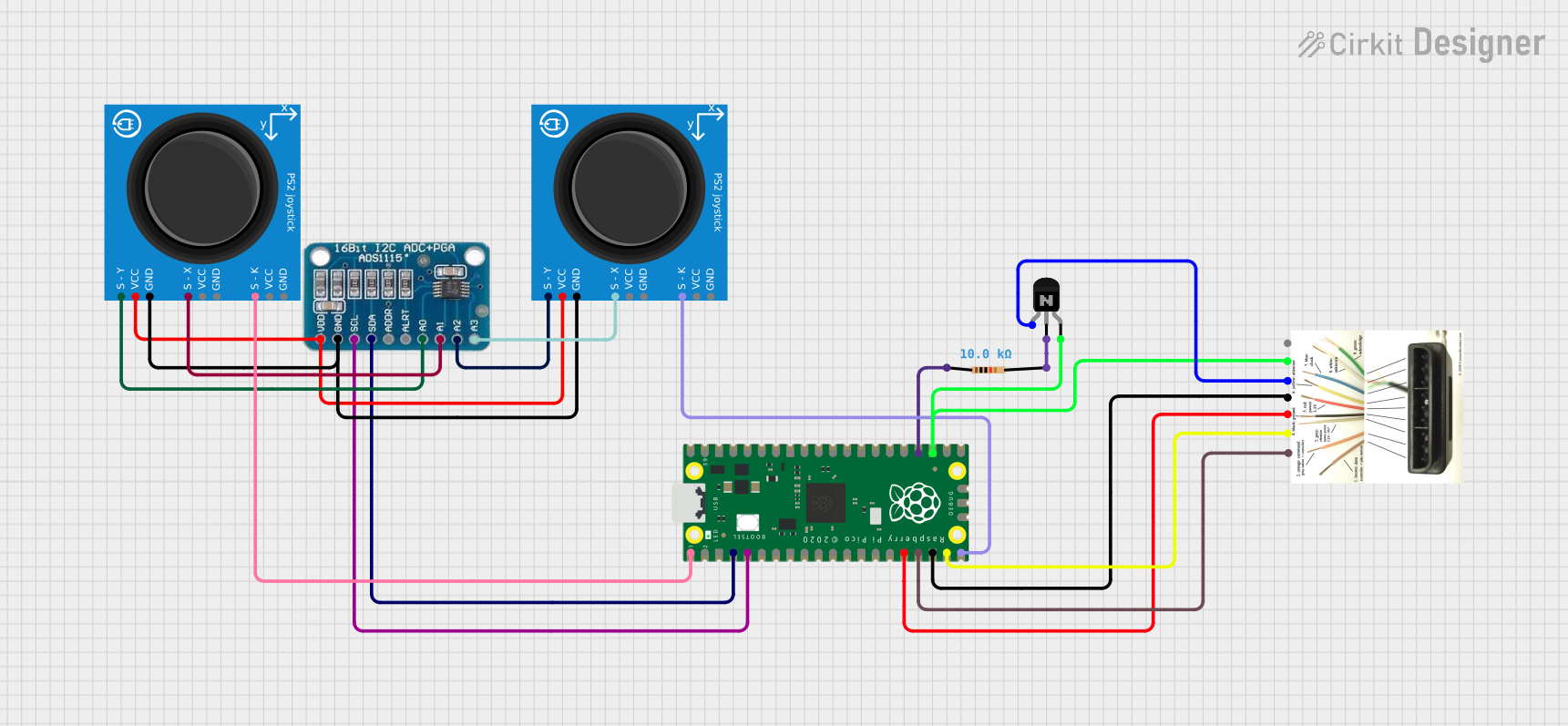
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer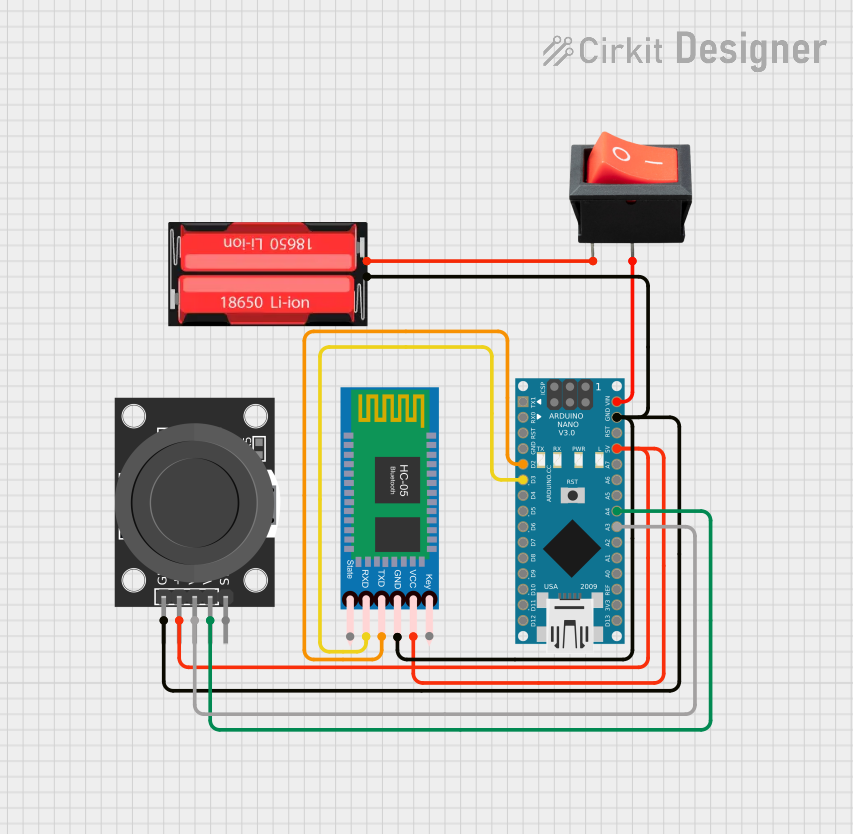
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer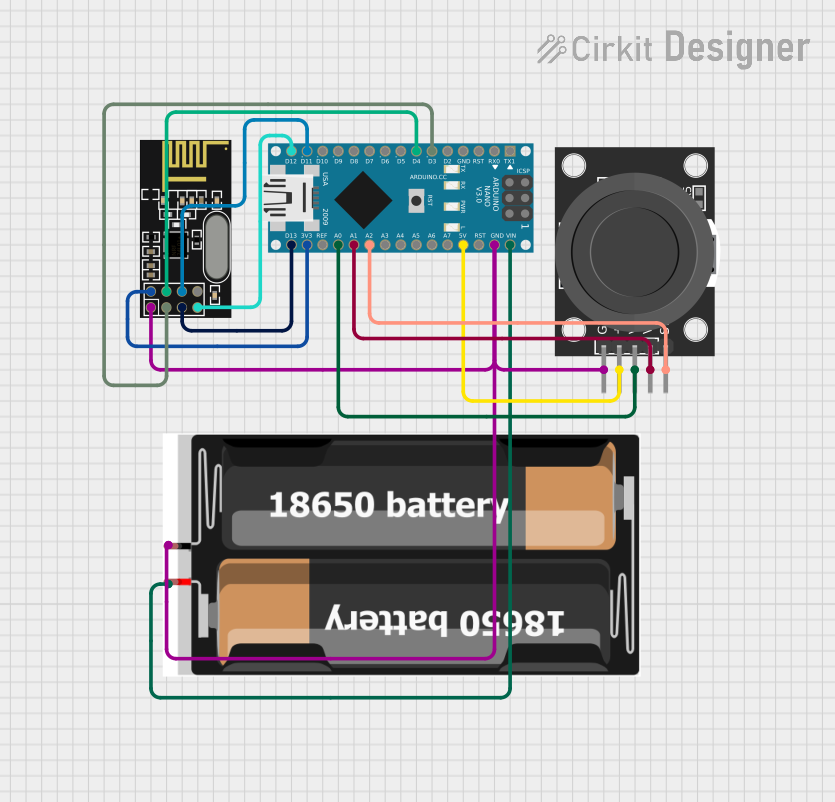
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer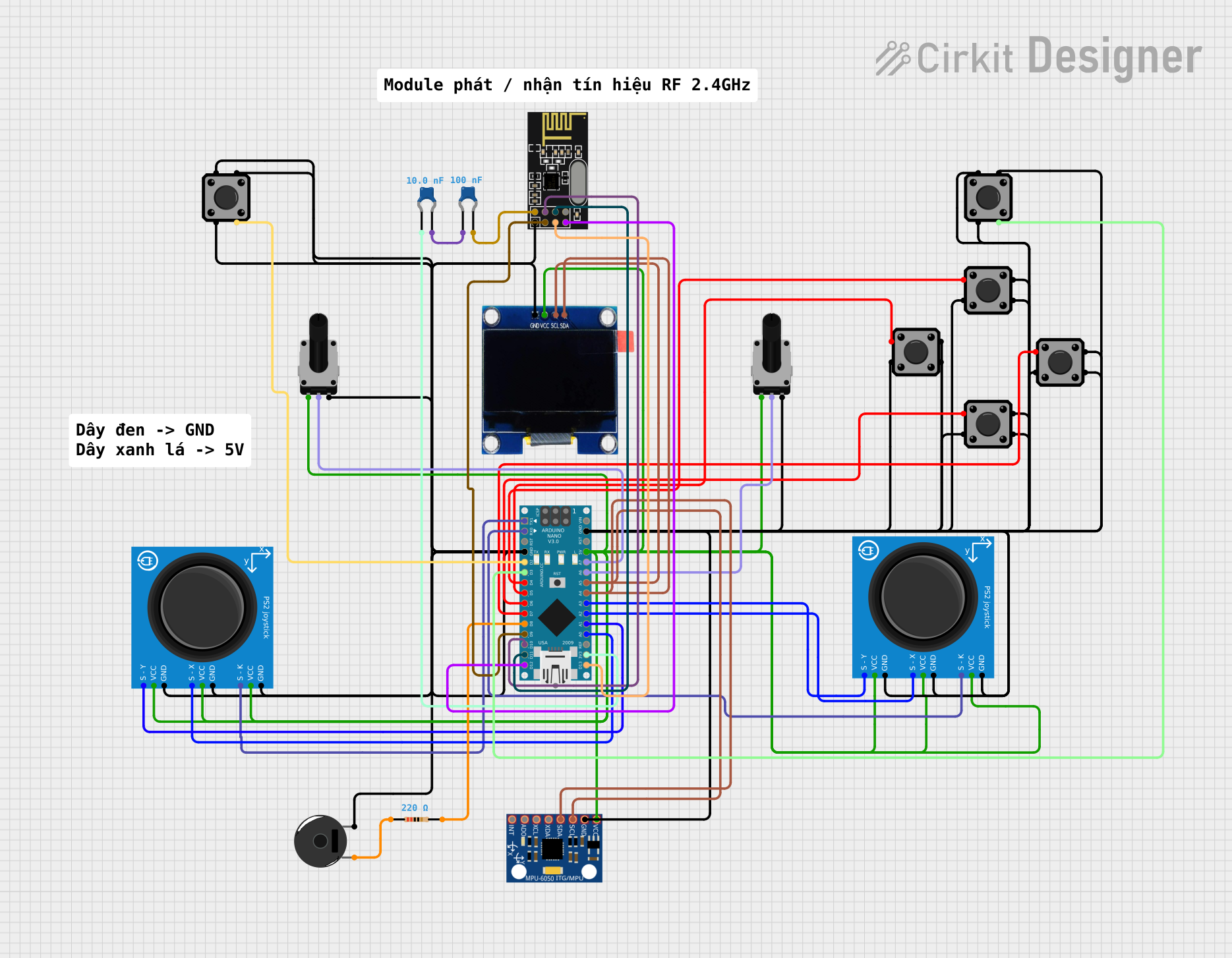
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with PS2 Joystick

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Game controllers and simulators
- Robotic control systems
- Camera gimbal control
- DIY projects requiring analog input
- Interactive art installations
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Keyes PS2 Joystick with Button:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Output Type | Analog (X, Y axes) and Digital (Button) |
| X-Axis Range | 0V to Vcc (centered at ~Vcc/2) |
| Y-Axis Range | 0V to Vcc (centered at ~Vcc/2) |
| Button Output | Digital (Active Low) |
| Dimensions | 34mm x 26mm x 32mm |
| Interface Type | 5-pin header |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The PS2 Joystick module has a 5-pin header for interfacing. The table below describes each pin:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | Ground connection |
| 2 | +5V | Power supply (3.3V to 5V) |
| 3 | VRx | Analog output for X-axis movement (0V to Vcc, centered at ~Vcc/2) |
| 4 | VRy | Analog output for Y-axis movement (0V to Vcc, centered at ~Vcc/2) |
| 5 | SW | Digital output for the push-button (Active Low: 0V when pressed, Vcc otherwise) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Joystick: Connect the
+5Vpin to the 5V output of your microcontroller and theGNDpin to ground. - Read Analog Outputs: Connect the
VRxandVRypins to the analog input pins of your microcontroller to read the X and Y axis values. - Read Button State: Connect the
SWpin to a digital input pin to detect button presses. - Pull-Up Resistor for Button: If the microcontroller does not have an internal pull-up resistor, add an external pull-up resistor (e.g., 10kΩ) to the
SWpin.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Compatibility: Ensure the joystick's operating voltage matches your microcontroller's input voltage (3.3V or 5V).
- Debouncing the Button: Use software debouncing to handle any noise or false triggers from the push-button.
- Center Calibration: The joystick's analog outputs are centered at approximately half the supply voltage when in the neutral position. Account for this in your code.
- Avoid Over-Pressing: Excessive force on the joystick or button may damage the module.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example Arduino sketch to read the joystick's X, Y, and button states:
// Define pin connections
const int VRxPin = A0; // X-axis connected to analog pin A0
const int VRyPin = A1; // Y-axis connected to analog pin A1
const int SWPin = 2; // Button connected to digital pin 2
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
// Configure the button pin as input with an internal pull-up resistor
pinMode(SWPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop() {
// Read the X and Y axis values (0 to 1023)
int xValue = analogRead(VRxPin);
int yValue = analogRead(VRyPin);
// Read the button state (LOW when pressed, HIGH otherwise)
int buttonState = digitalRead(SWPin);
// Print the values to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("X: ");
Serial.print(xValue);
Serial.print(" | Y: ");
Serial.print(yValue);
Serial.print(" | Button: ");
Serial.println(buttonState == LOW ? "Pressed" : "Released");
// Add a small delay for stability
delay(100);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Joystick Outputs Not Centered
- Cause: The joystick may not be perfectly calibrated.
- Solution: In your code, account for small deviations from the expected center value (e.g., ±10 units).
Button Not Responding
- Cause: Missing pull-up resistor or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Ensure the
SWpin is connected to a pull-up resistor (internal or external).
No Analog Output
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or damaged module.
- Solution: Verify the power connections and ensure the module is receiving 3.3V or 5V.
Erratic Readings
- Cause: Electrical noise or loose connections.
- Solution: Use shorter wires, secure connections, and add decoupling capacitors if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the joystick with a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, the joystick can be used with a Raspberry Pi. Connect the analog outputs to an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) module, as the Raspberry Pi lacks built-in analog input pins.
Q: What is the lifespan of the joystick?
A: The joystick is designed for long-term use, but its lifespan depends on the frequency and intensity of use. Avoid excessive force to prolong its life.
Q: Can I use the joystick with 3.3V systems?
A: Yes, the joystick is compatible with 3.3V systems. Ensure all connections and microcontroller pins are configured accordingly.
Q: How do I debounce the button in software?
A: Implement a delay (e.g., 50ms) after detecting a button press to filter out noise or false triggers.