
How to Use boost converter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with boost converter in Cirkit Designer
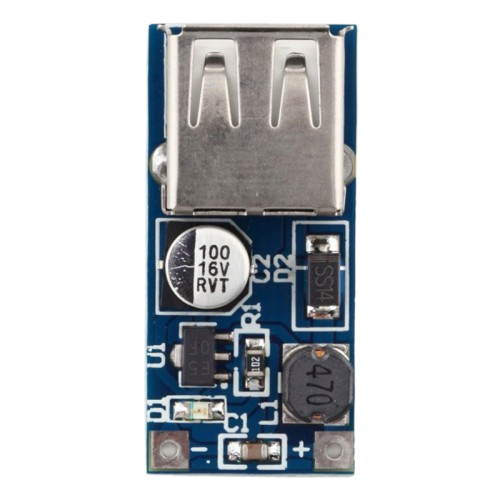
Design with boost converter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A boost converter is a DC-DC power converter that steps up (increases) the input voltage to a higher output voltage while maintaining the same polarity. It operates using an inductor, a switch (typically a transistor), a diode, and a capacitor to achieve efficient voltage conversion. Boost converters are widely used in applications where a higher voltage is required from a lower voltage source, such as in battery-powered devices, renewable energy systems, and automotive electronics.
Explore Projects Built with boost converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer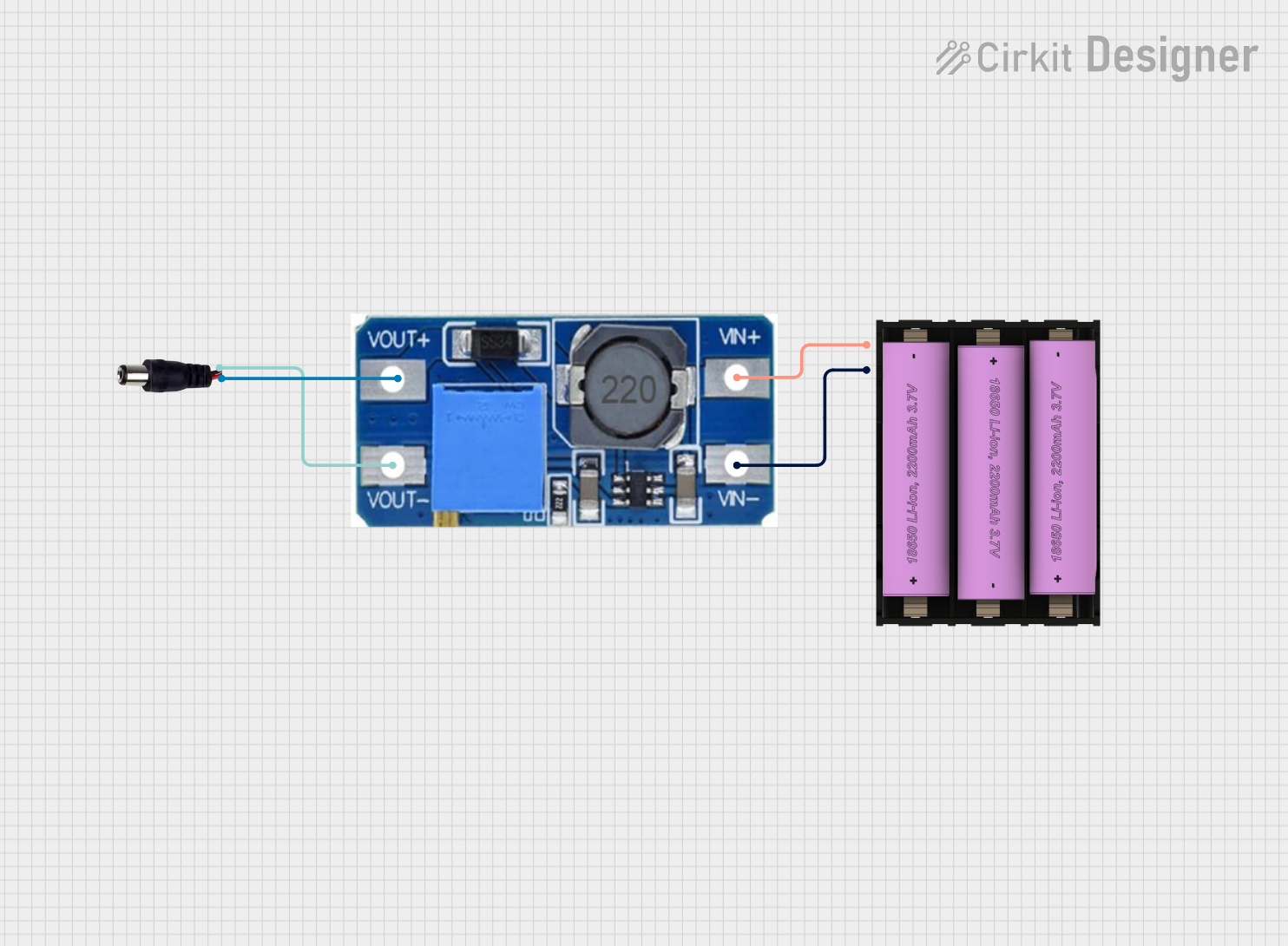
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with boost converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Powering high-voltage devices from low-voltage batteries (e.g., LED drivers, portable electronics)
- Solar power systems to step up panel voltage for charging batteries
- Electric vehicles to boost battery voltage for motor operation
- Industrial and medical equipment requiring stable high-voltage outputs
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical boost converter. Note that actual values may vary depending on the specific model or design.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 2V to 36V (varies by design) |
| Output Voltage Range | Up to 60V (varies by design) |
| Output Current | Typically 0.5A to 10A (depends on design) |
| Efficiency | 80% to 95% (depending on load and design) |
| Switching Frequency | 100 kHz to 1 MHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration of a boost converter module (e.g., a pre-assembled module) typically includes the following:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin (connect to the power source) |
| GND | Ground pin (common ground for input and output) |
| VOUT | Output voltage pin (connect to the load) |
| EN (optional) | Enable pin (used to turn the converter on/off) |
| FB (optional) | Feedback pin (used for voltage regulation and control) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage (VIN):
- Attach the positive terminal of the power source to the VIN pin.
- Connect the negative terminal of the power source to the GND pin.
Connect the Output Voltage (VOUT):
- Attach the load (e.g., an LED, motor, or other device) to the VOUT pin.
- Ensure the load's voltage and current requirements are within the boost converter's specifications.
Enable the Converter (if applicable):
- If the module has an EN (Enable) pin, connect it to a HIGH signal (e.g., 5V) to activate the converter.
- To disable the converter, connect the EN pin to GND.
Adjust the Output Voltage (if adjustable):
- Some boost converters have a potentiometer for adjusting the output voltage.
- Rotate the potentiometer clockwise or counterclockwise to increase or decrease the output voltage.
- Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage while adjusting.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Input Voltage Range: Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range of the boost converter. Exceeding this range can damage the module.
- Output Voltage Limit: Do not exceed the maximum output voltage rating of the converter.
- Heat Dissipation: Boost converters can generate heat during operation. Use a heatsink or ensure proper ventilation if the module gets too hot.
- Load Requirements: Verify that the load does not draw more current than the converter can supply.
- Ripple and Noise: Use additional capacitors at the input and output to reduce voltage ripple and noise, especially in sensitive applications.
Example: Using a Boost Converter with Arduino UNO
A boost converter can be used to power devices requiring higher voltage than the Arduino UNO's 5V output. Below is an example of using a boost converter to power a 12V LED strip.
Circuit Connections
- Connect the Arduino's 5V pin to the VIN pin of the boost converter.
- Connect the GND pin of the Arduino to the GND pin of the boost converter.
- Adjust the boost converter's output to 12V using the potentiometer.
- Connect the VOUT pin of the boost converter to the positive terminal of the LED strip.
- Connect the negative terminal of the LED strip to the GND pin of the boost converter.
Arduino Code Example
// This code demonstrates controlling the LED strip using a PWM signal
// from the Arduino UNO. The PWM signal adjusts the brightness of the LED strip.
const int pwmPin = 9; // PWM pin connected to the LED strip (via a transistor)
void setup() {
pinMode(pwmPin, OUTPUT); // Set the PWM pin as an output
}
void loop() {
// Gradually increase brightness
for (int brightness = 0; brightness <= 255; brightness++) {
analogWrite(pwmPin, brightness); // Write PWM signal to the pin
delay(10); // Small delay for smooth transition
}
// Gradually decrease brightness
for (int brightness = 255; brightness >= 0; brightness--) {
analogWrite(pwmPin, brightness); // Write PWM signal to the pin
delay(10); // Small delay for smooth transition
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Input voltage is too low or not connected properly.
Solution: Verify the input voltage and connections. Ensure it is within the specified range. - Cause: EN pin is not enabled.
Solution: Check the EN pin and connect it to a HIGH signal if required.
- Cause: Input voltage is too low or not connected properly.
Output Voltage is Incorrect:
- Cause: Potentiometer is not adjusted correctly.
Solution: Use a multimeter to measure the output voltage and adjust the potentiometer.
- Cause: Potentiometer is not adjusted correctly.
Excessive Heat:
- Cause: Load is drawing too much current.
Solution: Reduce the load or use a boost converter with a higher current rating. - Cause: Poor ventilation.
Solution: Add a heatsink or improve airflow around the module.
- Cause: Load is drawing too much current.
High Ripple or Noise:
- Cause: Insufficient filtering.
Solution: Add additional capacitors at the input and output terminals.
- Cause: Insufficient filtering.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a boost converter to power a microcontroller?
A: Yes, but ensure the output voltage is stable and within the microcontroller's operating range. Use additional capacitors to reduce ripple.
Q: What happens if the input voltage exceeds the specified range?
A: Exceeding the input voltage range can damage the boost converter. Always use a power source within the recommended range.
Q: Can I use a boost converter to step down voltage?
A: No, a boost converter is designed to step up voltage. For stepping down voltage, use a buck converter instead.