
How to Use Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector in Cirkit Designer
Design with Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector is a soil moisture sensor designed to measure the volumetric water content in soil. It provides an analog or digital output that corresponds to the moisture level, making it an essential tool for monitoring soil health. This sensor is widely used in agricultural applications, gardening, and automated irrigation systems to optimize water usage and ensure plant health.
Explore Projects Built with Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector
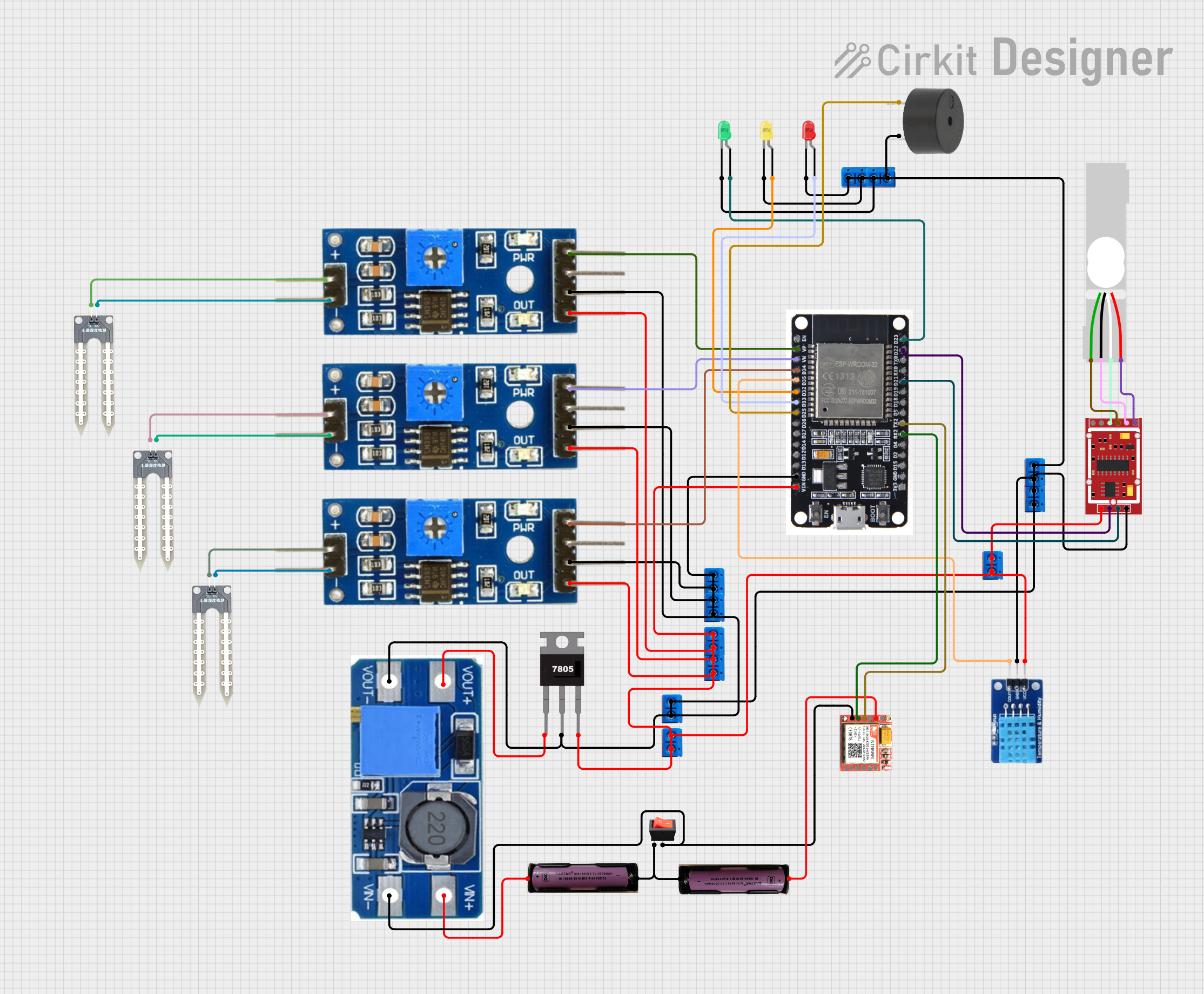
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer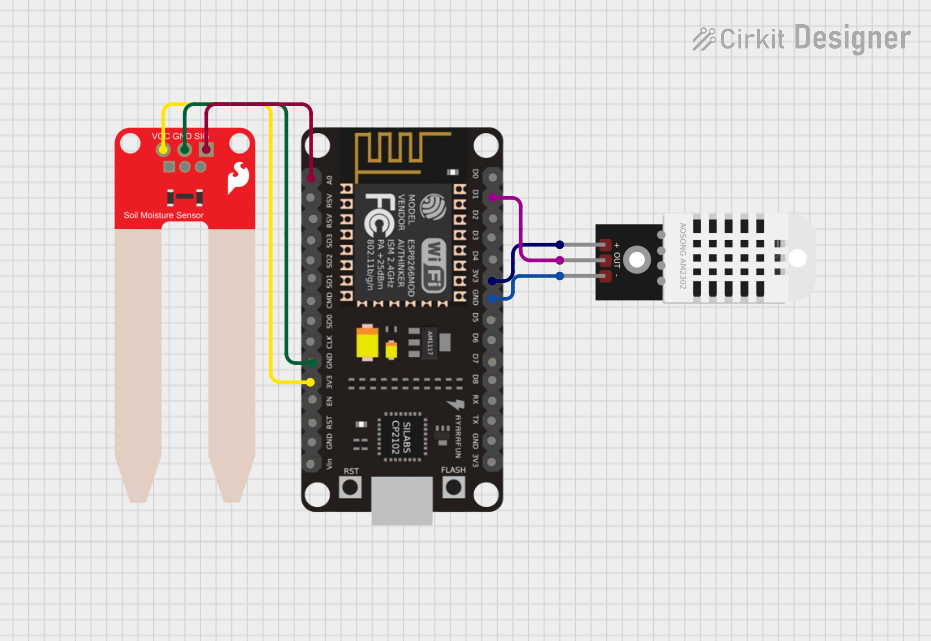
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer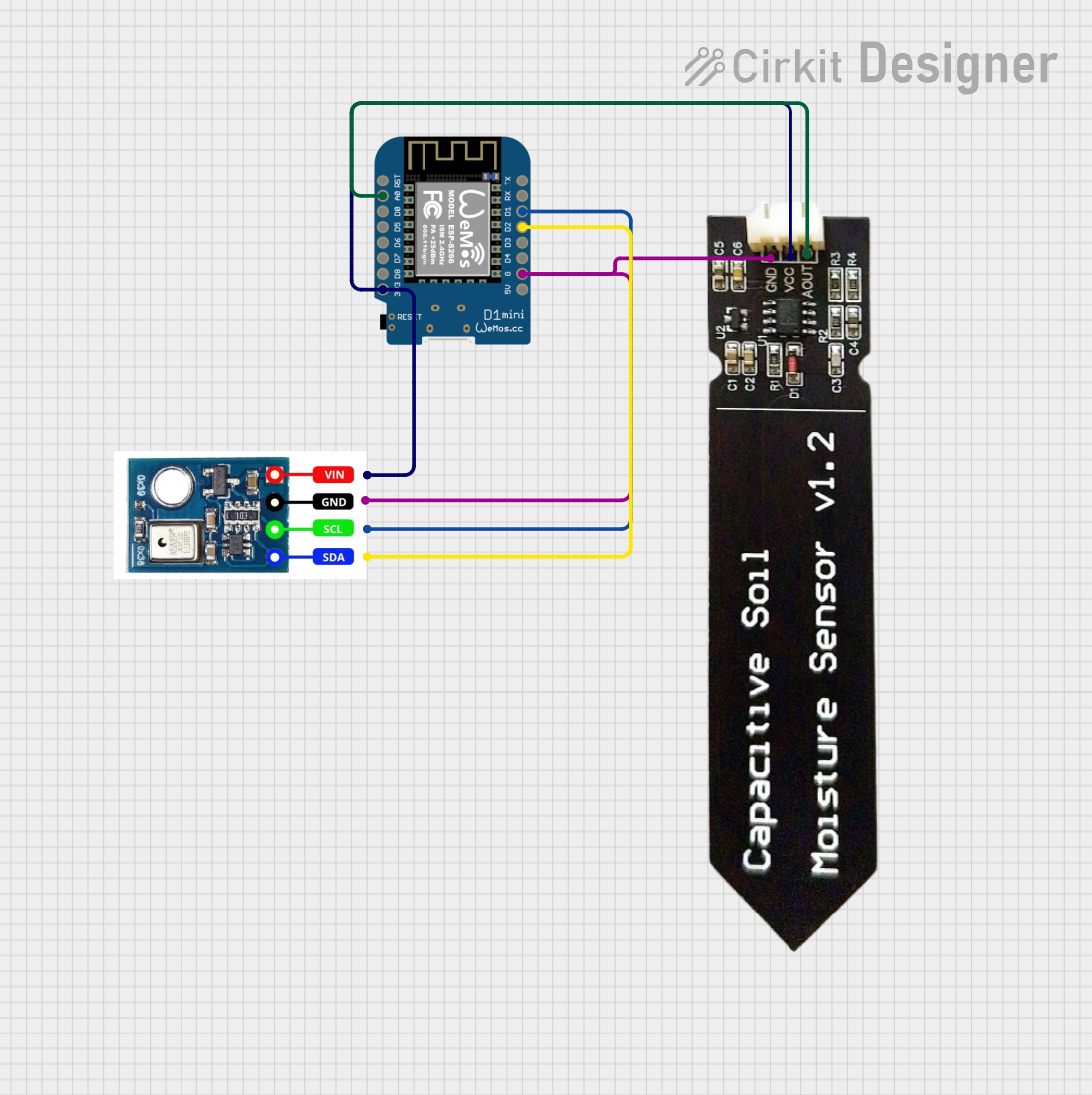
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer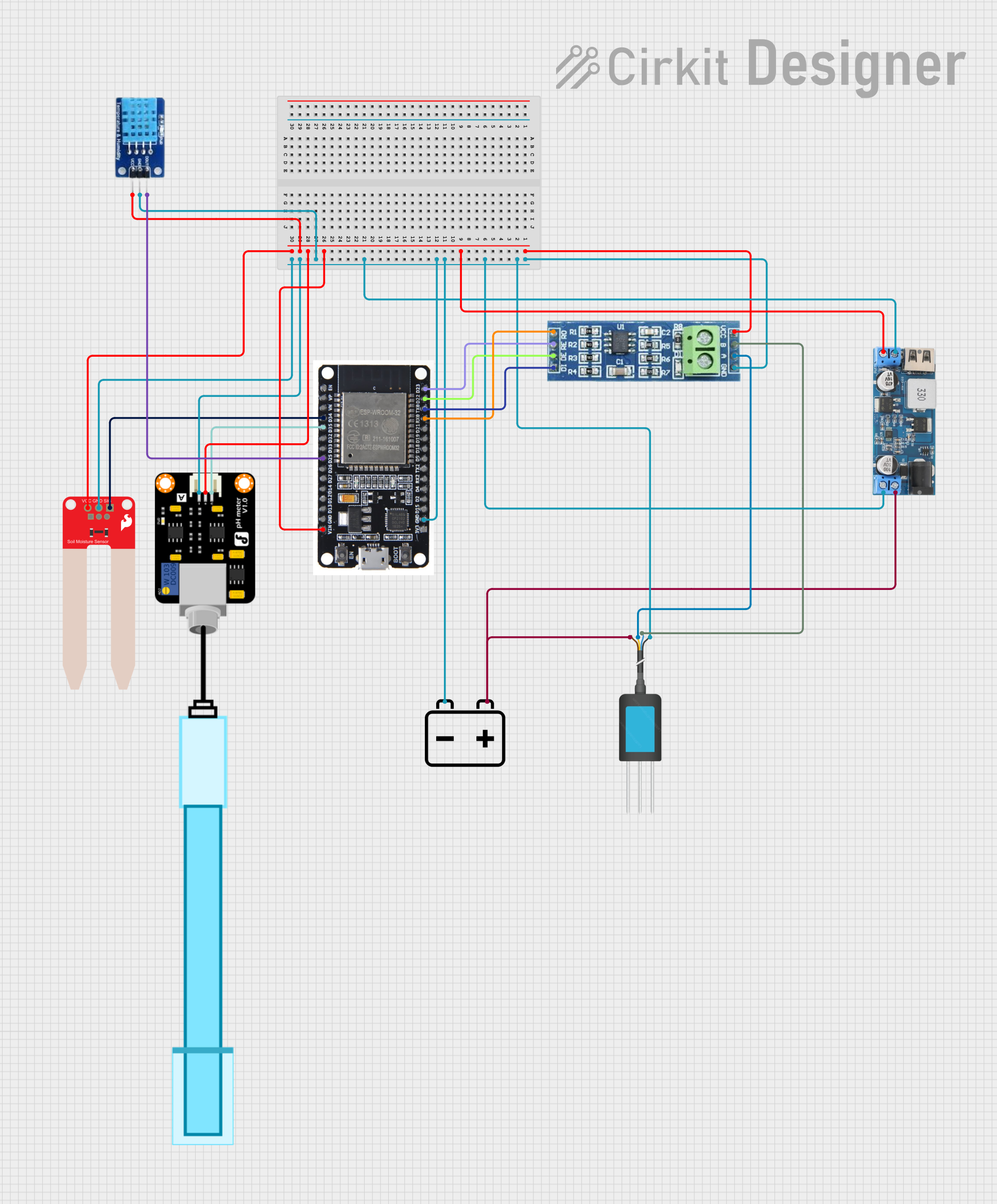
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automated irrigation systems for agriculture and gardening
- Soil moisture monitoring in greenhouses
- Environmental monitoring and research
- Smart gardening projects
- Educational projects involving Arduino or other microcontrollers
Technical Specifications
The Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector consists of two main parts: the sensor probe and the control board. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V
- Output Types: Analog and Digital
- Current Consumption: < 20mA
- Dimensions:
- Sensor Probe: 60mm x 20mm
- Control Board: 30mm x 15mm
- Interface: 4-pin connector (VCC, GND, A0, D0)
- Moisture Range: 0% (dry) to 100% (fully wet)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The HW-080 Connector has a 4-pin interface. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin. Connect to 3.3V or 5V. |
| 2 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the power source. |
| 3 | A0 | Analog output pin. Provides a voltage proportional to the soil moisture level. |
| 4 | D0 | Digital output pin. Outputs HIGH or LOW based on the adjustable threshold. |
Adjustable Threshold
The control board includes a potentiometer to adjust the threshold for the digital output (D0). This allows users to set a specific moisture level at which the digital output switches between HIGH and LOW.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector in a Circuit
Connect the Sensor:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5V power source.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the power source.
- Connect the A0 pin to an analog input pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
- Optionally, connect the D0 pin to a digital input pin if you want to use the threshold-based output.
Adjust the Threshold:
- Use a small screwdriver to turn the potentiometer on the control board.
- Turning clockwise increases the threshold, while turning counterclockwise decreases it.
Read the Output:
- For analog readings, use the A0 pin to measure the voltage corresponding to the soil moisture level.
- For digital readings, monitor the D0 pin to check if the soil moisture is above or below the set threshold.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid prolonged exposure of the sensor probe to water, as it may corrode over time.
- Use the sensor in well-drained soil to prevent waterlogging, which can damage the probe.
- Calibrate the sensor for your specific soil type to improve accuracy.
- If using the sensor outdoors, consider waterproofing the control board to protect it from environmental damage.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example code to read both analog and digital outputs from the Soil Sensor HW-080 Connector:
// Define pin connections
const int analogPin = A0; // Analog output pin connected to A0 on Arduino
const int digitalPin = 2; // Digital output pin connected to pin 2 on Arduino
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
pinMode(digitalPin, INPUT); // Set digital pin as input
}
void loop() {
// Read analog value from the sensor
int analogValue = analogRead(analogPin);
// Read digital value from the sensor
int digitalValue = digitalRead(digitalPin);
// Print the analog value (moisture level)
Serial.print("Analog Value (Moisture Level): ");
Serial.println(analogValue);
// Print the digital value (threshold status)
Serial.print("Digital Value (Threshold Status): ");
if (digitalValue == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Dry");
} else {
Serial.println("Wet");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output from the Sensor:
- Ensure the sensor is properly connected to the power supply and ground.
- Verify that the VCC pin is receiving 3.3V or 5V.
Inaccurate Readings:
- Check for corrosion on the sensor probe and clean it if necessary.
- Calibrate the sensor for your specific soil type by comparing its readings with a known moisture level.
Digital Output Always HIGH or LOW:
- Adjust the potentiometer to set an appropriate threshold for your soil conditions.
- Ensure the D0 pin is correctly connected to the microcontroller.
Sensor Probe Corrosion:
- Avoid leaving the probe in waterlogged soil for extended periods.
- Consider using a corrosion-resistant coating on the probe for long-term use.
FAQs
Q: Can the sensor be used with a 3.3V microcontroller like ESP8266 or ESP32?
A: Yes, the sensor is compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers. Ensure the VCC pin is connected to a 3.3V power source.
Q: How do I waterproof the control board?
A: You can use a waterproof enclosure or apply a conformal coating to protect the control board from moisture.
Q: What is the lifespan of the sensor probe?
A: The lifespan depends on usage and environmental conditions. Regular cleaning and avoiding prolonged exposure to water can extend its life.
Q: Can I use multiple sensors in the same project?
A: Yes, you can connect multiple sensors to different analog or digital pins on your microcontroller. Ensure each sensor has a unique connection.