
How to Use Battery Li-Po 1100 mAh: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Battery Li-Po 1100 mAh in Cirkit Designer
Design with Battery Li-Po 1100 mAh in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Battery Li-Po 1100 mAh is a lightweight, high-energy-density lithium polymer rechargeable battery manufactured by Red. With a capacity of 1100 mAh, it is ideal for powering portable electronic devices, drones, RC vehicles, and embedded systems. Its compact size and reliable performance make it a popular choice for applications requiring efficient energy storage in a small form factor.
Explore Projects Built with Battery Li-Po 1100 mAh
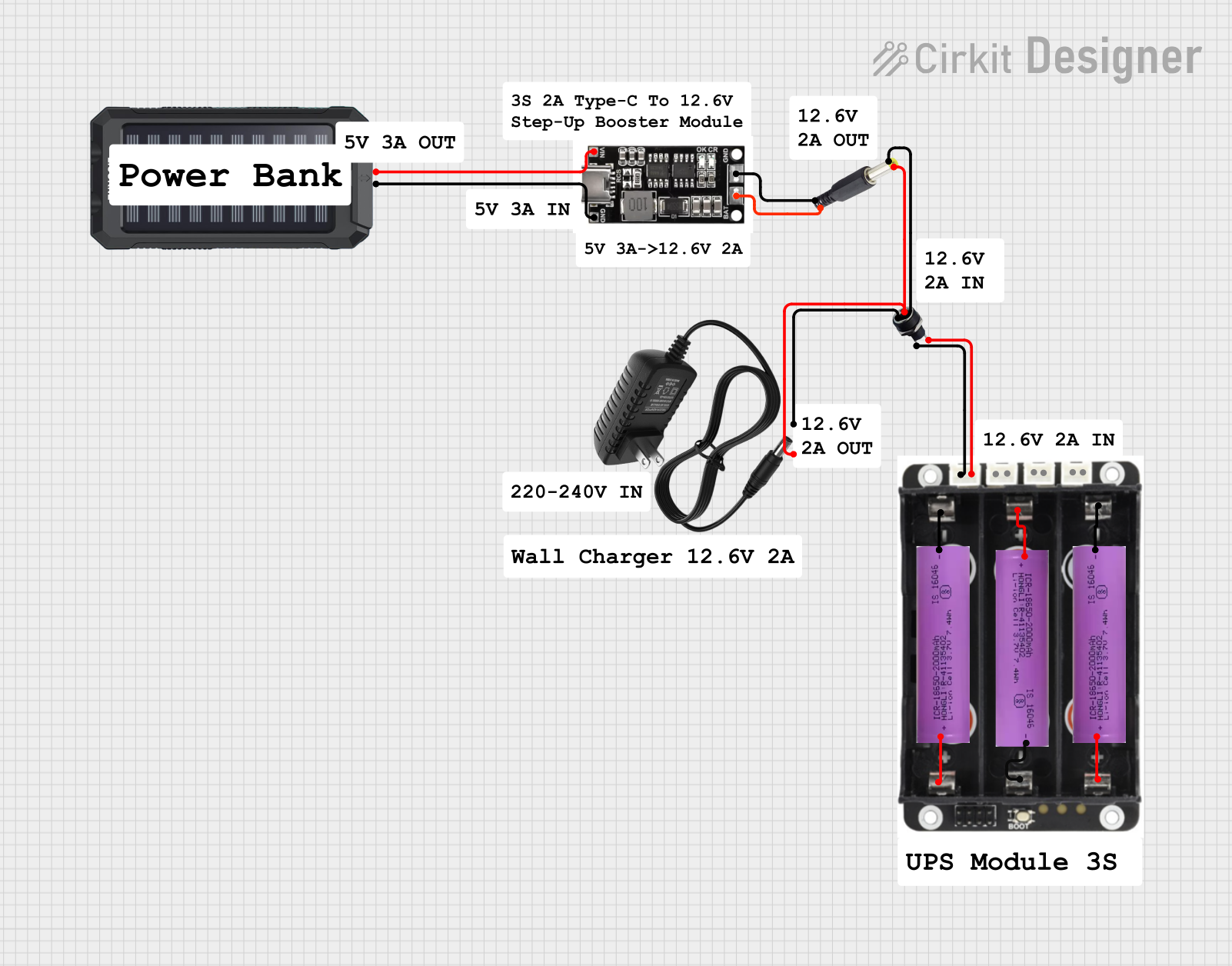
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer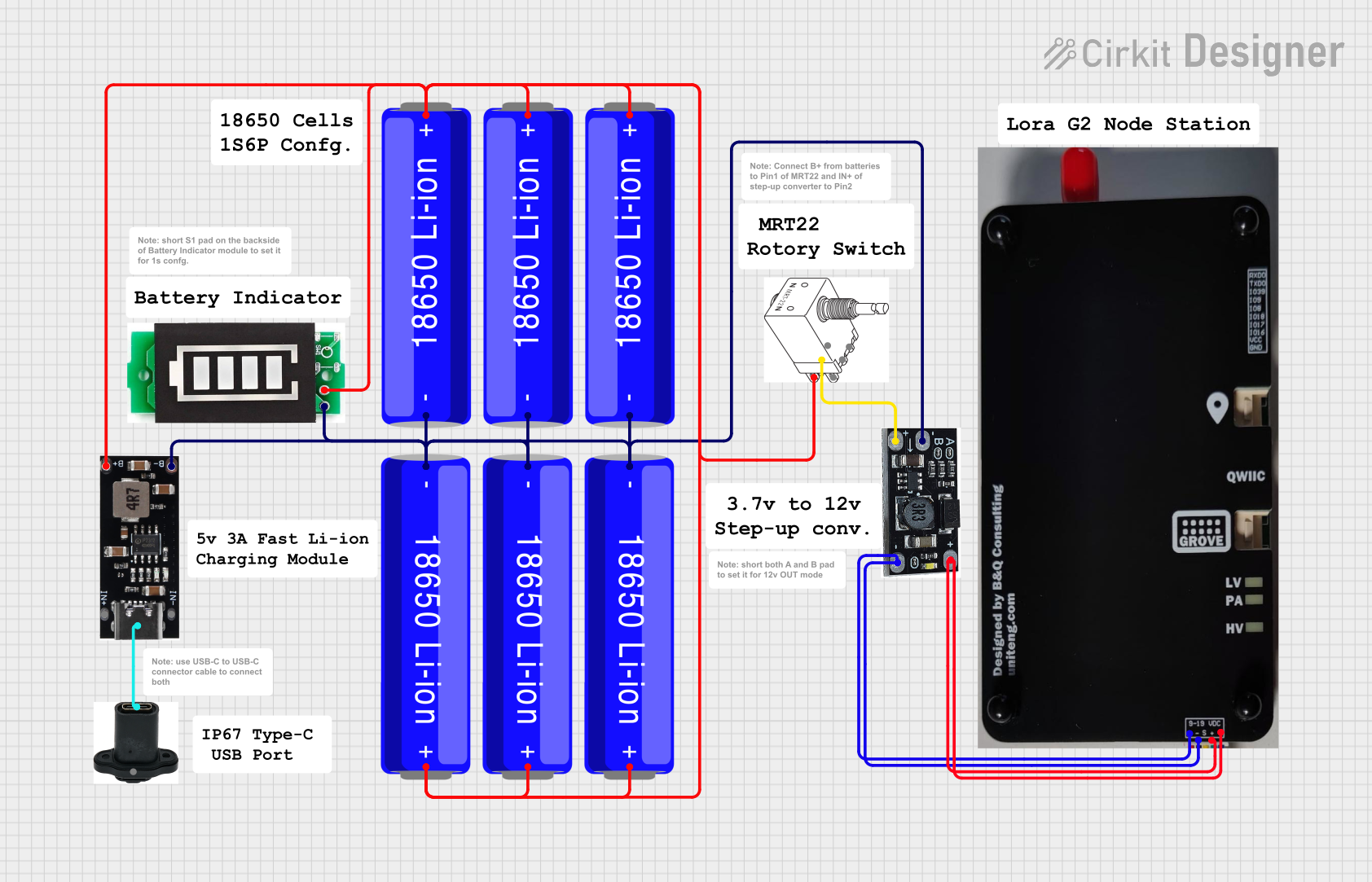
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Battery Li-Po 1100 mAh

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Portable electronic devices (e.g., handheld gadgets, wearables)
- Drones and remote-controlled vehicles
- Embedded systems and IoT devices
- Robotics and prototyping projects
- Backup power supplies for small circuits
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details of the Battery Li-Po 1100 mAh:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 3.7 V |
| Capacity | 1100 mAh |
| Maximum Discharge Rate | 20C (22 A) |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2 V (maximum) |
| Charging Current | 0.5C (550 mA recommended) |
| Dimensions | 50 mm x 30 mm x 7 mm |
| Weight | ~25 g |
| Connector Type | JST-XH or custom (varies) |
| Protection Circuit | No (external protection required) |
Pin Configuration
The battery typically comes with a JST-XH connector, which has two pins:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Positive (+) | Connects to the positive terminal of the circuit |
| 2 | Negative (-) | Connects to the ground or negative terminal |
Note: Always verify the connector type and pinout before connecting the battery to your circuit.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Battery in a Circuit
- Connection: Connect the battery's positive (+) and negative (-) terminals to the corresponding inputs of your circuit or device. Ensure the polarity is correct to avoid damage.
- Charging: Use a dedicated Li-Po battery charger with a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile. Set the charging voltage to 4.2 V and the current to 0.5C (550 mA) for optimal performance.
- Discharge: Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum discharge rate of 20C (22 A). Use a current-limiting circuit if necessary.
- Protection: Since the battery lacks an internal protection circuit, use an external battery management system (BMS) or protection module to prevent overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Overcharging: Never charge the battery above 4.2 V, as this can cause overheating or damage.
- Avoid Over-Discharging: Do not let the voltage drop below 3.0 V, as this can permanently reduce capacity.
- Storage: Store the battery at ~50% charge (3.7–3.8 V) in a cool, dry place to prolong its lifespan.
- Handling: Avoid puncturing, bending, or exposing the battery to high temperatures.
- Balancing: For multi-cell setups, use a balancing charger to ensure all cells are charged evenly.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
To power an Arduino UNO with the Li-Po battery, use a voltage regulator module (e.g., LM7805) to step down the 3.7 V to 5 V. Below is an example circuit and code:
Circuit Setup
- Connect the battery's positive terminal to the input of the voltage regulator.
- Connect the regulator's output to the Arduino's 5V pin.
- Connect the battery's negative terminal to the Arduino's GND pin.
Sample Code
// Example code to read battery voltage using Arduino UNO
// Assumes the battery is connected to an analog pin via a voltage divider
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 2.0; // Adjust based on your resistor values
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino's reference voltage (5V)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog value
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue / 1023.0) * referenceVoltage * voltageDividerRatio;
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider to scale down the battery voltage to a safe range for the Arduino's analog input (0–5 V).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging
- Cause: Incorrect charger or damaged battery.
- Solution: Verify the charger specifications (4.2 V, 0.5C) and check the battery for physical damage.
Battery Drains Quickly
- Cause: Over-discharge or aging battery.
- Solution: Avoid discharging below 3.0 V and replace the battery if it has degraded.
Device Not Powering On
- Cause: Incorrect connection or insufficient current.
- Solution: Check the polarity and ensure the battery can supply the required current.
Battery Swells or Overheats
- Cause: Overcharging or physical damage.
- Solution: Stop using the battery immediately and dispose of it safely.
FAQs
Can I use this battery for high-current applications? Yes, the battery supports a maximum discharge rate of 20C (22 A), making it suitable for high-current devices like drones and RC vehicles.
Do I need a protection circuit? Yes, since the battery lacks an internal protection circuit, an external BMS or protection module is essential.
How long does the battery last? The lifespan depends on usage and care. Typically, it can handle 300–500 charge cycles with proper maintenance.
Can I connect multiple batteries in series or parallel? Yes, but ensure you use a balancing circuit for series connections and match the capacities for parallel connections.
Warning: Always handle Li-Po batteries with care to prevent accidents or damage.