
How to Use Lipo battery : Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
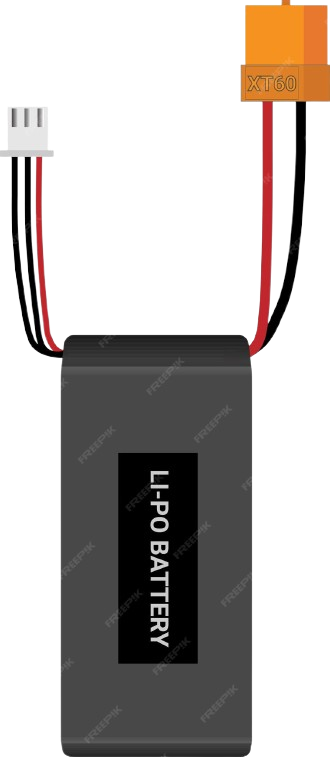
 Design with Lipo battery in Cirkit Designer
Design with Lipo battery in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Sandip Lipo Battery 12V is a high-performance lithium polymer (LiPo) rechargeable battery designed for applications requiring lightweight, high-energy-density power sources. Unlike traditional batteries, LiPo batteries use a polymer electrolyte, which allows for a compact and versatile form factor. This makes them ideal for portable electronics, remote-controlled (RC) devices, drones, robotics, and other applications where weight and size are critical.
Explore Projects Built with Lipo battery
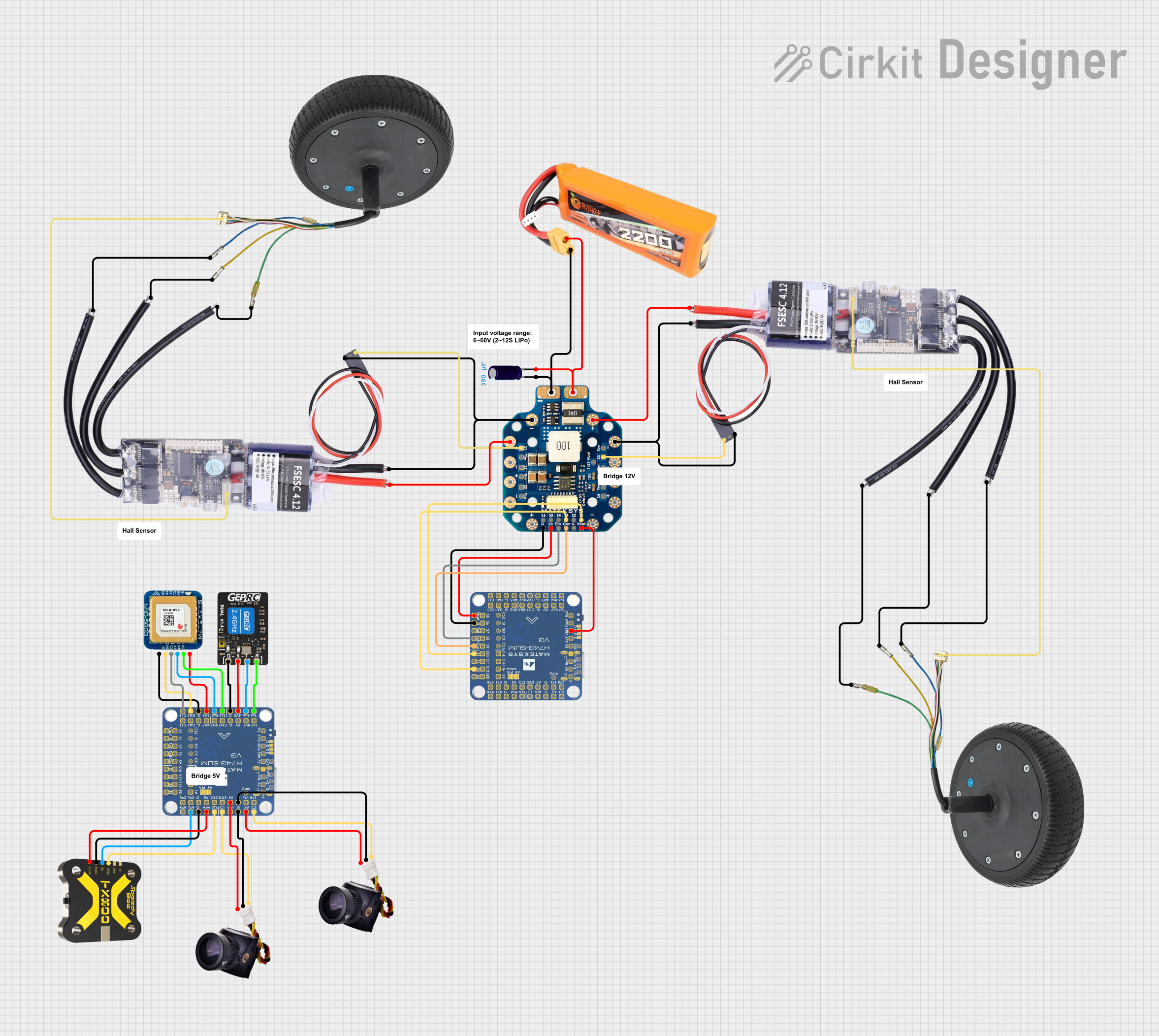
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer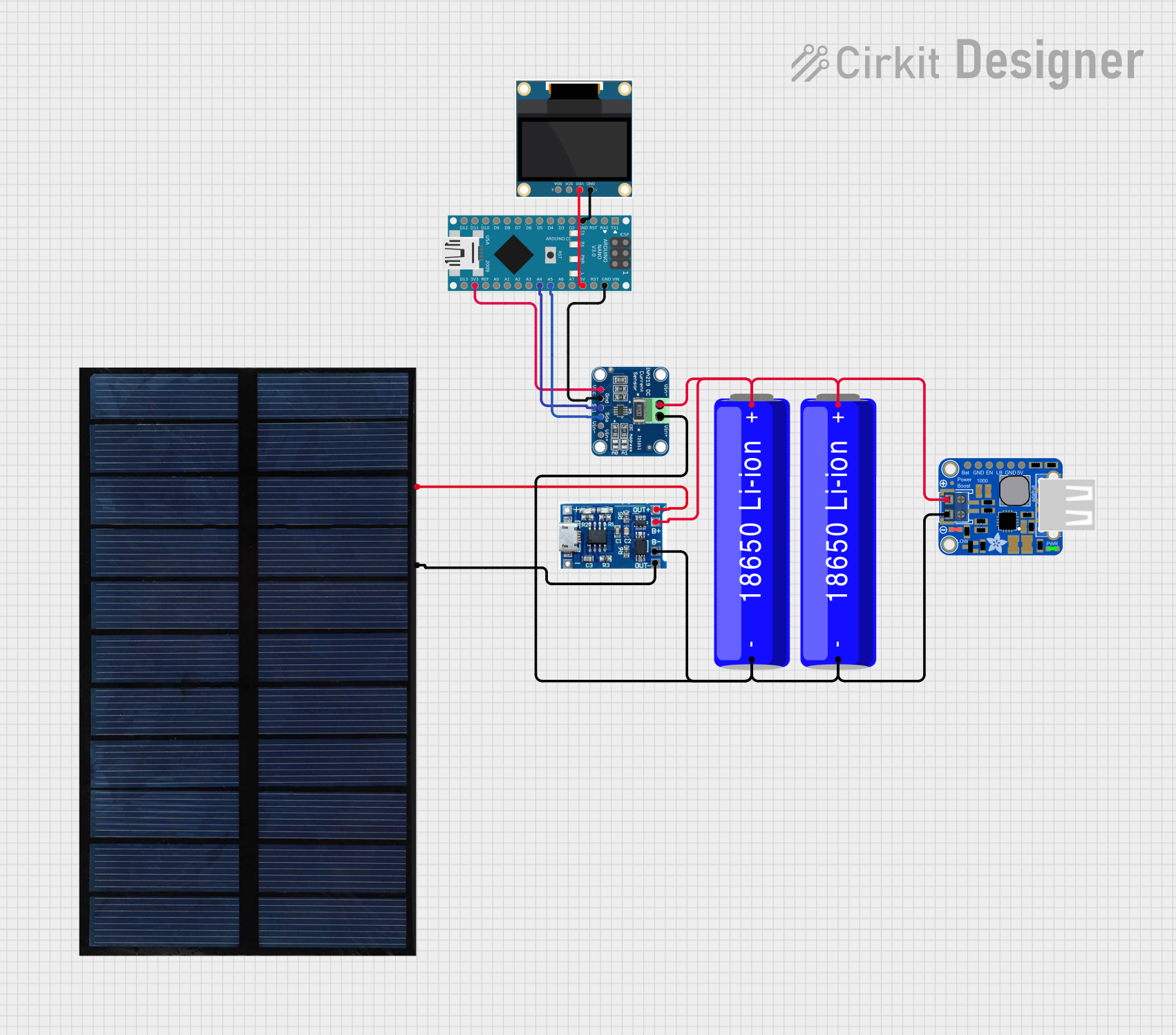
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer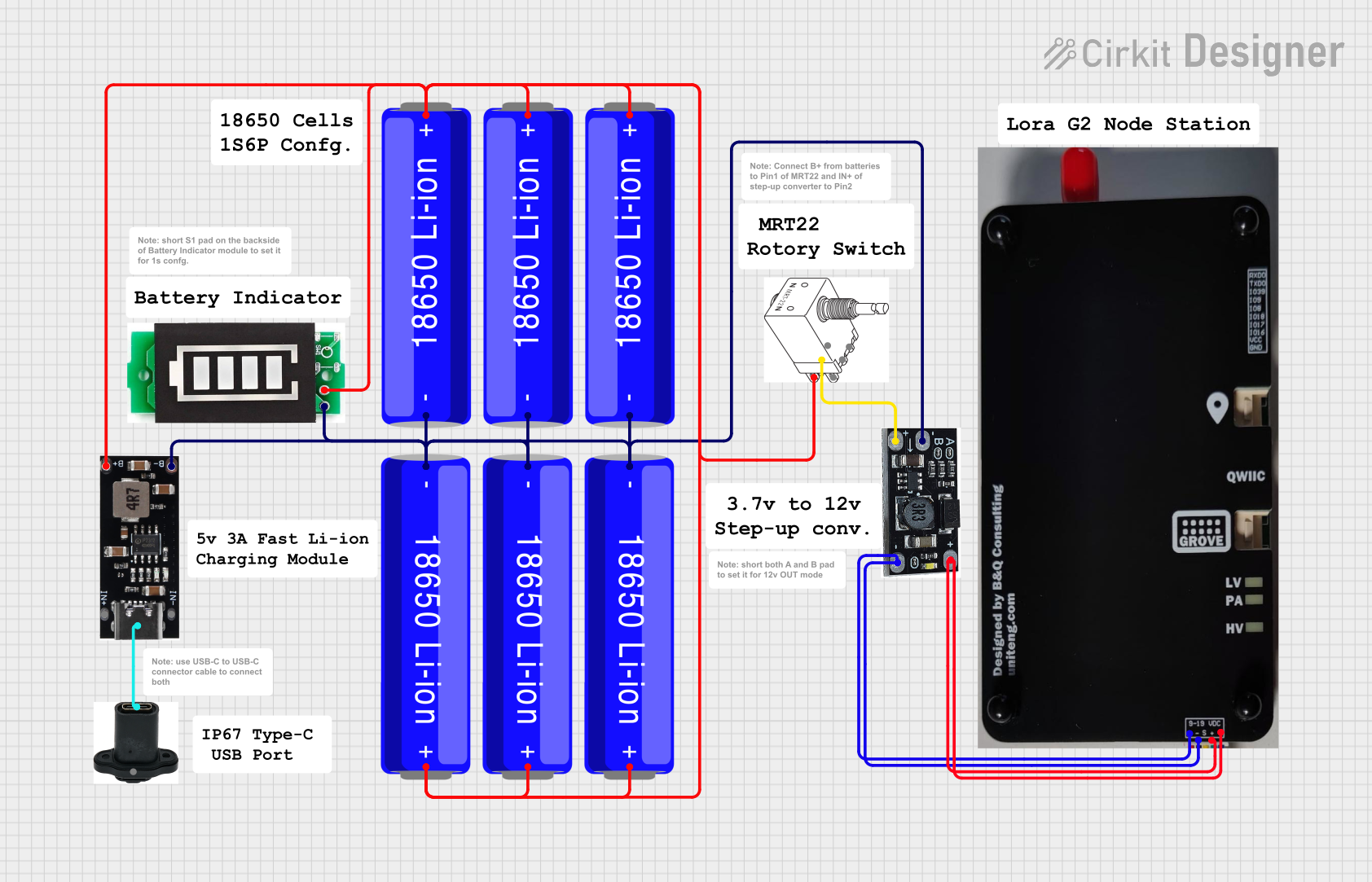
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Lipo battery

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Remote-controlled (RC) vehicles, drones, and aircraft
- Portable electronic devices (e.g., smartphones, tablets, and wearables)
- Robotics and IoT devices
- Backup power supplies
- DIY electronics projects
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the Sandip Lipo Battery 12V:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Sandip |
| Part ID | Lipo Battery 12V |
| Nominal Voltage | 12V |
| Capacity | 2200mAh (varies by model) |
| Maximum Discharge Rate | 25C |
| Charging Voltage | 12.6V (max) |
| Charging Current | 1C (2.2A for 2200mAh model) |
| Weight | ~150g |
| Dimensions | 100mm x 35mm x 25mm |
| Connector Type | XT60 (or JST, depending on model) |
| Cell Configuration | 3S (3 cells in series) |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 60°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Sandip Lipo Battery 12V typically includes two connectors: a power connector and a balance connector. The pin configuration is as follows:
Power Connector (e.g., XT60)
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| + | Positive terminal |
| - | Negative terminal |
Balance Connector (e.g., JST-XH)
| Pin | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Cell 1 positive |
| 2 | Cell 2 positive |
| 3 | Cell 3 positive |
| 4 | Common ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Connecting the Battery:
- Use the power connector (e.g., XT60) to connect the battery to your circuit or device.
- Ensure the polarity matches the circuit's requirements to avoid damage.
- For charging, connect the balance connector to a LiPo-compatible charger to ensure all cells are charged evenly.
Charging the Battery:
- Use a dedicated LiPo charger with a balance charging feature.
- Set the charger to the correct voltage (12.6V for a 3S battery) and current (1C or lower).
- Never leave the battery unattended while charging.
Discharging the Battery:
- Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum discharge rate (25C for this model).
- Monitor the battery voltage to avoid over-discharging. The minimum safe voltage per cell is 3.0V (9.0V for a 3S battery).
Mounting and Handling:
- Secure the battery in your device using straps or holders to prevent movement during operation.
- Avoid puncturing, bending, or exposing the battery to high temperatures.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Monitoring: Use a voltage alarm or battery management system (BMS) to monitor the battery's voltage during use.
- Storage: Store the battery at a 50% charge level in a cool, dry place to prolong its lifespan.
- Safety: Avoid short circuits, overcharging, or over-discharging, as these can lead to battery damage or fire.
- Disposal: Dispose of the battery according to local regulations for electronic waste.
Example: Using with an Arduino UNO
To power an Arduino UNO with the Sandip Lipo Battery 12V, follow these steps:
- Connect the battery's positive terminal to the Arduino's VIN pin.
- Connect the battery's negative terminal to the Arduino's GND pin.
- Use a voltage regulator if the battery's voltage exceeds the Arduino's input voltage range.
Sample Code for Monitoring Battery Voltage
// This code reads the battery voltage using an analog pin on the Arduino UNO.
// Ensure a voltage divider is used to step down the 12V to a safe level for the Arduino.
const int voltagePin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float resistorRatio = 5.7; // Ratio of the voltage divider resistors
const float referenceVoltage = 5.0; // Arduino's reference voltage (5V)
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication
}
void loop() {
int rawValue = analogRead(voltagePin); // Read the analog value
float batteryVoltage = (rawValue * referenceVoltage / 1023.0) * resistorRatio;
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Battery Not Charging:
- Cause: Incorrect charger settings or damaged balance connector.
- Solution: Verify the charger is set to 12.6V and the correct current. Inspect the connectors for damage.
Battery Swelling:
- Cause: Overcharging, over-discharging, or exposure to high temperatures.
- Solution: Stop using the battery immediately and dispose of it safely.
Device Not Powering On:
- Cause: Low battery voltage or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Check the battery voltage with a multimeter and ensure proper connections.
Uneven Cell Voltages:
- Cause: Imbalanced charging or aging cells.
- Solution: Use a balance charger to equalize the cell voltages.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this battery for high-current applications?
A: Yes, the battery supports a maximum discharge rate of 25C, which is suitable for high-current applications. Ensure your load does not exceed this limit.
Q: How do I know when the battery is fully charged?
A: The charger will indicate a full charge when the voltage reaches 12.6V, and the charging current drops to near zero.
Q: Can I connect multiple batteries in series or parallel?
A: Yes, but ensure proper balancing and use a battery management system (BMS) to prevent overcharging or over-discharging.
Q: What is the expected lifespan of this battery?
A: With proper care, the battery can last for 300-500 charge cycles. Avoid overcharging, over-discharging, and high temperatures to maximize lifespan.