
How to Use MPU6050: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
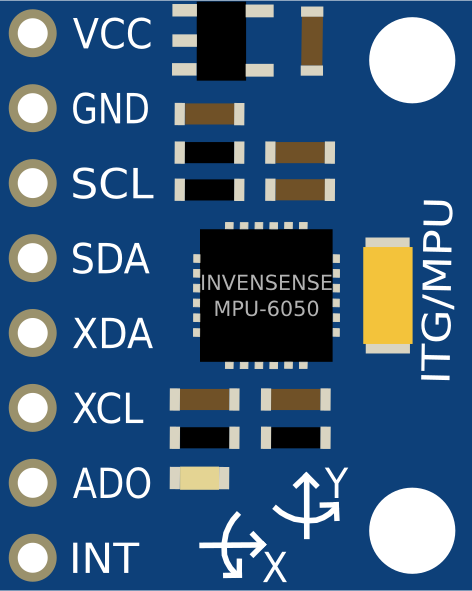
 Design with MPU6050 in Cirkit Designer
Design with MPU6050 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The MPU6050 is a 6-axis motion tracking device that integrates a 3-axis gyroscope and a 3-axis accelerometer into a single chip. This compact and versatile sensor is widely used in applications requiring precise motion tracking and orientation measurement. It is commonly found in robotics, drones, gaming devices, and mobile applications to measure acceleration, angular velocity, and orientation.
The MPU6050 also features a Digital Motion Processor (DMP) that can process complex motion algorithms internally, reducing the computational load on the host microcontroller. Its I2C interface makes it easy to integrate with microcontrollers like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, and other embedded systems.
Explore Projects Built with MPU6050
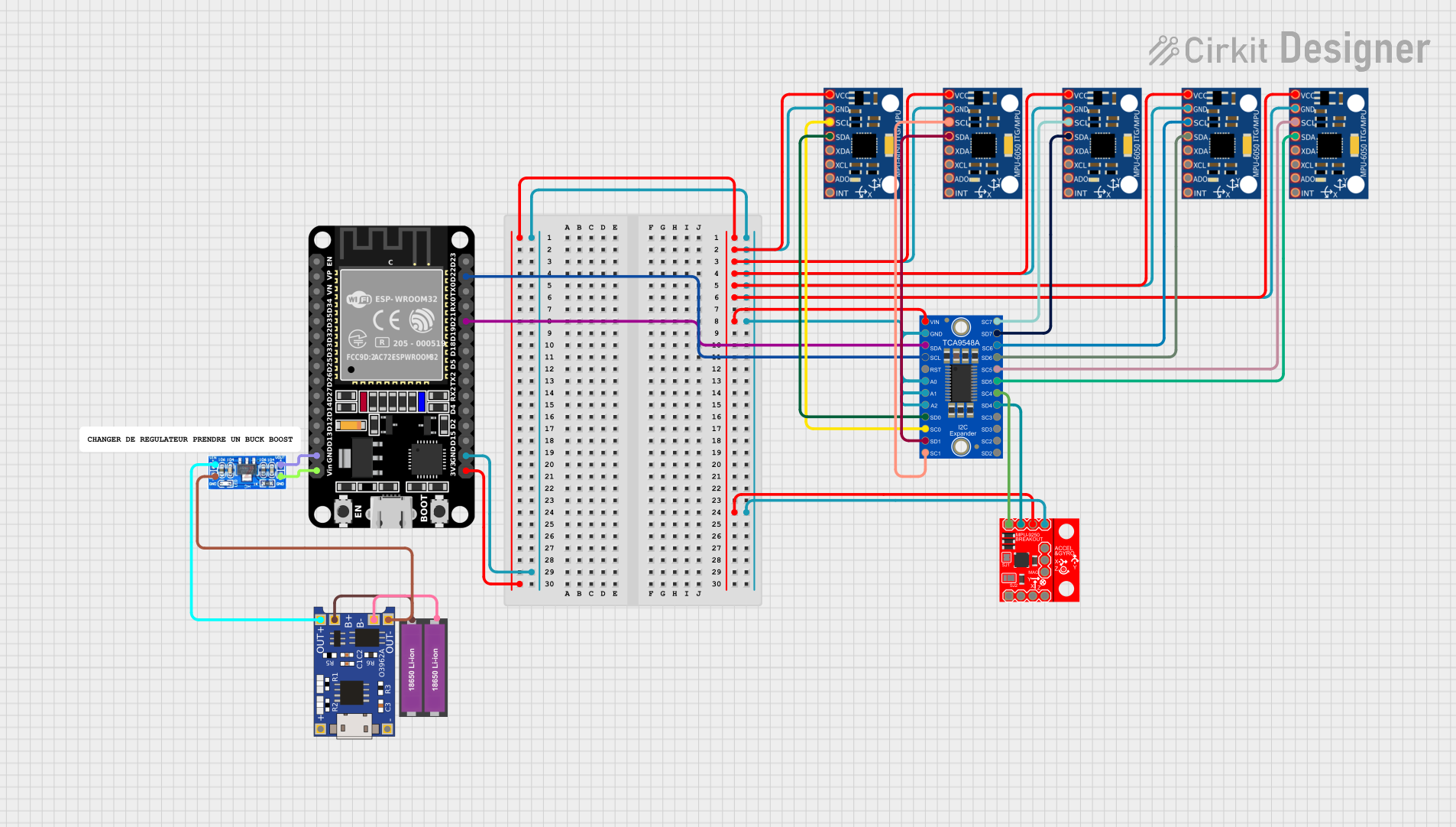
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer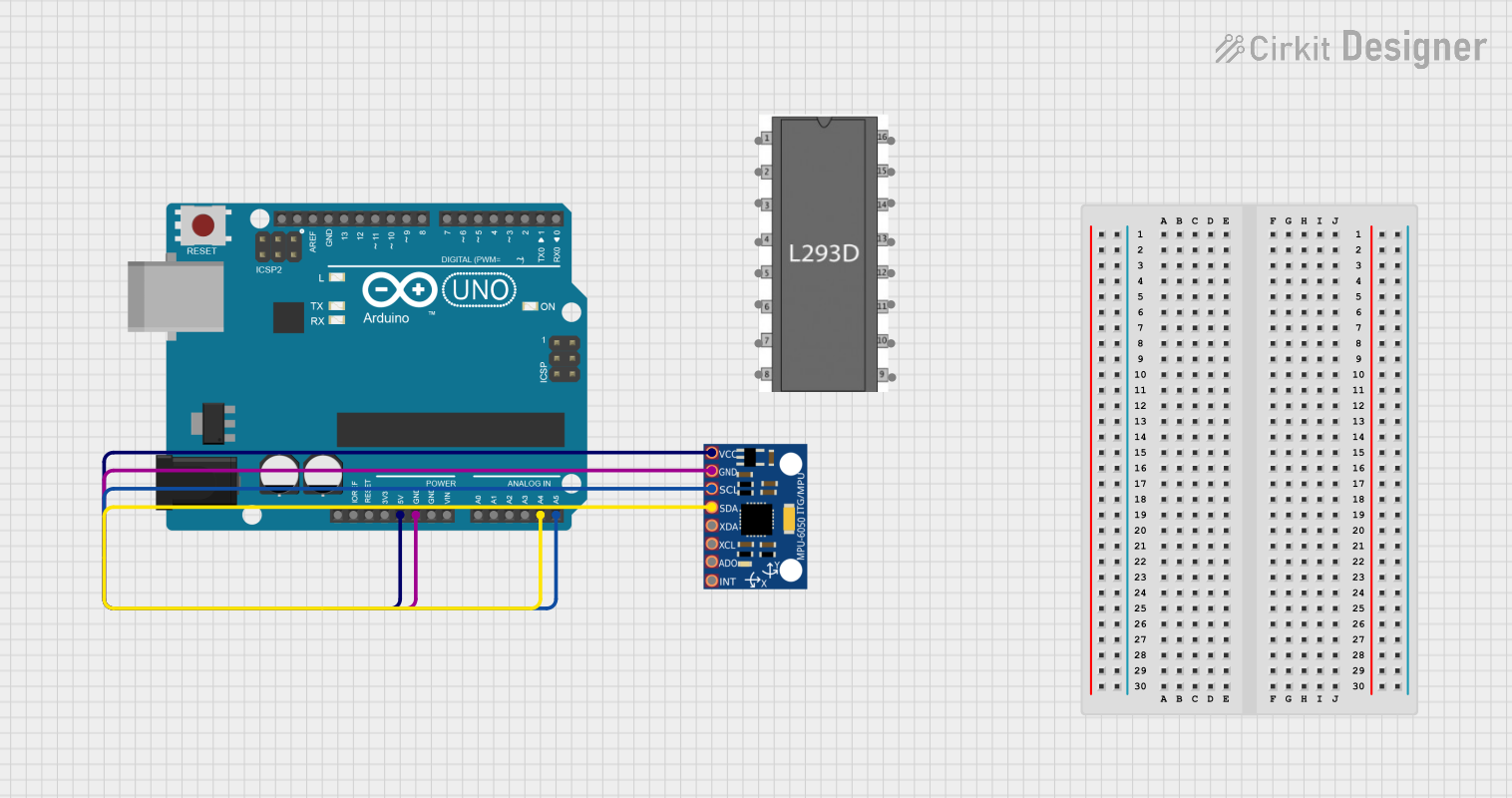
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer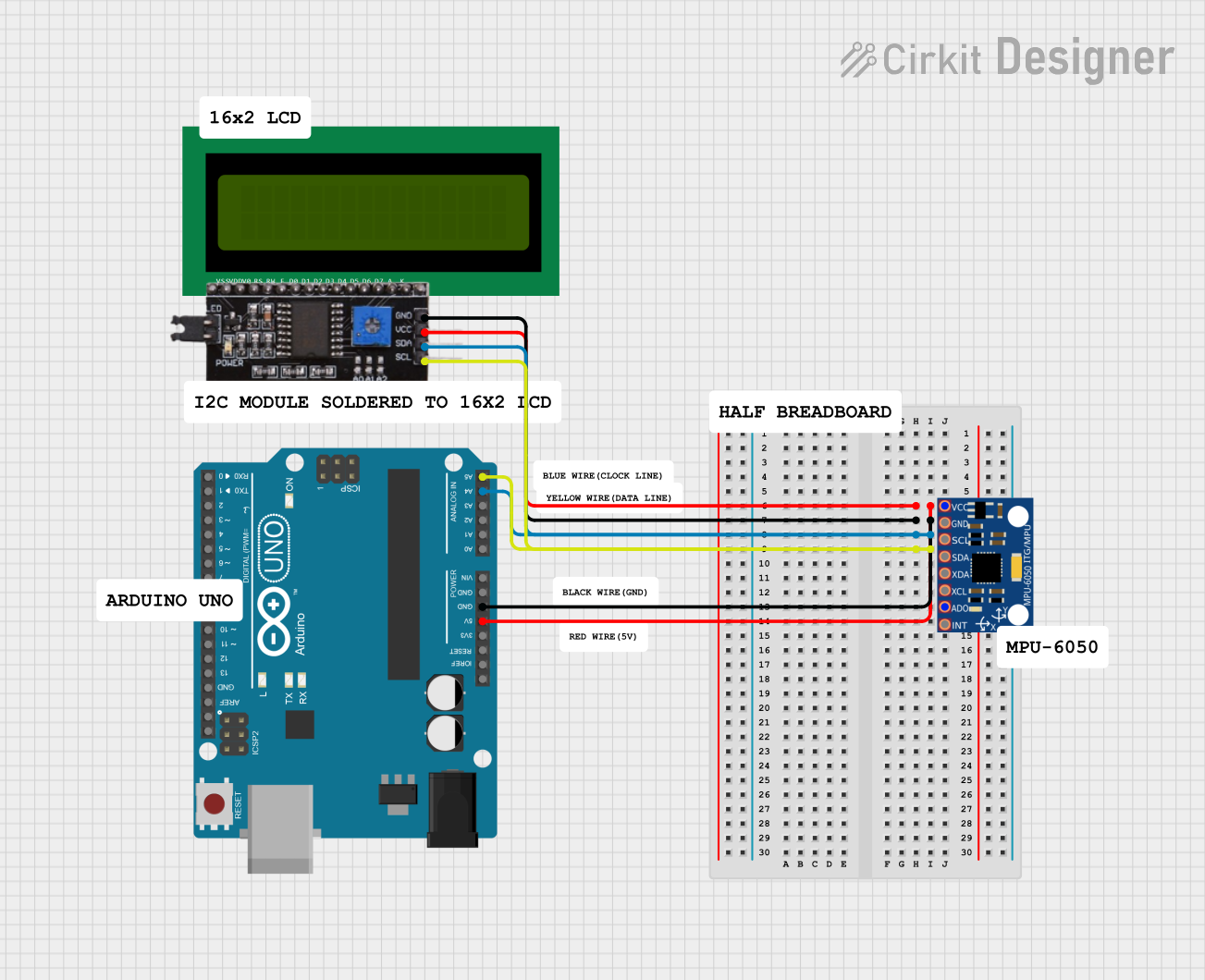
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer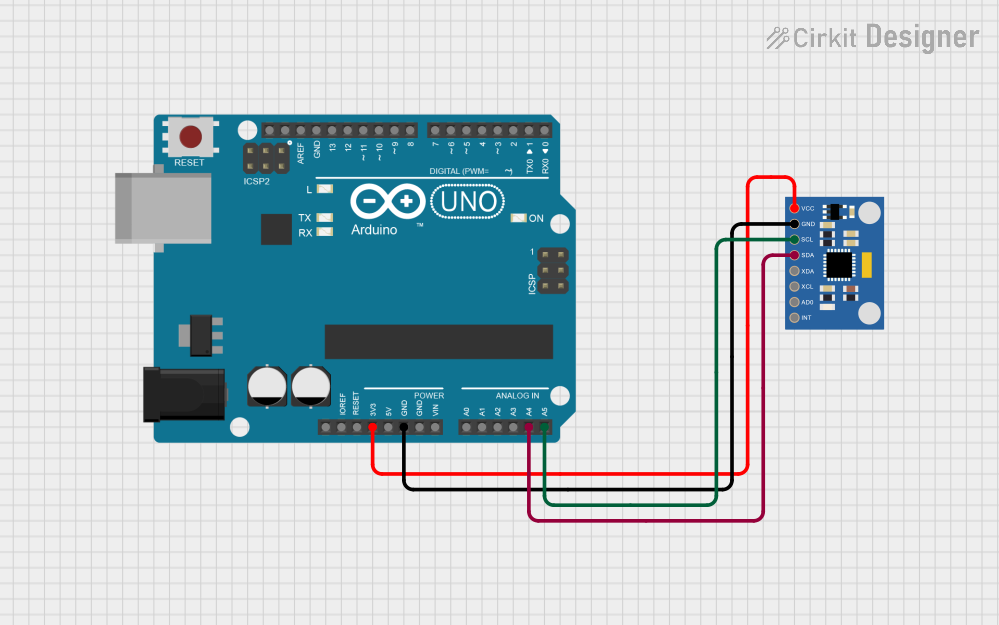
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with MPU6050

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Supply Voltage: 2.375V to 3.46V (3.3V typical)
- Logic Voltage: 3.3V (compatible with 5V logic via pull-up resistors)
- Gyroscope Range: ±250, ±500, ±1000, ±2000 degrees/second
- Accelerometer Range: ±2g, ±4g, ±8g, ±16g
- Communication Interface: I2C (up to 400kHz)
- Operating Temperature: -40°C to +85°C
- Package: 24-pin QFN
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The MPU6050 has 8 primary pins for operation. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Name | Pin Number | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 1 | Power supply input (2.375V to 3.46V). Typically connected to 3.3V. |
| GND | 2 | Ground connection. |
| SCL | 3 | I2C clock line. Connect to the microcontroller's SCL pin. |
| SDA | 4 | I2C data line. Connect to the microcontroller's SDA pin. |
| AD0 | 5 | I2C address select. Connect to GND (address 0x68) or VCC (address 0x69). |
| INT | 6 | Interrupt output. Can be used to signal data availability or motion detection. |
| FSYNC | 7 | Frame synchronization input. Typically left unconnected in most applications. |
| RESV | 8 | Reserved. Do not connect. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the MPU6050 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- I2C Communication: Connect the SCL and SDA pins to the corresponding I2C pins on your microcontroller. Use pull-up resistors (typically 4.7kΩ) on the SCL and SDA lines if not already present.
- Address Selection: Connect the AD0 pin to GND for the default I2C address (0x68) or to VCC for the alternate address (0x69).
- Interrupts (Optional): If using the interrupt feature, connect the INT pin to a digital input pin on your microcontroller.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1µF) near the VCC pin to stabilize the power supply.
- Ensure proper pull-up resistors are used on the I2C lines if not already included in your setup.
- Avoid excessive noise on the I2C lines to ensure reliable communication.
- Mount the MPU6050 on a stable platform to minimize vibrations and improve measurement accuracy.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to interface the MPU6050 with an Arduino UNO using the Wire library:
#include <Wire.h>
// MPU6050 I2C address (default is 0x68 when AD0 is connected to GND)
const int MPU6050_ADDR = 0x68;
// MPU6050 register addresses
const int PWR_MGMT_1 = 0x6B; // Power management register
const int ACCEL_XOUT_H = 0x3B; // Accelerometer X-axis high byte
void setup() {
Wire.begin(); // Initialize I2C communication
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication for debugging
// Wake up the MPU6050 (it starts in sleep mode)
Wire.beginTransmission(MPU6050_ADDR);
Wire.write(PWR_MGMT_1); // Access power management register
Wire.write(0); // Set to 0 to wake up the sensor
Wire.endTransmission();
Serial.println("MPU6050 initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Request accelerometer data
Wire.beginTransmission(MPU6050_ADDR);
Wire.write(ACCEL_XOUT_H); // Start reading from ACCEL_XOUT_H register
Wire.endTransmission(false);
Wire.requestFrom(MPU6050_ADDR, 6); // Request 6 bytes (X, Y, Z high and low)
if (Wire.available() == 6) {
int16_t accelX = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read(); // Combine high and low bytes
int16_t accelY = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read();
int16_t accelZ = (Wire.read() << 8) | Wire.read();
// Print accelerometer values
Serial.print("Accel X: "); Serial.print(accelX);
Serial.print(" | Accel Y: "); Serial.print(accelY);
Serial.print(" | Accel Z: "); Serial.println(accelZ);
}
delay(500); // Delay for readability
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Data from the Sensor:
- Ensure the MPU6050 is powered correctly (3.3V on VCC and GND connected).
- Verify the I2C connections (SCL and SDA) and check for proper pull-up resistors.
- Confirm the I2C address (default is 0x68 unless AD0 is connected to VCC).
Inconsistent or Noisy Readings:
- Minimize vibrations and external noise sources near the sensor.
- Use proper decoupling capacitors to stabilize the power supply.
- Calibrate the sensor to account for offsets and biases.
I2C Communication Errors:
- Check the I2C clock speed (should not exceed 400kHz).
- Ensure the I2C lines are not too long or improperly terminated.
FAQs
Can the MPU6050 work with 5V logic?
- Yes, the MPU6050 can interface with 5V logic if proper pull-up resistors are used on the I2C lines.
How do I calibrate the MPU6050?
- Calibration involves reading raw data from the sensor and calculating offsets for each axis. These offsets can then be subtracted from subsequent readings to improve accuracy.
What is the maximum sampling rate of the MPU6050?
- The MPU6050 supports a maximum sampling rate of 1kHz for both the accelerometer and gyroscope.
This concludes the documentation for the MPU6050.