
How to Use 2N3904 NPN BJT Transistor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 2N3904 NPN BJT Transistor in Cirkit Designer
Design with 2N3904 NPN BJT Transistor in Cirkit Designer2N3904 NPN Bipolar Junction Transistor Documentation
1. Introduction
The 2N3904 is a widely used general-purpose NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) designed for low-power amplification and switching applications. Known for its affordability, reliability, and versatility, the 2N3904 is a staple in many electronic projects, from hobbyist circuits to professional designs. It is particularly well-suited for applications requiring small signal amplification or low-current switching.
Common Applications:
- Signal amplification in audio and RF circuits
- Low-power switching in digital and analog circuits
- Driving small loads such as LEDs or relays
- Oscillator and timer circuits
- General-purpose use in prototyping and educational projects
The 2N3904 is often used in conjunction with microcontrollers like the Arduino UNO, making it a popular choice for beginners and experienced engineers alike.
2. Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the 2N3904 transistor:
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Transistor Type | NPN | Current flows from collector to emitter when base is biased. |
| Maximum Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCEO) | 40V | Maximum voltage between collector and emitter. |
| Maximum Collector-Base Voltage (VCBO) | 60V | Maximum voltage between collector and base. |
| Maximum Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO) | 6V | Maximum voltage between emitter and base. |
| Maximum Collector Current (IC) | 200mA | Maximum current through the collector. |
| Power Dissipation (PD) | 625mW | Maximum power the transistor can dissipate. |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 30–300 | Amplification factor (varies with current). |
| Transition Frequency (fT) | 300MHz | Maximum frequency for small signal amplification. |
| Package Type | TO-92 | Standard through-hole package. |
Pin Configuration
The 2N3904 is housed in a TO-92 package with three pins. The pinout is as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter (E) | Current flows out of the transistor. |
| 2 | Base (B) | Controls the transistor's operation. |
| 3 | Collector (C) | Current flows into the transistor. |
Below is a diagram of the TO-92 package for reference:
_______
| |
| 2N |
| 3904 |
|_______|
| | |
E B C
(Front View)
3. Usage Instructions
Using the 2N3904 in a Circuit
The 2N3904 can be used in two primary modes: switching and amplification.
1. Switching Mode
In switching mode, the transistor acts as an electronic switch. When a small current is applied to the base, it allows a larger current to flow from the collector to the emitter.
Example Circuit: Controlling an LED with an Arduino UNO
- Connect the emitter to ground.
- Connect the collector to one terminal of the LED (with a current-limiting resistor in series).
- Connect the other terminal of the LED to the positive voltage supply.
- Use a resistor (typically 1kΩ) between the Arduino's digital pin and the base of the transistor.
Arduino Code Example:
// Define the pin connected to the transistor's base
const int transistorBasePin = 9;
void setup() {
pinMode(transistorBasePin, OUTPUT); // Set the pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(transistorBasePin, HIGH); // Turn on the transistor (LED ON)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(transistorBasePin, LOW); // Turn off the transistor (LED OFF)
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
2. Amplification Mode
In amplification mode, the transistor amplifies a small input signal at the base into a larger output signal at the collector. This is commonly used in audio or RF circuits.
Example Circuit: Audio Amplifier
- Connect the emitter to ground through a resistor.
- Connect the base to the input signal through a coupling capacitor and a biasing resistor.
- Connect the collector to the positive voltage supply through a load resistor.
Important Considerations
- Base Resistor: Always use a resistor between the base and the control signal to limit the base current and prevent damage to the transistor.
- Power Dissipation: Ensure the transistor does not exceed its maximum power dissipation (625mW). Use a heatsink if necessary.
- Voltage Ratings: Do not exceed the maximum voltage ratings (e.g., 40V for VCEO).
- Current Ratings: Ensure the collector current does not exceed 200mA.
4. Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Transistor does not turn on | Insufficient base current | Use a smaller base resistor to increase current. |
| Transistor overheats | Exceeding power dissipation limit | Reduce load current or use a heatsink. |
| Output signal is distorted | Incorrect biasing in amplification mode | Adjust biasing resistors for proper operation. |
| LED does not light up in switching mode | Incorrect wiring or damaged transistor | Double-check connections and replace the transistor if necessary. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Can I use the 2N3904 to drive a motor?
A1: The 2N3904 can drive small motors with currents below 200mA. For larger motors, use a power transistor or MOSFET.
Q2: What is the purpose of the base resistor?
A2: The base resistor limits the current flowing into the base to prevent damage to the transistor and the control circuit.
Q3: Can the 2N3904 be used in high-frequency circuits?
A3: Yes, the 2N3904 has a transition frequency (fT) of 300MHz, making it suitable for high-frequency applications.
Q4: How do I test if my 2N3904 is working?
A4: Use a multimeter in diode mode to check the base-emitter and base-collector junctions. Both should show a forward voltage drop (~0.6–0.7V) when forward-biased.
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, using, and troubleshooting the 2N3904 NPN BJT transistor. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced engineer, the 2N3904 is a versatile and reliable component for your electronic projects.
Explore Projects Built with 2N3904 NPN BJT Transistor
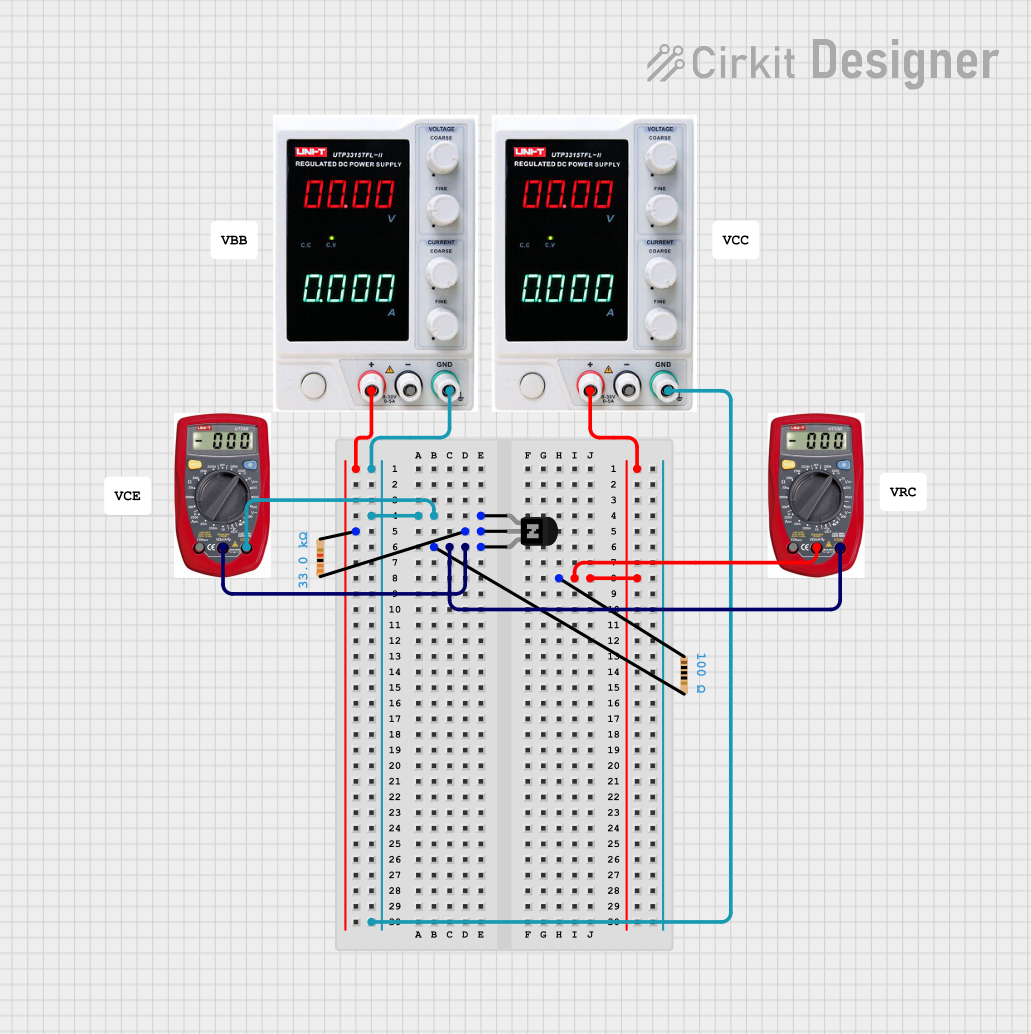
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer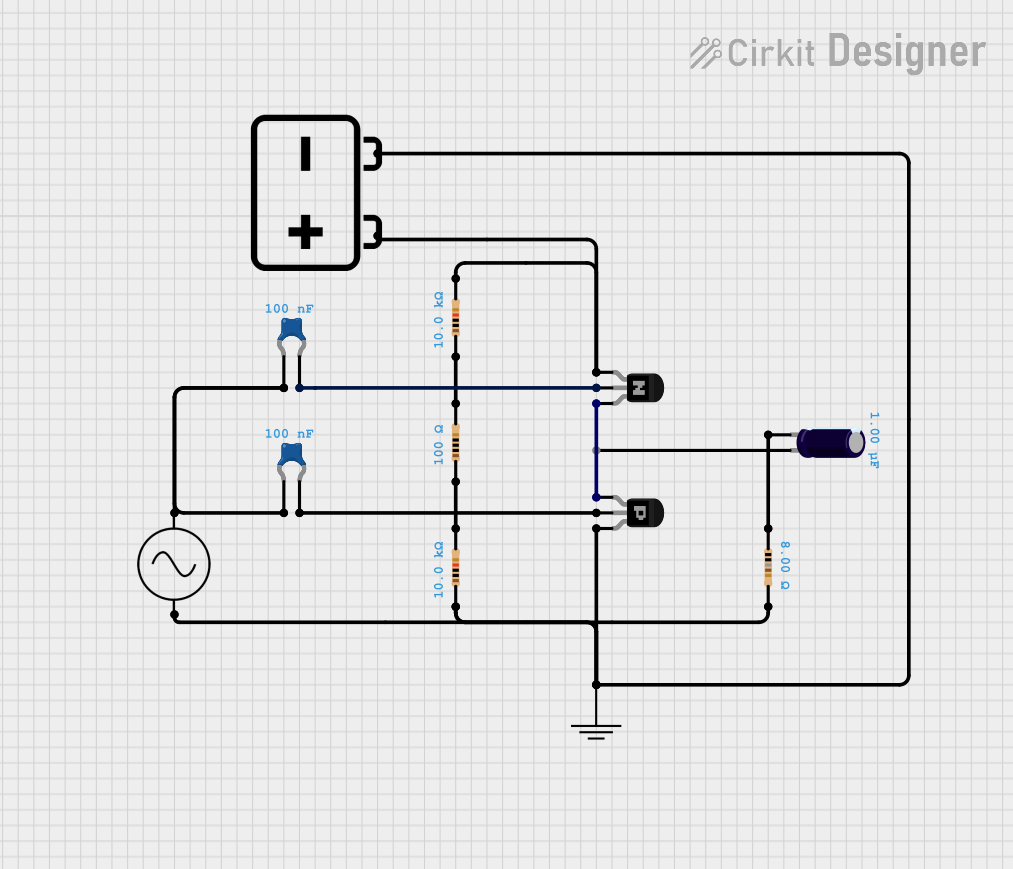
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer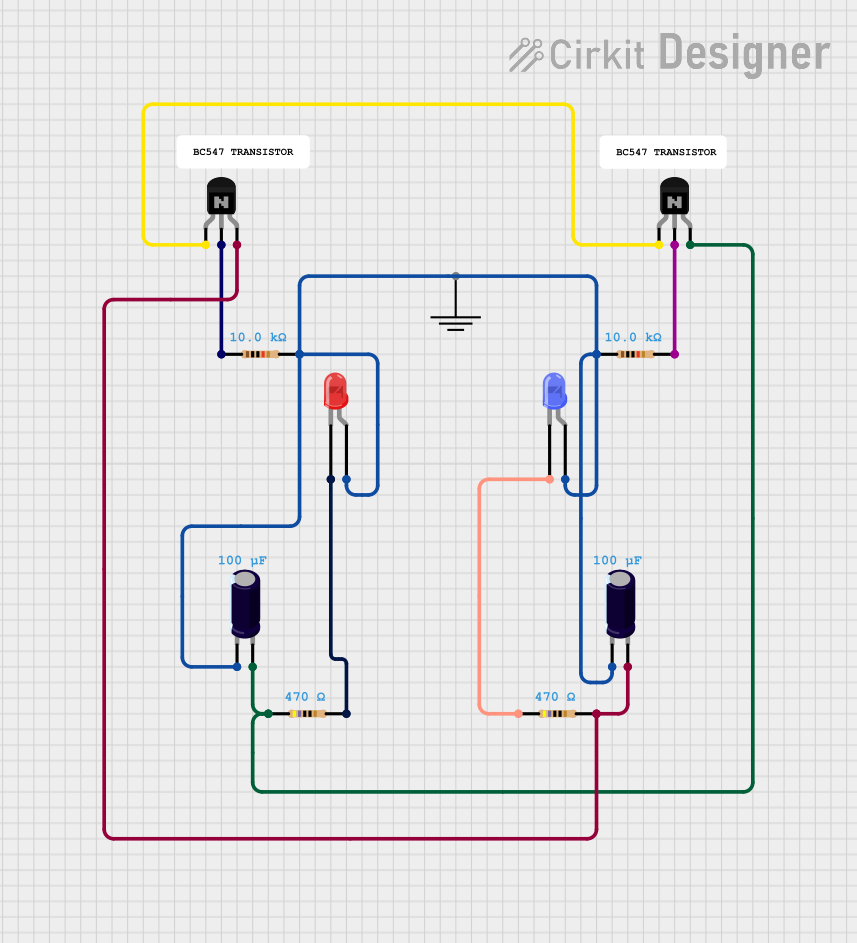
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer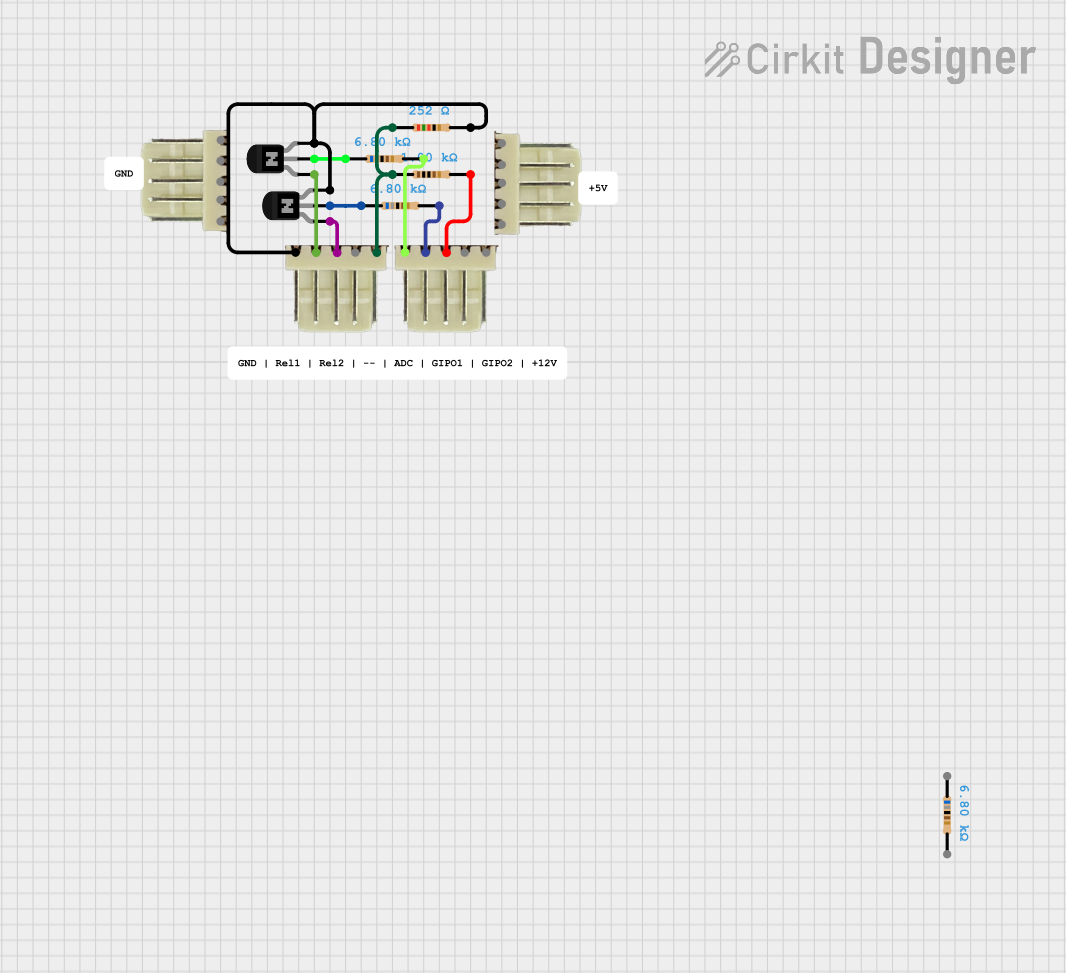
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 2N3904 NPN BJT Transistor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer