
How to Use BZ-215 GPS: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
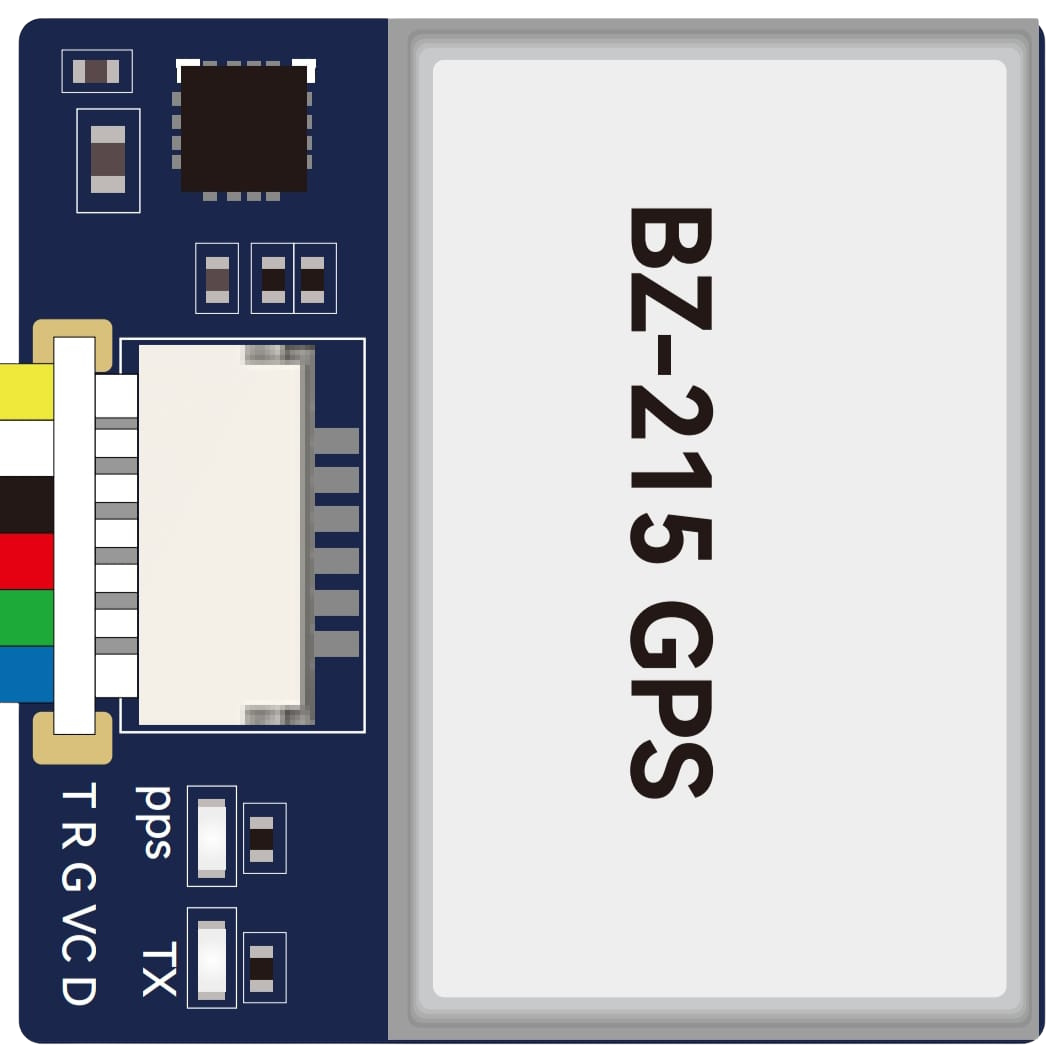
 Design with BZ-215 GPS in Cirkit Designer
Design with BZ-215 GPS in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The BZ-215 GPS is a compact and highly efficient global positioning system (GPS) module designed to provide accurate location data for a wide range of applications. With its high sensitivity and low power consumption, the BZ-215 GPS is ideal for navigation, tracking, and geolocation projects. It supports multiple communication protocols, making it easy to integrate into various electronic systems, including microcontroller-based platforms like Arduino.
Explore Projects Built with BZ-215 GPS
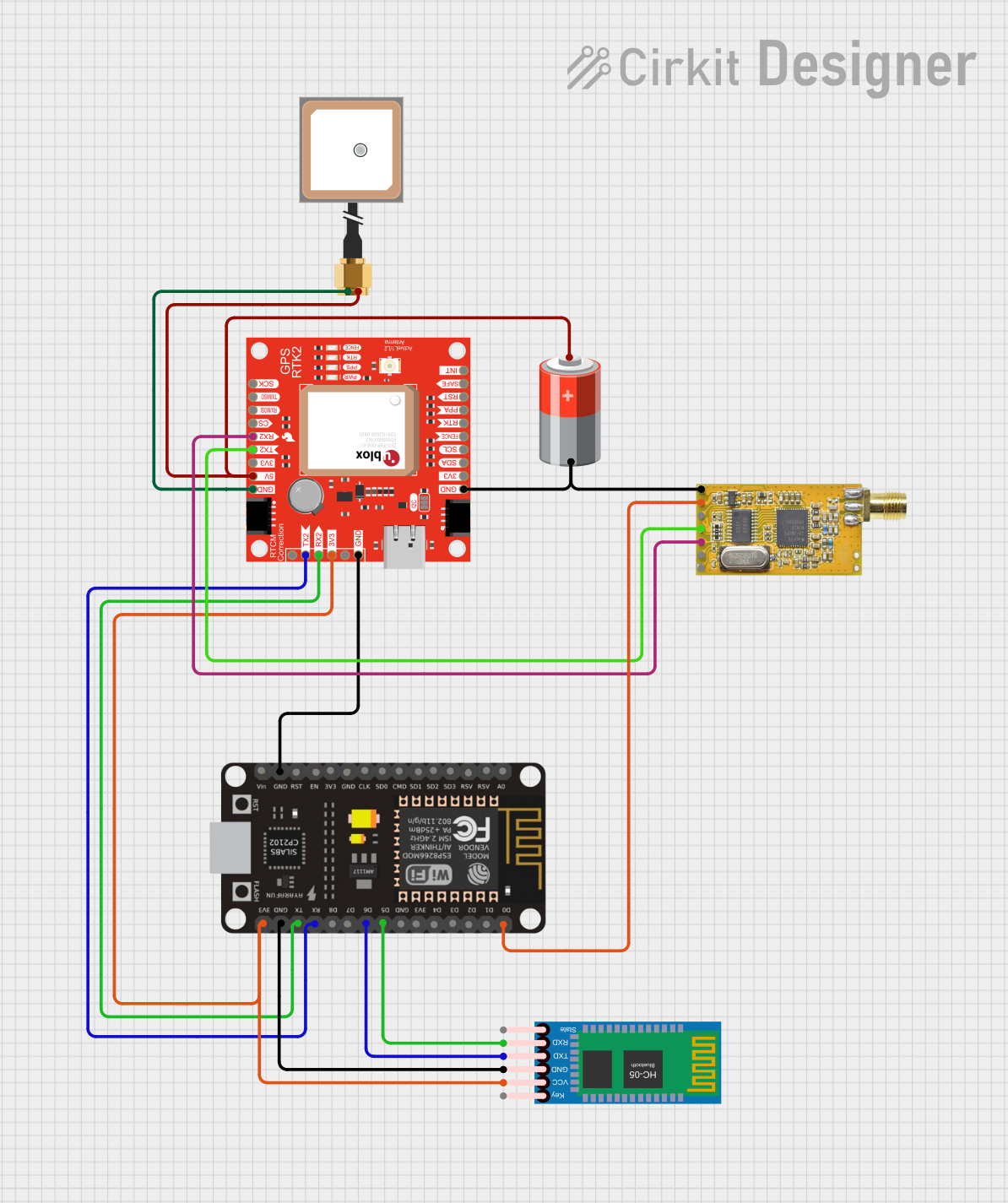
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer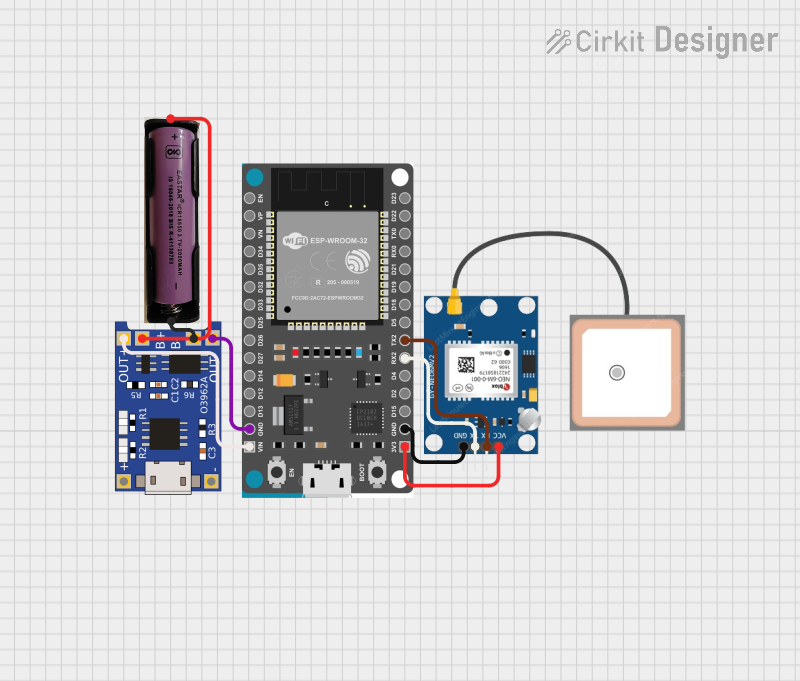
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer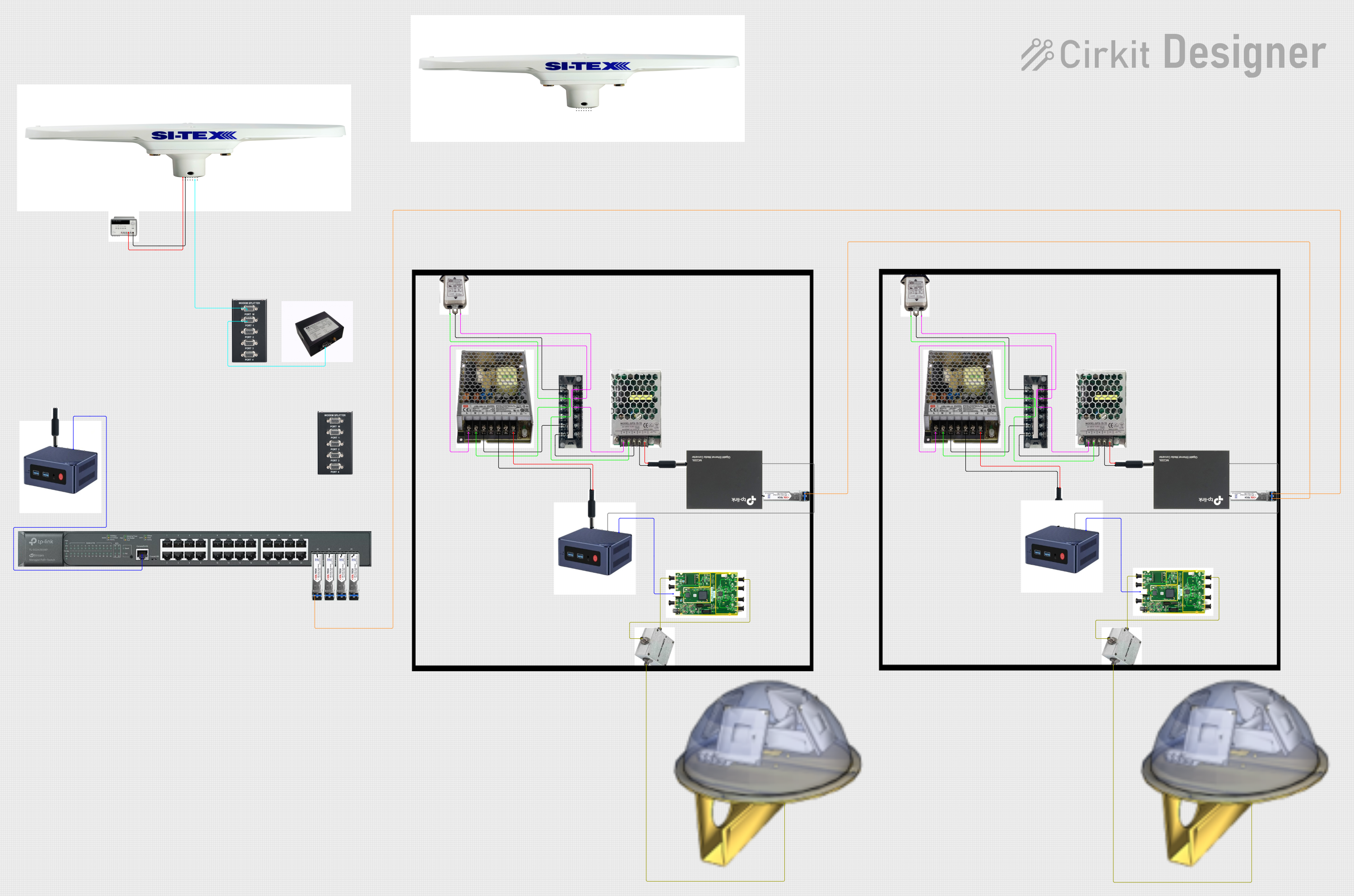
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer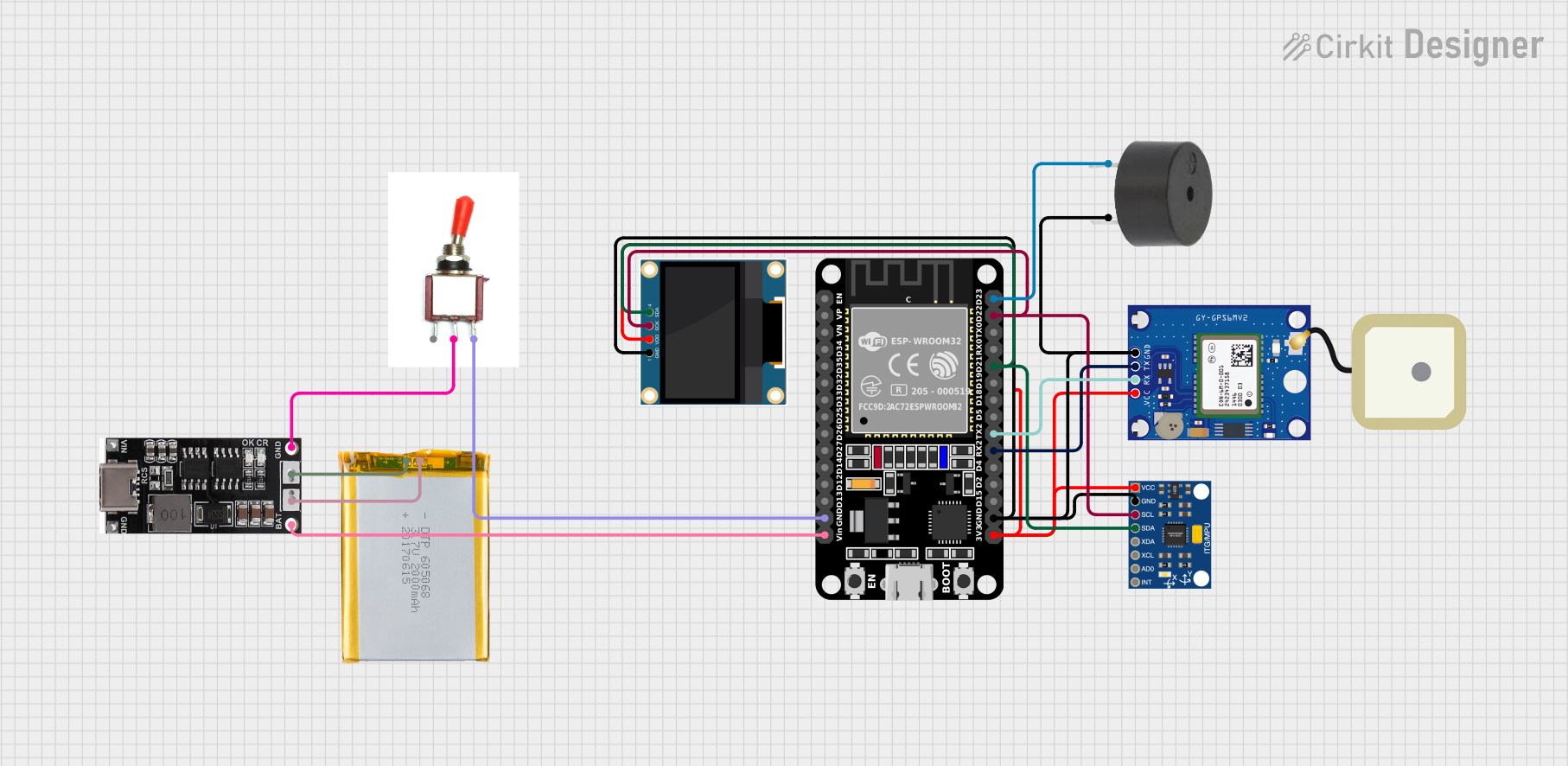
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with BZ-215 GPS

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Vehicle tracking and fleet management
- Personal navigation devices
- Drones and UAVs
- IoT devices requiring geolocation
- Outdoor sports and fitness trackers
Technical Specifications
The BZ-215 GPS module is designed to deliver reliable performance in a compact form factor. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5.0V |
| Current Consumption | 25mA (typical) |
| Positioning Accuracy | ±2.5 meters |
| Communication Protocols | UART, I2C, SPI |
| Baud Rate (Default) | 9600 bps |
| Sensitivity | -165 dBm |
| Update Rate | 1 Hz to 10 Hz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 25mm x 25mm x 5mm |
Pin Configuration
The BZ-215 GPS module has a simple pinout for easy integration. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V to 5.0V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | TX | UART Transmit (data output) |
| 4 | RX | UART Receive (data input) |
| 5 | PPS | Pulse Per Second output for timing synchronization |
| 6 | SDA | I2C Data line |
| 7 | SCL | I2C Clock line |
| 8 | SPI_CS | SPI Chip Select |
| 9 | SPI_MOSI | SPI Master Out Slave In |
| 10 | SPI_MISO | SPI Master In Slave Out |
| 11 | SPI_CLK | SPI Clock |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the BZ-215 GPS in a Circuit
- Power the Module: Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V or 5.0V power source and the GND pin to ground.
- Choose Communication Protocol: Select the desired communication protocol (UART, I2C, or SPI) based on your project requirements.
- For UART, connect the TX and RX pins to the corresponding UART pins on your microcontroller.
- For I2C, connect the SDA and SCL pins to the I2C bus.
- For SPI, connect SPI_CS, SPI_MOSI, SPI_MISO, and SPI_CLK to the SPI interface.
- Configure the Module: Use the default baud rate of 9600 bps for UART communication or configure the module as needed using AT commands.
- Read GPS Data: Parse the NMEA sentences (e.g., GPGGA, GPRMC) output by the module to extract location, time, and other data.
Important Considerations
- Ensure the module has a clear view of the sky for optimal satellite reception.
- Use decoupling capacitors near the VCC pin to reduce noise and ensure stable operation.
- Avoid placing the module near high-frequency noise sources, such as switching power supplies or motors.
- If using the PPS pin for timing, ensure your microcontroller can handle the pulse signal.
Example: Connecting to an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to connect the BZ-215 GPS module to an Arduino UNO using UART:
Wiring
| BZ-215 Pin | Arduino Pin |
|---|---|
| VCC | 5V |
| GND | GND |
| TX | Pin 10 (RX) |
| RX | Pin 11 (TX) |
Code Example
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial gpsSerial(10, 11); // RX = Pin 10, TX = Pin 11
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start Serial Monitor at 9600 bps
gpsSerial.begin(9600); // Start GPS module communication at 9600 bps
Serial.println("BZ-215 GPS Module Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Check if data is available from the GPS module
while (gpsSerial.available()) {
char c = gpsSerial.read(); // Read one character from GPS
Serial.print(c); // Print the character to the Serial Monitor
// Note: GPS data is output as NMEA sentences. You can parse these
// sentences to extract specific information like latitude, longitude,
// and time.
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No GPS Data Output
- Cause: The module may not have a clear view of the sky.
- Solution: Move the module to an open area with minimal obstructions.
Incorrect or Inconsistent Location Data
- Cause: Poor satellite signal or interference.
- Solution: Ensure the module is away from sources of RF interference and has a stable power supply.
Module Not Responding
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or baud rate mismatch.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the baud rate matches the module's configuration.
PPS Signal Not Detected
- Cause: PPS pin not connected or microcontroller not configured to read the signal.
- Solution: Verify the PPS pin connection and ensure your microcontroller is set up to handle the pulse.
FAQs
Q: Can the BZ-215 GPS module work indoors?
A: While the module may work indoors near windows, its performance is significantly better outdoors with a clear view of the sky.
Q: How do I change the baud rate of the module?
A: You can use AT commands sent via UART to configure the baud rate. Refer to the module's AT command set for details.
Q: What is the purpose of the PPS pin?
A: The PPS (Pulse Per Second) pin provides a precise timing signal that can be used for synchronization in time-sensitive applications.
Q: Can I use the BZ-215 GPS with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A: Yes, the module supports both 3.3V and 5.0V logic levels, making it compatible with a wide range of microcontrollers.