
How to Use IRFP460 Mosfet: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with IRFP460 Mosfet in Cirkit Designer
Design with IRFP460 Mosfet in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The IRFP460 is a high-power N-channel MOSFET manufactured by International Rectifier. It is designed for high-speed switching applications and features a low on-resistance, high voltage rating, and excellent thermal performance. These characteristics make it ideal for use in power supplies, motor control systems, inverters, and other high-current applications. Its robust design ensures reliable operation in demanding environments.
Explore Projects Built with IRFP460 Mosfet
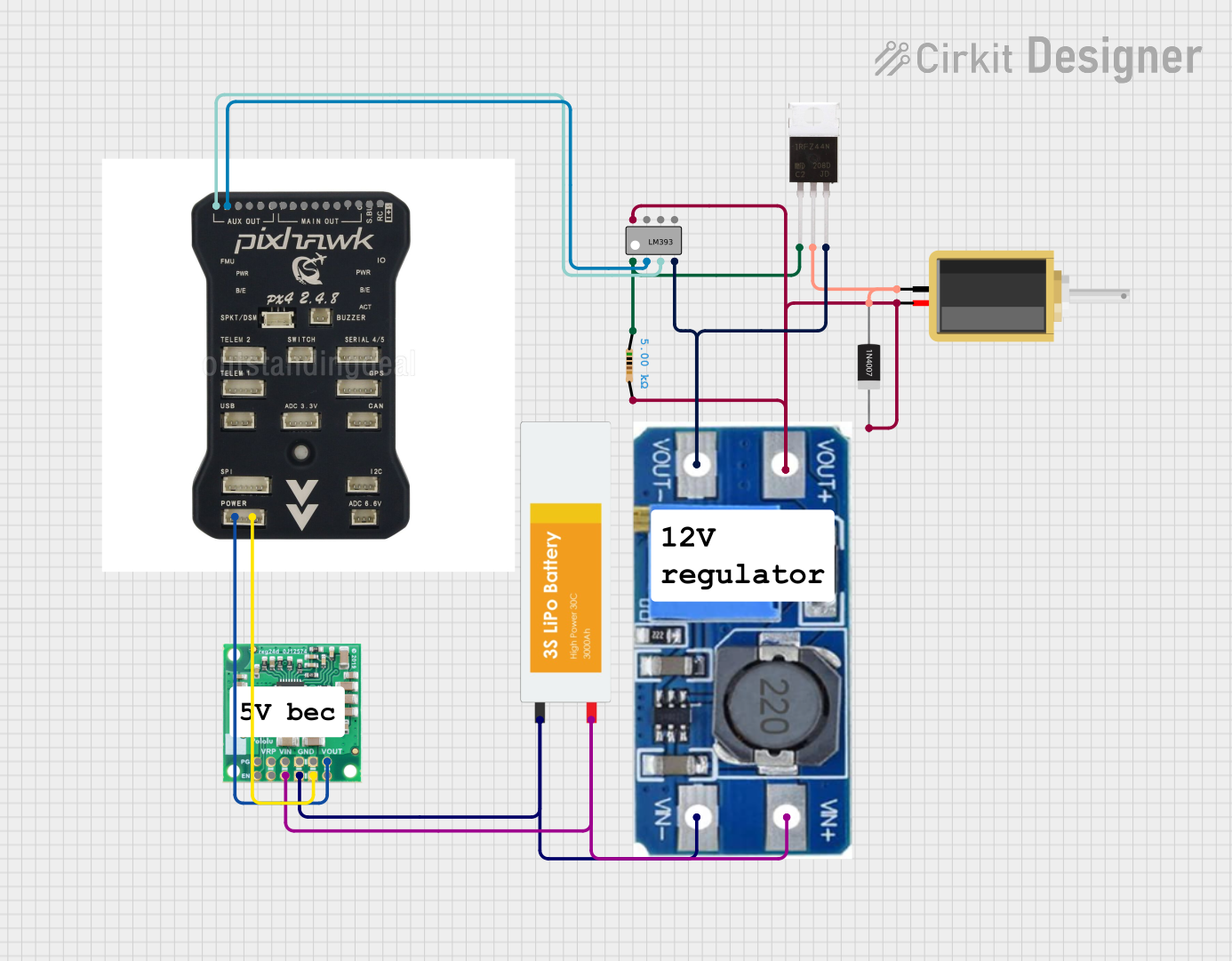
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer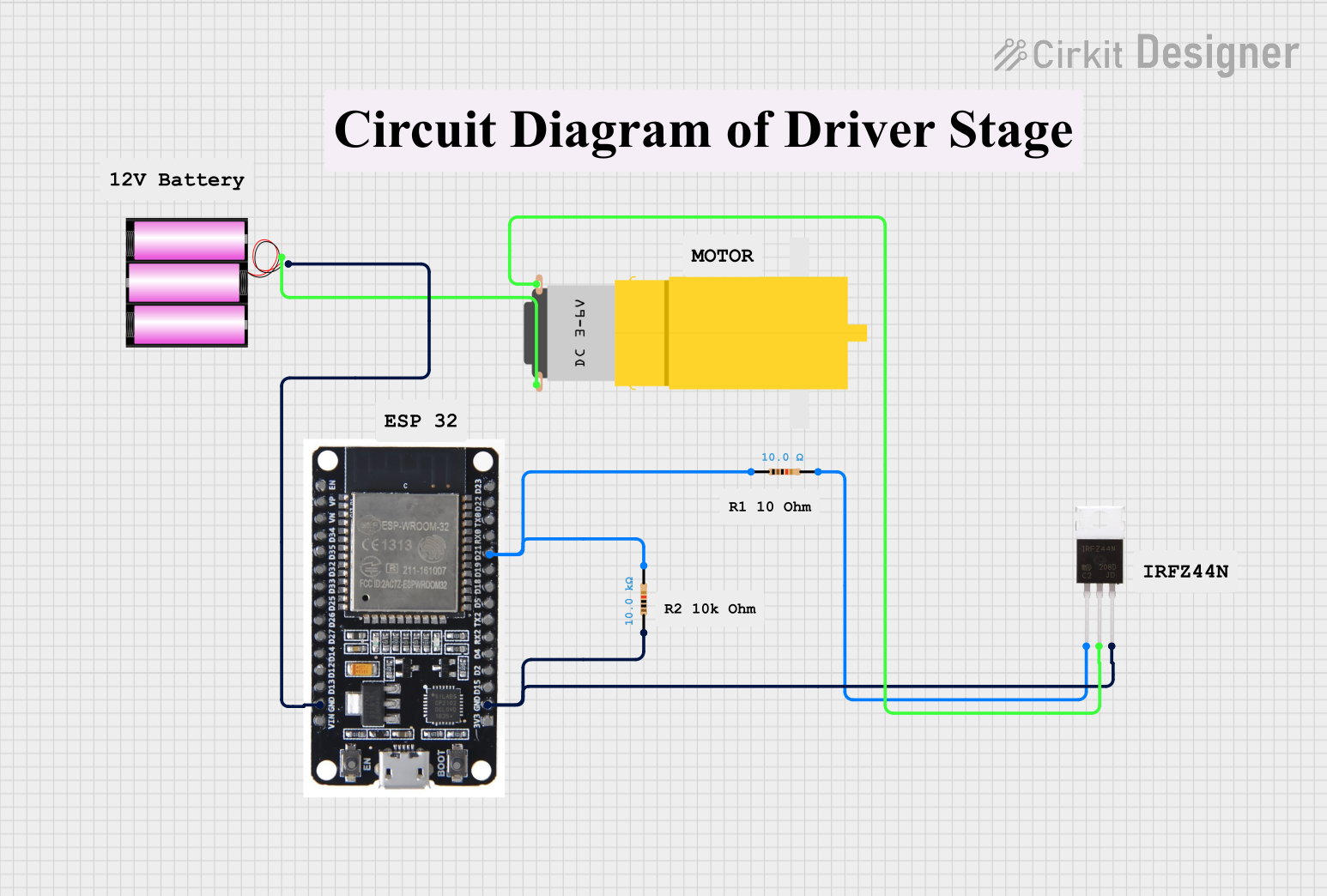
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer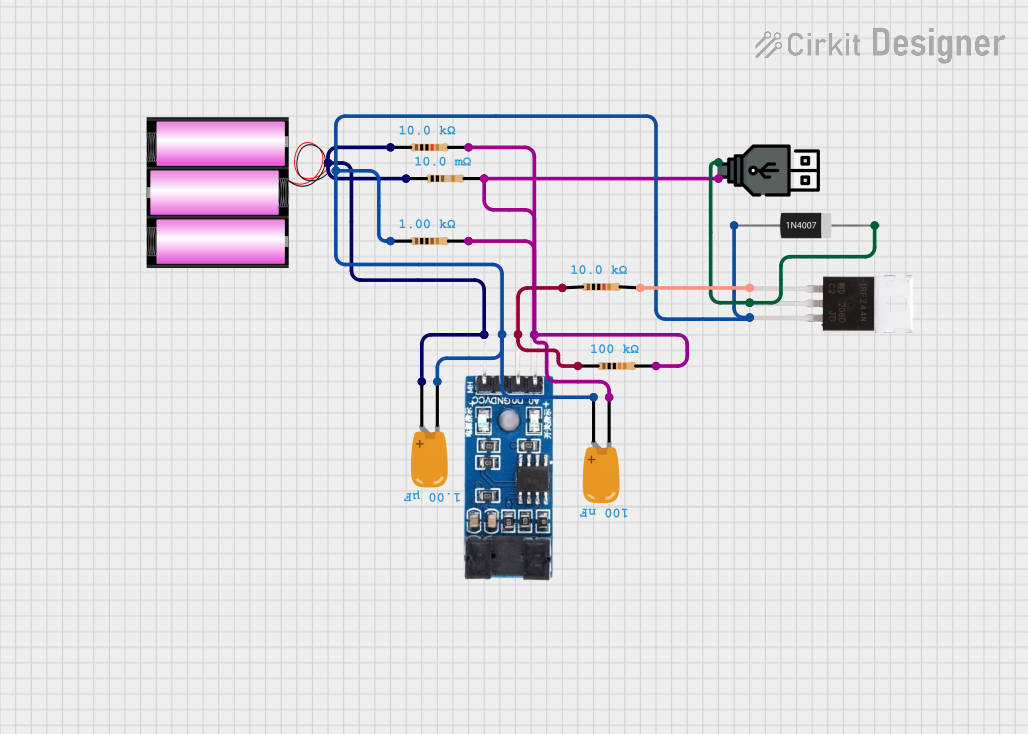
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer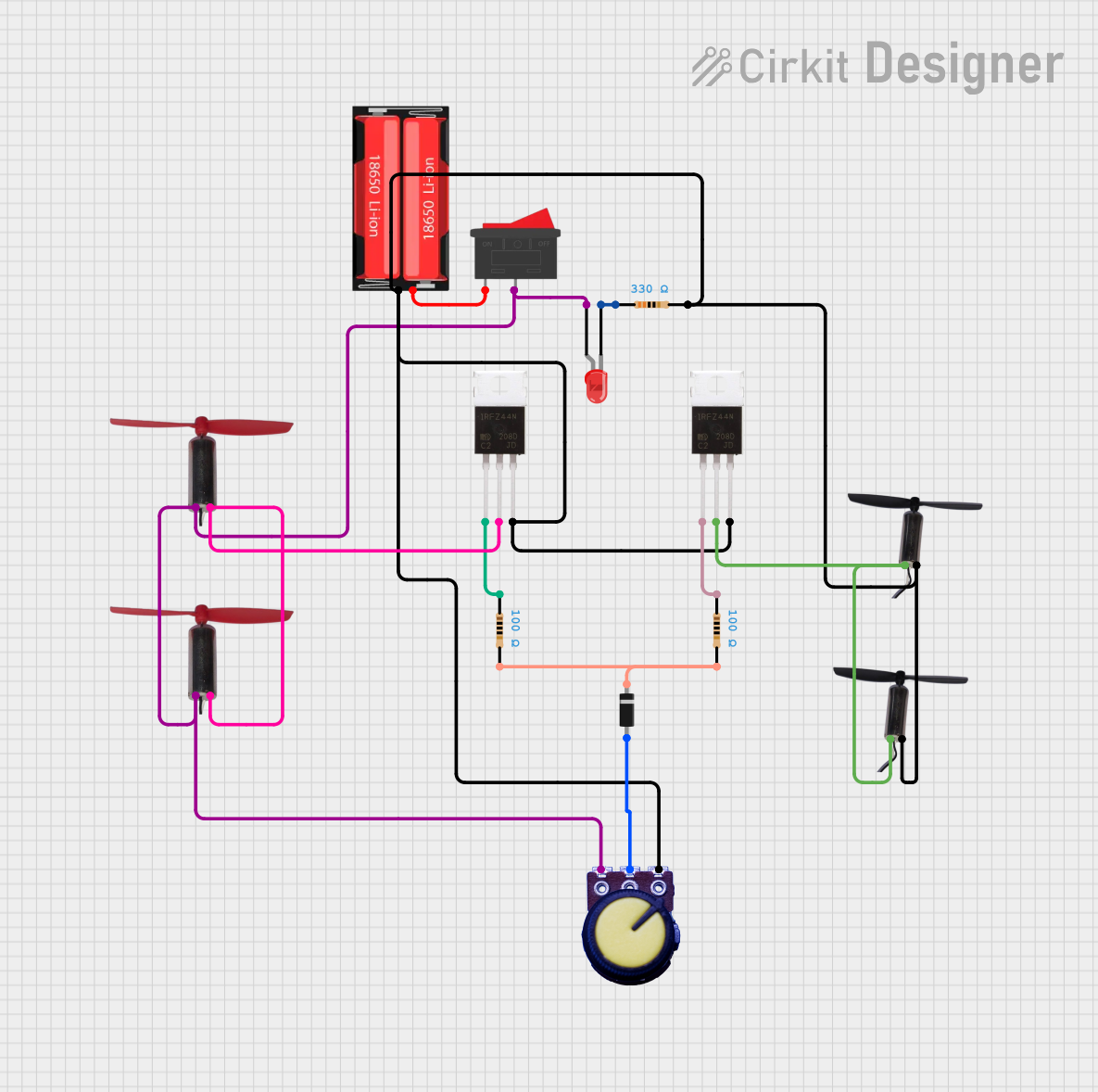
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with IRFP460 Mosfet

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications
- Switch-mode power supplies (SMPS)
- Motor drivers and control circuits
- DC-DC converters
- Inverters for renewable energy systems
- High-frequency switching circuits
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical specifications of the IRFP460 MOSFET:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer Part ID | IRFP460 |
| Type | N-Channel MOSFET |
| Maximum Drain-Source Voltage (VDS) | 500V |
| Continuous Drain Current (ID) | 20A (at 25°C) |
| Pulsed Drain Current (IDM) | 80A |
| Gate-Source Voltage (VGS) | ±20V |
| Maximum Power Dissipation (PD) | 280W (at 25°C) |
| RDS(on) (On-Resistance) | 0.27Ω (typical) |
| Gate Charge (Qg) | 140nC (typical) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -55°C to +175°C |
| Package Type | TO-247 |
Pin Configuration
The IRFP460 is housed in a TO-247 package with three pins. The pin configuration is as follows:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gate (G) | Controls the MOSFET switching state |
| 2 | Drain (D) | Current flows into this terminal |
| 3 | Source (S) | Current flows out of this terminal |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the IRFP460 in a Circuit
- Gate Drive Voltage: Ensure the gate voltage (VGS) is within the range of 10V to 20V for optimal switching performance. A gate resistor (e.g., 10Ω) can be used to limit inrush current to the gate.
- Heat Dissipation: The IRFP460 can dissipate significant power. Use a heatsink or active cooling to maintain the junction temperature below 175°C.
- Load Connection: Connect the load between the drain and the positive supply voltage. The source is typically connected to ground in most configurations.
- Protection: Add a flyback diode across inductive loads to protect the MOSFET from voltage spikes during switching.
Example Circuit with Arduino UNO
The IRFP460 can be used with an Arduino UNO to control high-power loads. Below is an example of how to connect and control the MOSFET:
Circuit Diagram
- Gate: Connect to an Arduino digital pin (e.g., D9) through a 10Ω resistor.
- Drain: Connect to the negative terminal of the load.
- Source: Connect to ground.
- Load: Connect the positive terminal to the power supply.
Arduino Code
// Example code to control an IRFP460 MOSFET with Arduino UNO
// This code toggles the MOSFET on and off every second.
const int mosfetGatePin = 9; // Pin connected to the MOSFET gate
void setup() {
pinMode(mosfetGatePin, OUTPUT); // Set the gate pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(mosfetGatePin, HIGH); // Turn the MOSFET on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(mosfetGatePin, LOW); // Turn the MOSFET off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Best Practices
- Use a gate driver IC for high-speed switching or when driving the MOSFET with a microcontroller.
- Avoid exceeding the maximum ratings for voltage, current, and power dissipation.
- Ensure proper grounding to prevent noise and instability in the circuit.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
MOSFET Overheating
- Cause: Insufficient cooling or excessive current.
- Solution: Use a larger heatsink or active cooling. Ensure the current is within the rated limits.
MOSFET Not Switching
- Cause: Insufficient gate voltage or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Verify the gate voltage is at least 10V. Check the wiring and connections.
High Power Loss
- Cause: High RDS(on) or slow switching.
- Solution: Use a gate driver to improve switching speed. Ensure the gate voltage is optimal.
Voltage Spikes
- Cause: Inductive loads causing back EMF.
- Solution: Add a flyback diode across the load to suppress voltage spikes.
FAQs
Q1: Can the IRFP460 be used for AC applications?
Yes, the IRFP460 can be used in AC applications such as inverters, provided the circuit design accounts for the bidirectional nature of AC current.
Q2: What is the maximum PWM frequency for the IRFP460?
The maximum PWM frequency depends on the gate drive circuit and load conditions. Typically, it can handle frequencies up to 100kHz with proper gate drive circuitry.
Q3: Can I drive the IRFP460 directly from an Arduino?
Yes, but it is recommended to use a gate driver for better performance, especially at high frequencies or with high loads.
Q4: How do I calculate the required heatsink size?
Use the formula:Heatsink Thermal Resistance (°C/W) = (Tj - Ta) / P
Where Tj is the junction temperature, Ta is the ambient temperature, and P is the power dissipation.
By following these guidelines, the IRFP460 can be effectively used in a wide range of high-power applications.