
How to Use Solar charge controller: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Solar charge controller in Cirkit Designer
Design with Solar charge controller in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A solar charge controller is an essential device in solar power systems. It regulates the voltage and current coming from a solar panel to a battery, ensuring optimal charging and preventing overcharging. By managing the energy flow, it protects the battery from damage and extends its lifespan. Solar charge controllers are commonly used in off-grid solar systems, RVs, boats, and remote power setups.
Explore Projects Built with Solar charge controller
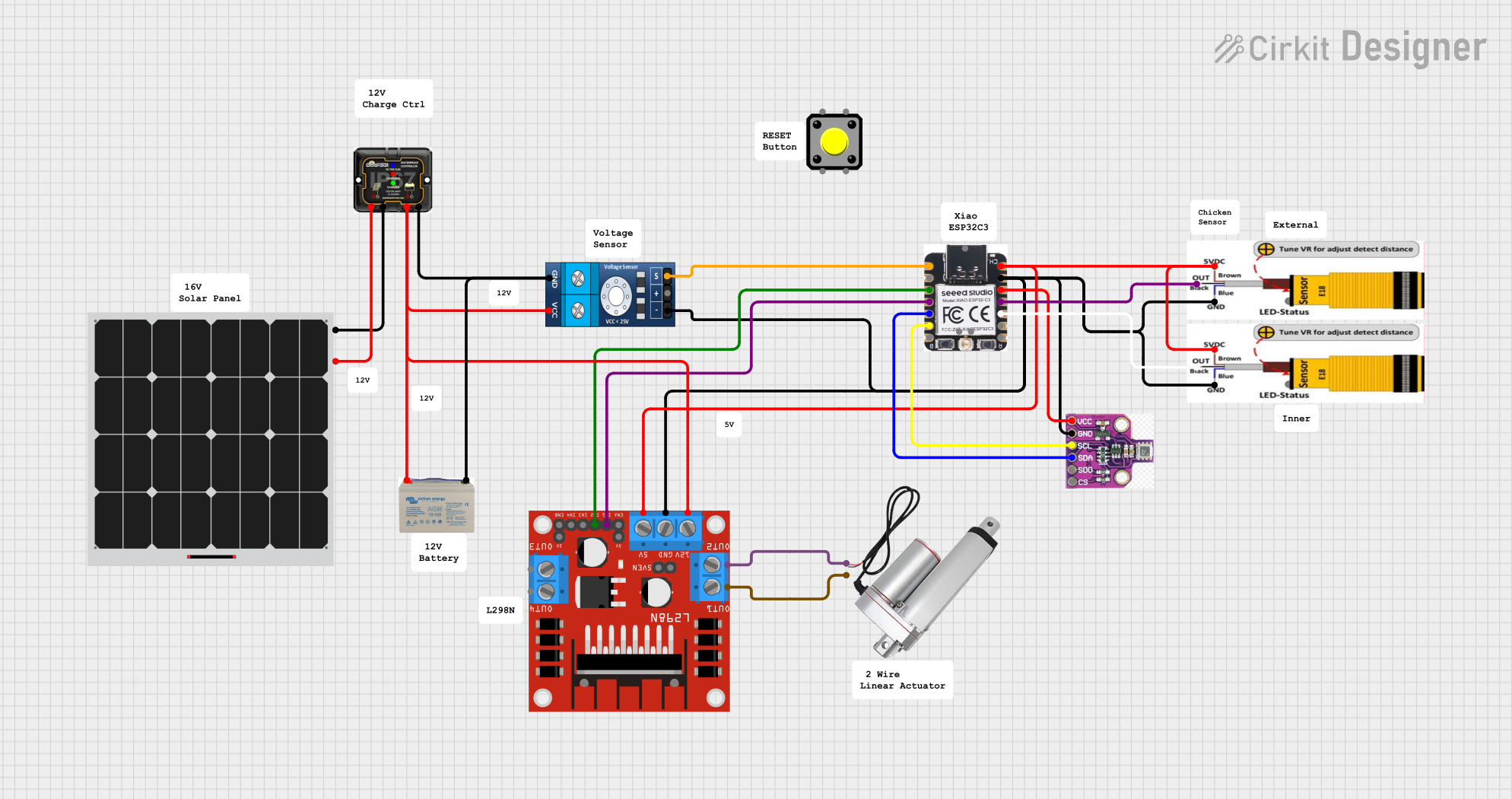
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer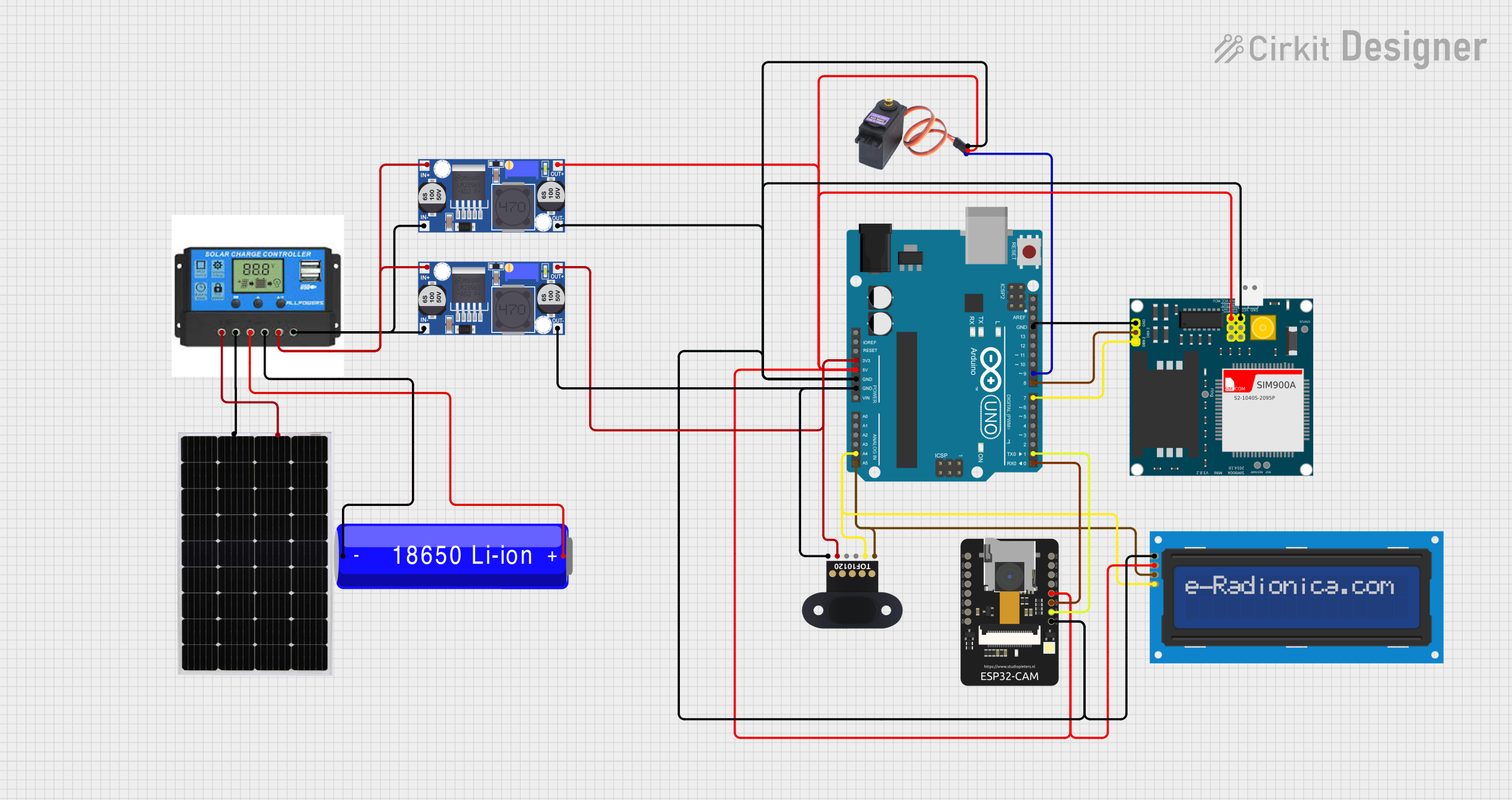
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer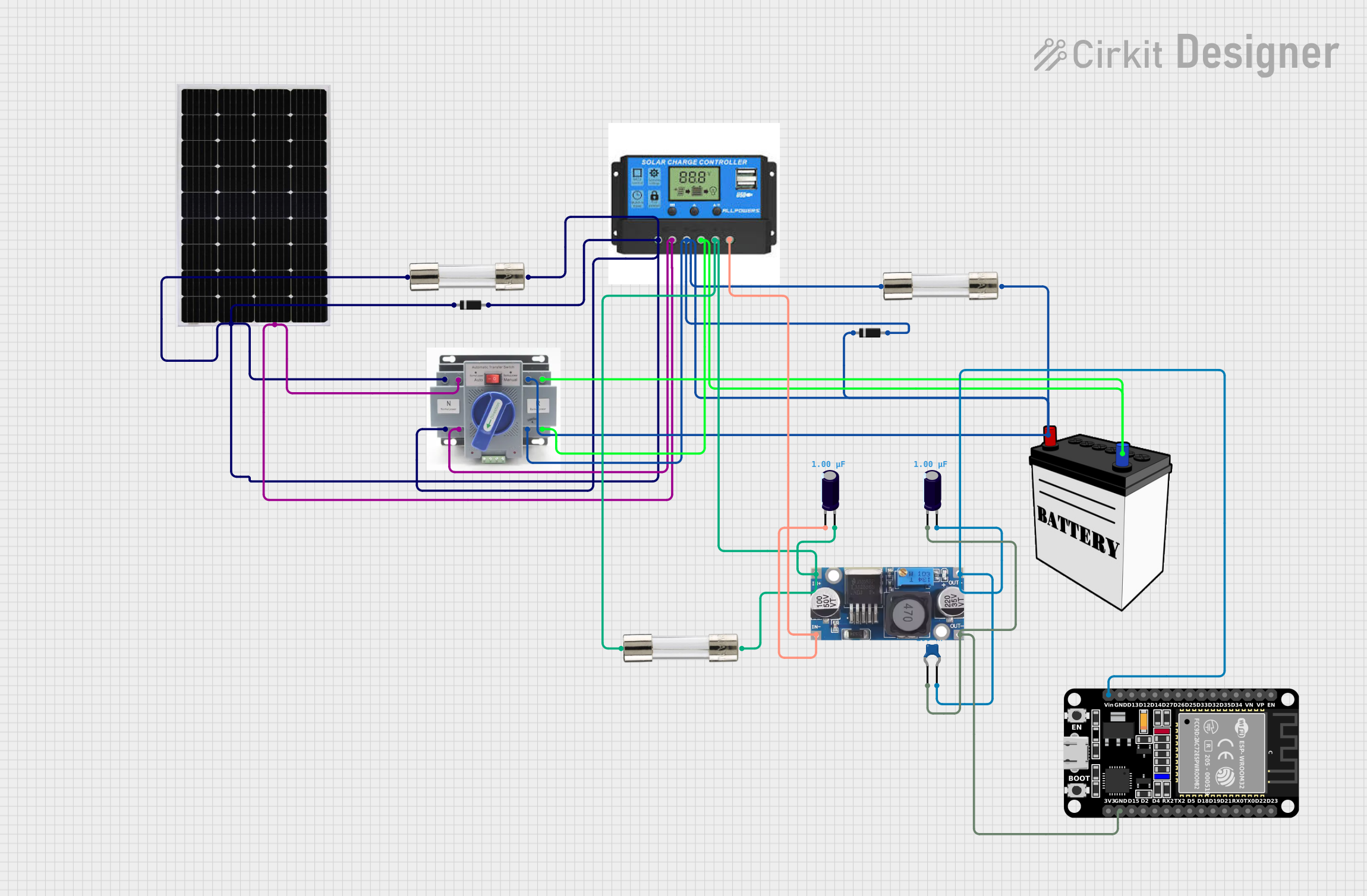
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer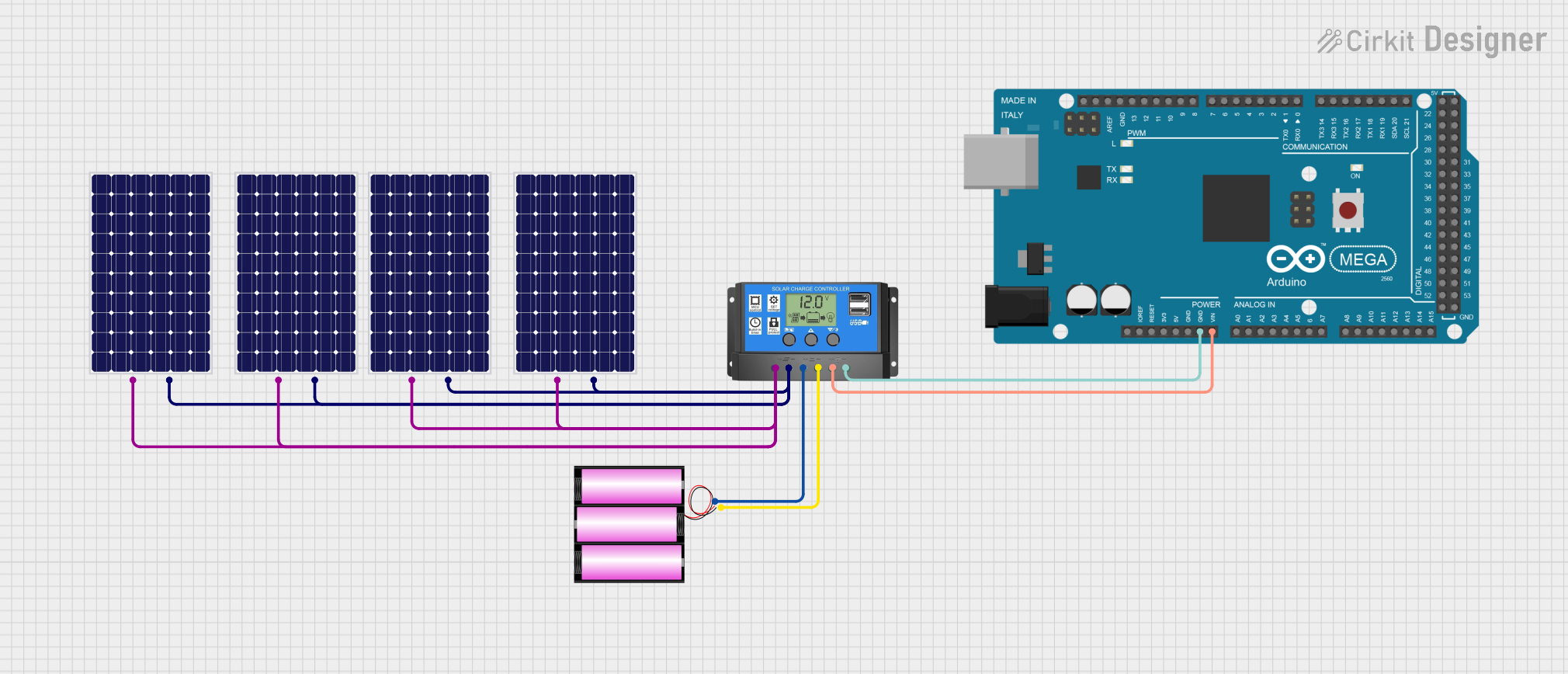
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Solar charge controller

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Off-grid solar power systems
- Solar-powered lighting systems
- RVs, boats, and caravans
- Remote monitoring and communication systems
- Backup power systems
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a typical solar charge controller. Always refer to the specific datasheet for your model.
Key Technical Details
- Input Voltage Range: 12V/24V auto-detect (common models)
- Maximum Input Current: 10A, 20A, 30A, or higher (depending on the model)
- Battery Voltage: 12V/24V
- Charging Modes: PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) or MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking)
- Operating Temperature: -20°C to 60°C
- Efficiency: Up to 98% (for MPPT models)
- Load Control: Overload, short circuit, and reverse polarity protection
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The solar charge controller typically has the following terminals:
| Pin/Terminal | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Solar Panel (+) | Positive terminal for connecting the solar panel. |
| 2 | Solar Panel (-) | Negative terminal for connecting the solar panel. |
| 3 | Battery (+) | Positive terminal for connecting the battery. |
| 4 | Battery (-) | Negative terminal for connecting the battery. |
| 5 | Load (+) | Positive terminal for connecting the DC load (e.g., lights, fans). |
| 6 | Load (-) | Negative terminal for connecting the DC load. |
| 7 | Ground (optional) | Ground terminal for additional grounding (if available). |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Solar Charge Controller in a Circuit
Connect the Battery First:
- Connect the battery's positive terminal to the "Battery (+)" pin and the negative terminal to the "Battery (-)" pin.
- This step ensures the controller powers up and detects the system voltage (12V or 24V).
Connect the Solar Panel:
- Connect the solar panel's positive terminal to the "Solar Panel (+)" pin and the negative terminal to the "Solar Panel (-)" pin.
- Ensure the solar panel is not exposed to sunlight during this step to avoid sparking.
Connect the Load (Optional):
- If you want to power a DC load, connect the load's positive terminal to the "Load (+)" pin and the negative terminal to the "Load (-)" pin.
Power On:
- Once all connections are secure, expose the solar panel to sunlight. The controller will begin regulating the charging process.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Battery Type: Ensure the controller is compatible with your battery type (e.g., lead-acid, lithium-ion).
- System Voltage: Verify that the controller supports the system voltage (12V or 24V).
- Wire Gauge: Use appropriately rated wires to handle the current without overheating.
- Placement: Install the controller in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating.
- Polarity: Double-check all connections for correct polarity to avoid damage.
Arduino Integration Example
If you want to monitor the solar charge controller's output using an Arduino UNO, you can use an analog input pin to measure the battery voltage. Below is an example code snippet:
// Solar Charge Controller Monitoring with Arduino
// This code reads the battery voltage from the charge controller and displays it
// on the Serial Monitor. Ensure the voltage divider is used to step down the
// battery voltage to a safe range for the Arduino's analog input (0-5V).
const int batteryPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the voltage divider
const float voltageDividerRatio = 5.7; // Adjust based on your resistor values
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(batteryPin); // Read the analog input
float batteryVoltage = (sensorValue * 5.0 / 1023.0) * voltageDividerRatio;
// Print the battery voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Battery Voltage: ");
Serial.print(batteryVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Note: Use a voltage divider circuit to step down the battery voltage to a safe range (0-5V) for the Arduino's analog input.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Controller Not Powering On:
- Cause: Battery not connected or low voltage.
- Solution: Ensure the battery is properly connected and charged.
No Charging from Solar Panel:
- Cause: Incorrect solar panel connection or insufficient sunlight.
- Solution: Check the solar panel connections and ensure it is exposed to direct sunlight.
Load Not Powering On:
- Cause: Load exceeds the controller's rated current or incorrect connection.
- Solution: Verify the load's current rating and check the connections.
Overheating:
- Cause: Poor ventilation or excessive current.
- Solution: Install the controller in a well-ventilated area and ensure the load is within the rated capacity.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the controller with a 48V system?
A: No, most controllers are designed for 12V/24V systems. Check the specifications for compatibility.Q: What is the difference between PWM and MPPT controllers?
A: PWM controllers are simpler and less expensive, while MPPT controllers are more efficient and extract maximum power from the solar panel.Q: Can I connect multiple solar panels to the controller?
A: Yes, but ensure the combined voltage and current do not exceed the controller's ratings.Q: How do I know if the battery is fully charged?
A: Most controllers have an LED indicator or display to show the battery's charging status.
By following this documentation, you can effectively use and troubleshoot a solar charge controller in your solar power system.