
How to Use converter: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with converter in Cirkit Designer
Design with converter in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A converter is an electronic device designed to transform electrical energy from one form to another. This transformation can involve converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), changing voltage levels, or even modifying the frequency of the electrical signal. Converters are essential in modern electronics, enabling compatibility between different power sources and devices.
Common applications of converters include:
- Power supplies for electronic devices (e.g., converting AC mains power to DC for laptops or smartphones).
- Voltage regulation in renewable energy systems (e.g., solar inverters).
- Motor control in industrial applications.
- Battery charging systems.
- Automotive electronics for adapting voltage levels.
Explore Projects Built with converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer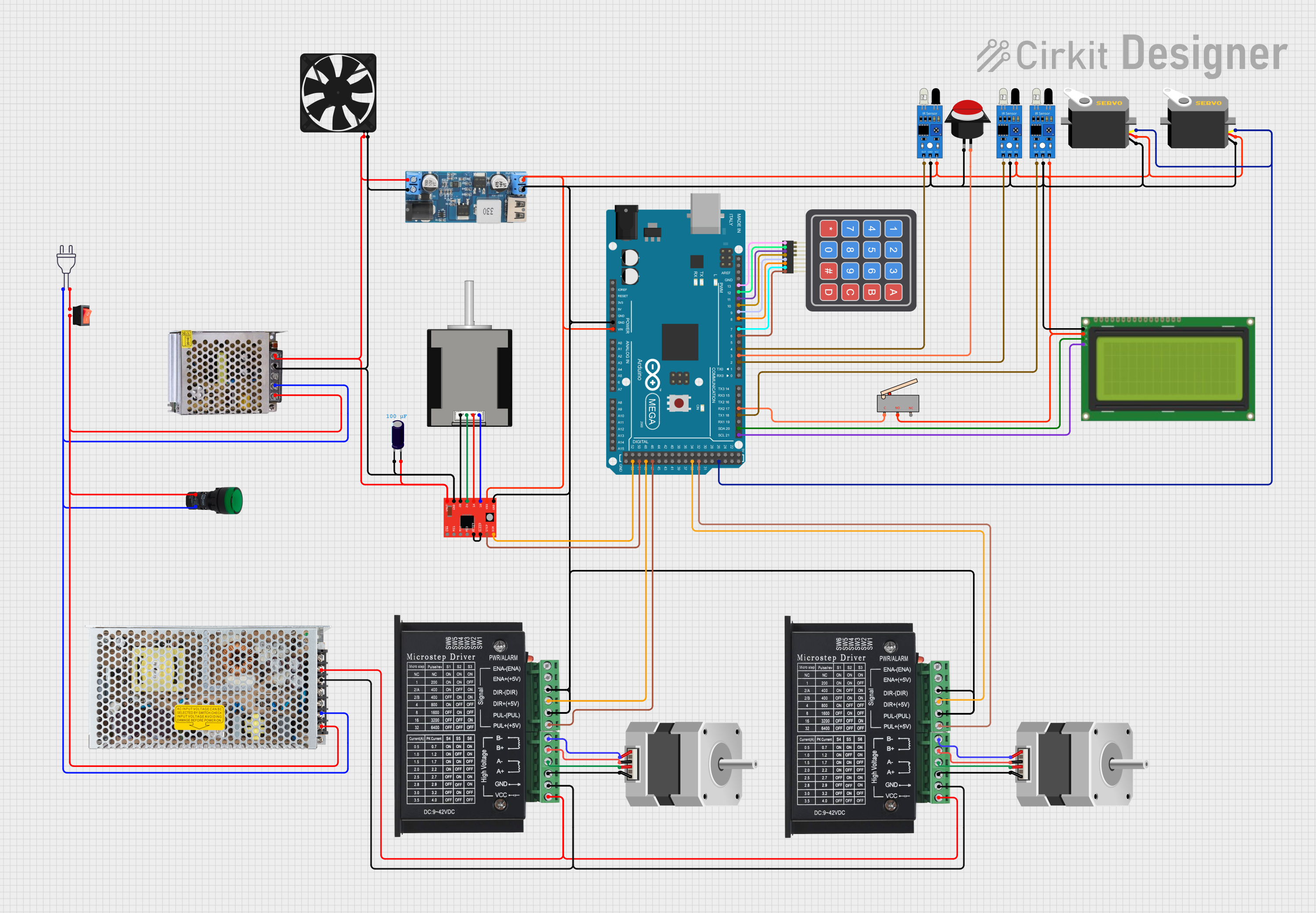
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer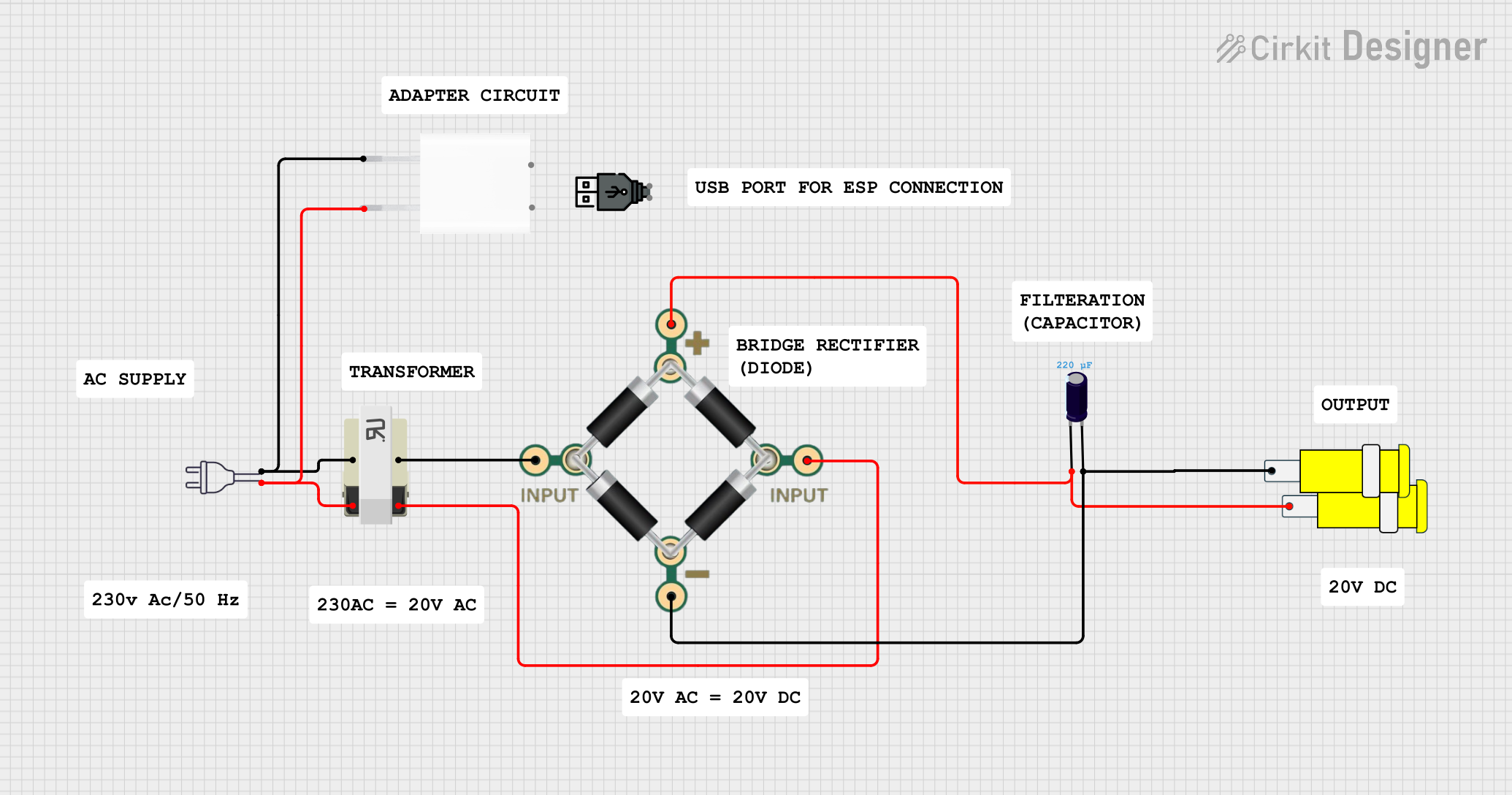
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer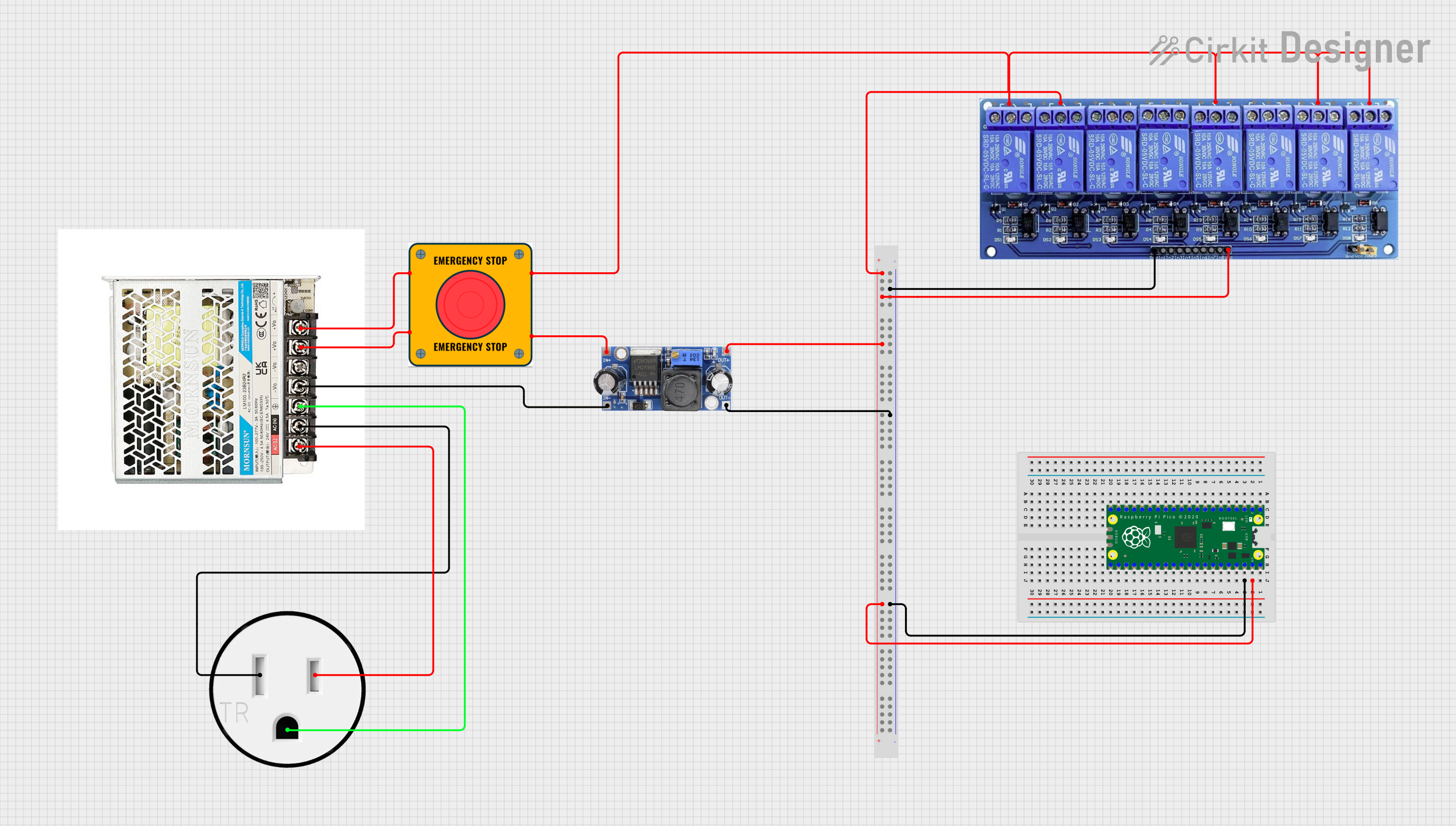
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with converter

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
The technical specifications of a converter can vary depending on its type and application. Below are general specifications for a DC-DC step-down (buck) converter as an example:
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.5V to 40V |
| Output Voltage Range | 1.25V to 37V |
| Output Current | Up to 3A |
| Efficiency | Up to 92% |
| Switching Frequency | 150 kHz |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
Pin Configuration
The pin configuration for a typical DC-DC buck converter module is as follows:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage pin. Connect to the power source (e.g., battery or adapter). |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| VOUT | Output voltage pin. Provides the regulated output voltage. |
| EN (Enable) | Optional pin to enable or disable the converter. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Converter in a Circuit
Connect the Input Voltage (VIN):
- Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range of the converter.
- Connect the positive terminal of the power source to the VIN pin and the negative terminal to the GND pin.
Set the Output Voltage (if adjustable):
- For adjustable converters, use the onboard potentiometer to set the desired output voltage.
- Measure the output voltage using a multimeter while adjusting the potentiometer.
Connect the Load:
- Attach the load (e.g., a microcontroller or motor) to the VOUT and GND pins.
- Ensure the load does not exceed the maximum current rating of the converter.
Enable the Converter (if applicable):
- If the converter has an EN (Enable) pin, connect it to a HIGH signal (e.g., 5V) to activate the converter.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Heat Dissipation: High current loads may cause the converter to heat up. Use a heatsink or ensure proper ventilation to prevent overheating.
- Input Voltage Range: Always verify that the input voltage is within the specified range to avoid damaging the converter.
- Output Filtering: For sensitive applications, consider adding capacitors at the output to reduce noise and ripple.
- Polarity Protection: Double-check the polarity of the input and output connections to prevent damage.
Example: Using a Converter with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example of using a DC-DC buck converter to power an Arduino UNO from a 12V power source:
- Connect the 12V power source to the VIN and GND pins of the converter.
- Adjust the output voltage of the converter to 5V using the potentiometer.
- Connect the VOUT pin of the converter to the 5V pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the GND pin of the converter to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
// Example Arduino code to blink an LED using a converter-powered Arduino UNO
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Voltage:
- Cause: Input voltage is not connected or is outside the specified range.
- Solution: Verify the input voltage and connections.
Overheating:
- Cause: Excessive current draw or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Reduce the load current or add a heatsink to the converter.
Output Voltage Fluctuations:
- Cause: Insufficient input power or unstable input voltage.
- Solution: Ensure the input power source is stable and capable of supplying sufficient current.
Load Not Powering On:
- Cause: Incorrect output voltage or polarity.
- Solution: Double-check the output voltage and polarity before connecting the load.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a converter to power a Raspberry Pi?
A: Yes, but ensure the converter provides a stable 5V output with sufficient current (at least 2.5A for most Raspberry Pi models).
Q: How do I know if my converter is overloaded?
A: Overloading can cause the converter to overheat, shut down, or output an unstable voltage. Check the current draw of your load and ensure it is within the converter's maximum current rating.
Q: Can I use a converter to step up voltage?
A: No, a buck converter can only step down voltage. For stepping up voltage, use a boost converter instead.
Q: Is it safe to use a converter without a heatsink?
A: For low current applications, a heatsink may not be necessary. However, for high current loads, a heatsink is recommended to prevent overheating.