
How to Use Ac Supply: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Ac Supply in Cirkit Designer
Design with Ac Supply in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An AC Supply is a crucial component in the world of electronics, providing alternating current (AC) voltage to power a wide array of electronic circuits and devices. Unlike direct current (DC), AC voltage alternates in polarity and varies in magnitude over time, typically in a sinusoidal waveform. This characteristic makes AC supplies essential for powering household appliances, industrial machinery, and various types of electronic equipment that require AC for operation.
Explore Projects Built with Ac Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer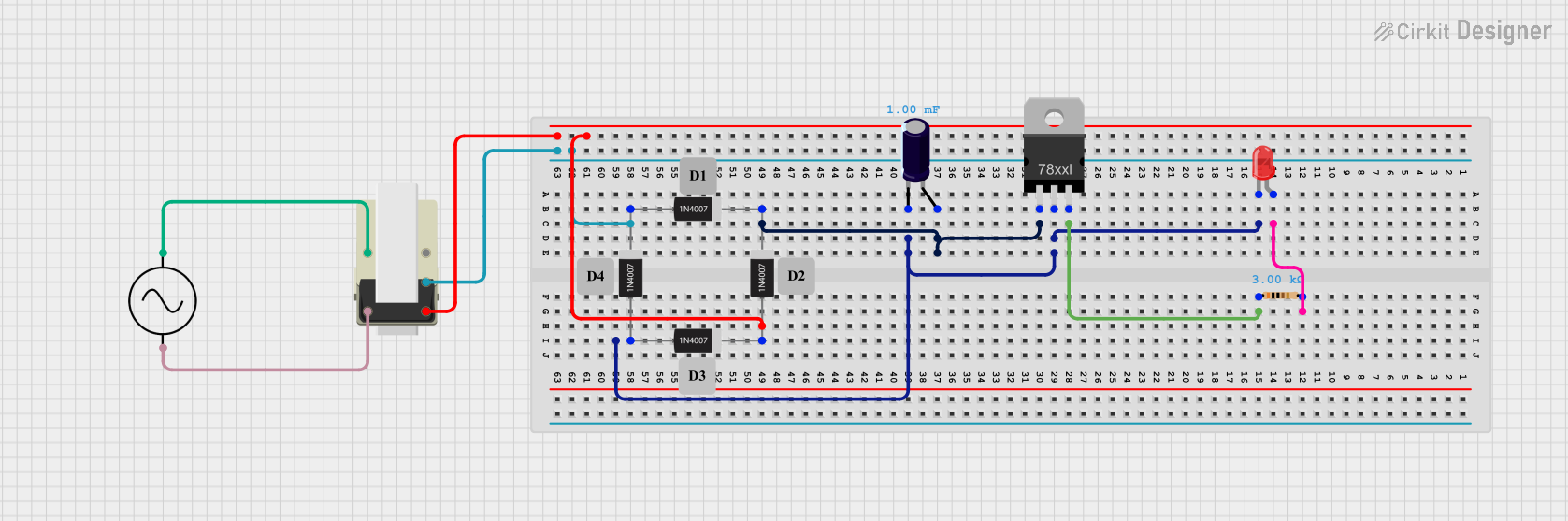
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer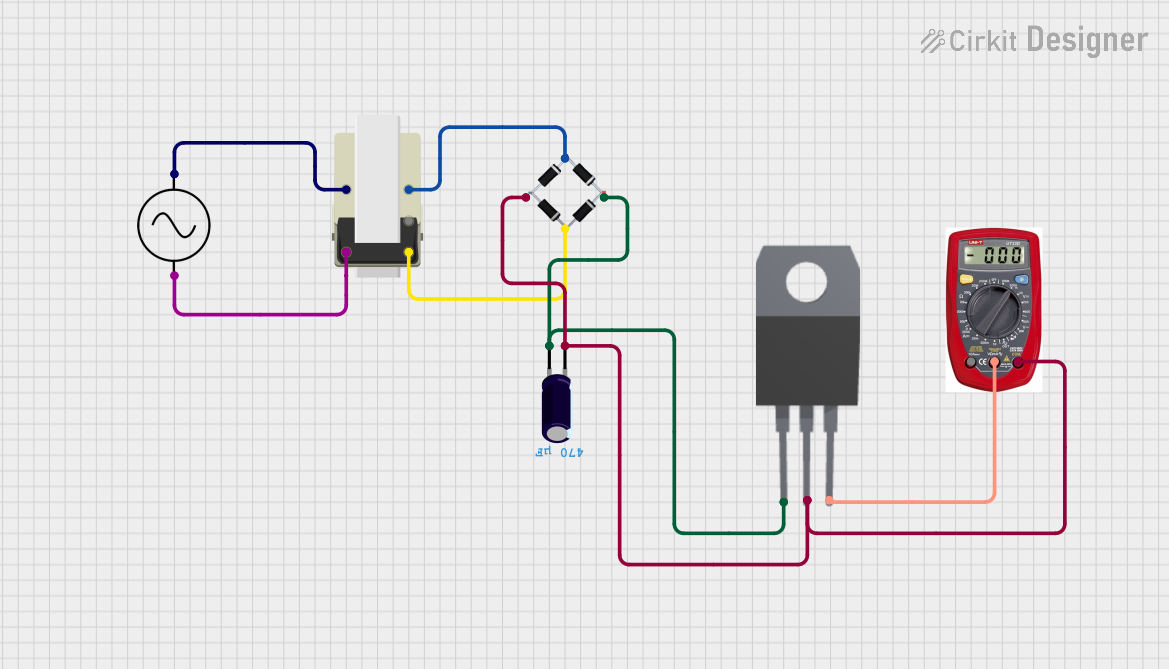
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Ac Supply

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Household appliances (e.g., refrigerators, washing machines)
- Office equipment (e.g., printers, computers)
- Industrial machinery (e.g., motors, pumps)
- Powering AC motors
- Test benches for electronic components
- Laboratory research and educational purposes
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Specification | Description |
|---|---|
| Voltage Range | 100V – 240V AC (depending on region) |
| Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz (depending on region) |
| Maximum Power Output | Varies (e.g., 500W, 1000W, 2000W) |
| Output Type | Single-phase or Three-phase (depending on model) |
| Regulation | Typically ±1% or better |
| Efficiency | Varies with load and model, often >85% |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin/Connector | Description |
|---|---|
| Live (L) | Carries the AC voltage |
| Neutral (N) | Completes the AC circuit |
| Ground (⏚) | Safety connection to earth ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the AC Supply in a Circuit
- Safety First: Ensure that the AC supply is disconnected from any power source before wiring.
- Wiring: Connect the 'Live' and 'Neutral' wires to the AC input terminals of your device or circuit. Ensure proper insulation and secure connections.
- Grounding: Attach the 'Ground' wire to the earth ground terminal of the AC supply and your device for safety.
- Power On: Once all connections are secure, plug in the AC supply to the mains power outlet.
- Settings Adjustment: If your AC supply has adjustable settings (e.g., voltage, current limit), set them according to your device's requirements before turning on the supply.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Always adhere to local electrical codes and standards.
- Use appropriate gauge wiring for the current rating of your application.
- Ensure that the AC supply's maximum power output meets or exceeds the power requirements of your device.
- If using an adjustable AC supply, start with lower settings and gradually increase to the desired levels to prevent damage.
- Use a surge protector to safeguard against voltage spikes and surges.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
- No Power Output: Check connections, ensure the AC supply is plugged in, and verify that the circuit breaker or fuse is intact.
- Unexpected Voltage Fluctuations: Confirm that the load is within the AC supply's specifications and that the voltage settings are correctly adjusted.
- Overheating: Ensure adequate ventilation around the AC supply and that the load does not exceed the supply's maximum power rating.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Circuit Breaker Tripping: Reduce the load or check for wiring faults.
- Device Not Working Properly: Verify that the frequency and voltage settings match the device's requirements.
- Noise or Interference: Use shielded cables and proper grounding techniques to minimize electrical noise.
FAQs
Q: Can I use an AC supply with a device rated for DC? A: No, devices rated for DC require a DC power supply or an AC to DC converter.
Q: How do I know if my AC supply is single-phase or three-phase? A: Check the technical specifications or the label on the AC supply. Three-phase supplies will have additional connections for the extra phases.
Q: What should I do if my AC supply is making a loud noise? A: Loud noises could indicate an internal fault or a cooling fan issue. Disconnect the supply and seek professional assistance.
Code Example for Arduino UNO
Since an AC Supply is not directly interfaced with an Arduino UNO, there is no relevant code to include for this component. However, if you are controlling AC devices using an Arduino, you would typically use a relay or a solid-state switch to safely switch the AC supply on and off.
// Example code to control an AC device using a relay module with an Arduino UNO
const int relayPin = 7; // Relay connected to digital pin 7
void setup() {
pinMode(relayPin, OUTPUT); // Set relay pin as an output
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Ensure relay is off at start
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(relayPin, HIGH); // Turn on the AC device
delay(5000); // Keep it on for 5 seconds
digitalWrite(relayPin, LOW); // Turn off the AC device
delay(5000); // Keep it off for 5 seconds
}
Remember, when dealing with AC power, safety is paramount. Always ensure that any AC-related work is performed by qualified individuals and that all safety protocols are followed.