
How to Use Water Level Sensor: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Water Level Sensor in Cirkit Designer
Design with Water Level Sensor in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Water Level Sensor is a device designed to detect and measure the level of water in a tank, reservoir, or other liquid-containing systems. It is commonly used in automation systems to control water pumps, trigger alarms, or monitor water levels in real-time. This sensor is simple to use and integrates seamlessly with microcontrollers like Arduino, making it a popular choice for DIY projects, industrial automation, and home automation systems.
Explore Projects Built with Water Level Sensor
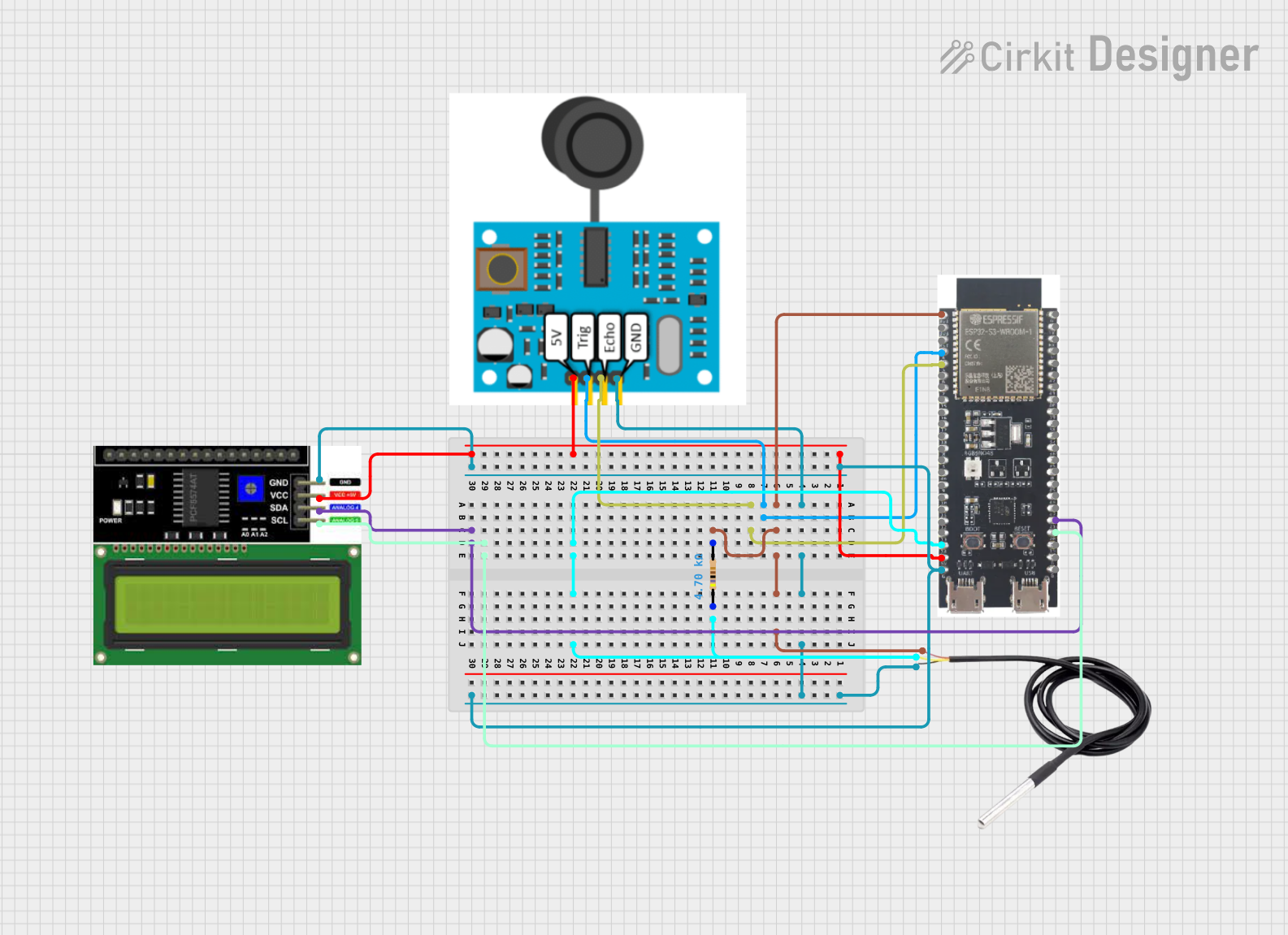
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer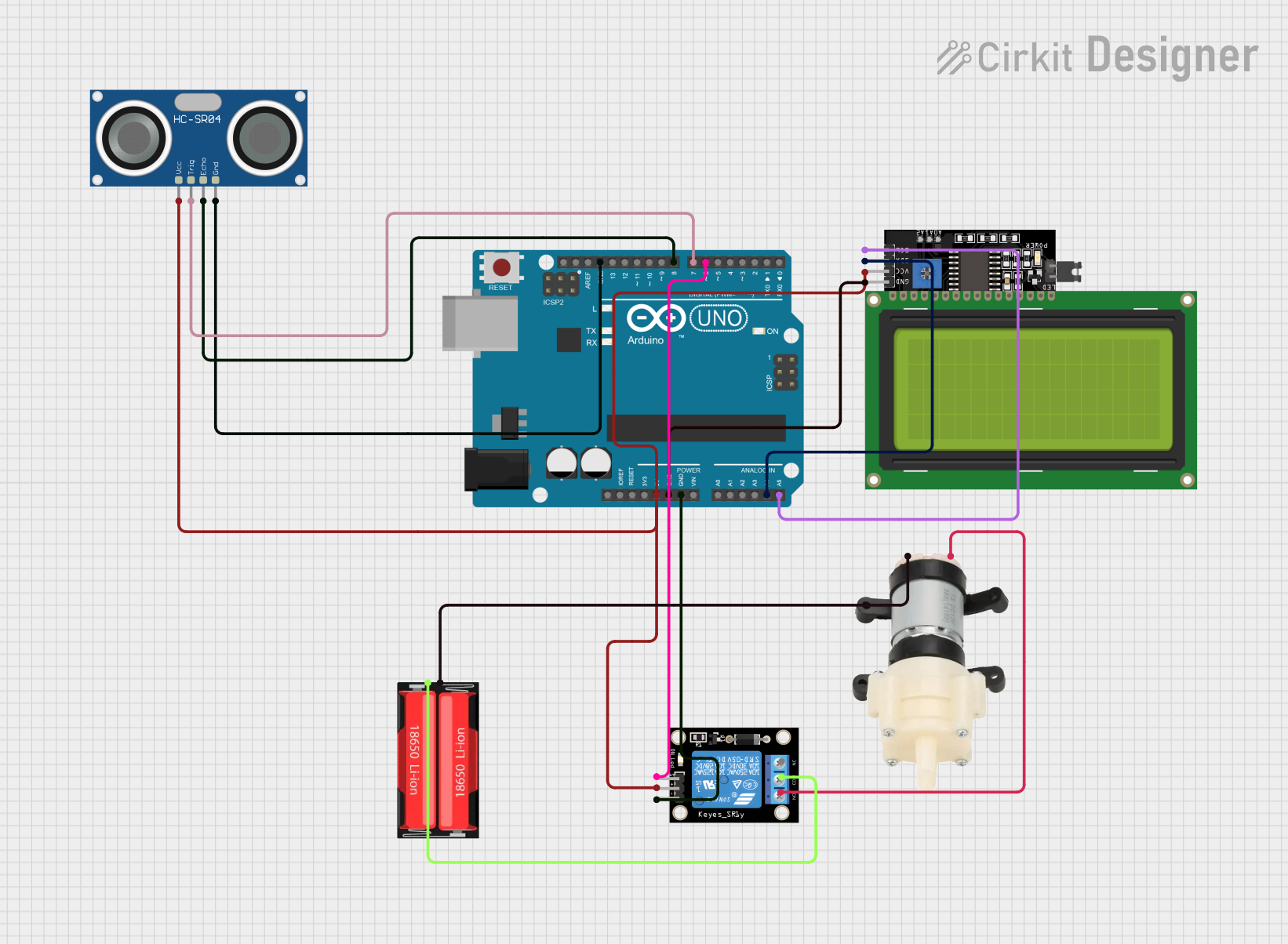
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer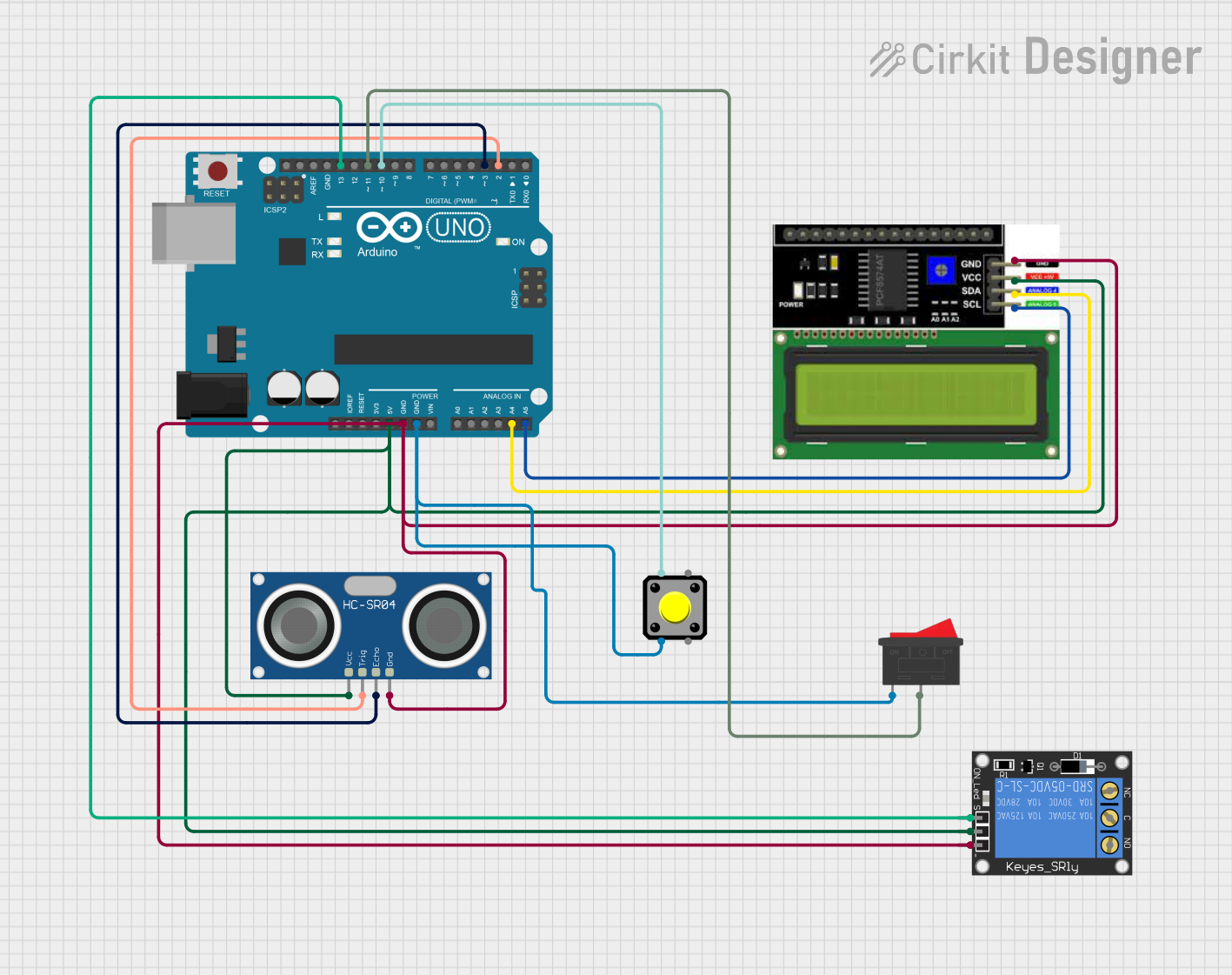
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer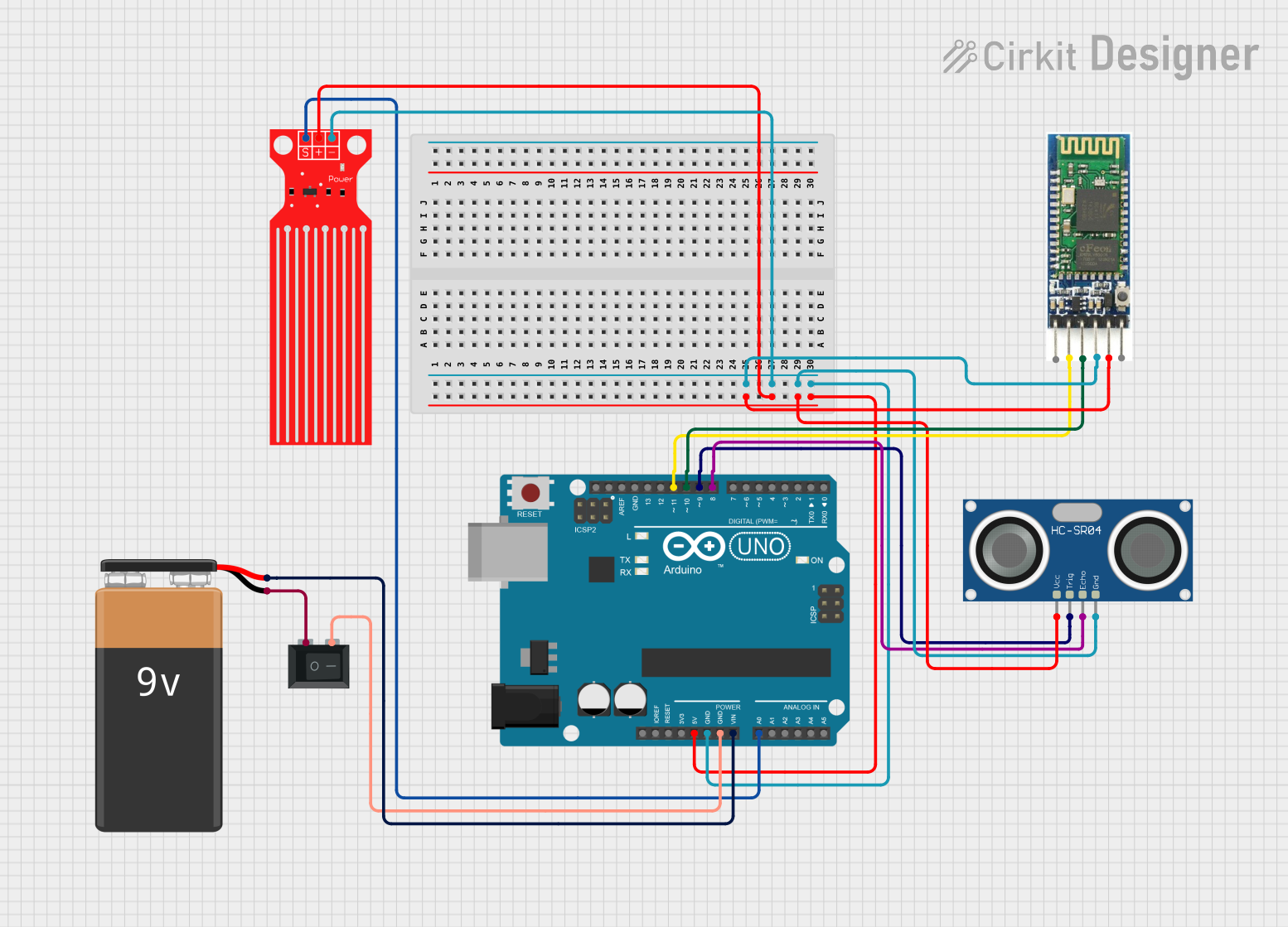
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Water Level Sensor

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automatic water pump control systems
- Water level monitoring in tanks and reservoirs
- Flood detection systems
- Smart irrigation systems
- Home automation projects
- Industrial liquid level monitoring
Technical Specifications
The Water Level Sensor typically consists of a series of exposed conductive traces that detect water levels based on conductivity. Below are the key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V - 5V |
| Operating Current | < 20mA |
| Output Type | Analog and Digital |
| Detection Range | 0 - 100% of sensor length |
| Dimensions | ~65mm x 20mm x 8mm |
| Interface Type | 3-pin interface (VCC, GND, OUT) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Power supply pin. Connect to 3.3V or 5V from the microcontroller or power source. |
| GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| OUT | Output pin. Provides an analog voltage proportional to the water level or a |
| digital HIGH/LOW signal depending on the sensor configuration. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Water Level Sensor in a Circuit
Connect the Sensor:
- Connect the
VCCpin of the sensor to the 5V (or 3.3V) pin of your microcontroller. - Connect the
GNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the
OUTpin to an analog input pin (e.g., A0) or a digital input pin (e.g., D2) on your microcontroller.
- Connect the
Read the Output:
- If using the analog output, the voltage on the
OUTpin will vary based on the water level. A higher water level corresponds to a higher voltage. - If using the digital output, the sensor will output a HIGH signal when water is detected and a LOW signal when no water is detected.
- If using the analog output, the voltage on the
Write Code:
- Use a microcontroller like Arduino to read the sensor's output and take appropriate actions, such as turning on a pump or triggering an alarm.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Corrosion: The exposed conductive traces on the sensor can corrode over time if submerged in water for extended periods. Use the sensor for intermittent measurements or consider waterproofing solutions.
- Power Supply: Ensure the sensor is powered within its operating voltage range (3.3V - 5V) to avoid damage.
- Signal Noise: Use proper filtering techniques in your code or circuit to minimize noise in the analog signal.
- Placement: Install the sensor vertically in the tank or reservoir for accurate readings.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the Water Level Sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Water Level Sensor Example Code for Arduino UNO
// This code reads the analog output of the sensor and prints the water level
// to the Serial Monitor. It also turns on an LED if water is detected.
const int sensorPin = A0; // Analog pin connected to the sensor's OUT pin
const int ledPin = 13; // Digital pin connected to an LED
int sensorValue = 0; // Variable to store the sensor reading
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Print the sensor value to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Water Level (Analog Value): ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
// If the sensor value exceeds a threshold, turn on the LED
if (sensorValue > 500) { // Adjust the threshold as needed
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn on the LED
} else {
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn off the LED
}
delay(500); // Wait for 500ms before the next reading
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, ensuring the VCC, GND, and OUT pins are properly connected.
Fluctuating Analog Readings:
- Cause: Electrical noise or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Add a capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) between the VCC and GND pins to stabilize the power supply.
Sensor Corrosion:
- Cause: Prolonged exposure to water.
- Solution: Use the sensor intermittently or apply a protective coating to the conductive traces.
Digital Output Always HIGH or LOW:
- Cause: Incorrect threshold setting or damaged sensor.
- Solution: Verify the sensor's functionality using the analog output. Replace the sensor if necessary.
FAQs
Q: Can this sensor detect liquids other than water?
A: Yes, the sensor can detect other conductive liquids, but its accuracy may vary depending on the liquid's conductivity.
Q: How do I extend the lifespan of the sensor?
A: Minimize continuous exposure to water and use protective coatings to prevent corrosion.
Q: Can I use this sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller like ESP8266?
A: Yes, the sensor operates at 3.3V - 5V, making it compatible with 3.3V microcontrollers.
Q: What is the maximum depth this sensor can measure?
A: The sensor can measure up to the length of its conductive traces, typically around 65mm. For deeper measurements, consider using multiple sensors or a different type of water level sensor.