
How to Use Stepper Motor 2: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Stepper Motor 2 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Stepper Motor 2 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Stepper Motor 2 (STP-MTRD-17038E), manufactured by Automation Direct, is a high-performance stepper motor designed for precise control of angular position and speed. Unlike traditional DC motors, stepper motors divide a full rotation into a large number of discrete steps, making them ideal for applications requiring accurate positioning and repeatable motion.
Explore Projects Built with Stepper Motor 2
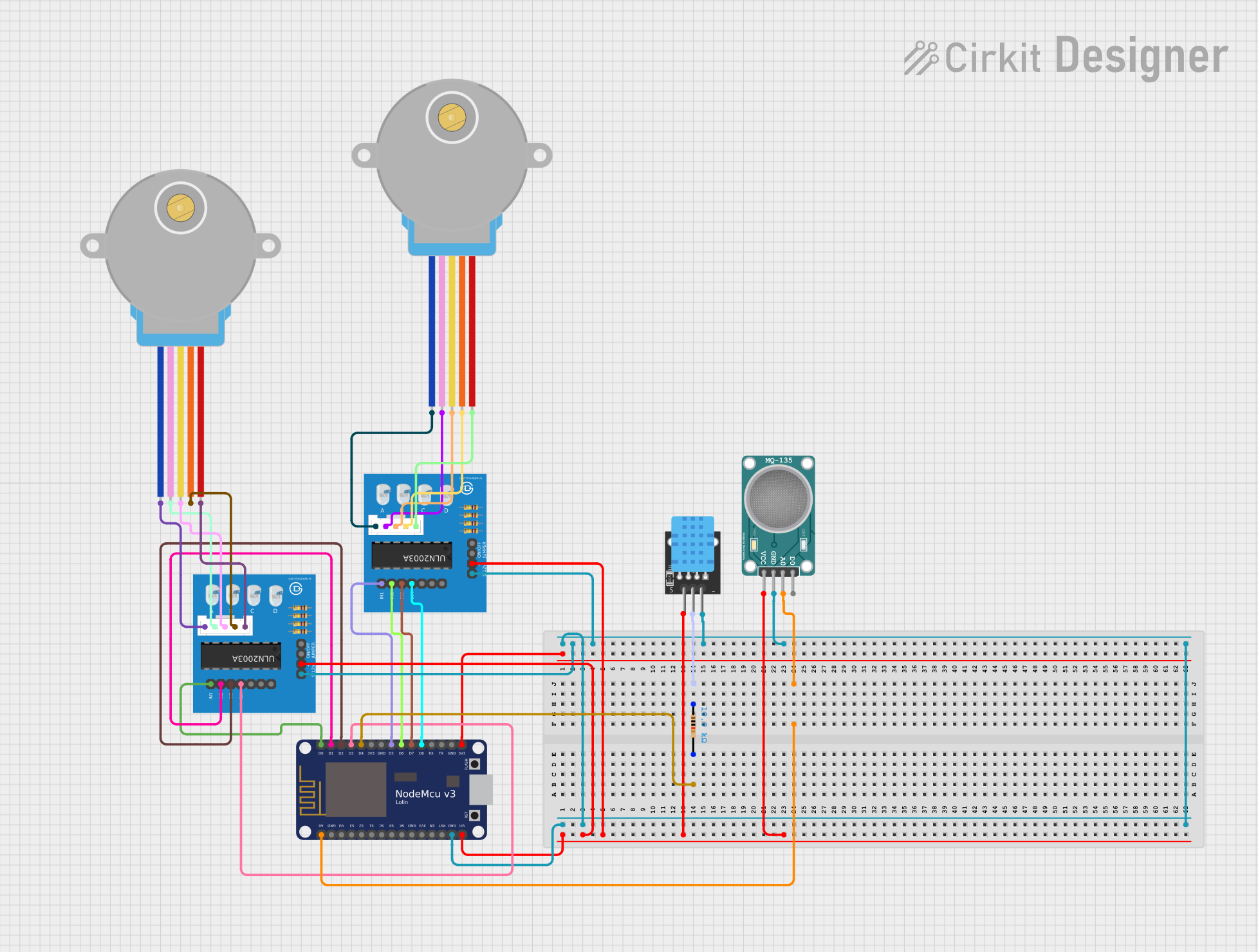
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer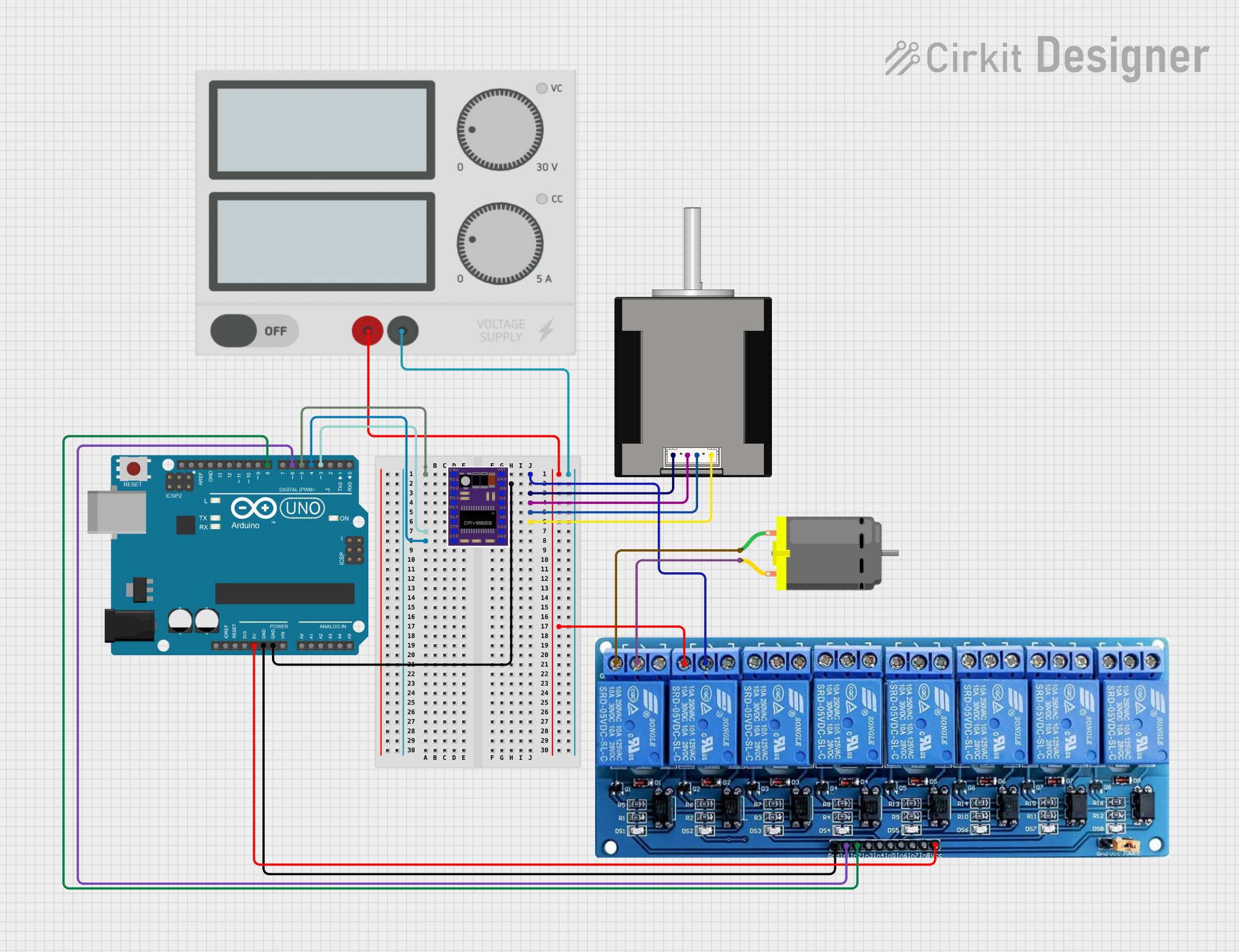
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer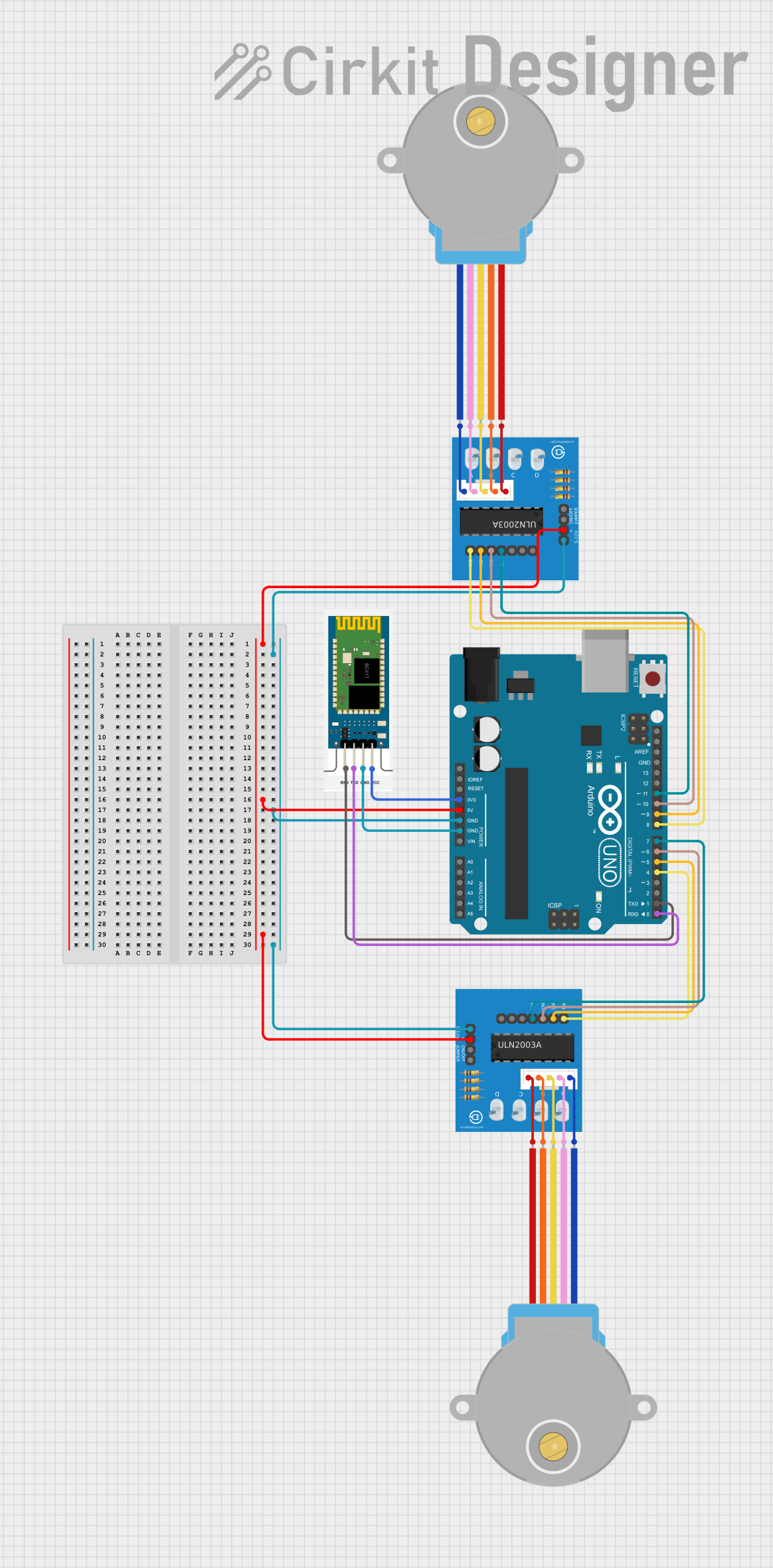
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer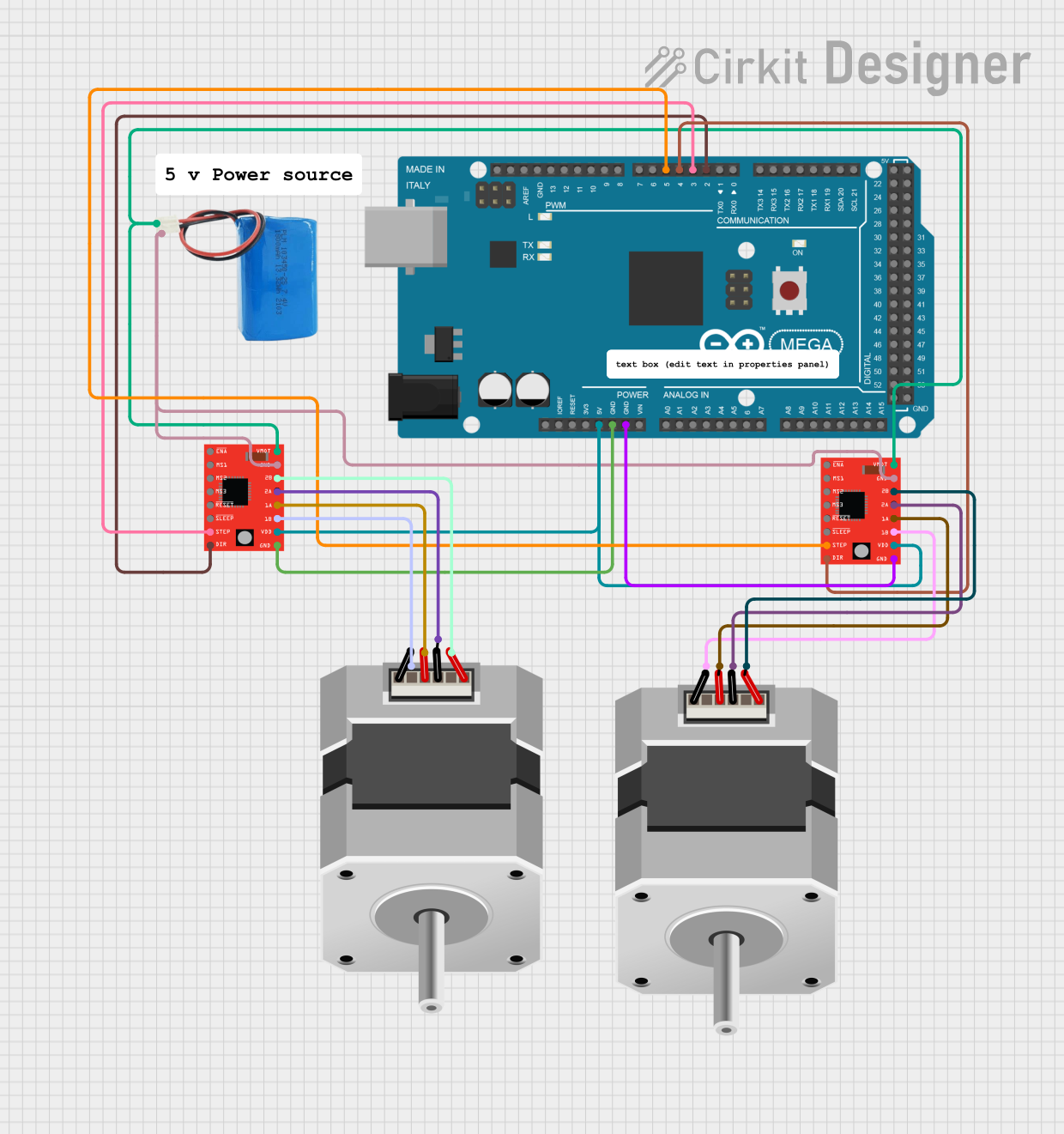
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Stepper Motor 2

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- 3D Printers: For precise movement of print heads and platforms.
- CNC Machines: To control tool positioning with high accuracy.
- Robotics: For controlling joint movements and actuators.
- Automated Systems: Such as conveyor belts and pick-and-place machines.
- Camera Gimbals: For smooth and precise camera positioning.
Technical Specifications
The following table outlines the key technical details of the STP-MTRD-17038E stepper motor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Automation Direct |
| Part Number | STP-MTRD-17038E |
| Step Angle | 1.8° per step |
| Holding Torque | 1.26 Nm (178 oz-in) |
| Rated Current per Phase | 2.8 A |
| Voltage | 2.55 V |
| Resistance per Phase | 0.91 Ω |
| Inductance per Phase | 3.6 mH |
| Number of Leads | 4 |
| Shaft Diameter | 6.35 mm (0.25 in) |
| Motor Frame Size | NEMA 17 |
| Weight | 0.5 kg (1.1 lbs) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The STP-MTRD-17038E is a 4-wire bipolar stepper motor. The pinout and wiring details are as follows:
| Lead Color | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Red | Phase A+ | Positive terminal of Phase A coil |
| Blue | Phase A- | Negative terminal of Phase A coil |
| Green | Phase B+ | Positive terminal of Phase B coil |
| Black | Phase B- | Negative terminal of Phase B coil |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the motor is powered by a suitable driver capable of handling the rated current (2.8 A per phase) and voltage (2.55 V). A stepper motor driver such as the Automation Direct STP-DRV-4850 is recommended.
- Wiring: Connect the motor leads to the driver as per the pin configuration table. Ensure proper polarity to avoid incorrect operation.
- Control Signals: Use a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino UNO) or a motion controller to send step and direction signals to the driver.
- Step Resolution: Configure the driver for the desired microstepping resolution (e.g., full step, half step, 1/8 step) to achieve the required precision.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Current Limiting: Set the current limit on the driver to match the motor's rated current (2.8 A) to prevent overheating.
- Cooling: Ensure adequate ventilation or heat dissipation for the motor and driver during operation.
- Backlash and Load: Avoid excessive mechanical backlash or overloading the motor, as this can reduce accuracy and lifespan.
- Power Supply: Use a regulated power supply with sufficient current capacity to handle the motor and driver.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control the STP-MTRD-17038E stepper motor using an Arduino UNO and a compatible stepper motor driver:
// Include the Stepper library for easy motor control
#include <Stepper.h>
// Define the number of steps per revolution (360° / 1.8° = 200 steps)
#define STEPS_PER_REV 200
// Initialize the Stepper library with the motor's step count and pin connections
// Pins 8 and 9 control Phase A, Pins 10 and 11 control Phase B
Stepper stepperMotor(STEPS_PER_REV, 8, 9, 10, 11);
void setup() {
// Set the motor speed in RPM (revolutions per minute)
stepperMotor.setSpeed(60); // 60 RPM
// Initialize serial communication for debugging
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Stepper Motor Test Initialized");
}
void loop() {
// Rotate the motor 1 full revolution clockwise
Serial.println("Rotating clockwise...");
stepperMotor.step(STEPS_PER_REV);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
// Rotate the motor 1 full revolution counterclockwise
Serial.println("Rotating counterclockwise...");
stepperMotor.step(-STEPS_PER_REV);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Notes:
- Replace the pin numbers (8, 9, 10, 11) with the actual pins connected to your driver.
- Adjust the speed and step count as needed for your application.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Motor Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or loose connections.
- Solution: Double-check the wiring and ensure all connections are secure.
Motor Vibrates but Does Not Rotate:
- Cause: Incorrect step sequence or driver configuration.
- Solution: Verify the step sequence and microstepping settings on the driver.
Overheating:
- Cause: Current limit set too high or insufficient cooling.
- Solution: Reduce the current limit on the driver and ensure proper ventilation.
Skipping Steps:
- Cause: Excessive load or insufficient torque.
- Solution: Reduce the load or increase the current limit (within safe limits).
Noisy Operation:
- Cause: Low microstepping resolution or mechanical issues.
- Solution: Increase the microstepping resolution and check for mechanical alignment.
FAQs
Q: Can I use this motor with a unipolar driver?
A: No, the STP-MTRD-17038E is a bipolar stepper motor and requires a bipolar driver.Q: What is the maximum speed of this motor?
A: The maximum speed depends on the driver, power supply, and load. Typically, it can achieve speeds up to 1000 RPM under optimal conditions.Q: Can I run this motor without a driver?
A: No, a stepper motor driver is required to generate the precise step signals needed for operation.Q: How do I calculate the torque required for my application?
A: Use the formula: Torque = Force × Distance. Ensure the required torque is within the motor's holding torque (1.26 Nm).
By following this documentation, users can effectively integrate and operate the STP-MTRD-17038E stepper motor in their projects.