
How to Use ESP32-P4-Eth: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with ESP32-P4-Eth in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32-P4-Eth in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32-P4-Eth by WaveShare is a high-performance microcontroller designed for Internet of Things (IoT) applications. It combines integrated Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities with an Ethernet interface, offering both wireless and wired connectivity options. This makes it ideal for projects requiring stable and reliable internet access. The ESP32-P4-Eth is widely recognized for its low power consumption, high processing speed, and ability to interface with a variety of sensors and peripherals.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32-P4-Eth
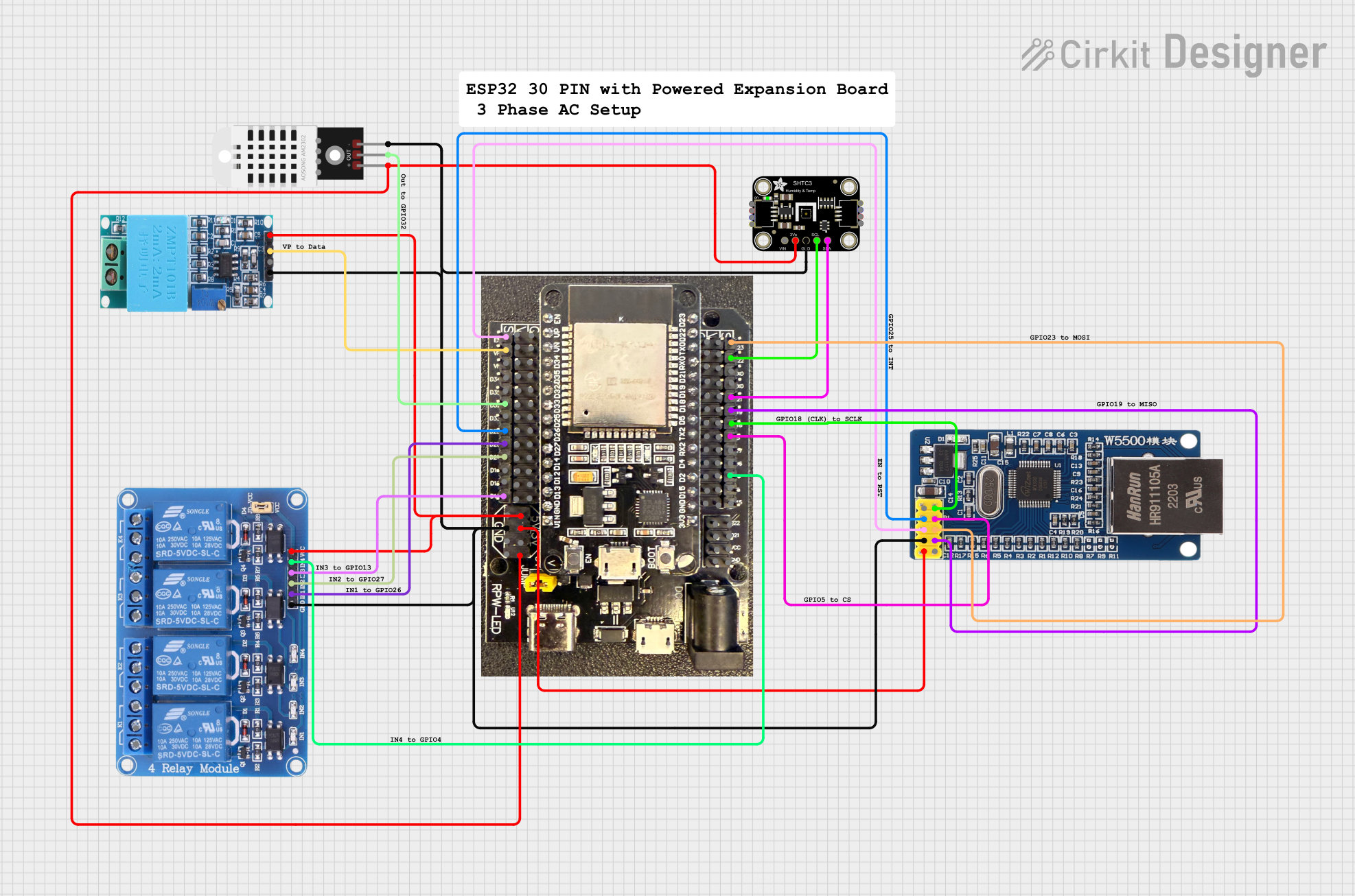
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer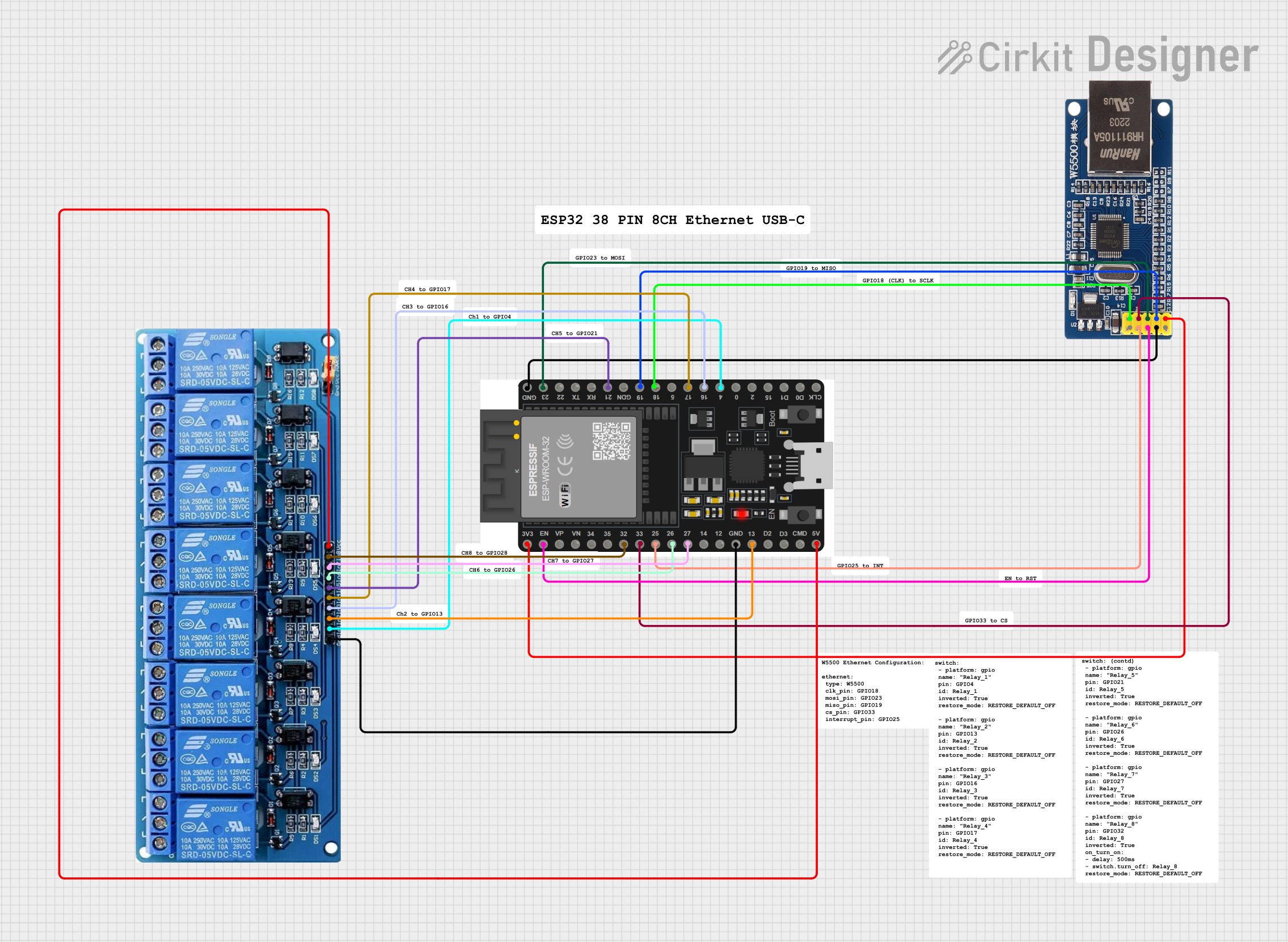
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer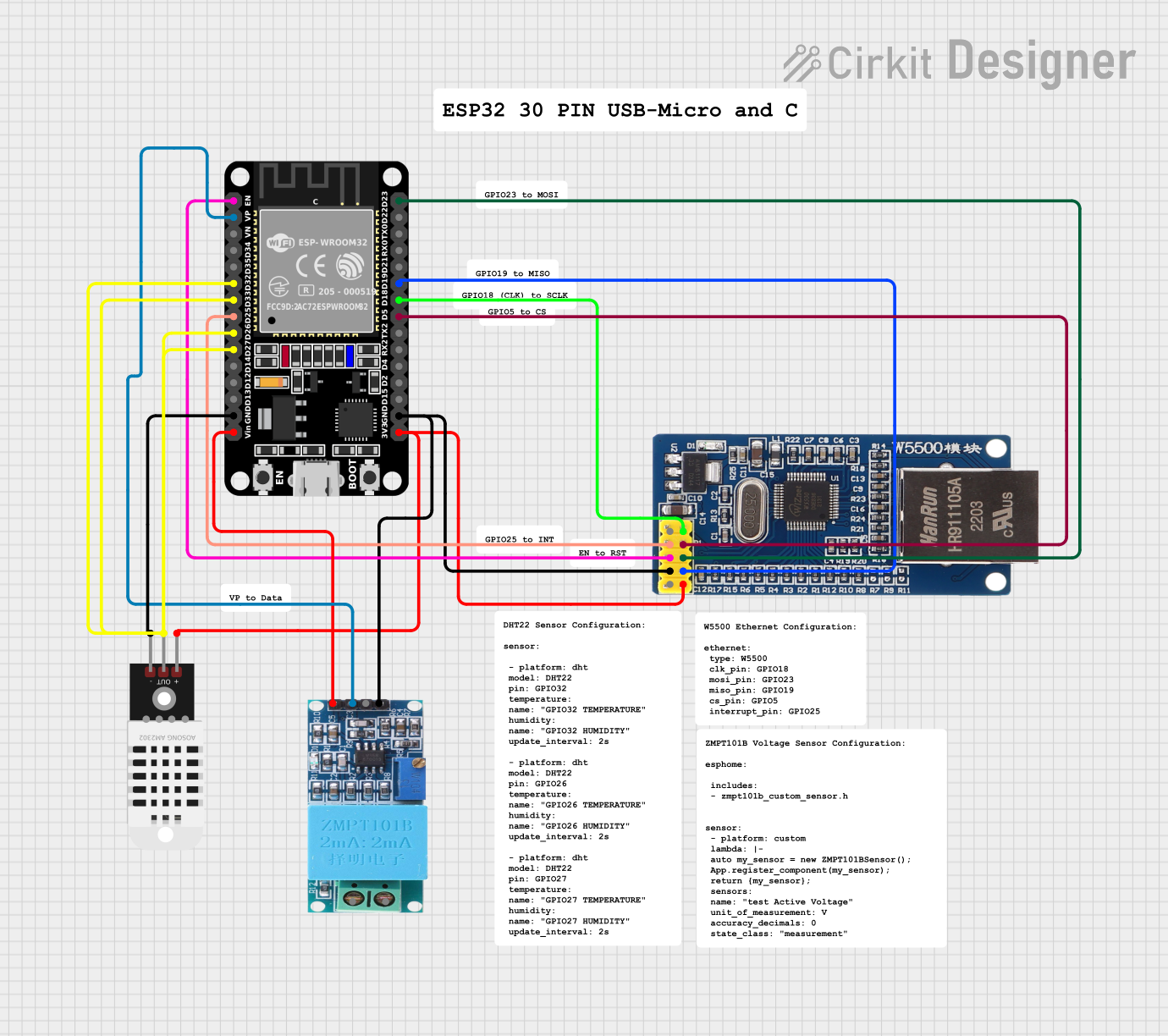
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer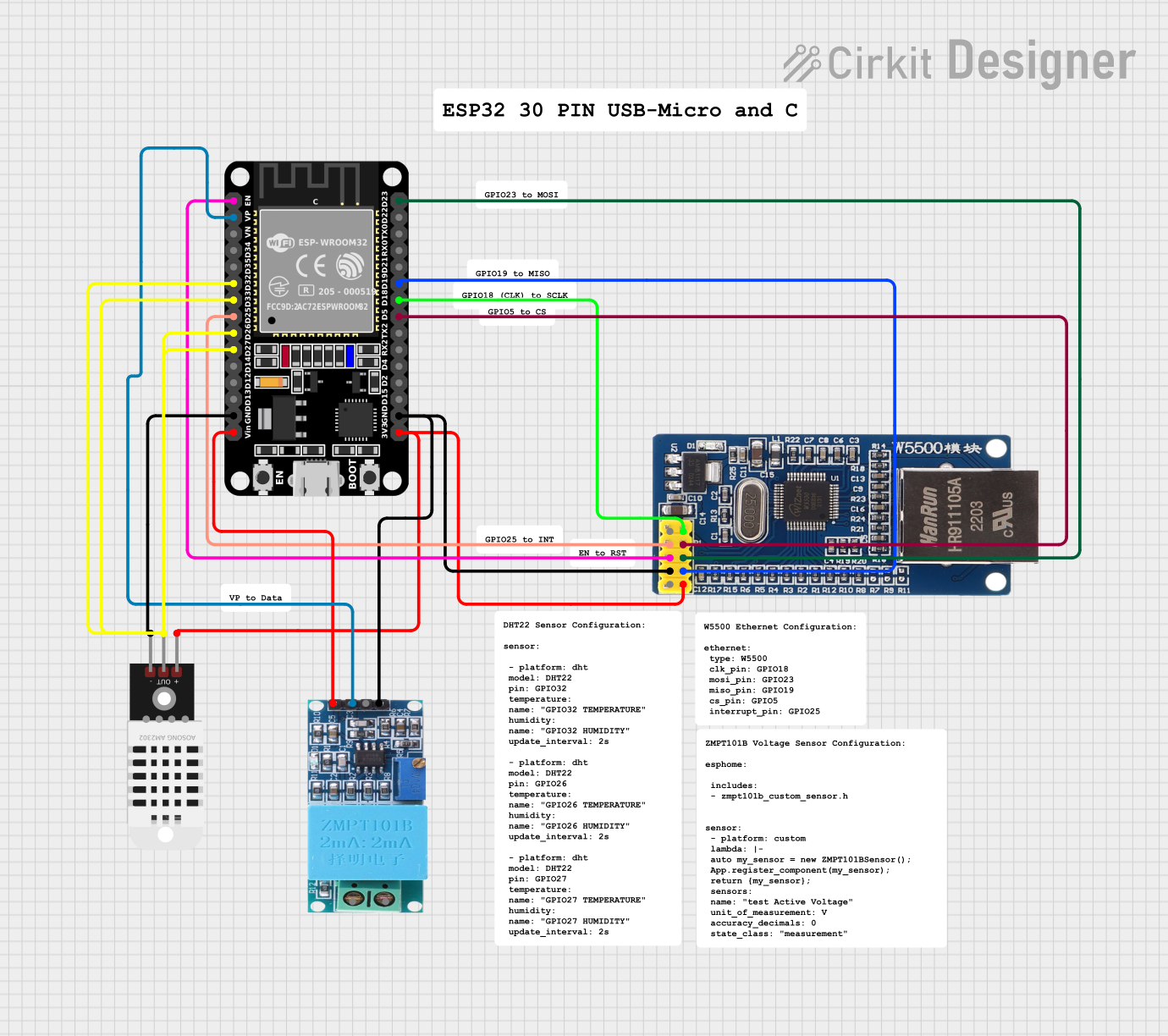
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32-P4-Eth

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Smart home automation systems
- Industrial IoT applications
- Data logging and monitoring systems
- Networked sensor hubs
- Robotics and automation
- Projects requiring hybrid (wired and wireless) connectivity
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Microcontroller | ESP32-P4 |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi 802.11 b/g/n, Bluetooth 5.0 |
| Wired Connectivity | Ethernet (10/100 Mbps) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V |
| Input Voltage Range | 5V (via USB) or 7-12V (via VIN pin) |
| Flash Memory | 4MB |
| SRAM | 512KB |
| GPIO Pins | 34 |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, CAN, PWM |
| Power Consumption | Ultra-low power mode supported |
| Dimensions | 58mm x 25mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32-P4-Eth features a variety of pins for interfacing with external devices. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VIN | Power | Input voltage (7-12V) for powering the board |
| 3V3 | Power | 3.3V output for powering external components |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection |
| GPIO0 | GPIO | General-purpose I/O pin, often used for boot mode selection |
| GPIO1 | UART TX | UART transmit pin |
| GPIO3 | UART RX | UART receive pin |
| GPIO12 | GPIO | General-purpose I/O pin |
| GPIO13 | GPIO | General-purpose I/O pin |
| GPIO14 | GPIO | General-purpose I/O pin |
| GPIO15 | GPIO | General-purpose I/O pin |
| EN | Enable | Enable pin to reset the microcontroller |
| ETH_TXD0 | Ethernet | Ethernet transmit data pin 0 |
| ETH_TXD1 | Ethernet | Ethernet transmit data pin 1 |
| ETH_RXD0 | Ethernet | Ethernet receive data pin 0 |
| ETH_RXD1 | Ethernet | Ethernet receive data pin 1 |
| ETH_CLK | Ethernet | Ethernet clock signal |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP32-P4-Eth in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Use the VIN pin to supply 7-12V, or connect a 5V USB power source.
- Ensure the power supply is stable to avoid damage to the board.
Connecting to Ethernet:
- Connect the Ethernet cable to the RJ45 port on the board.
- Use the Ethernet pins (e.g., ETH_TXD0, ETH_RXD0) for custom Ethernet interfacing if needed.
Programming the Board:
- Use the USB interface to connect the ESP32-P4-Eth to your computer.
- Install the necessary drivers and use the Arduino IDE or ESP-IDF for programming.
Interfacing with Sensors and Devices:
- Use the GPIO pins for connecting sensors, actuators, or other peripherals.
- Configure the pins in your code as input or output based on your application.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure all connected devices operate at 3.3V logic levels to avoid damaging the board.
- Ethernet Usage: For stable Ethernet connectivity, use high-quality cables and ensure proper grounding.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth: Avoid placing the board in areas with significant RF interference to maintain wireless performance.
- Heat Management: If the board is used in high-performance applications, consider adding a heat sink to manage heat dissipation.
Example Code for Arduino IDE
Below is an example of how to use the ESP32-P4-Eth to connect to a Wi-Fi network and send data over Ethernet:
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <ETH.h>
// Wi-Fi credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
// Ethernet configuration
#define ETH_CLK_MODE ETH_CLOCK_GPIO17_OUT // Set Ethernet clock mode
#define ETH_PHY_POWER 12 // GPIO pin for Ethernet PHY power
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize Wi-Fi
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
Serial.print("Connecting to Wi-Fi");
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("\nWi-Fi connected!");
// Initialize Ethernet
ETH.begin(ETH_PHY_ADDR, ETH_PHY_POWER, ETH_CLK_MODE, ETH_PHY_MDC, ETH_PHY_MDIO);
Serial.println("Ethernet initialized!");
}
void loop() {
// Print IP addresses
Serial.print("Wi-Fi IP: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
Serial.print("Ethernet IP: ");
Serial.println(ETH.localIP());
delay(5000); // Wait 5 seconds before printing again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The board does not power on:
- Ensure the power supply voltage is within the specified range (7-12V for VIN or 5V via USB).
- Check the connections and ensure the power source is functional.
Wi-Fi connection fails:
- Verify the SSID and password in your code.
- Check for RF interference or weak signal strength.
- Restart the board and try reconnecting.
Ethernet does not work:
- Ensure the Ethernet cable is securely connected.
- Verify the Ethernet pins are correctly configured in your code.
- Check the network settings and ensure the router is functional.
GPIO pins not responding:
- Confirm the pins are correctly configured as input or output in your code.
- Check for short circuits or incorrect wiring.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the ESP32-P4-Eth with the Arduino IDE?
A: Yes, the ESP32-P4-Eth is fully compatible with the Arduino IDE. Install the ESP32 board package to get started.
Q: Does the board support PoE (Power over Ethernet)?
A: No, the ESP32-P4-Eth does not support PoE. You must provide power via VIN or USB.
Q: How do I reset the board?
A: Press the EN (Enable) button on the board to reset the microcontroller.
Q: Can I use both Wi-Fi and Ethernet simultaneously?
A: Yes, the ESP32-P4-Eth supports simultaneous use of Wi-Fi and Ethernet for hybrid connectivity.