
How to Use 3A Fuse: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with 3A Fuse in Cirkit Designer
Design with 3A Fuse in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A 3A fuse is a safety device designed to protect electrical circuits by interrupting the flow of current when it exceeds 3 amperes. This prevents damage to sensitive components, reduces the risk of overheating, and minimizes the chance of electrical fires. Fuses are essential in a wide range of applications, from household appliances to automotive systems and industrial equipment.
Explore Projects Built with 3A Fuse

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer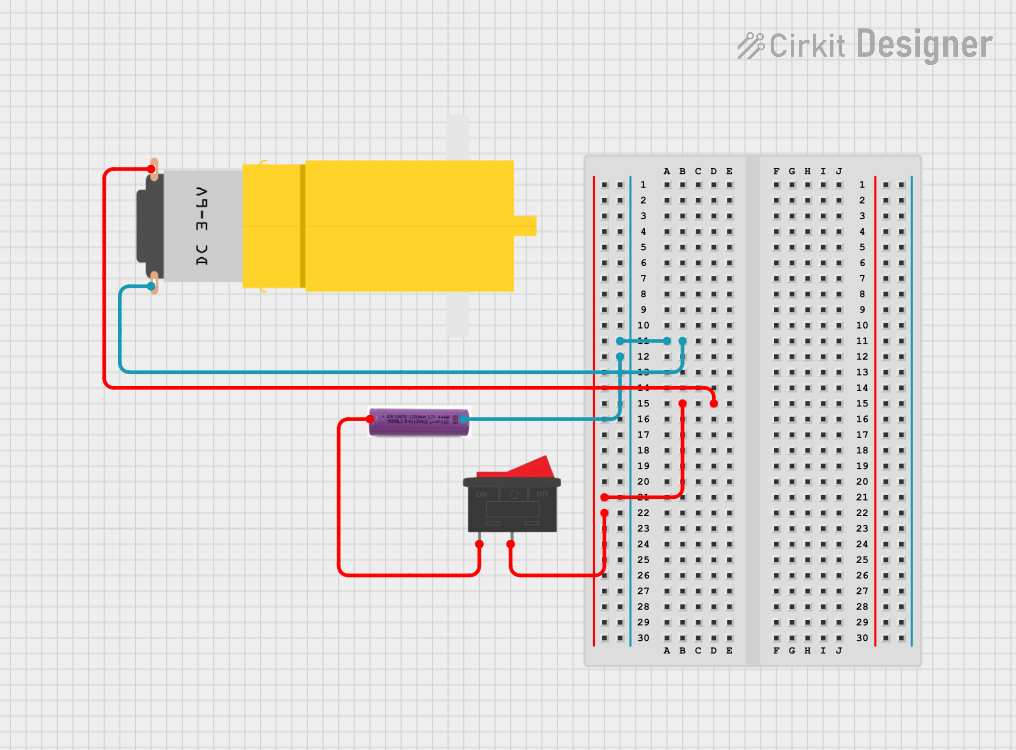
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer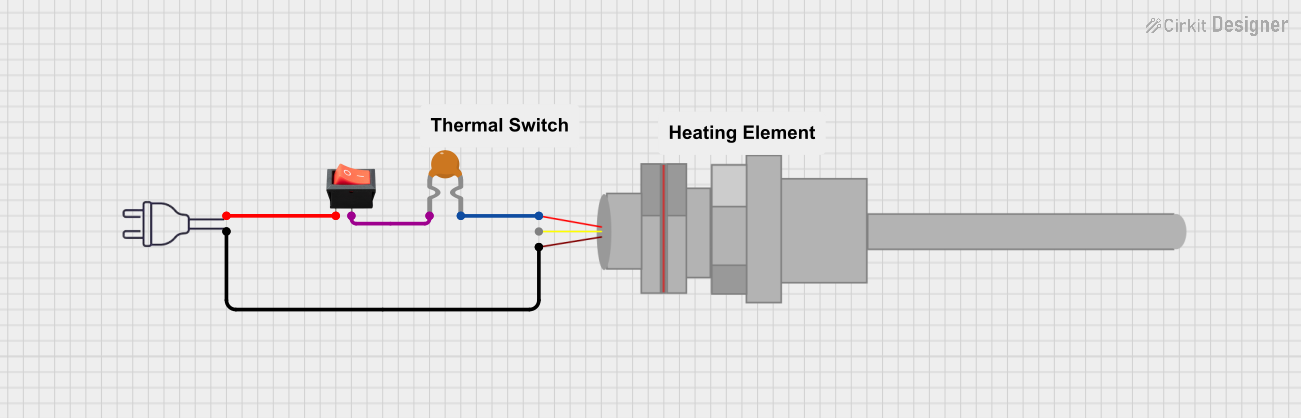
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with 3A Fuse

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Household Electronics: Protecting devices like chargers, lamps, and small appliances.
- Automotive Systems: Safeguarding circuits in vehicles, such as lighting and infotainment systems.
- Industrial Equipment: Ensuring the safety of control panels and machinery.
- DIY Electronics Projects: Preventing damage to components in custom circuits.
Technical Specifications
The 3A fuse is available in various types, such as glass tube, ceramic, and blade fuses. Below are the general specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Rated Current | 3 Amperes |
| Rated Voltage | Typically 250V AC or 32V DC |
| Breaking Capacity | Varies (e.g., 35A, 100A) |
| Fuse Type | Fast-blow or slow-blow |
| Material | Glass, ceramic, or plastic |
| Dimensions | Depends on type (e.g., 5x20mm for glass fuses) |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Fuses do not have traditional pins like ICs or transistors. Instead, they have two terminals for connection. Below is a description of the terminals:
| Terminal | Description |
|---|---|
| Terminal 1 | Connects to the power source or input side of the circuit. |
| Terminal 2 | Connects to the load or output side of the circuit. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the 3A Fuse in a Circuit
- Determine the Fuse Type: Choose between fast-blow (for sensitive electronics) or slow-blow (for circuits with inrush currents).
- Select the Fuse Holder: Use a compatible fuse holder or clip for secure installation.
- Insert the Fuse: Place the fuse in series with the circuit's power line. Ensure proper contact with the terminals.
- Verify the Circuit: Double-check the connections and ensure the fuse rating matches the circuit's requirements.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Rating: Ensure the fuse's voltage rating exceeds the circuit's operating voltage.
- Current Rating: The fuse should be rated slightly above the circuit's normal operating current but below the maximum current the circuit can handle.
- Environment: Use ceramic fuses for high-temperature or high-vibration environments.
- Testing: Regularly inspect and test fuses to ensure they are functioning correctly.
- Replacement: Always replace a blown fuse with one of the same type and rating.
Example: Using a 3A Fuse with an Arduino UNO
When connecting an Arduino UNO to a power supply, a 3A fuse can protect the board from overcurrent. Below is an example circuit:
- Connect the positive terminal of the power supply to one terminal of the 3A fuse.
- Connect the other terminal of the fuse to the VIN pin of the Arduino UNO.
- Connect the negative terminal of the power supply to the GND pin of the Arduino UNO.
Here is a simple Arduino sketch to demonstrate a basic setup:
// Example Arduino code to blink an LED
// Ensure a 3A fuse is connected in series with the power supply for protection.
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Fuse Blows Frequently:
- Cause: The circuit's current exceeds the fuse's rating.
- Solution: Check for short circuits or reduce the load on the circuit. Use a higher-rated fuse if appropriate.
Fuse Does Not Blow When Expected:
- Cause: The fuse rating is too high for the circuit.
- Solution: Replace the fuse with one that matches the circuit's requirements.
Fuse Holder Overheats:
- Cause: Poor contact between the fuse and holder.
- Solution: Ensure the fuse is securely seated and the holder is clean and undamaged.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 3A fuse in a 5A circuit?
A: No, the fuse will blow if the current exceeds 3A, which may not be suitable for a 5A circuit. Use a fuse rated for 5A instead.Q: What is the difference between fast-blow and slow-blow fuses?
A: Fast-blow fuses respond quickly to overcurrent, while slow-blow fuses tolerate short surges before blowing.Q: How do I test if a fuse is blown?
A: Use a multimeter in continuity mode. If the fuse is intact, the multimeter will beep or show a low resistance value. If blown, it will show no continuity.
By following this documentation, you can safely and effectively use a 3A fuse in your circuits.