
How to Use Servo: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
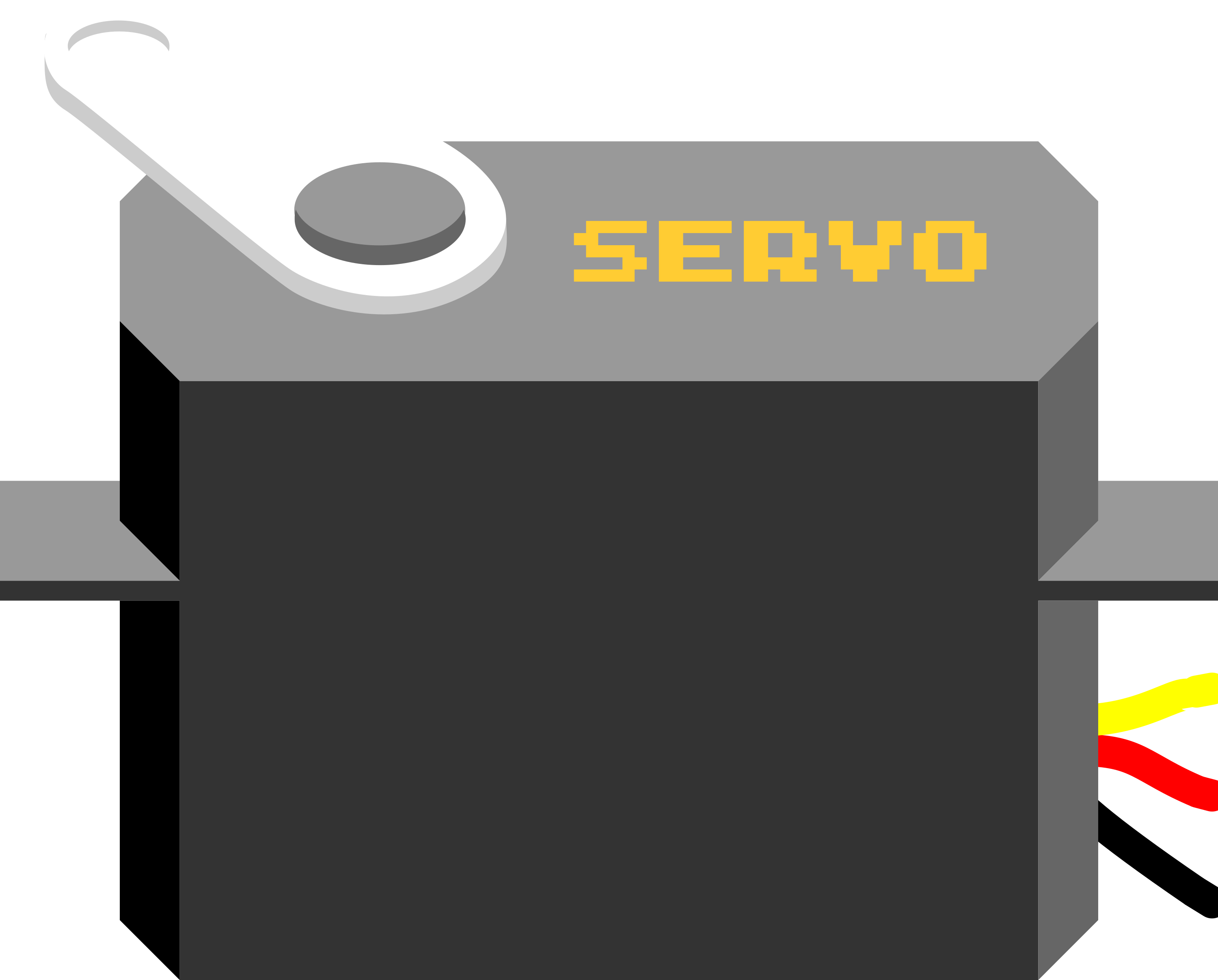
 Design with Servo in Cirkit Designer
Design with Servo in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A servo is a rotary actuator that allows for precise control of angular position, velocity, and acceleration. It consists of a motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback, along with a control circuit. Servos are widely used in robotics, automation, remote-controlled vehicles, and industrial machinery due to their ability to provide accurate and repeatable motion.
Explore Projects Built with Servo
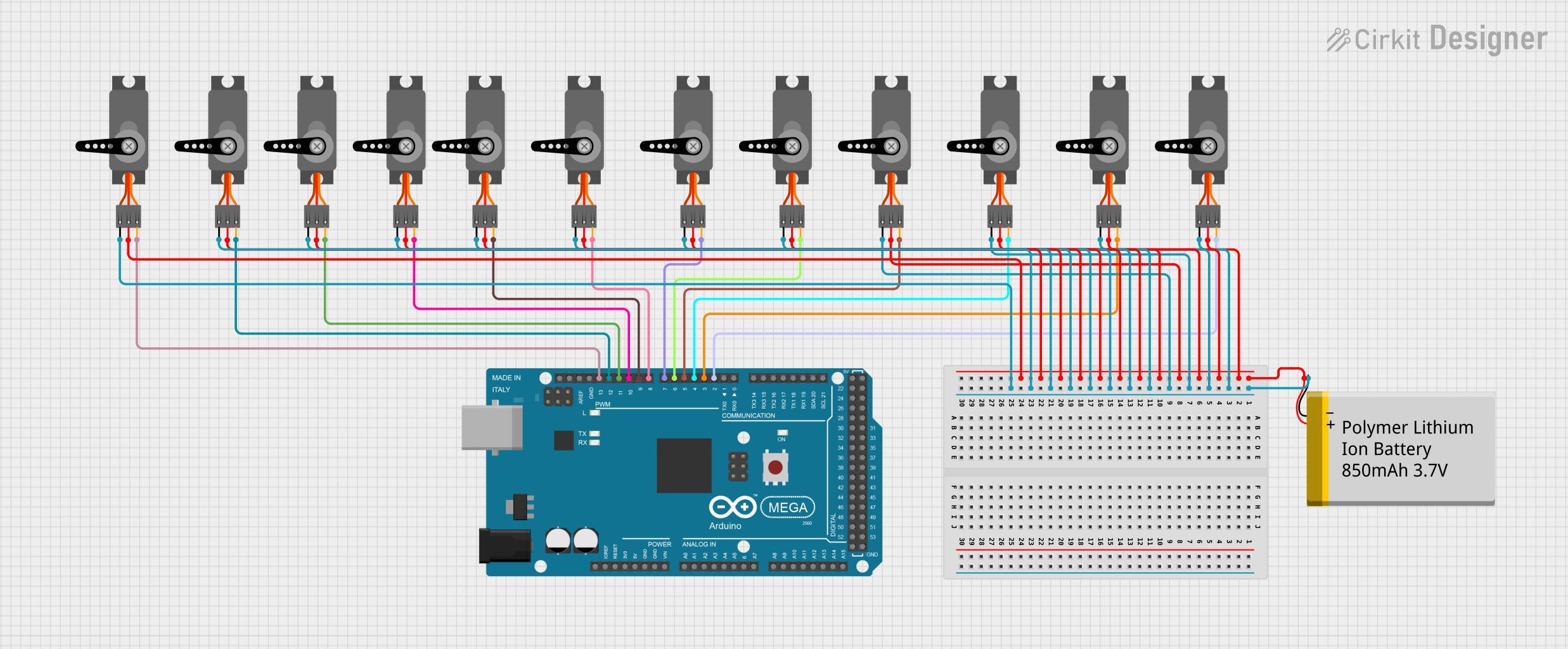
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer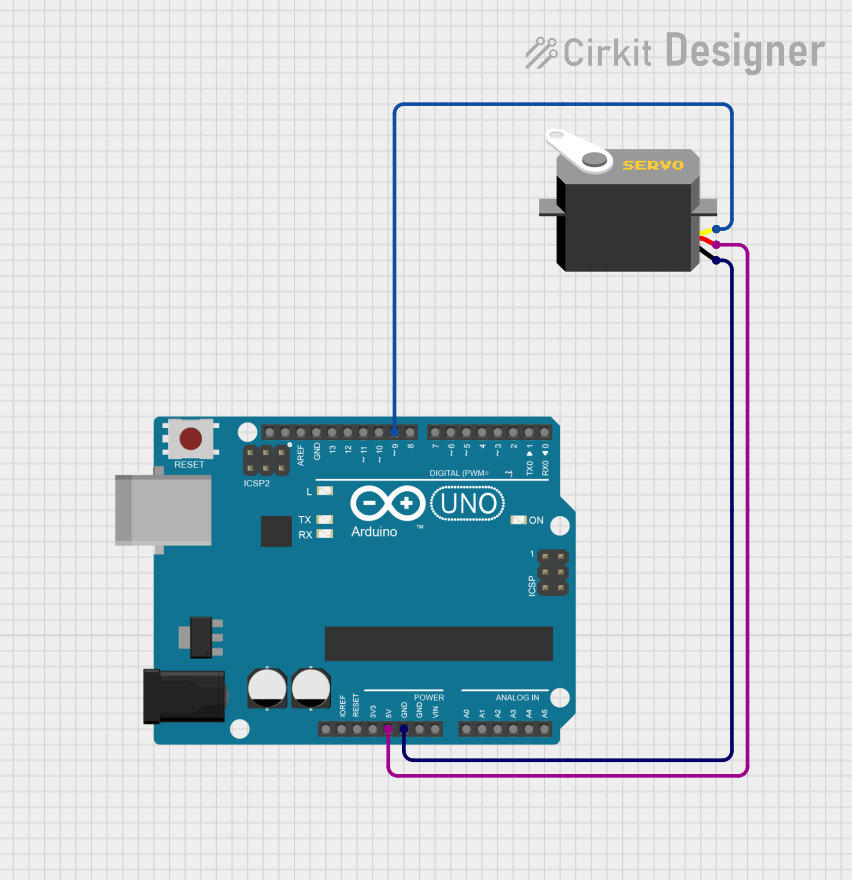
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer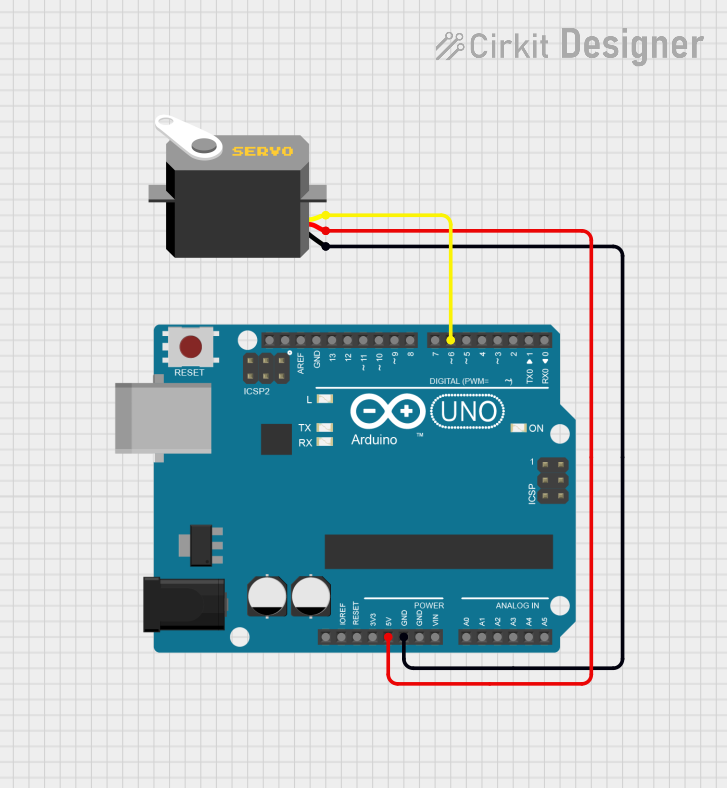
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer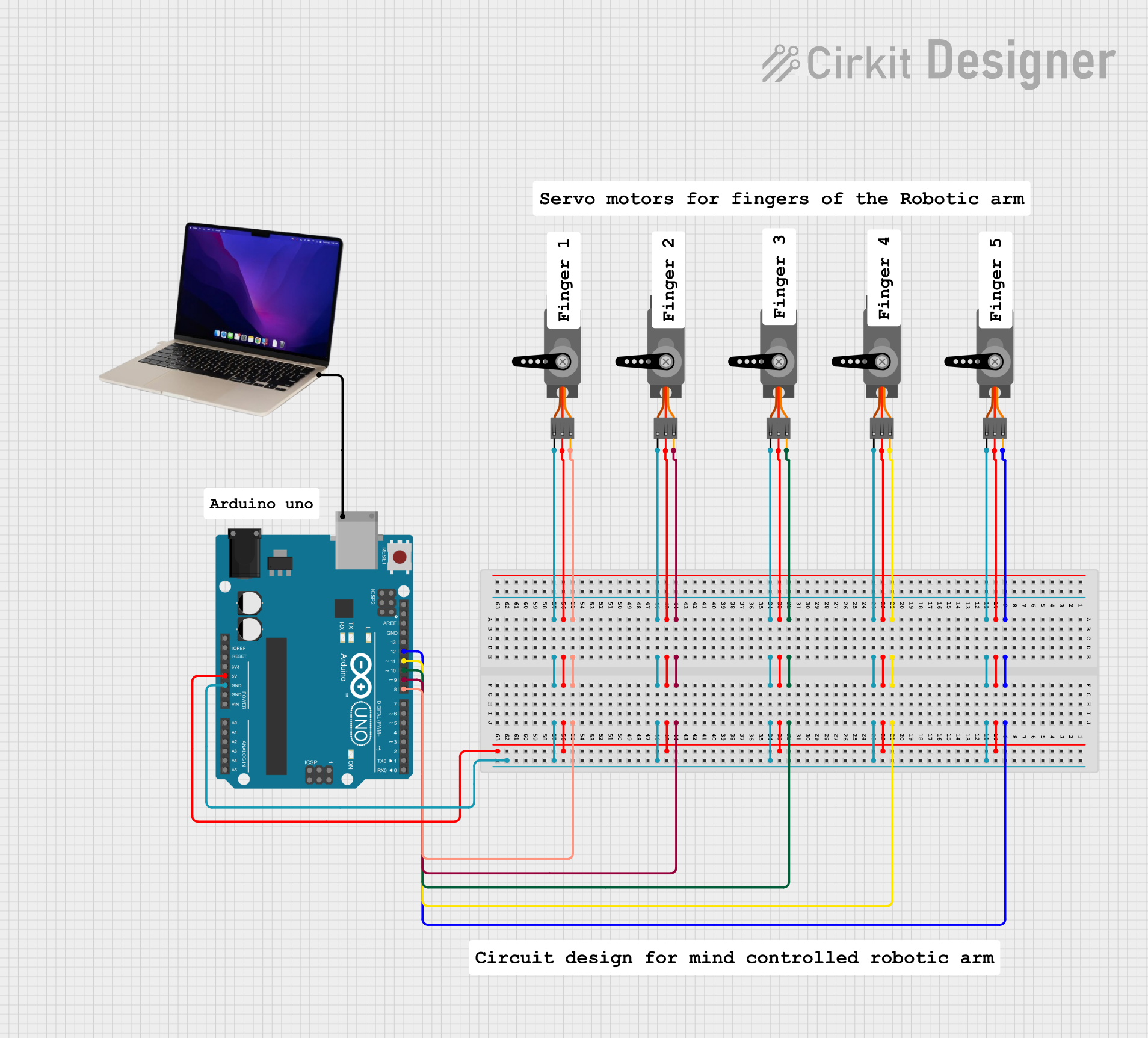
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Servo

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Robotics: For controlling robotic arms, grippers, and joints.
- RC Vehicles: Steering and throttle control in remote-controlled cars, boats, and planes.
- Automation Systems: Used in conveyor belts, pick-and-place machines, and other automated systems.
- Camera Gimbals: For stabilizing and controlling camera angles.
- DIY Projects: Popular in hobbyist projects involving Arduino and other microcontrollers.
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard hobby servo. Note that specifications may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer.
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 4.8V to 6V (typical for standard servos)
- Operating Current: 100mA to 1A (depending on load)
- Torque: 1.5 kg-cm to 20 kg-cm (varies by model)
- Rotation Range: 0° to 180° (standard), 360° for continuous rotation servos
- Control Signal: Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)
- Pulse width: 1ms (0°), 1.5ms (90°), 2ms (180°)
- Frequency: 50Hz (20ms period)
- Connector: 3-pin (Signal, VCC, GND)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Name | Description | Wire Color (Typical) |
|---|---|---|
| Signal | Receives PWM signal for control | Orange/White |
| VCC | Power supply (4.8V to 6V) | Red |
| GND | Ground connection | Brown/Black |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Servo in a Circuit
- Connect the Servo to a Power Source:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 5V power supply (or 6V if supported by the servo).
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of the power supply and the microcontroller.
- Connect the Signal Pin:
- Connect the Signal pin to a PWM-capable pin on your microcontroller (e.g., Arduino).
- Control the Servo:
- Use PWM signals to control the servo's position. The pulse width determines the angle:
- 1ms pulse: 0° position
- 1.5ms pulse: 90° position
- 2ms pulse: 180° position
- Use PWM signals to control the servo's position. The pulse width determines the angle:
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Ensure the servo has a stable power supply. Using a separate power source for the servo (instead of powering it directly from the microcontroller) is recommended to avoid voltage drops.
- Current Requirements: High-torque servos may draw significant current under load. Use a power supply capable of providing sufficient current.
- Signal Timing: Ensure the PWM signal frequency is set to 50Hz for standard servos.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the torque rating of the servo to prevent damage.
Example: Controlling a Servo with Arduino UNO
Below is an example code to control a servo using an Arduino UNO and the Servo library.
#include <Servo.h> // Include the Servo library
Servo myServo; // Create a Servo object
void setup() {
myServo.attach(9); // Attach the servo to pin 9 on the Arduino
}
void loop() {
myServo.write(0); // Move the servo to 0 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(90); // Move the servo to 90 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
myServo.write(180); // Move the servo to 180 degrees
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Notes on the Code
- The
Servolibrary simplifies the process of generating PWM signals for controlling the servo. - The
myServo.attach(9)function links the servo to pin 9, which must be a PWM-capable pin. - The
myServo.write(angle)function sets the servo to a specific angle (0° to 180°).
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Servo Not Moving:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Double-check the connections and ensure the power supply meets the servo's voltage and current requirements.
Jittery or Erratic Movement:
- Cause: Electrical noise or unstable power supply.
- Solution: Use a capacitor (e.g., 100µF) across the power supply to stabilize it.
Servo Overheating:
- Cause: Overloading the servo or running it continuously at high torque.
- Solution: Reduce the load or use a higher-torque servo.
Servo Not Responding to PWM Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect PWM frequency or pulse width.
- Solution: Ensure the PWM signal is set to 50Hz and the pulse width is within the 1ms to 2ms range.
FAQs
Q: Can I power the servo directly from the Arduino?
A: While it is possible for small, low-power servos, it is not recommended. Servos can draw significant current, which may exceed the Arduino's power output capacity. Use an external power supply for reliable operation.
Q: Can I control multiple servos with one Arduino?
A: Yes, you can control multiple servos using the Servo library. However, ensure your power supply can handle the combined current draw of all servos.
Q: What is the difference between a standard servo and a continuous rotation servo?
A: A standard servo is used for precise angular positioning (0° to 180°), while a continuous rotation servo is used for speed and direction control, similar to a DC motor.
Q: How do I increase the torque of my servo?
A: You cannot increase the torque of a servo beyond its rated capacity. If more torque is needed, use a servo with a higher torque rating.