
How to Use Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
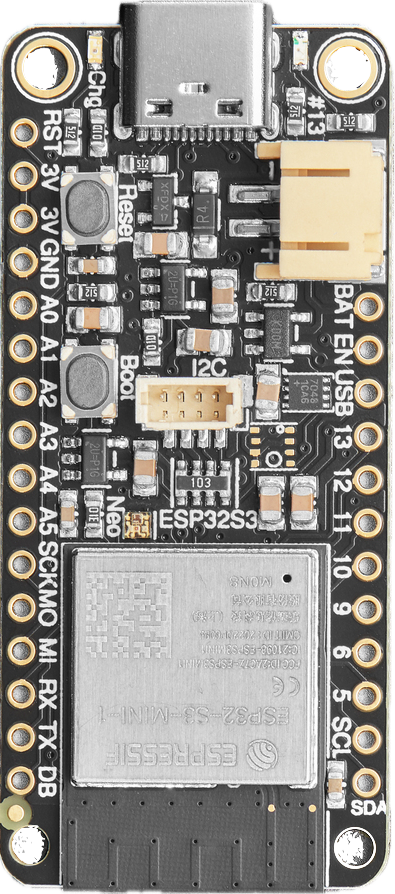
 Design with Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather in Cirkit Designer
Design with Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather (Part ID: 5323) is a compact and versatile microcontroller board designed for IoT and wearable applications. Powered by the ESP32-S3 chip, it features dual-core processing, integrated Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) capabilities. This board is part of Adafruit's Feather ecosystem, making it compatible with a wide range of FeatherWing add-ons for extended functionality. Its small form factor and robust connectivity options make it an excellent choice for projects requiring wireless communication, low power consumption, and high performance.
Explore Projects Built with Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather
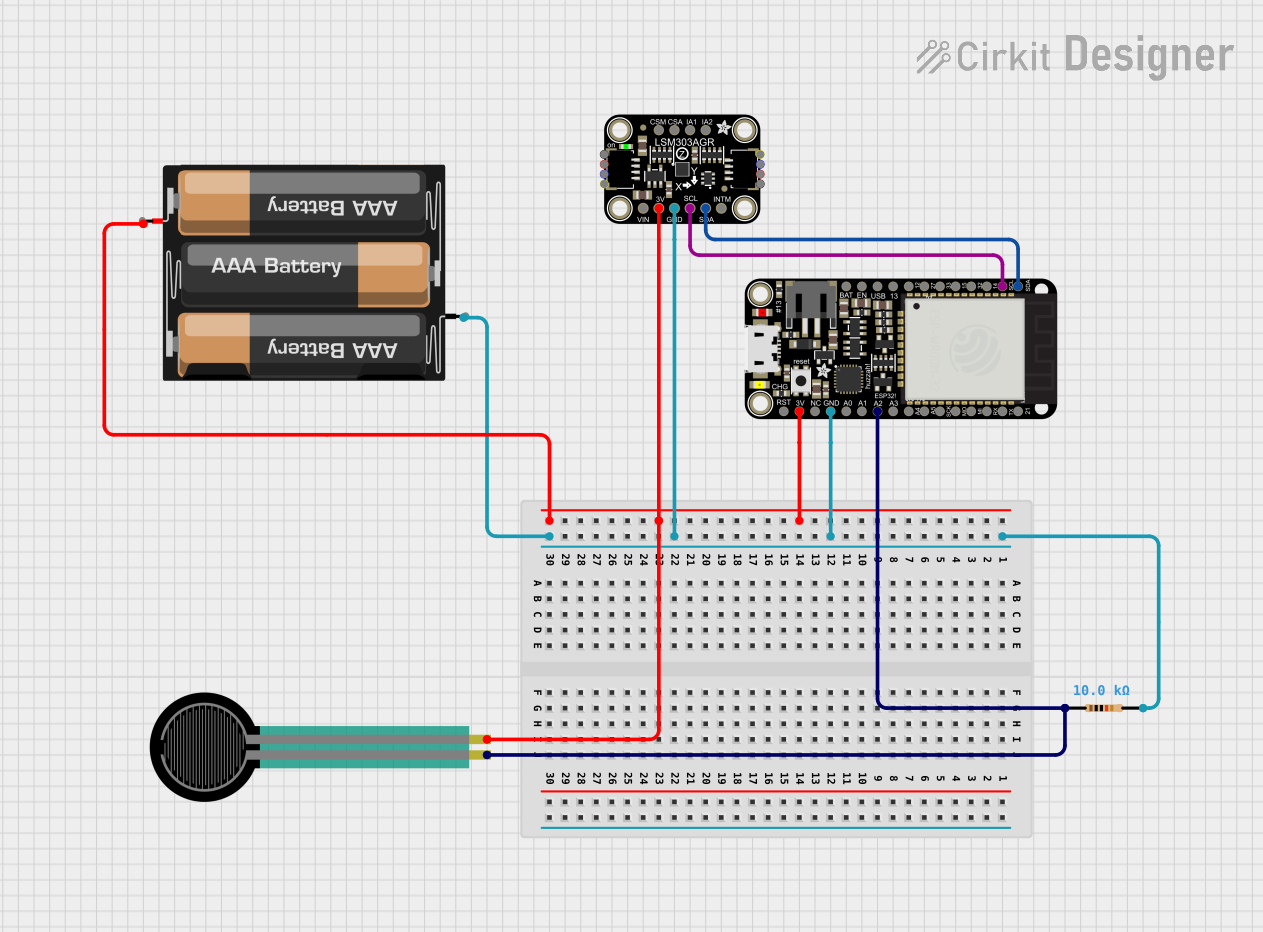
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer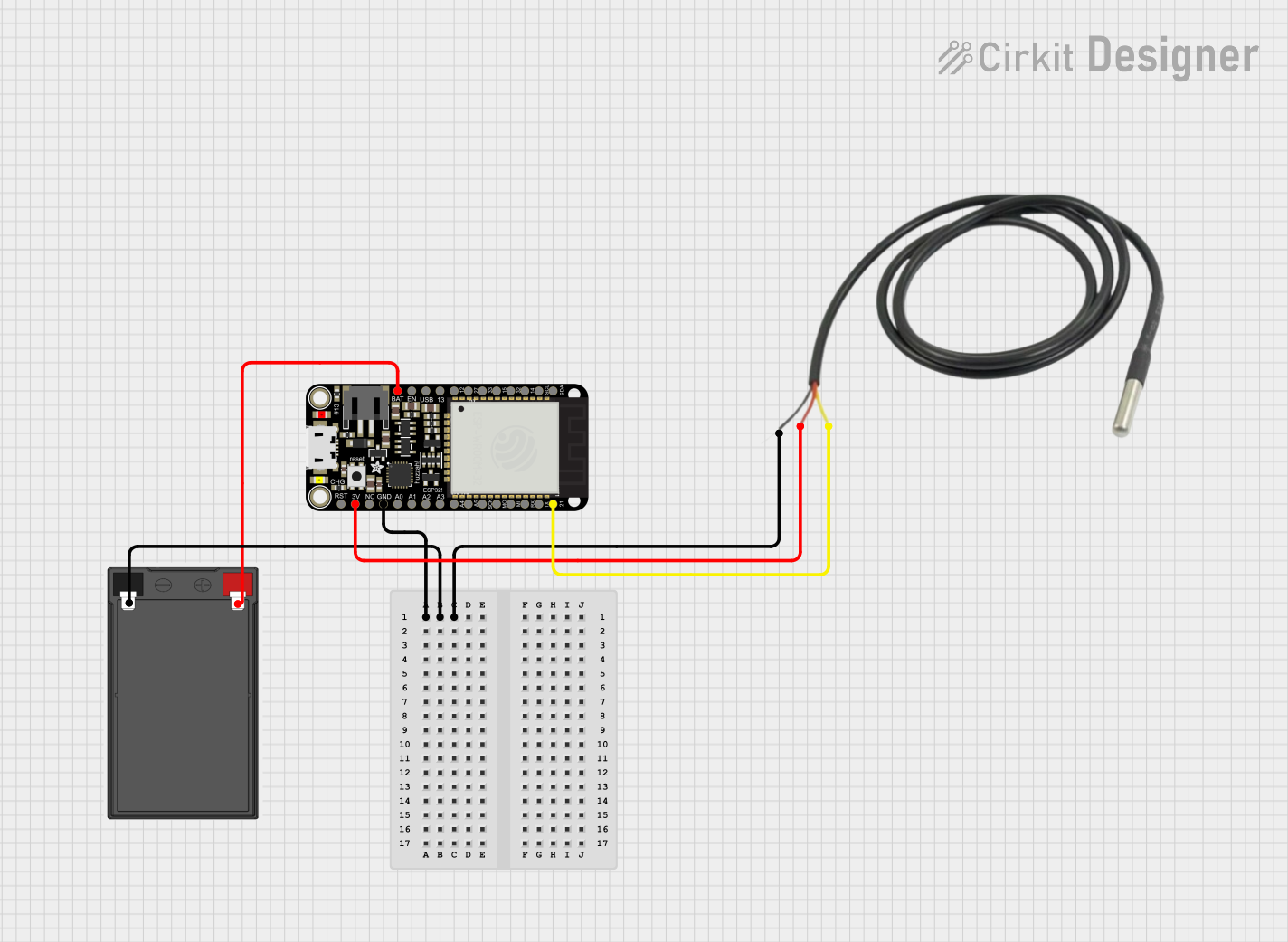
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer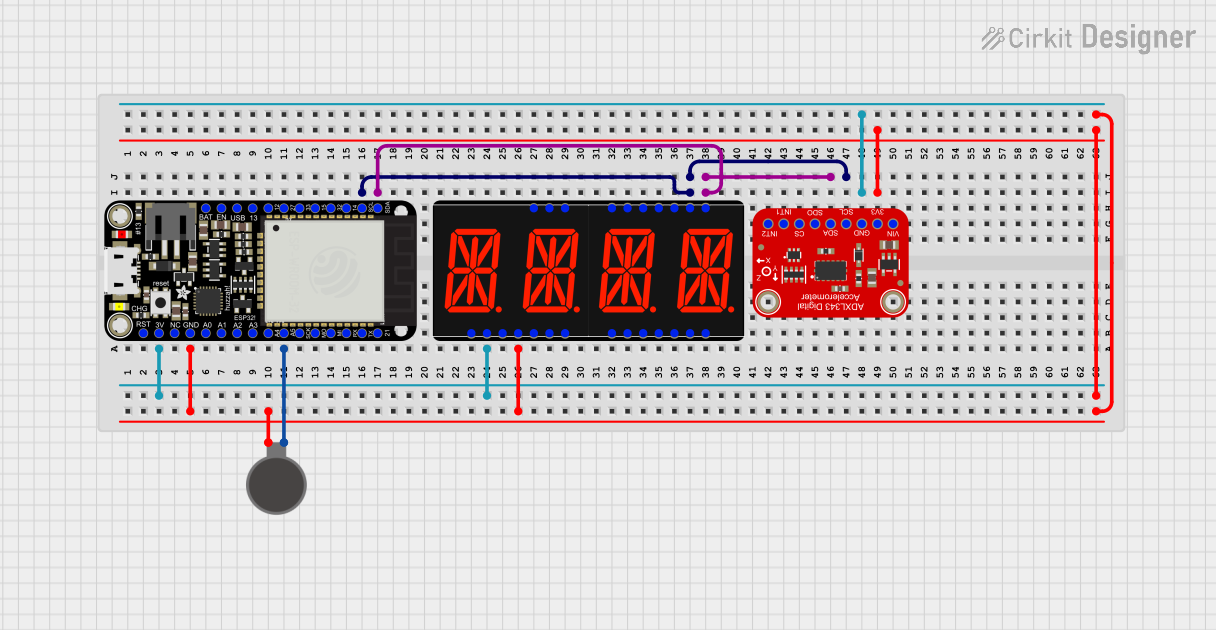
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer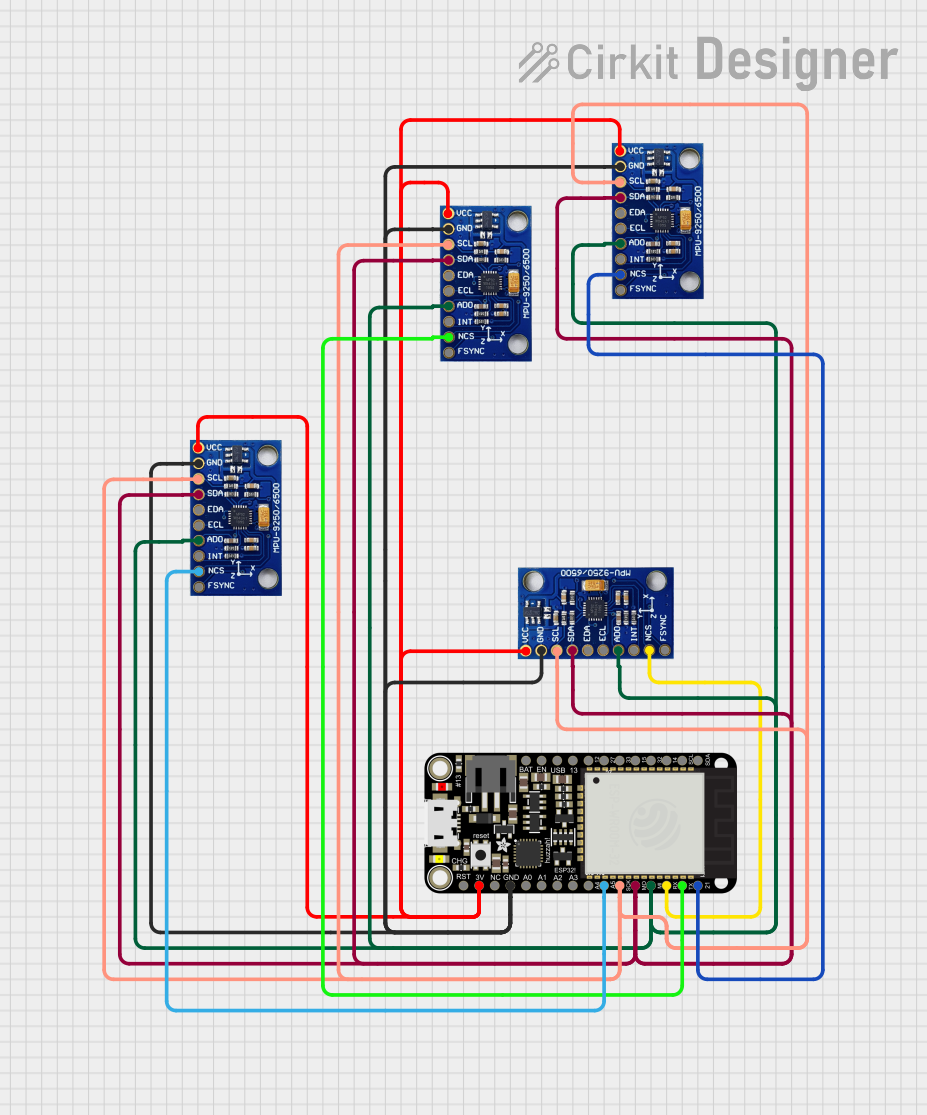
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home automation
- Wearable electronics
- Wireless data logging and monitoring
- Robotics and sensor networks
- Prototyping and development of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi-enabled applications
Technical Specifications
The Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather is packed with features to support a variety of applications. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
- Microcontroller: ESP32-S3 (dual-core Xtensa LX7 processor)
- Clock Speed: Up to 240 MHz
- Flash Memory: 8 MB
- PSRAM: 2 MB
- Connectivity: Wi-Fi (802.11 b/g/n) and Bluetooth 5.0 (LE)
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V
- Power Supply: USB-C or LiPo battery (3.7V)
- GPIO Pins: 21 (including ADC, DAC, I2C, SPI, UART, PWM)
- USB Interface: USB-C with native USB support
- Dimensions: 51mm x 23mm x 8mm
- Weight: 5.5g
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather has a standard Feather pinout. Below is the pin configuration:
| Pin Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VIN | Power Input | Input voltage (3.7V LiPo battery or 5V via USB-C). |
| 3V3 | Power Output | Regulated 3.3V output for external components. |
| GND | Ground | Ground connection. |
| A0 - A5 | Analog Input | ADC pins for analog signal input (12-bit resolution). |
| D0 - D13 | Digital I/O | General-purpose digital input/output pins. |
| SDA | I2C Data | I2C data line for communication with I2C devices. |
| SCL | I2C Clock | I2C clock line for communication with I2C devices. |
| RX | UART RX | UART receive pin for serial communication. |
| TX | UART TX | UART transmit pin for serial communication. |
| SCK | SPI Clock | SPI clock line for communication with SPI devices. |
| MOSI | SPI Data Out | SPI Master Out Slave In (data output). |
| MISO | SPI Data In | SPI Master In Slave Out (data input). |
| EN | Enable | Enable pin to reset or wake the microcontroller. |
| BAT | Battery Input | LiPo battery input (3.7V nominal). |
| USB | USB Power | USB-C power input for powering the board and charging the battery. |
Usage Instructions
The Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather is easy to use in a variety of projects. Follow the steps below to get started:
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
Powering the Board:
- Connect a 3.7V LiPo battery to the BAT pin or use a USB-C cable to power the board.
- The onboard regulator will provide a stable 3.3V to the microcontroller and peripherals.
Connecting Peripherals:
- Use the GPIO pins for connecting sensors, actuators, or other devices.
- For I2C devices, connect to the SDA and SCL pins.
- For SPI devices, use the SCK, MOSI, and MISO pins.
Programming the Board:
- Install the ESP32-S3 board support package in the Arduino IDE or use MicroPython.
- Connect the board to your computer via USB-C and select the appropriate COM port.
Uploading Code:
- Write your code in the Arduino IDE or MicroPython editor.
- Compile and upload the code to the board.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the input voltage does not exceed the recommended range to avoid damaging the board.
- Use level shifters when interfacing with 5V logic devices, as the ESP32-S3 operates at 3.3V logic.
- For battery-powered applications, monitor the battery voltage to prevent over-discharge.
- Use the onboard USB-C connector for both programming and charging the LiPo battery.
Example Code for Arduino UNO Integration
Below is an example of how to use the Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather to read an analog sensor and send data over Wi-Fi:
#include <WiFi.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "Your_SSID";
const char* password = "Your_PASSWORD";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200); // Initialize serial communication
WiFi.begin(ssid, password); // Connect to Wi-Fi
// Wait for connection
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(1000);
Serial.println("Connecting to Wi-Fi...");
}
Serial.println("Connected to Wi-Fi!");
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(A0); // Read analog value from pin A0
Serial.print("Sensor Value: ");
Serial.println(sensorValue);
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before reading again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Board Not Detected by Computer:
- Ensure the USB-C cable is a data cable, not a charge-only cable.
- Check that the correct COM port is selected in the Arduino IDE.
Wi-Fi Connection Fails:
- Verify the SSID and password are correct.
- Ensure the Wi-Fi network is within range and supports 2.4 GHz (ESP32-S3 does not support 5 GHz).
Code Upload Fails:
- Press and hold the BOOT button while clicking the upload button in the Arduino IDE.
- Ensure the correct board and port are selected in the IDE.
Battery Not Charging:
- Check the LiPo battery connection and ensure it is within the recommended voltage range.
- Verify the USB-C cable is providing power.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE to debug and view error messages.
- Update the ESP32-S3 board support package to the latest version.
- Refer to the Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather product page for additional resources and support.
By following this documentation, you can effectively utilize the Adafruit ESP32-S3 Feather in your projects and troubleshoot common issues with ease.