
How to Use VCC 5V: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
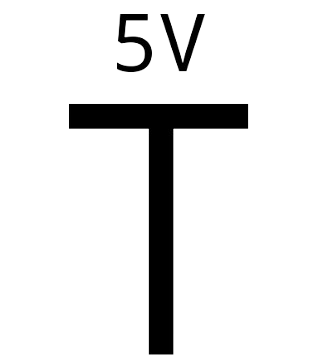
 Design with VCC 5V in Cirkit Designer
Design with VCC 5V in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
- The VCC 5V is a power supply voltage reference that provides a constant 5 volts. It is widely used in electronic circuits to power digital components, microcontrollers, sensors, and other low-power devices.
- Common applications include powering Arduino boards, logic circuits, sensors, and modules such as LCD displays, Wi-Fi modules, and motor drivers.
Explore Projects Built with VCC 5V
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with VCC 5V

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerTechnical Specifications
- Voltage Output: 5V DC (Direct Current)
- Current Rating: Typically up to 1A (varies depending on the power source)
- Power Source: Can be derived from USB, batteries, or regulated power supplies
- Polarity: Positive voltage reference (VCC) with respect to ground (GND)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The VCC 5V is typically represented as a pin or terminal in circuits. Below is a general description of its connections:
| Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|
| VCC | Positive 5V power supply output |
| GND | Ground connection (0V reference point) |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the VCC 5V in a Circuit
- Connect the Power Source: Ensure the power source (e.g., USB, battery, or regulated power supply) provides a stable 5V output.
- Polarity Check: Always connect the VCC pin to the positive terminal of the circuit and the GND pin to the ground terminal.
- Powering Components: Use the VCC 5V to power digital ICs, sensors, and modules that require a 5V input. Ensure the total current draw does not exceed the power source's capacity.
- Bypass Capacitors: Add a 0.1µF ceramic capacitor and a 10µF electrolytic capacitor near the VCC pin to filter noise and stabilize the voltage.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Regulation: If the input power source is higher than 5V, use a voltage regulator (e.g., 7805 or LM317) to step down the voltage to 5V.
- Current Limitations: Ensure the total current drawn by the circuit does not exceed the maximum current rating of the power source.
- Heat Dissipation: If using a linear regulator to generate 5V, ensure proper heat dissipation to avoid overheating.
- Avoid Reverse Polarity: Connecting the VCC and GND pins incorrectly can damage the circuit.
Example: Using VCC 5V with an Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO has a built-in 5V VCC pin that can be used to power external components. Below is an example of powering an LED with a resistor using the VCC 5V pin:
// Example: Powering an LED using the Arduino UNO's VCC 5V pin
// Define the pin connected to the LED
const int ledPin = 13; // Pin 13 is connected to the onboard LED
void setup() {
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT); // Set the LED pin as an output
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
- In this example, the Arduino's onboard 5V VCC pin powers the microcontroller and the LED circuit. Ensure the LED has a current-limiting resistor (e.g., 220Ω) to prevent damage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues
Voltage Drop: The VCC 5V output is lower than expected.
- Solution: Check the power source's capacity and ensure it can supply sufficient current. Verify connections and add bypass capacitors to stabilize the voltage.
Overheating: The voltage regulator or power source becomes hot.
- Solution: Reduce the current draw by disconnecting unnecessary components. Use a heatsink or switch to a more efficient power source.
No Power Output: The circuit does not receive 5V from the VCC pin.
- Solution: Verify the polarity of the connections. Check for loose wires or damaged components.
FAQs
Q: Can I use the VCC 5V to power a 3.3V device?
A: No, 3.3V devices may be damaged by a 5V supply. Use a voltage regulator or level shifter to step down the voltage.Q: What happens if I exceed the current rating of the VCC 5V?
A: Exceeding the current rating can cause the power source to overheat, shut down, or fail. Always ensure the total current draw is within the power source's limits.Q: Can I connect multiple devices to the VCC 5V pin?
A: Yes, as long as the total current draw of all devices does not exceed the power source's capacity.
By following these guidelines, you can effectively use the VCC 5V in your electronic projects.