
How to Use esp8266: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
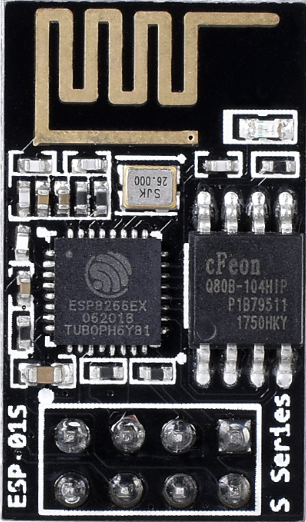
 Design with esp8266 in Cirkit Designer
Design with esp8266 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP8266 is a low-cost Wi-Fi microchip with a full TCP/IP stack and microcontroller capability. It is widely used in Internet of Things (IoT) applications to enable devices to connect to the internet. The ESP8266 is highly versatile, offering a compact design, low power consumption, and robust wireless communication capabilities. It can operate as both a standalone microcontroller or as a Wi-Fi module for other microcontrollers.
Explore Projects Built with esp8266
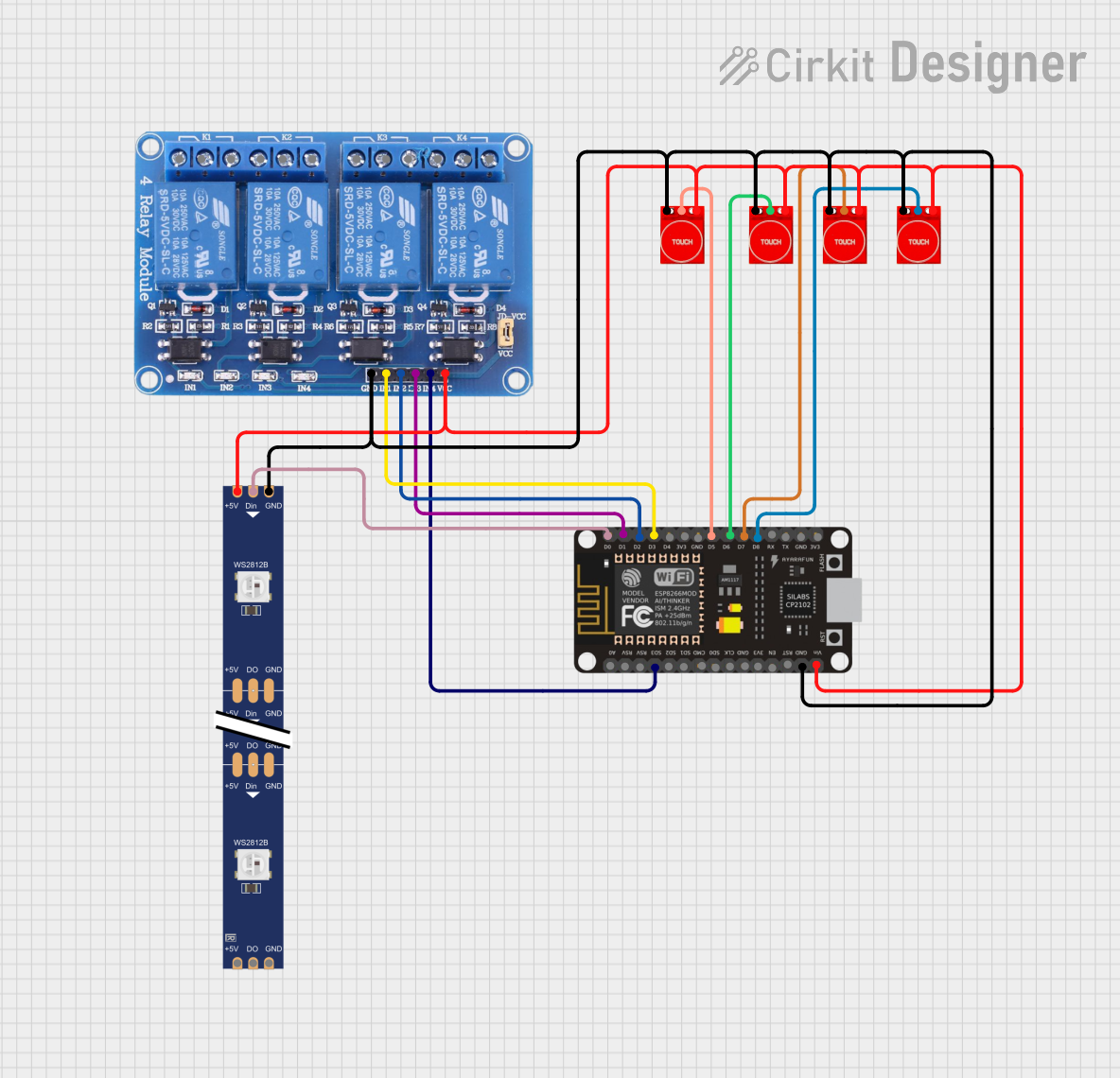
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer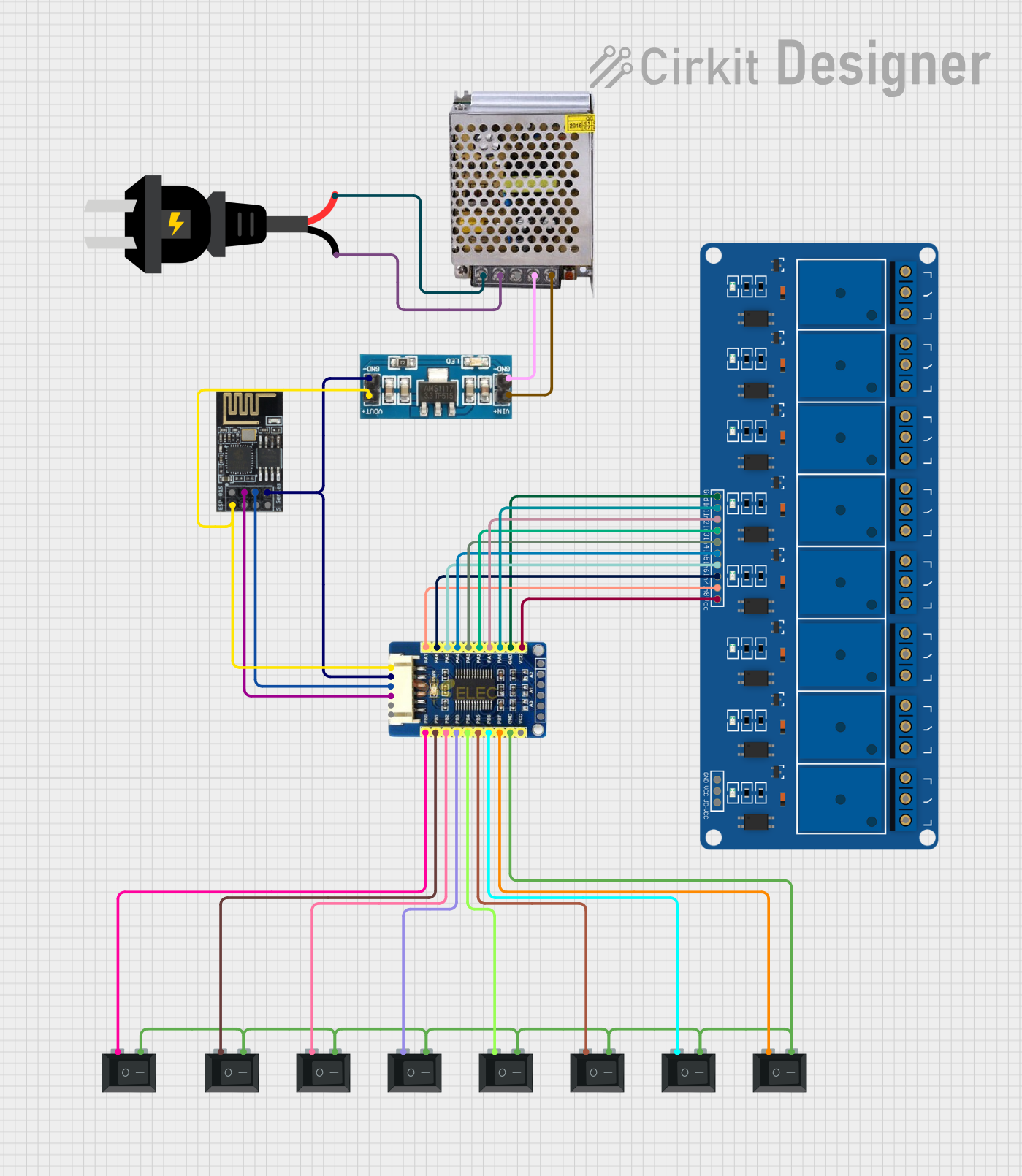
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer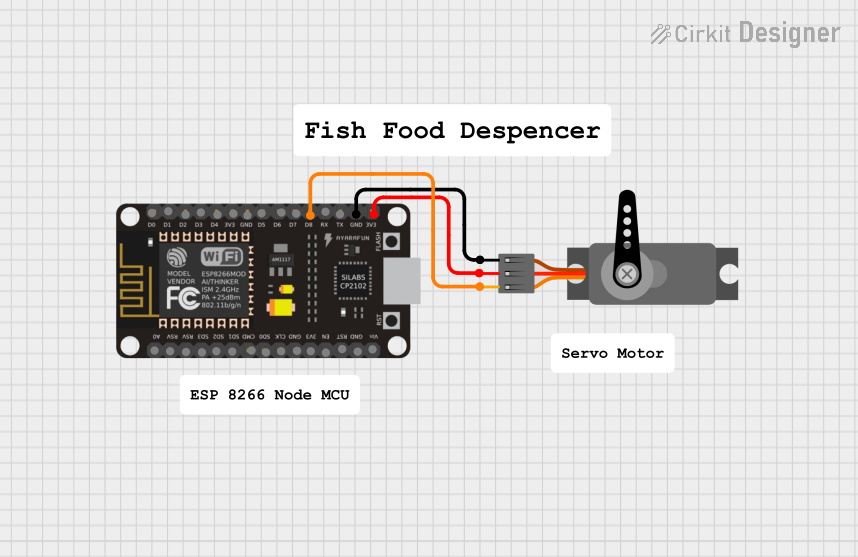
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with esp8266

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Home automation systems
- Smart appliances
- Wireless sensor networks
- Remote monitoring and control
- IoT prototyping and development
- Data logging and cloud integration
Technical Specifications
The ESP8266 is available in various module formats, with the ESP-01 being one of the most popular. Below are the key technical specifications:
General Specifications
- Microcontroller: 32-bit Tensilica L106 running at 80 MHz (can be overclocked to 160 MHz)
- Wi-Fi: IEEE 802.11 b/g/n, 2.4 GHz
- Flash Memory: 512 KB to 4 MB (depending on the module)
- Operating Voltage: 3.0V to 3.6V
- Power Consumption:
- Deep Sleep: ~10 µA
- Idle: ~70 mA
- Active: ~200 mA (transmitting)
- GPIO Pins: Up to 17 (depending on the module)
- Communication Protocols: UART, SPI, I2C, PWM, ADC (10-bit)
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
Below is the pinout for the ESP-01 module, one of the most common ESP8266 variants:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply (3.3V). Do not exceed 3.6V. |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection. |
| 3 | TX | UART Transmit pin. Used for serial communication. |
| 4 | RX | UART Receive pin. Used for serial communication. |
| 5 | CH_PD/EN | Chip enable. Must be pulled HIGH (3.3V) to enable the module. |
| 6 | GPIO0 | General-purpose I/O pin. Used for boot mode selection during startup. |
| 7 | GPIO2 | General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 8 | RST | Reset pin. Pull LOW to reset the module. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the ESP8266 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Ensure the ESP8266 is powered with a stable 3.3V source. Using a voltage regulator is recommended to avoid damage.
- Connections:
- Connect the VCC pin to a 3.3V power source.
- Connect the GND pin to the ground of your circuit.
- Use a logic level shifter if interfacing with 5V microcontrollers like Arduino UNO.
- Boot Mode:
- For normal operation, pull GPIO0 HIGH.
- For flashing firmware, pull GPIO0 LOW during power-up.
- Serial Communication:
- Connect the TX pin of the ESP8266 to the RX pin of your microcontroller.
- Connect the RX pin of the ESP8266 to the TX pin of your microcontroller.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 10 µF) near the VCC and GND pins to stabilize the power supply.
- Avoid exposing the module to voltages higher than 3.6V to prevent damage.
- Ensure proper heat dissipation if the module operates for extended periods.
- Use an external antenna for better Wi-Fi range if your module supports it.
Example: Connecting ESP8266 to Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the ESP8266 with an Arduino UNO to connect to a Wi-Fi network and send data to a server.
Circuit Diagram
- ESP8266 VCC → 3.3V (via voltage regulator)
- ESP8266 GND → Arduino GND
- ESP8266 TX → Arduino RX (via voltage divider for 5V to 3.3V conversion)
- ESP8266 RX → Arduino TX
Arduino Code
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Define RX and TX pins for SoftwareSerial
SoftwareSerial esp8266(2, 3); // RX, TX
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Start Serial Monitor
esp8266.begin(9600); // Start ESP8266 communication
// Connect to Wi-Fi
sendCommand("AT+RST", 2000); // Reset the module
sendCommand("AT+CWMODE=1", 1000); // Set Wi-Fi mode to Station
sendCommand("AT+CWJAP=\"YourSSID\",\"YourPassword\"", 5000); // Connect to Wi-Fi
}
void loop() {
// Example: Send data to a server
sendCommand("AT+CIPSTART=\"TCP\",\"example.com\",80", 2000); // Connect to server
sendCommand("AT+CIPSEND=18", 1000); // Prepare to send 18 bytes
esp8266.println("GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n"); // Send HTTP GET request
delay(2000);
}
void sendCommand(String command, int timeout) {
esp8266.println(command); // Send command to ESP8266
long int time = millis();
while ((time + timeout) > millis()) {
while (esp8266.available()) {
char c = esp8266.read(); // Read response
Serial.print(c); // Print response to Serial Monitor
}
}
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
ESP8266 Not Responding to AT Commands:
- Ensure the baud rate matches the module's default (usually 9600 or 115200).
- Check the wiring, especially the TX and RX connections.
- Verify that the CH_PD/EN pin is pulled HIGH.
Wi-Fi Connection Fails:
- Double-check the SSID and password in the
AT+CWJAPcommand. - Ensure the Wi-Fi network is within range and supports 2.4 GHz.
- Double-check the SSID and password in the
Module Overheating:
- Use a proper heat sink or ensure adequate ventilation.
- Verify that the power supply is stable and within the recommended range.
Frequent Resets:
- Add a decoupling capacitor near the power pins.
- Check for power supply fluctuations.
FAQs
Q: Can the ESP8266 be programmed directly without an Arduino?
A: Yes, the ESP8266 can be programmed using the Arduino IDE or other tools like NodeMCU firmware.Q: What is the maximum range of the ESP8266 Wi-Fi?
A: The range is approximately 100 meters in open space, but it may vary depending on obstacles and interference.Q: Can the ESP8266 operate on 5V?
A: No, the ESP8266 operates on 3.3V. Use a voltage regulator or level shifter when interfacing with 5V systems.