
How to Use Fan: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs

 Design with Fan in Cirkit Designer
Design with Fan in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
A fan is an electromechanical device designed to create airflow, which is essential for cooling or ventilating an area. In electronics, fans are commonly used to dissipate heat generated by components such as processors, power supplies, and other heat-sensitive devices. By maintaining proper airflow, fans help ensure the longevity and reliability of electronic systems.
Explore Projects Built with Fan
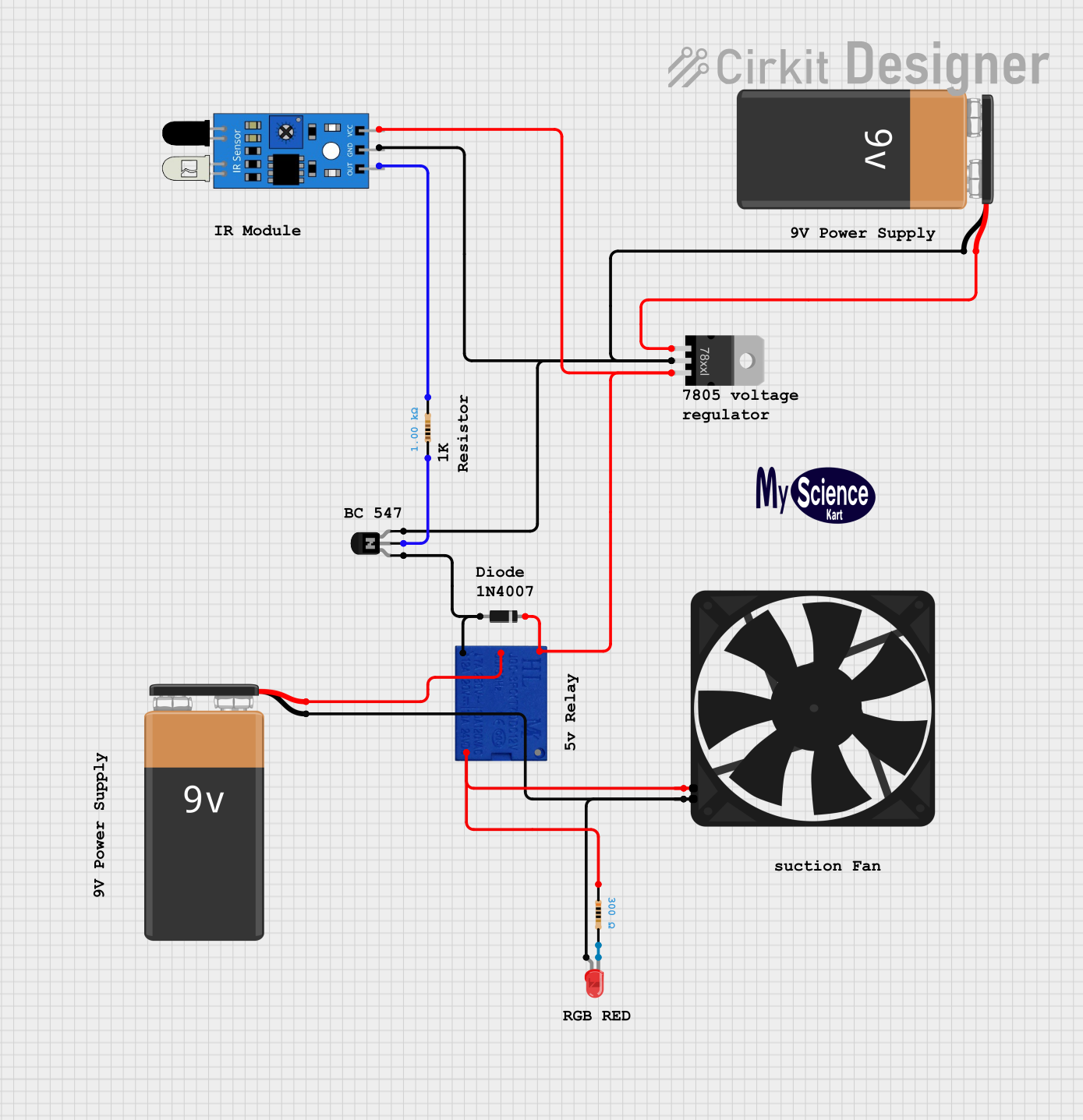
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer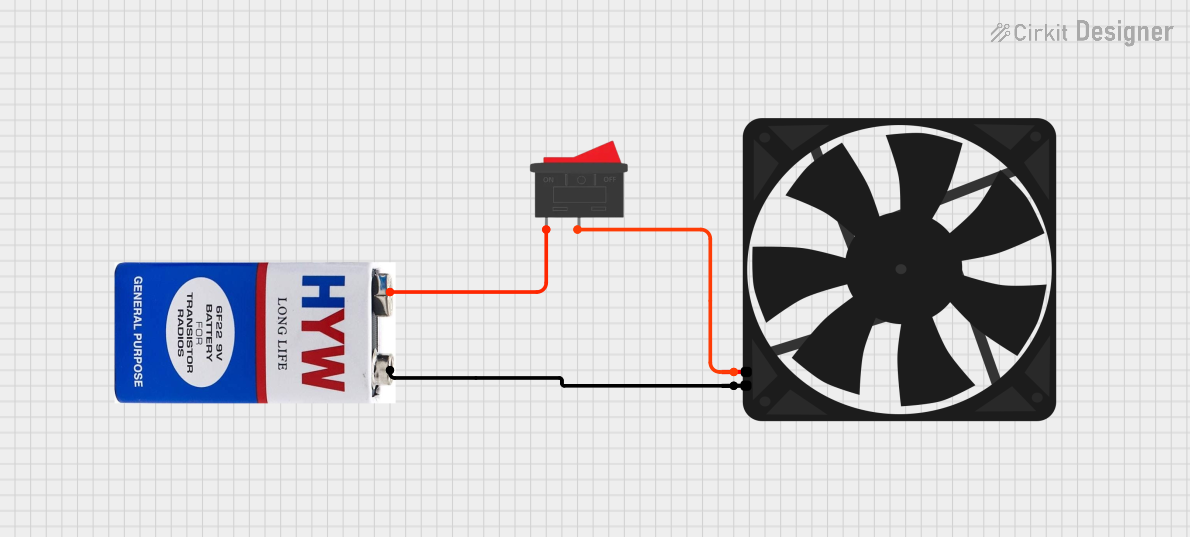
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer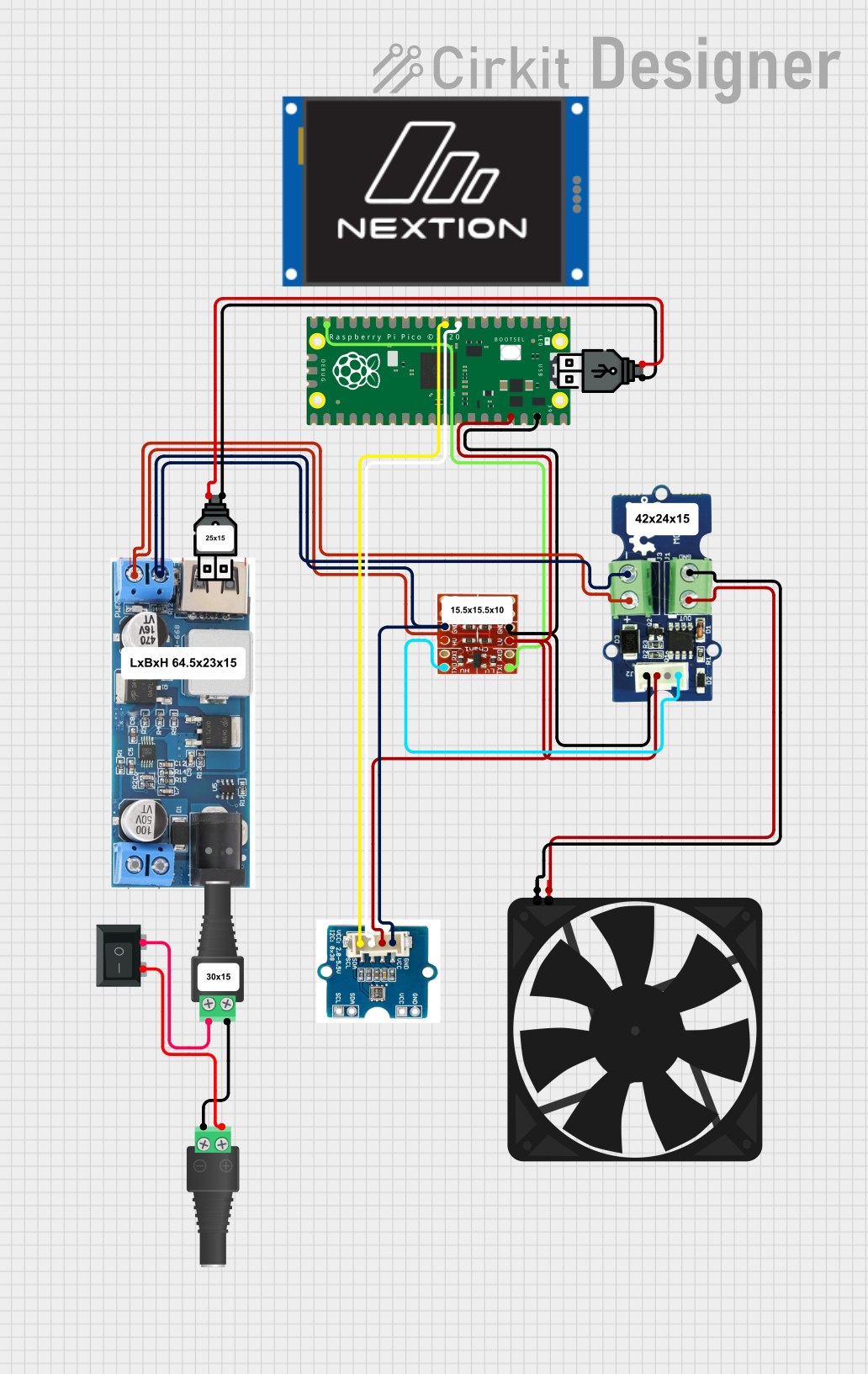
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Fan

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Cooling computer processors, GPUs, and power supplies
- Ventilating electronic enclosures and cabinets
- Heat dissipation in industrial equipment
- Air circulation in HVAC systems
- Cooling 3D printers and other machinery
Technical Specifications
Below are the general technical specifications for a standard DC cooling fan. Specifications may vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer.
General Specifications
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 5V, 12V, or 24V DC |
| Current Consumption | 0.1A to 0.5A (varies by size) |
| Power Rating | 0.5W to 5W |
| Speed | 1000 to 5000 RPM |
| Airflow | 10 to 100 CFM (Cubic Feet/Minute) |
| Noise Level | 20 to 40 dBA |
| Bearing Type | Sleeve or Ball Bearing |
| Connector Type | 2-pin, 3-pin, or 4-pin |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
2-Pin Fan
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Positive power supply (e.g., 12V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
3-Pin Fan
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Positive power supply (e.g., 12V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | Tachometer | Outputs a signal for speed monitoring |
4-Pin Fan
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Positive power supply (e.g., 12V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | Tachometer | Outputs a signal for speed monitoring |
| 4 | PWM | Pulse Width Modulation for speed control |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Fan in a Circuit
- Determine the Operating Voltage: Ensure the fan's voltage rating matches your power supply (e.g., 12V DC).
- Connect the Power Pins:
- For a 2-pin fan, connect the VCC pin to the positive terminal of the power supply and the GND pin to the ground.
- For a 3-pin or 4-pin fan, connect the VCC and GND pins as above.
- Optional Connections:
- For a 3-pin fan, connect the tachometer pin to a microcontroller or monitoring circuit to measure fan speed.
- For a 4-pin fan, connect the PWM pin to a microcontroller or PWM controller to adjust the fan speed.
- Secure the Fan: Mount the fan securely in the desired location using screws or brackets to ensure proper airflow.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Power Supply: Use a stable DC power supply with sufficient current capacity to avoid damaging the fan.
- Orientation: Install the fan in the correct orientation to ensure airflow is directed as needed.
- Noise Reduction: Use rubber mounts or grommets to minimize vibration and noise.
- Speed Control: For 4-pin fans, use PWM signals to adjust the speed and reduce power consumption when full speed is not required.
- Dust Management: Periodically clean the fan blades and surrounding area to prevent dust buildup, which can reduce efficiency.
Example: Controlling a 4-Pin Fan with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control a 4-pin fan using an Arduino UNO and PWM.
// Define the PWM pin connected to the fan's PWM input
const int fanPwmPin = 9;
void setup() {
// Set the PWM pin as an output
pinMode(fanPwmPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Set fan speed to 50% (128 out of 255)
analogWrite(fanPwmPin, 128);
delay(5000); // Run at 50% speed for 5 seconds
// Set fan speed to 100% (255 out of 255)
analogWrite(fanPwmPin, 255);
delay(5000); // Run at full speed for 5 seconds
// Set fan speed to 0% (fan off)
analogWrite(fanPwmPin, 0);
delay(5000); // Fan off for 5 seconds
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Fan Does Not Spin:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or insufficient power supply.
- Solution: Verify the connections and ensure the power supply matches the fan's voltage and current requirements.
Fan is Noisy:
- Cause: Dust buildup, loose mounting, or worn bearings.
- Solution: Clean the fan blades, tighten the mounting screws, or replace the fan if the bearings are worn.
Fan Speed is Not Adjustable:
- Cause: PWM signal not properly configured or incompatible fan.
- Solution: Check the PWM signal frequency and duty cycle. Ensure the fan supports PWM control.
Fan Overheats or Fails Prematurely:
- Cause: Overvoltage, undervoltage, or excessive dust.
- Solution: Use a regulated power supply, clean the fan regularly, and avoid operating the fan outside its rated voltage range.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a 12V fan with a 5V power supply?
A: No, a 12V fan requires a 12V power supply to operate correctly. Using a lower voltage will result in insufficient airflow or failure to spin.
Q: How do I measure the fan's speed using the tachometer pin?
A: Connect the tachometer pin to a microcontroller's input pin and use an interrupt or frequency measurement function to calculate the RPM.
Q: Can I control a 2-pin fan's speed?
A: Speed control for a 2-pin fan is limited. You can use a variable voltage power supply or a transistor-based circuit to adjust the voltage, but this is less precise than PWM control.
Q: How often should I clean the fan?
A: Clean the fan every 3-6 months, or more frequently in dusty environments, to maintain optimal performance.