
How to Use ESP32-WROOM-32UE: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
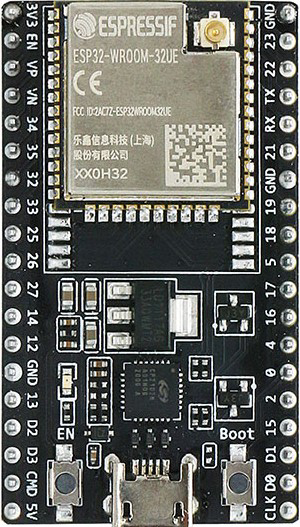
 Design with ESP32-WROOM-32UE in Cirkit Designer
Design with ESP32-WROOM-32UE in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The ESP32-WROOM-32UE is a high-performance Wi-Fi and Bluetooth microcontroller module developed by Espressif Systems. It features dual-core processing, making it an excellent choice for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, embedded systems, and wireless communication projects. With its compact design and robust capabilities, the ESP32-WROOM-32UE is widely used in smart devices, home automation, industrial automation, and wearable electronics.
Explore Projects Built with ESP32-WROOM-32UE
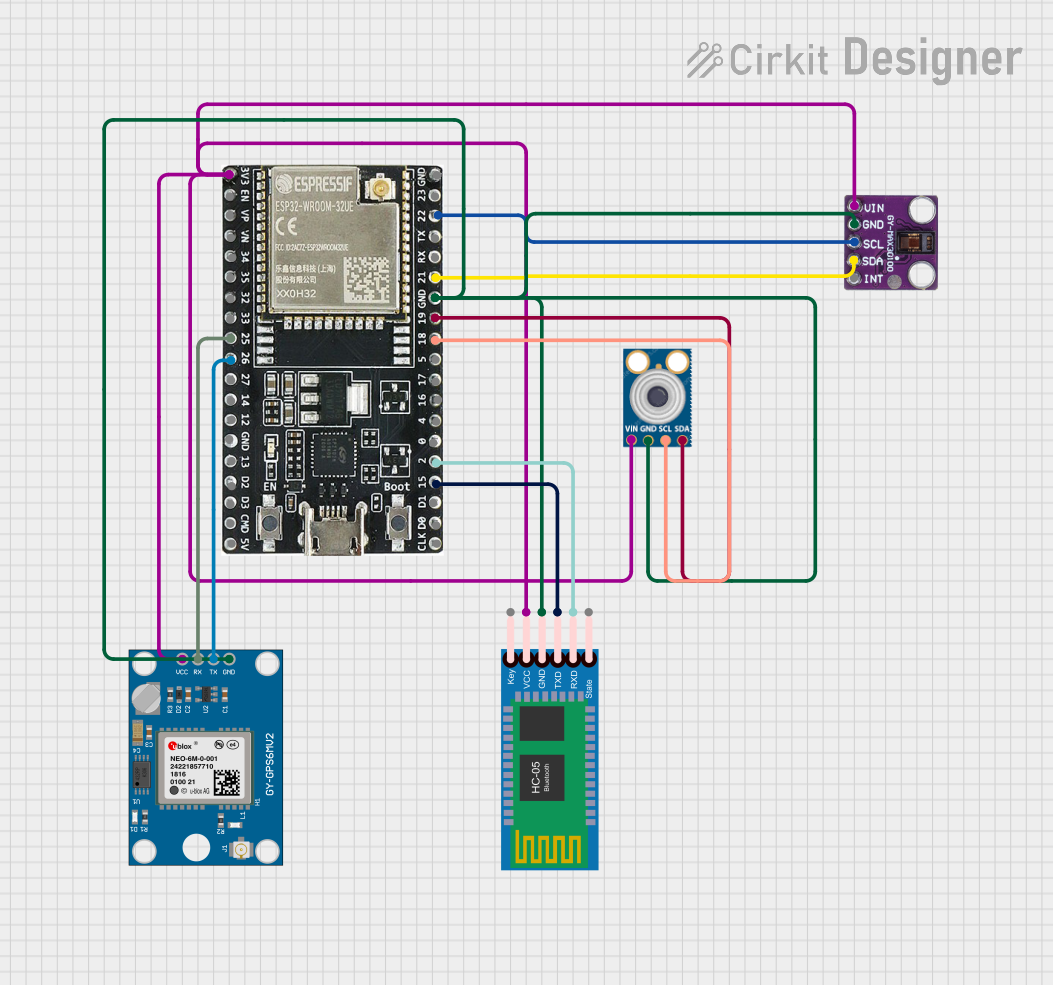
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer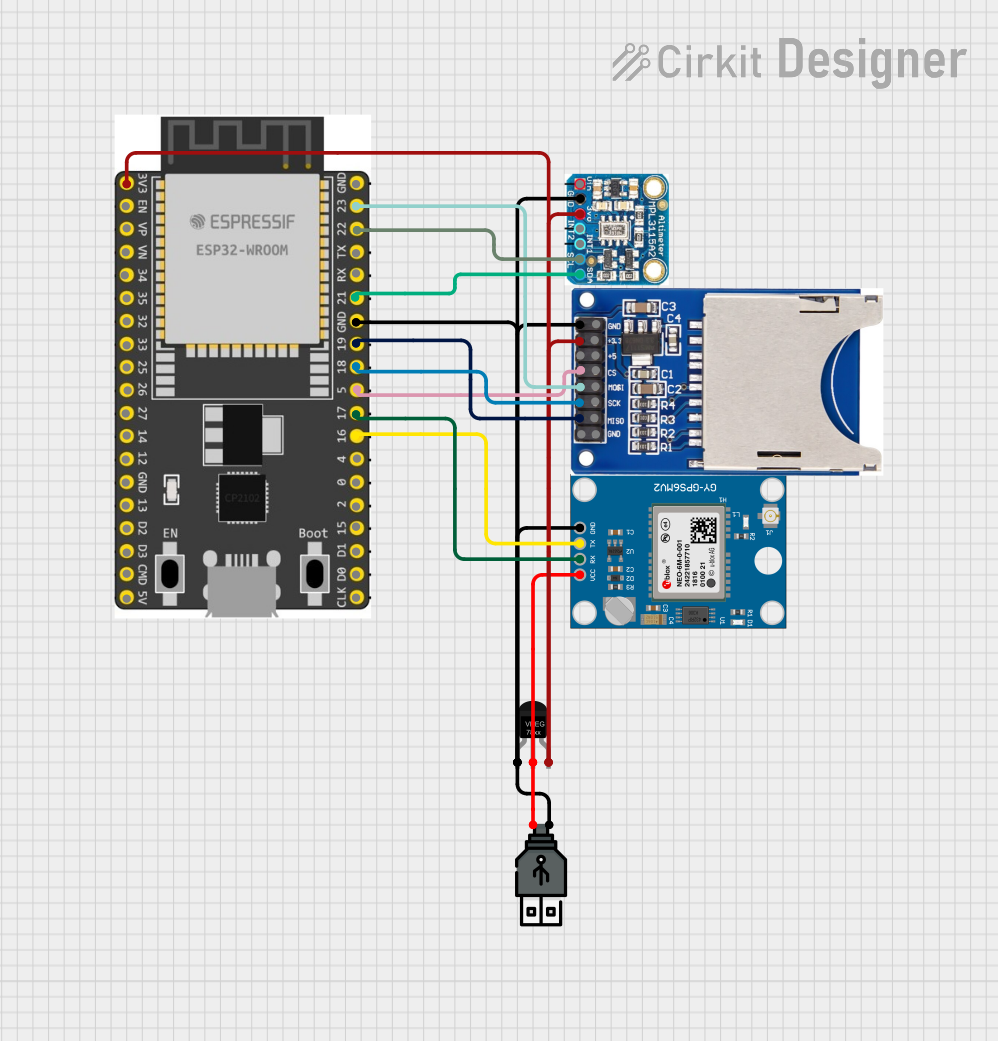
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer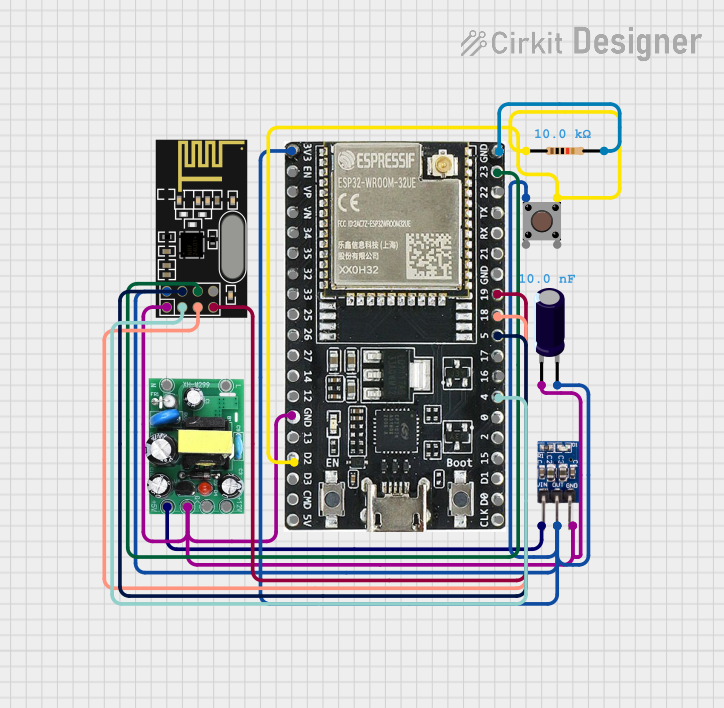
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer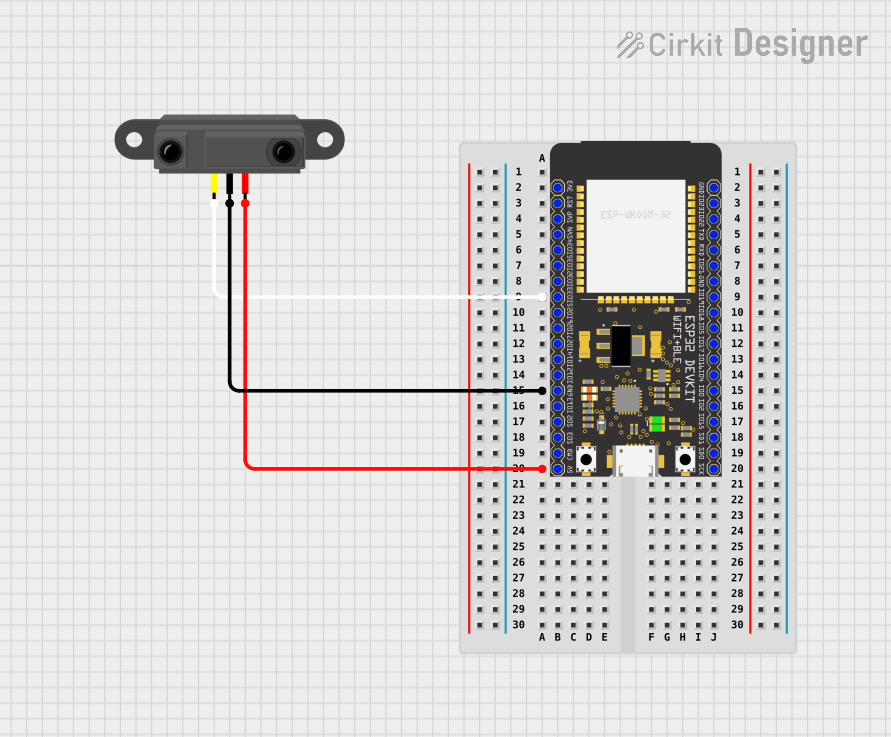
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with ESP32-WROOM-32UE

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- IoT devices and smart home systems
- Wireless sensor networks
- Industrial automation and control systems
- Wearable technology
- Robotics and drones
- Audio streaming and Bluetooth-enabled devices
Technical Specifications
The ESP32-WROOM-32UE is built for versatility and performance. Below are its key technical details:
Key Technical Details
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Espressif Systems |
| Part ID | ESP32 |
| Wireless Connectivity | Wi-Fi (802.11 b/g/n), Bluetooth v4.2 BR/EDR and BLE |
| Processor | Dual-core Xtensa® 32-bit LX6 microprocessor |
| Clock Speed | Up to 240 MHz |
| Flash Memory | 4 MB (external SPI flash) |
| SRAM | 520 KB |
| Operating Voltage | 3.0V to 3.6V |
| GPIO Pins | 34 |
| Communication Interfaces | UART, SPI, I2C, I2S, PWM, ADC, DAC |
| Wi-Fi Frequency Range | 2.4 GHz |
| Bluetooth Range | Up to 10 meters (depending on environment) |
| Antenna Type | External antenna (U.FL connector) |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Dimensions | 18 mm x 25.5 mm x 3.1 mm |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The ESP32-WROOM-32UE has 38 pins, with the most commonly used pins described below:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | EN | Enable pin. Pull high to enable the module, low to disable. |
| 2 | IO0 | GPIO0. Used for boot mode selection during programming. |
| 3 | IO2 | GPIO2. Can be used as a general-purpose I/O pin. |
| 4 | IO4 | GPIO4. General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 5 | IO5 | GPIO5. General-purpose I/O pin. |
| 6 | TXD0 | UART0 Transmit pin. |
| 7 | RXD0 | UART0 Receive pin. |
| 8 | IO12 | GPIO12. Can also function as an ADC or touch sensor input. |
| 9 | IO13 | GPIO13. Can also function as an ADC or touch sensor input. |
| 10 | IO14 | GPIO14. Can also function as an ADC or touch sensor input. |
| 11 | IO15 | GPIO15. Can also function as an ADC or touch sensor input. |
| 12 | GND | Ground pin. Connect to the ground of the circuit. |
| 13 | 3V3 | 3.3V power supply input. |
For a complete pinout, refer to the official datasheet provided by Espressif Systems.
Usage Instructions
The ESP32-WROOM-32UE is easy to integrate into a variety of projects. Below are the steps and best practices for using the module:
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Provide a stable 3.3V power supply to the module. Avoid exceeding 3.6V to prevent damage.
- Boot Mode: To program the ESP32, connect GPIO0 to GND during power-up or reset. This puts the module into bootloader mode.
- Connections:
- Connect the UART pins (TXD0 and RXD0) to a USB-to-serial converter for programming.
- Use GPIO pins for interfacing with sensors, actuators, or other peripherals.
- Antenna: Ensure the external antenna is securely connected to the U.FL connector for optimal wireless performance.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors (e.g., 0.1 µF) close to the power pins to reduce noise.
- GPIO Voltage Levels: Ensure that GPIO pins do not exceed 3.3V to avoid damage.
- Programming: Use the Espressif ESP-IDF or Arduino IDE for programming. The module supports a wide range of development environments.
- Antenna Placement: Keep the antenna area clear of metal objects to avoid signal interference.
Example Code for Arduino IDE
Below is an example of how to use the ESP32-WROOM-32UE with an Arduino UNO to blink an LED:
// Example: Blink an LED using ESP32-WROOM-32UE
// Connect an LED to GPIO2 with a 220-ohm resistor.
#define LED_PIN 2 // GPIO2 is connected to the LED
void setup() {
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); // Set GPIO2 as an output pin
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, HIGH); // Turn the LED on
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW); // Turn the LED off
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
Module Not Responding:
- Cause: Incorrect power supply or loose connections.
- Solution: Ensure a stable 3.3V power supply and check all connections.
Wi-Fi Connection Fails:
- Cause: Incorrect SSID or password.
- Solution: Double-check the Wi-Fi credentials in your code.
Programming Errors:
- Cause: GPIO0 not connected to GND during boot.
- Solution: Ensure GPIO0 is grounded when powering up the module for programming.
Bluetooth Not Discoverable:
- Cause: Bluetooth not initialized in the code.
- Solution: Verify that the Bluetooth stack is properly configured in your program.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Use a multimeter to verify power supply voltage.
- Check the serial monitor for error messages during programming.
- Update the ESP32 firmware if issues persist.
- Refer to the Espressif documentation for advanced debugging techniques.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the ESP32-WROOM-32UE into your projects and troubleshoot common issues with ease.