
How to Use analog switch: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
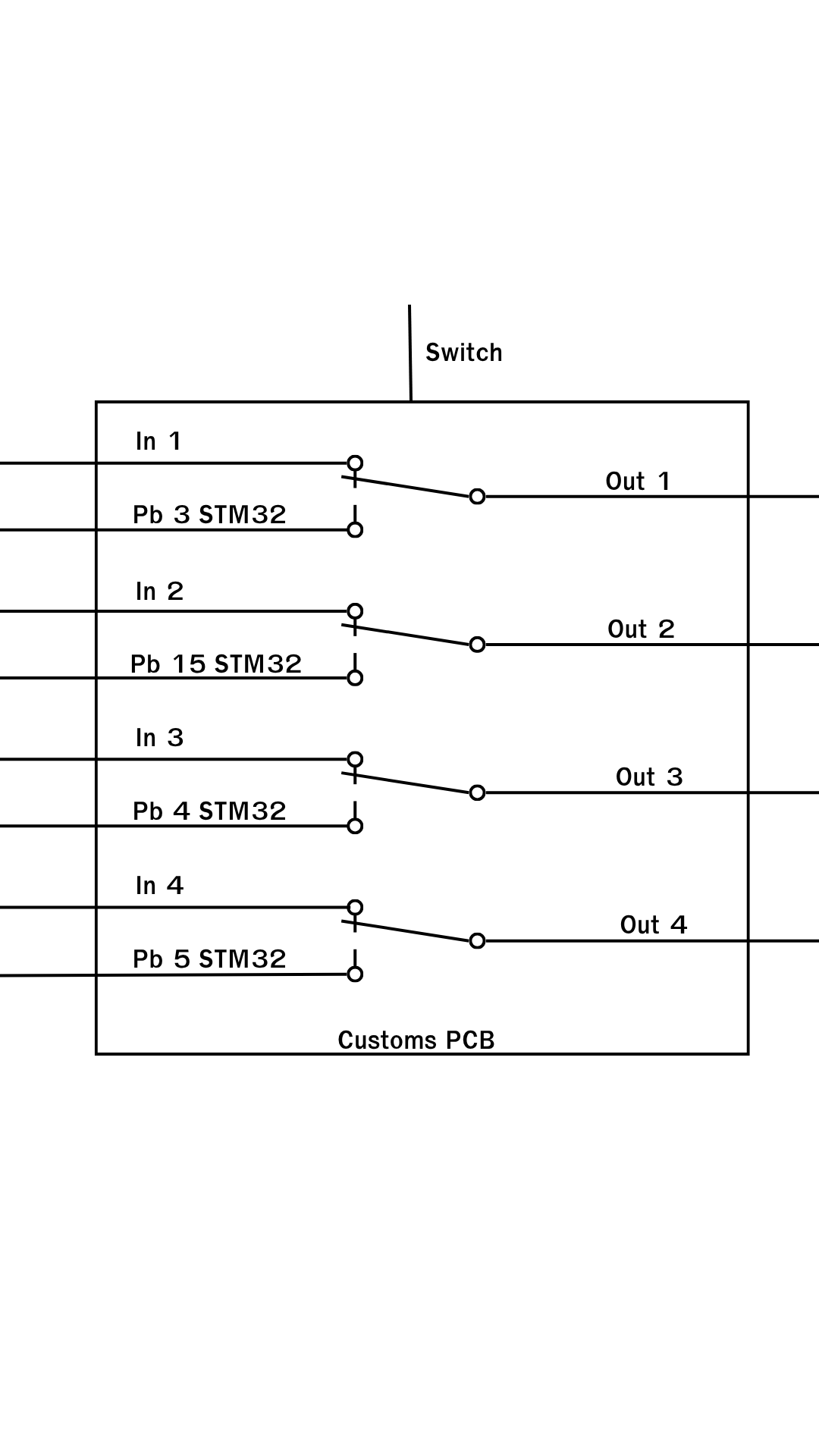
 Design with analog switch in Cirkit Designer
Design with analog switch in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
An analog switch is a semiconductor device designed to control the flow of analog signals in a circuit. It operates by allowing or blocking the passage of signals based on a digital control input. Analog switches are widely used in applications such as signal routing, multiplexing, and signal conditioning. They are essential in systems where precise control of analog signals is required, such as audio processing, data acquisition systems, and communication devices.
Explore Projects Built with analog switch
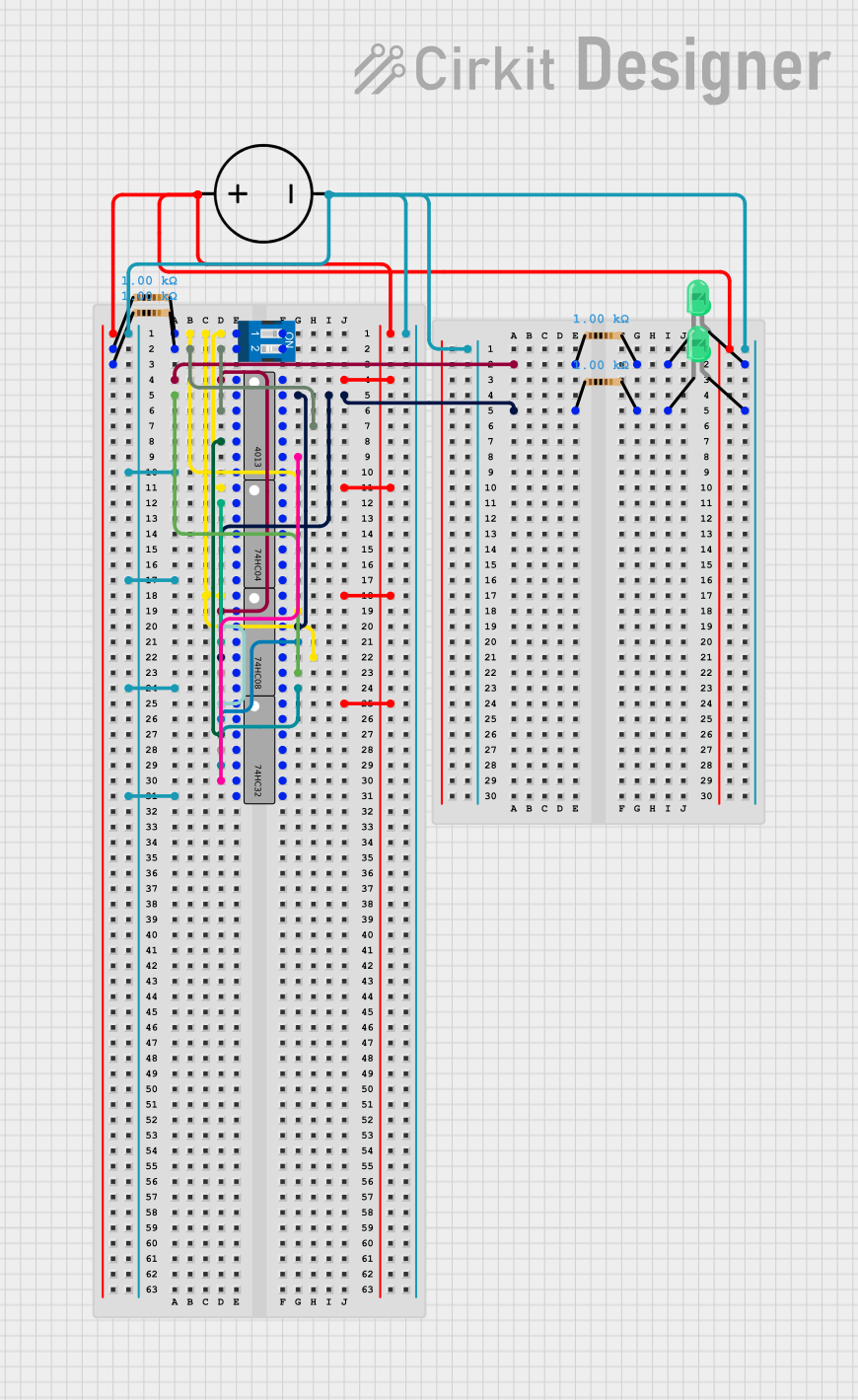
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer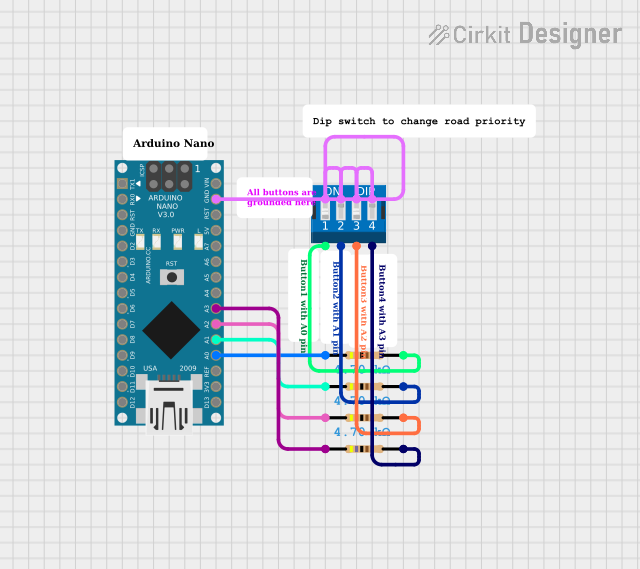
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with analog switch

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Signal Routing: Directing analog signals to different parts of a circuit.
- Multiplexing: Selecting one signal from multiple inputs for further processing.
- Sample-and-Hold Circuits: Capturing and holding an analog signal for a specific duration.
- Audio Systems: Switching between audio sources or channels.
- Test and Measurement Equipment: Controlling signal paths in automated test setups.
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for the analog switch:
General Specifications
- Manufacturer: Analog Switch
- Part ID: Analog Switch
- Signal Type: Analog
- Control Input: Digital (typically TTL or CMOS logic levels)
- Supply Voltage (Vcc): 3V to 15V (varies by model)
- On-Resistance (RON): Typically 10Ω to 100Ω
- Off-Leakage Current: Typically in the nanoampere range
- Bandwidth: Up to several MHz, depending on the model
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The pin configuration may vary depending on the specific model of the analog switch. Below is a general example of a single-pole single-throw (SPST) analog switch:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vcc | Positive power supply input |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | IN | Digital control input (logic high/low) |
| 4 | COM | Common terminal for the analog signal |
| 5 | NO | Normally open terminal for the signal |
For more complex analog switches (e.g., SPDT or multiplexer configurations), refer to the specific datasheet for the pinout.
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Analog Switch in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the Vcc pin to a stable power source within the specified voltage range (e.g., 5V or 12V). Connect the GND pin to the circuit ground.
- Control Input: Apply a digital signal (e.g., from a microcontroller or logic circuit) to the IN pin. A logic high typically enables the switch, while a logic low disables it.
- Signal Connections: Connect the analog signal source to the COM pin and the destination to the NO pin. When the switch is enabled, the signal will pass through; otherwise, it will be blocked.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Levels: Ensure that the analog signal voltage does not exceed the supply voltage (Vcc) or go below ground (GND).
- On-Resistance: Consider the RON value, as it can introduce a small voltage drop in the signal path.
- Bandwidth: Verify that the switch's bandwidth is sufficient for the frequency of the analog signal.
- Decoupling Capacitors: Place decoupling capacitors near the Vcc pin to reduce noise and ensure stable operation.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the maximum current rating of the switch to prevent damage.
Example: Using an Analog Switch with Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to control an analog switch using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the control pin connected to the IN pin of the analog switch
const int controlPin = 7;
void setup() {
// Set the control pin as an output
pinMode(controlPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// Enable the analog switch by setting the control pin HIGH
digitalWrite(controlPin, HIGH);
delay(1000); // Keep the switch on for 1 second
// Disable the analog switch by setting the control pin LOW
digitalWrite(controlPin, LOW);
delay(1000); // Keep the switch off for 1 second
}
Note: Ensure that the control signal voltage matches the logic level requirements of the analog switch.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Issue: The analog signal is not passing through the switch.
- Solution: Verify that the control input is set to the correct logic level (HIGH or LOW) to enable the switch. Check the power supply connections and ensure the Vcc and GND pins are properly connected.
Issue: Signal distortion or attenuation.
- Solution: Check the RON value of the switch and ensure it is suitable for your application. Verify that the signal frequency is within the bandwidth of the switch.
Issue: Excessive noise in the circuit.
- Solution: Add decoupling capacitors near the power supply pins to reduce noise. Ensure proper grounding and minimize interference from nearby components.
Issue: The switch is overheating.
- Solution: Ensure that the current through the switch does not exceed its maximum rating. If necessary, use a heat sink or improve ventilation.
FAQs
Q: Can an analog switch handle digital signals?
A: Yes, an analog switch can handle digital signals as long as the voltage levels are within the specified range.Q: Can I use an analog switch for bidirectional signals?
A: Yes, most analog switches are bidirectional and can pass signals in both directions.Q: What happens if the control input is left floating?
A: A floating control input can cause unpredictable behavior. Always connect the control input to a defined logic level.Q: How do I choose the right analog switch for my application?
A: Consider factors such as supply voltage, RON, bandwidth, and the number of channels required.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and troubleshoot an analog switch in your electronic projects.