
How to Use Micro USB Port: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Micro USB Port in Cirkit Designer
Design with Micro USB Port in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
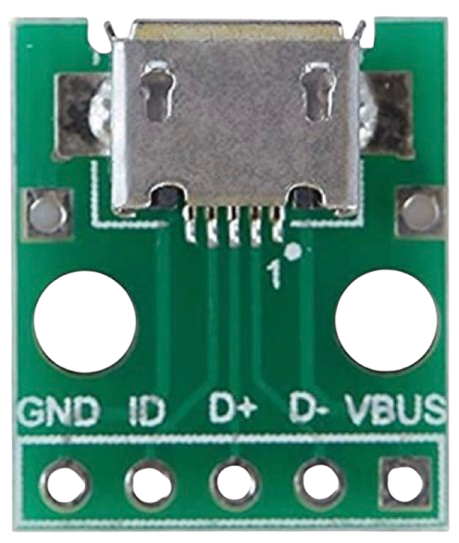
The Micro USB Port is a small, rectangular connector widely used in electronic devices for data transfer and charging purposes. It is a compact and durable interface that has been a standard in mobile phones, tablets, power banks, and other portable devices. Known for its reversible design, the Micro USB Port ensures ease of use and reliable connectivity.
Explore Projects Built with Micro USB Port
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer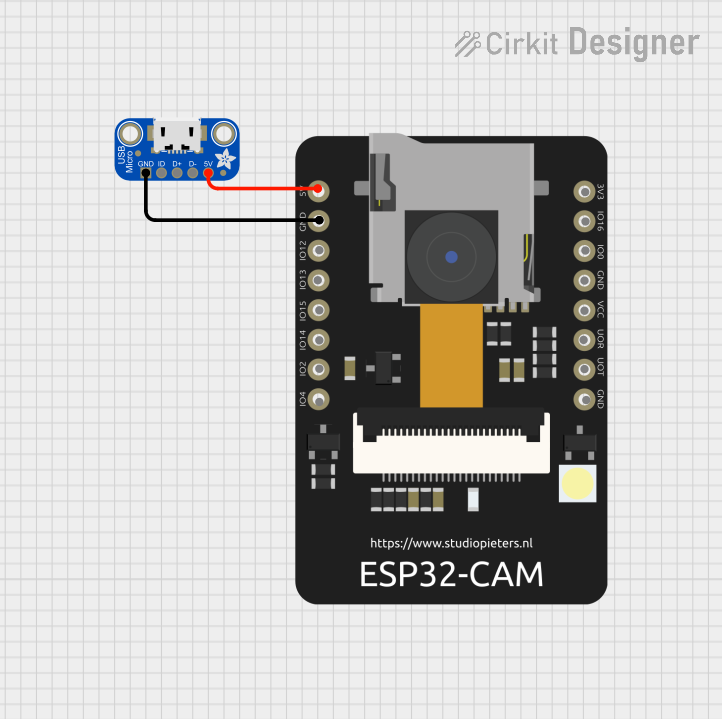
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Micro USB Port

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging portable electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, and cameras.
- Data transfer between devices and computers.
- Powering small electronic projects and development boards.
- Serving as a communication interface for embedded systems.
Technical Specifications
The Micro USB Port is available in two main variants: Micro USB Type-A and Micro USB Type-B. The most commonly used version is Micro USB Type-B. Below are the key technical details:
General Specifications
- Connector Type: Micro USB Type-B (most common)
- Voltage Rating: 5V DC (standard USB voltage)
- Current Rating: Up to 2A (depending on the cable and device)
- Data Transfer Speed: Up to 480 Mbps (USB 2.0 standard)
- Durability: Rated for 10,000 insertion/removal cycles
- Dimensions: Approximately 6.85mm x 1.8mm
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Micro USB Port typically has 5 pins. Below is the pinout for Micro USB Type-B:
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VBUS | Power supply (5V DC) |
| 2 | D- | Data line (negative) |
| 3 | D+ | Data line (positive) |
| 4 | ID | Identification pin (used for OTG functionality; connected to GND in standard) |
| 5 | GND | Ground |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Micro USB Port in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect the VBUS pin to a 5V power source and the GND pin to the ground of your circuit. Ensure the power source can supply sufficient current for your application.
- Data Communication: Use the D+ and D- pins for data transfer. These pins should be connected to the corresponding data lines of the device or microcontroller.
- OTG Functionality: For On-The-Go (OTG) applications, the ID pin can be used to determine the device's role (host or peripheral). Connect the ID pin to GND for standard device operation.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Regulation: Ensure the connected device can handle the 5V supply. Use a voltage regulator if necessary.
- Cable Quality: Use high-quality Micro USB cables to avoid voltage drops and ensure reliable data transfer.
- Insertion Orientation: Although the Micro USB Port is not fully reversible like USB-C, its design minimizes incorrect insertion. Always align the connector properly to avoid damage.
- Soldering: When soldering a Micro USB Port onto a PCB, ensure proper alignment and avoid overheating the pins.
Example: Connecting a Micro USB Port to an Arduino UNO
The Arduino UNO does not natively use a Micro USB Port, but you can use a Micro USB breakout board to power the Arduino or communicate with it. Below is an example of powering an Arduino UNO using a Micro USB breakout board:
// Example: Powering Arduino UNO with a Micro USB breakout board
// Connect the breakout board's VBUS pin to the Arduino's 5V pin
// Connect the breakout board's GND pin to the Arduino's GND pin
void setup() {
// No specific setup required for power-only connections
}
void loop() {
// Your Arduino code goes here
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
Device Not Charging or Powering On
- Cause: Insufficient current from the power source.
- Solution: Use a power source capable of supplying at least 1A or more, depending on the device's requirements.
Data Transfer Fails
- Cause: Faulty or low-quality cable.
- Solution: Replace the cable with a high-quality Micro USB cable.
Connector Feels Loose
- Cause: Worn-out port or connector.
- Solution: Replace the Micro USB Port or cable.
Overheating
- Cause: Excessive current draw or poor soldering.
- Solution: Check the circuit for short circuits or excessive load. Ensure proper soldering of the port.
FAQs
Q: Can I use a Micro USB Port for 3.3V devices?
A: Yes, but you must use a voltage regulator to step down the 5V supply to 3.3V.Q: Is the Micro USB Port compatible with USB-C?
A: No, but adapters are available to connect Micro USB devices to USB-C ports.Q: How do I identify the pins on a Micro USB Port?
A: Refer to the pinout table above. Use a multimeter to verify connections if needed.
This concludes the documentation for the Micro USB Port.