
Cirkit Designer
Your all-in-one circuit design IDE
Home /
Component Documentation
How to Use Turbidity Module: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
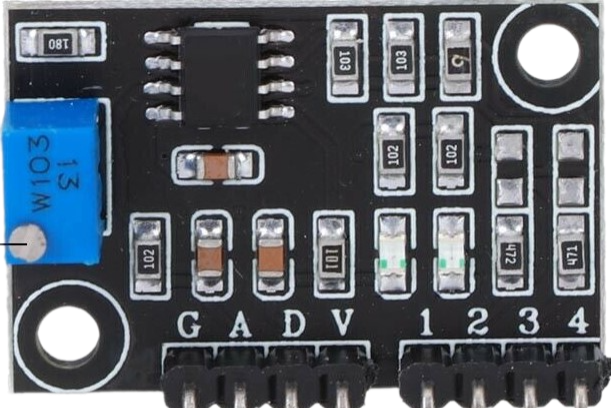

 Design with Turbidity Module in Cirkit Designer
Design with Turbidity Module in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Turbidity Module is an electronic sensor designed to measure the turbidity, or cloudiness, of a liquid. Turbidity is an important parameter in assessing the quality of water, as it can indicate the presence of pollutants, microorganisms, or other particulates. This sensor is commonly used in water purification systems, environmental monitoring, and laboratory experiments.
Explore Projects Built with Turbidity Module
Arduino UNO-Based Turbidity Sensor Module for Water Quality Monitoring
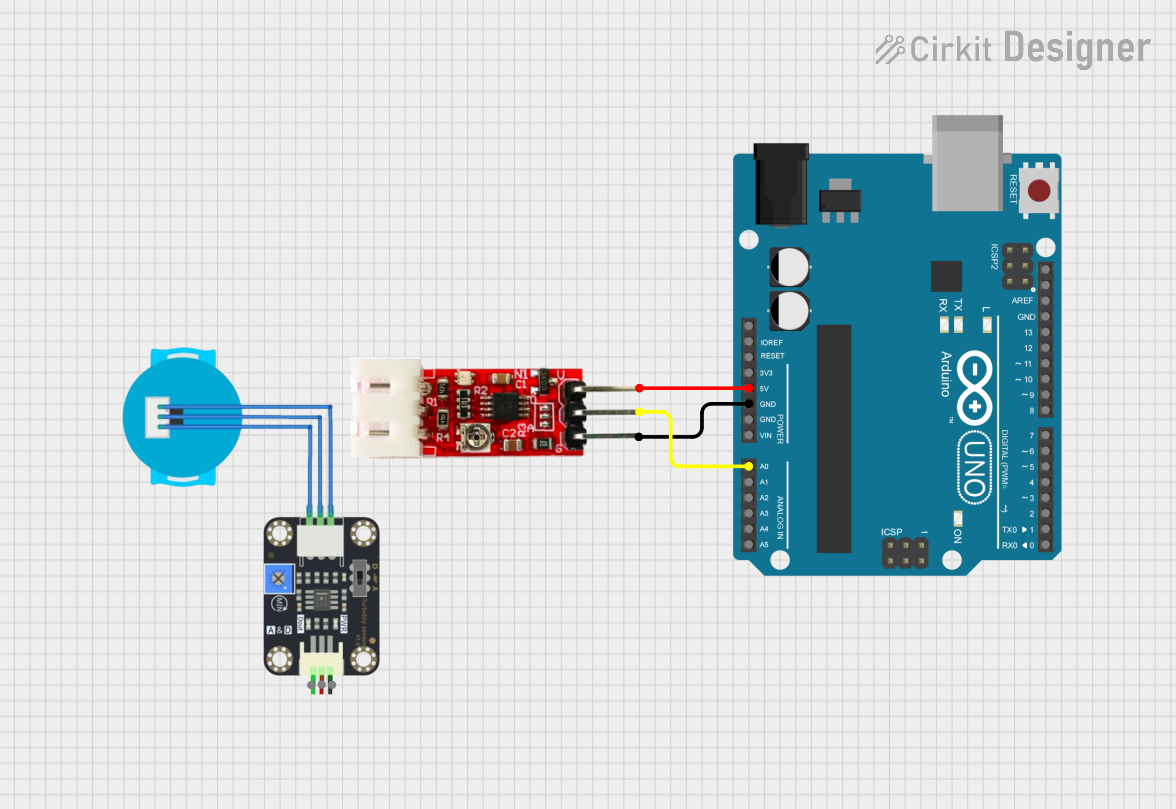
This circuit uses an Arduino UNO to read data from a turbidity module, which measures the cloudiness of a liquid. The turbidity module is powered by the Arduino's 5V and GND pins, and its output is connected to the Arduino's analog input pin A0 for data acquisition.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino GIGA R1 WIFI Turbidity Monitoring System
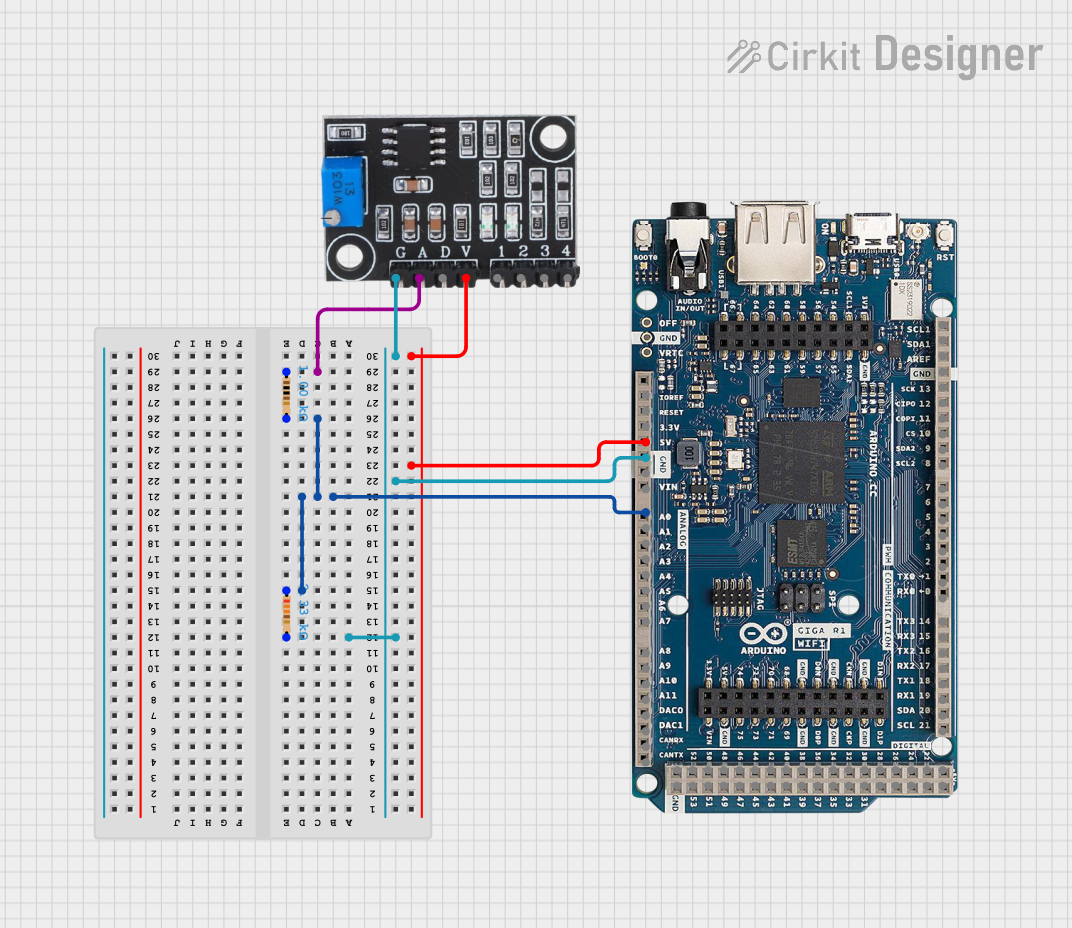
This circuit is designed to measure the turbidity of a liquid using a turbidity sensor module interfaced with an Arduino GIGA R1 WIFI. The sensor's output is conditioned by a voltage divider made of two resistors before being read by the Arduino's analog input. The Arduino can then process this information for further analysis or display.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerArduino Mega 2560-Based Soil Nutrient Testing System with Bluetooth and LCD Display
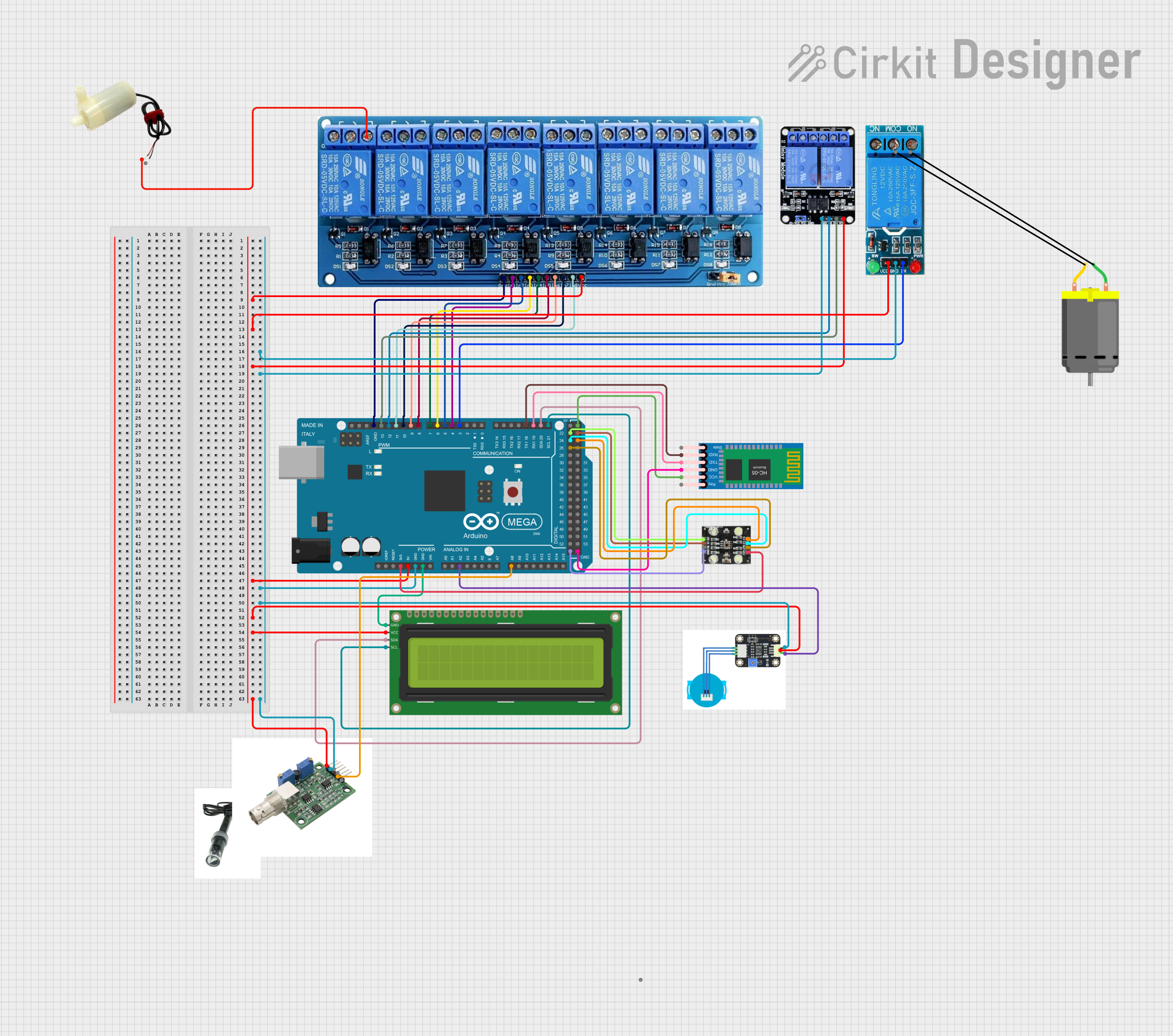
This circuit is an automated chemical testing system controlled by an Arduino Mega 2560. It uses various sensors, including a turbidity sensor and a color sensor, to measure water quality parameters, and it communicates results via an LCD display and Bluetooth module. The system also controls multiple relays to dispense chemicals for different tests.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerESP32-Based Water Quality Monitoring System with Turbidity, Temperature, pH, and Color Sensing
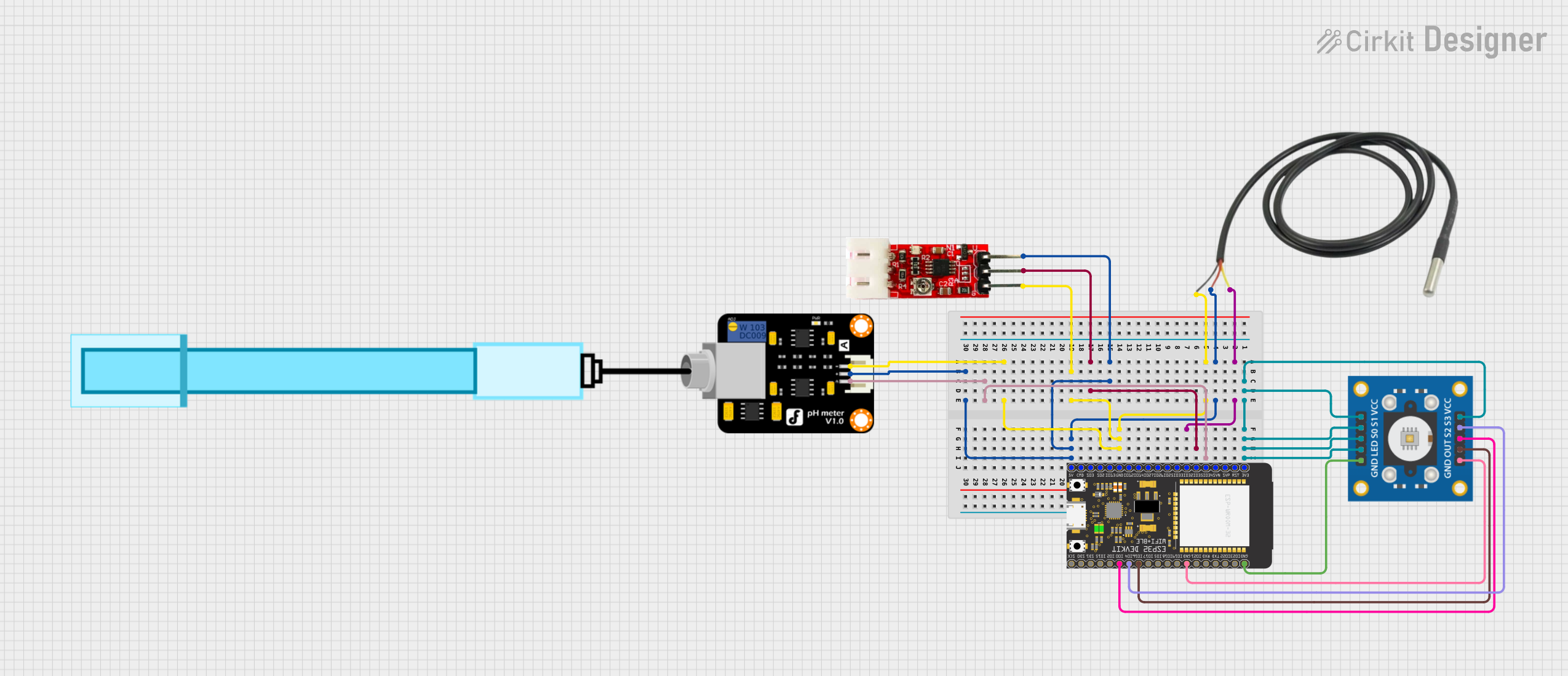
This circuit features an ESP32 Wroom microcontroller interfaced with multiple sensors: a tcs3200 color sensor, a turbidity module, a temperature sensor, and a pH meter. The ESP32 Wroom provides power to the sensors and reads their outputs through various GPIO pins. The circuit is designed to monitor and analyze water quality parameters such as color, turbidity, temperature, and pH level.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Turbidity Module

Arduino UNO-Based Turbidity Sensor Module for Water Quality Monitoring
This circuit uses an Arduino UNO to read data from a turbidity module, which measures the cloudiness of a liquid. The turbidity module is powered by the Arduino's 5V and GND pins, and its output is connected to the Arduino's analog input pin A0 for data acquisition.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino GIGA R1 WIFI Turbidity Monitoring System
This circuit is designed to measure the turbidity of a liquid using a turbidity sensor module interfaced with an Arduino GIGA R1 WIFI. The sensor's output is conditioned by a voltage divider made of two resistors before being read by the Arduino's analog input. The Arduino can then process this information for further analysis or display.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Arduino Mega 2560-Based Soil Nutrient Testing System with Bluetooth and LCD Display
This circuit is an automated chemical testing system controlled by an Arduino Mega 2560. It uses various sensors, including a turbidity sensor and a color sensor, to measure water quality parameters, and it communicates results via an LCD display and Bluetooth module. The system also controls multiple relays to dispense chemicals for different tests.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
ESP32-Based Water Quality Monitoring System with Turbidity, Temperature, pH, and Color Sensing
This circuit features an ESP32 Wroom microcontroller interfaced with multiple sensors: a tcs3200 color sensor, a turbidity module, a temperature sensor, and a pH meter. The ESP32 Wroom provides power to the sensors and reads their outputs through various GPIO pins. The circuit is designed to monitor and analyze water quality parameters such as color, turbidity, temperature, and pH level.
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Water quality testing in treatment plants
- Monitoring of natural water bodies like rivers and lakes
- Aquarium or pond maintenance
- Research and educational projects
Technical Specifications
Key Technical Details
- Operating Voltage: 5V DC
- Measurement Range: 0 to 3000 NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Units)
- Output Signal: Analog (0-4.5V)
- Response Time: <500ms
- Operating Current: 40mA (max)
- Operating Temperature: 0°C to 50°C
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
| Pin Number | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power |
| 2 | GND | Ground |
| 3 | Analog Output (A0) | Output |
| 4 | Digital Output (D0) | Output |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Connect the VCC pin to the 5V output on the Arduino MEGA.
- Connect the GND pin to one of the GND pins on the Arduino MEGA.
- Connect the Analog Output (A0) pin to one of the analog input pins on the Arduino MEGA if you wish to measure the turbidity value.
- Optionally, connect the Digital Output (D0) to a digital pin on the Arduino MEGA if you want to detect a threshold level of turbidity.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure that the sensor is properly calibrated before use.
- Avoid exposing the sensor to direct sunlight as it can affect the readings.
- Keep the sensor clean and free from any obstructions that could affect its accuracy.
- Use a stable power supply to prevent fluctuations in the readings.
Example Arduino Code
// Define the analog pin for turbidity sensor
const int turbidityPin = A0;
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud rate
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from sensor
int sensorValue = analogRead(turbidityPin);
// Convert the analog value to voltage
float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0);
// Print the voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Turbidity Voltage: ");
Serial.println(voltage);
// Delay for a stable reading
delay(1000);
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues Users Might Face
- Inaccurate Readings: Ensure the sensor is clean and calibrated correctly.
- No Readings: Check the connections to the Arduino and ensure the correct pins are used.
- Fluctuating Readings: Stabilize the power supply and avoid external light interference.
Solutions and Tips for Troubleshooting
- Calibration: Perform calibration with a known turbidity standard solution.
- Cleaning: Gently clean the sensor with distilled water and avoid touching the sensing area.
- Shielding: Use a shield to block out external light sources that may affect the readings.
FAQs
Q: Can the turbidity module be submerged in water?
- A: Yes, but only the sensing part should be submerged, and care should be taken to waterproof the electrical connections.
Q: What is the accuracy of the turbidity module?
- A: The accuracy can vary depending on calibration and environmental conditions. Refer to the manufacturer's datasheet for specific accuracy ratings.
Q: How often should the sensor be calibrated?
- A: Calibration frequency depends on usage, but it is generally recommended to calibrate the sensor before any critical measurements or after any significant changes in the operating conditions.