
How to Use Soil Moisture V2: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
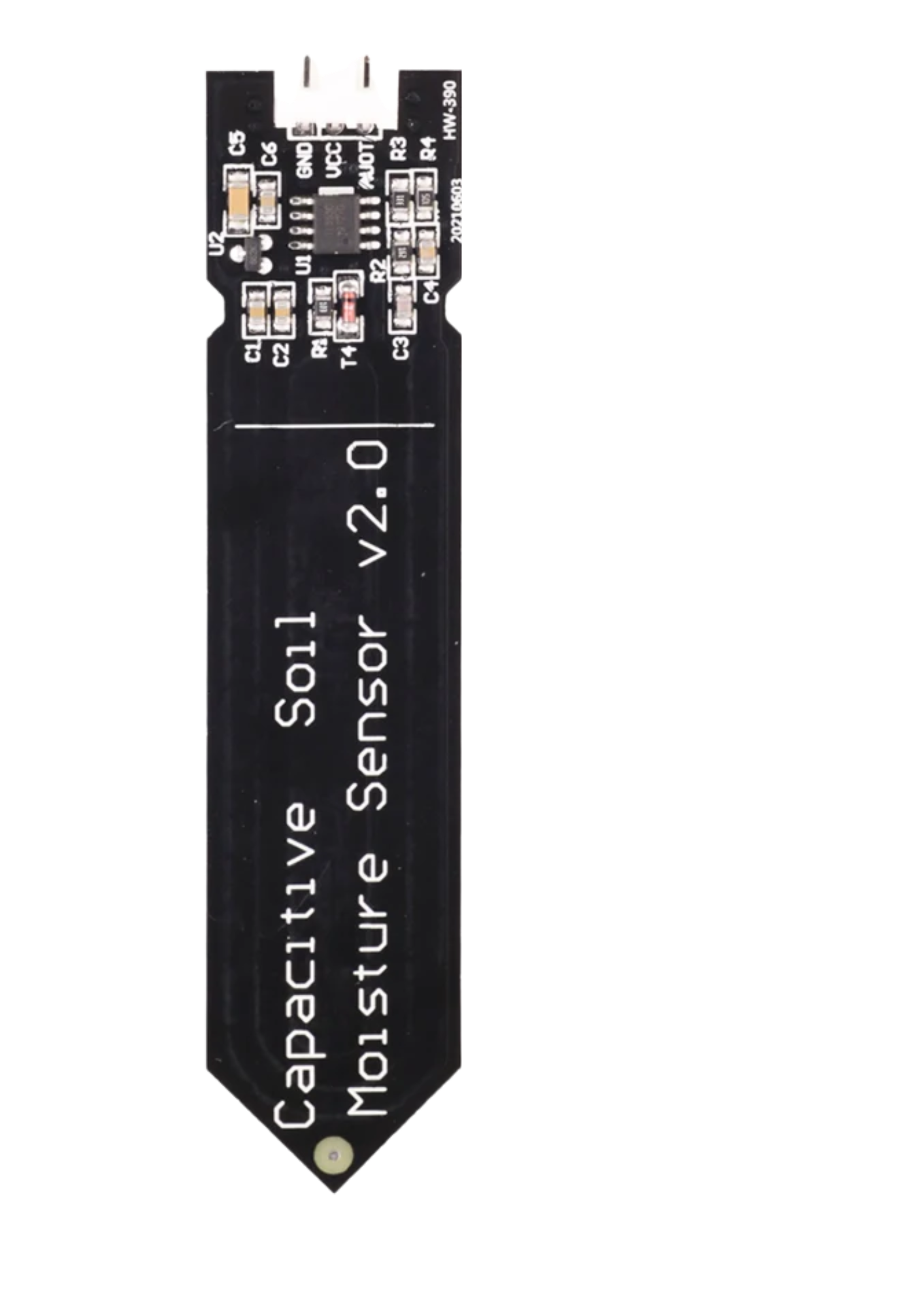
 Design with Soil Moisture V2 in Cirkit Designer
Design with Soil Moisture V2 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The Soil Moisture V2 sensor, manufactured by ESP32, is a reliable and efficient device designed to measure the volumetric water content in soil. This sensor provides accurate data that can be used for irrigation management, plant health monitoring, and other agricultural or gardening applications. Its compact design and ease of integration make it a popular choice for both hobbyists and professionals.
Explore Projects Built with Soil Moisture V2
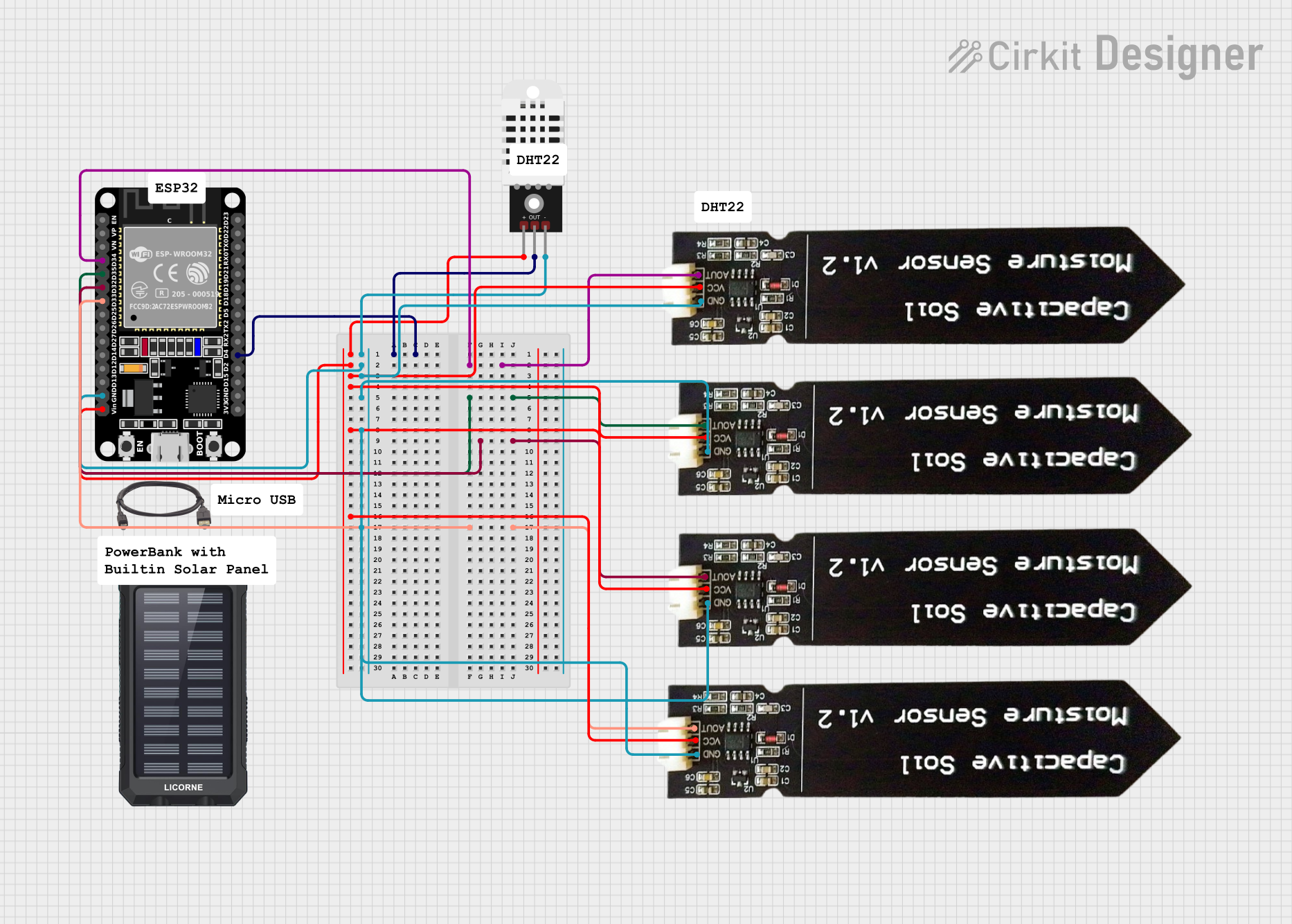
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer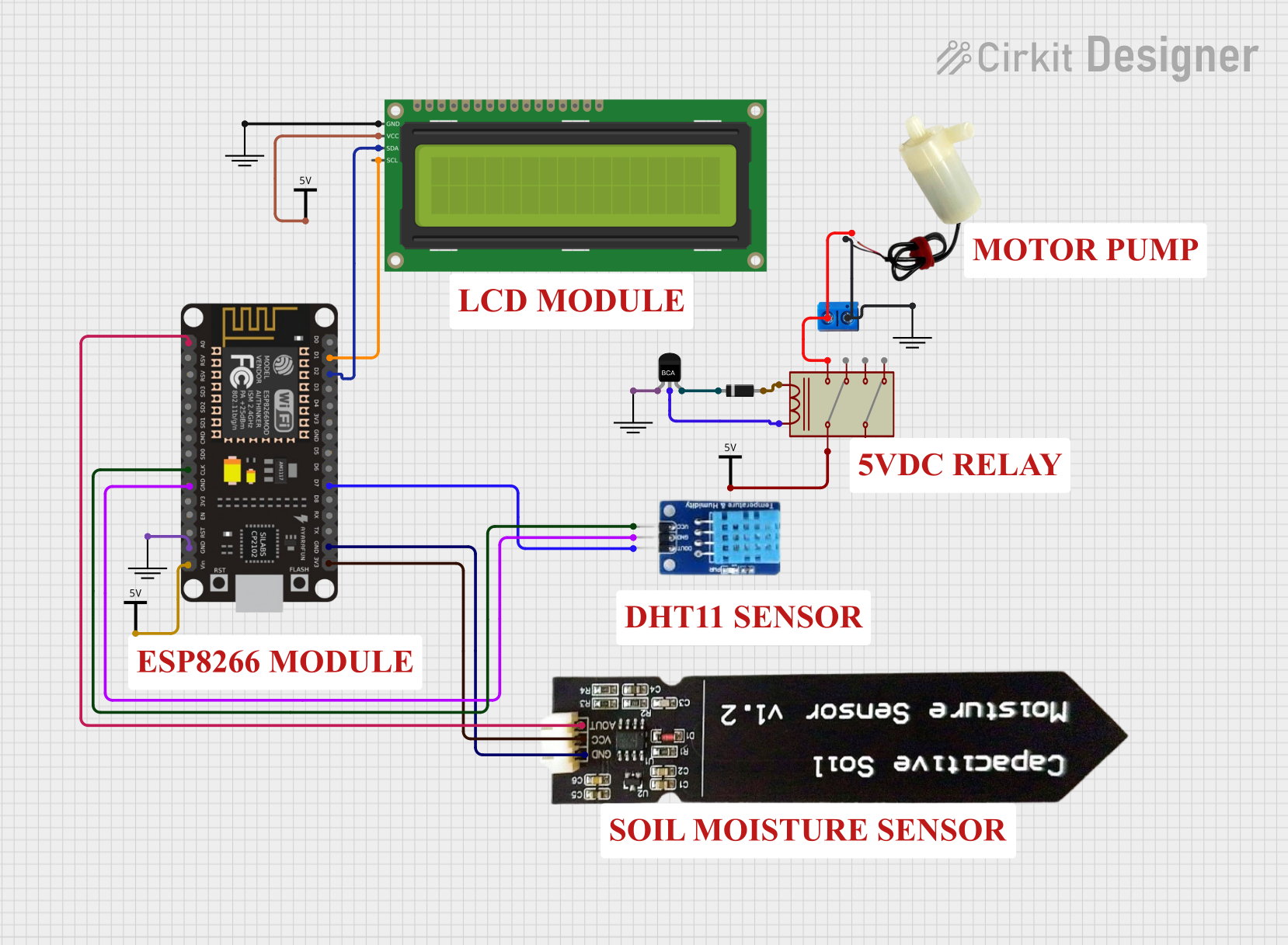
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer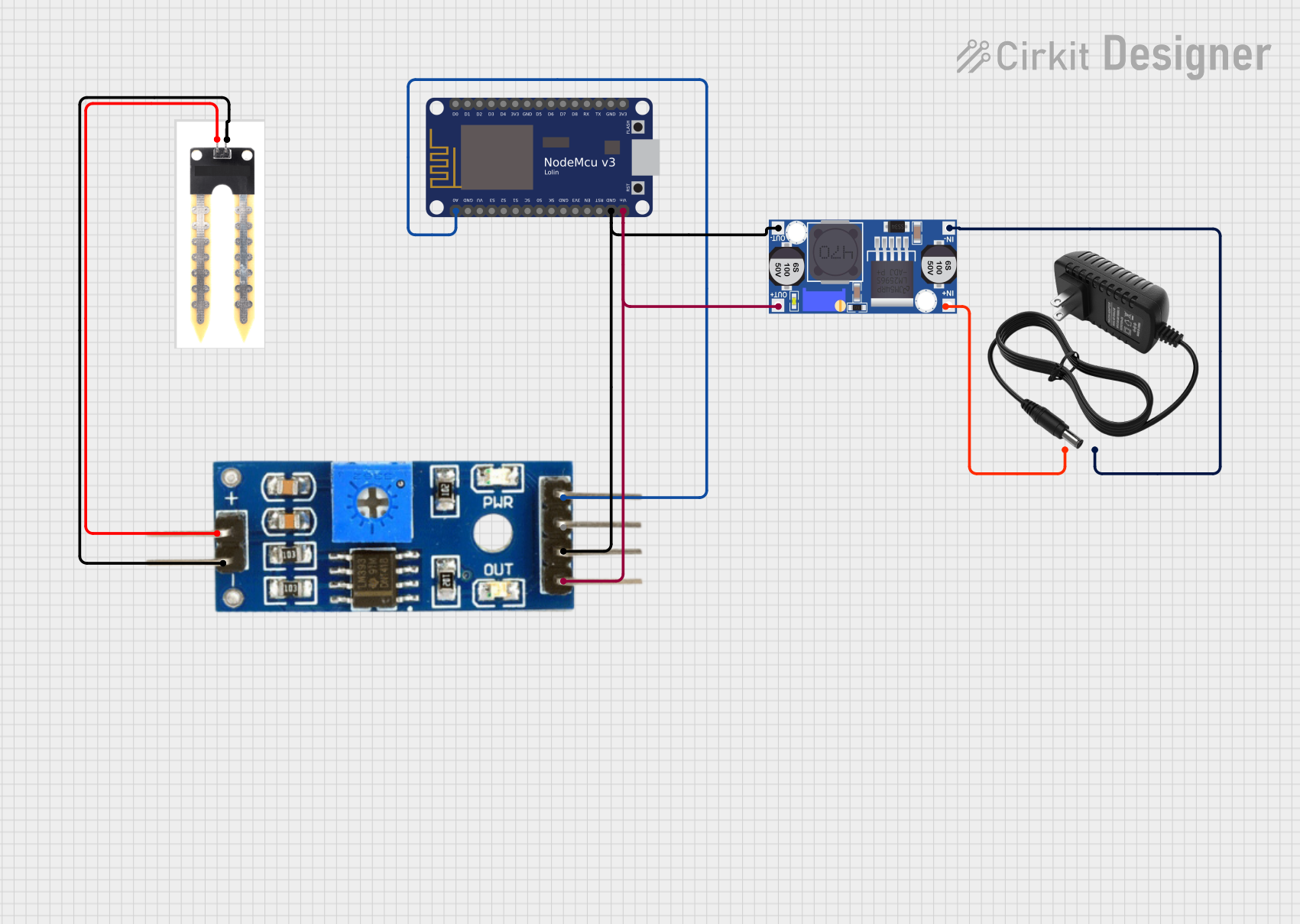
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer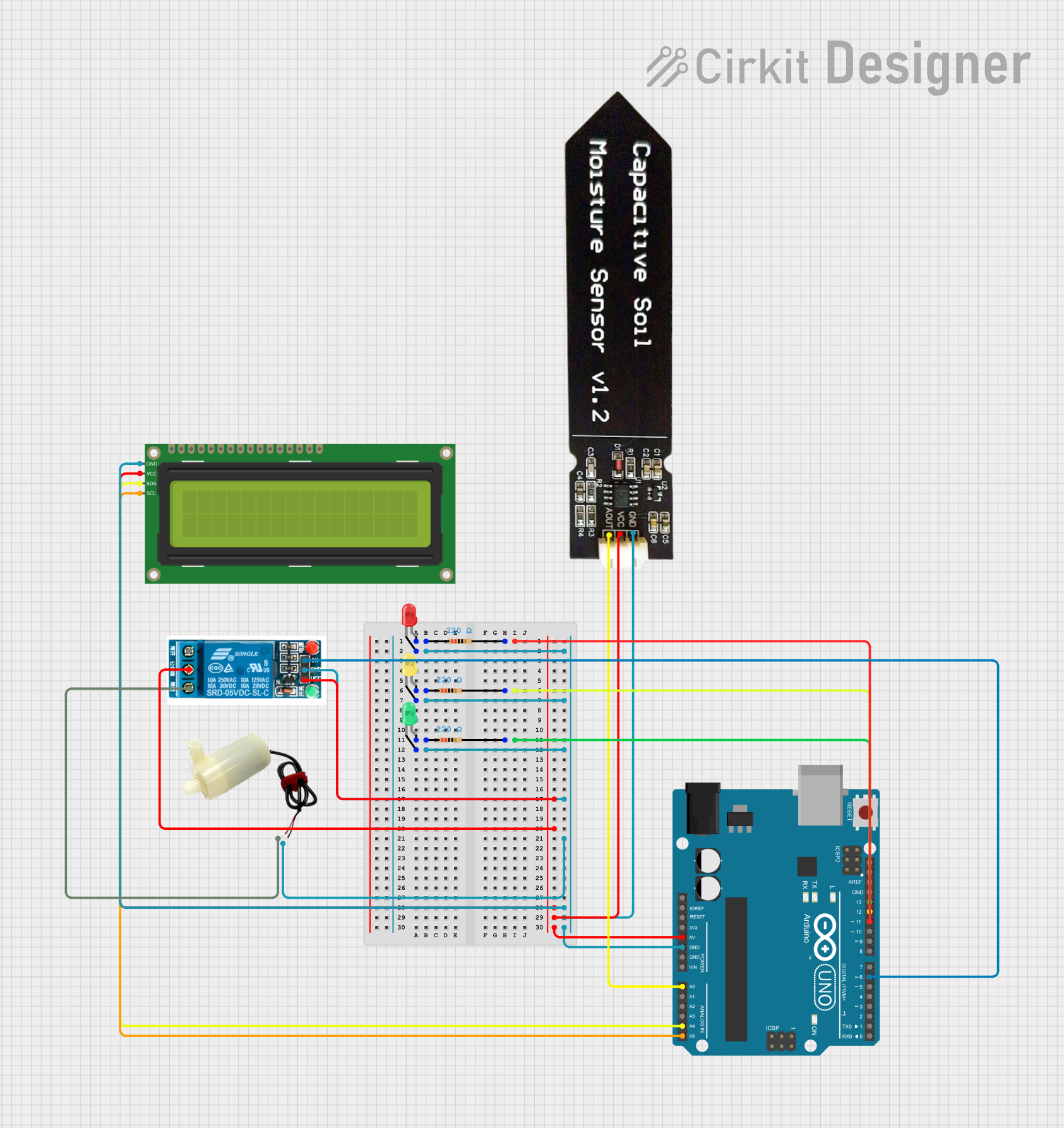
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Soil Moisture V2

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Automated irrigation systems
- Smart gardening projects
- Agricultural monitoring
- Soil moisture analysis for research
- Environmental monitoring systems
Technical Specifications
The Soil Moisture V2 sensor is designed to operate efficiently in a variety of environments. Below are its key technical details:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V |
| Operating Current | < 20mA |
| Output Signal | Analog voltage (0-3.3V) |
| Measurement Range | 0% to 100% soil moisture |
| Interface Type | Analog |
| Dimensions | 60mm x 20mm x 5mm |
| Operating Temperature | -10°C to 60°C |
| Material | Corrosion-resistant PCB coating |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The Soil Moisture V2 sensor has three pins for easy integration into circuits:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply pin (3.3V to 5V) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | AOUT | Analog output pin that provides soil moisture data |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Component in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V power source and theGNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Read the Output: Connect the
AOUTpin to an analog input pin of your microcontroller (e.g., ESP32 or Arduino UNO). - Calibrate the Sensor: Place the sensor in dry soil and note the analog output value. Then, place it in fully saturated soil and record the value. Use these readings to map the sensor's output to a percentage scale (0% to 100%).
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Avoid Corrosion: The sensor's PCB is coated to resist corrosion, but prolonged exposure to water can still degrade it. Use the sensor intermittently rather than leaving it in the soil permanently.
- Placement: Insert the sensor into the soil vertically for accurate readings. Ensure the sensor is fully in contact with the soil.
- Power Supply: Use a stable power source to avoid fluctuations in the output signal.
- Calibration: Regularly recalibrate the sensor to maintain accuracy, especially if used in different soil types.
Example Code for Arduino UNO
Below is an example of how to use the Soil Moisture V2 sensor with an Arduino UNO:
// Define the analog pin connected to the sensor
const int sensorPin = A0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin); // Read the analog value from the sensor
float moisturePercentage = map(sensorValue, 0, 1023, 0, 100);
// Map the sensor value to a percentage (0% to 100%)
Serial.print("Soil Moisture: ");
Serial.print(moisturePercentage);
Serial.println("%"); // Print the moisture percentage to the Serial Monitor
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before taking the next reading
}
Notes on the Code
- The
map()function is used to convert the raw analog reading (0-1023) to a percentage (0-100%). Adjust themap()parameters based on your sensor's calibration values. - Use the
Serial Monitorin the Arduino IDE to view the soil moisture readings in real time.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output or Incorrect Readings:
- Cause: Loose or incorrect wiring.
- Solution: Double-check all connections, ensuring the
VCC,GND, andAOUTpins are properly connected.
Fluctuating Readings:
- Cause: Unstable power supply or electrical noise.
- Solution: Use a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 0.1µF) between
VCCandGNDto stabilize the power supply.
Sensor Degradation:
- Cause: Prolonged exposure to water or corrosive soil.
- Solution: Use the sensor intermittently and clean it after use. Consider using a protective coating for extended durability.
Inaccurate Calibration:
- Cause: Soil type or environmental conditions differ from calibration conditions.
- Solution: Recalibrate the sensor in the specific soil and conditions where it will be used.
FAQs
Q1: Can the Soil Moisture V2 sensor be used with a Raspberry Pi?
A1: Yes, but since the Raspberry Pi lacks analog input pins, you will need an ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) module to read the sensor's output.
Q2: How deep should the sensor be inserted into the soil?
A2: Insert the sensor fully into the soil, ensuring the entire sensing area is in contact with the soil for accurate readings.
Q3: Can this sensor measure soil salinity?
A3: No, the Soil Moisture V2 sensor is designed specifically for measuring soil moisture, not salinity or other soil properties.
Q4: Is the sensor waterproof?
A4: The sensor is water-resistant due to its PCB coating, but it is not fully waterproof. Avoid submerging it in water for extended periods.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate and use the Soil Moisture V2 sensor in your projects.