
How to Use TP4056: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
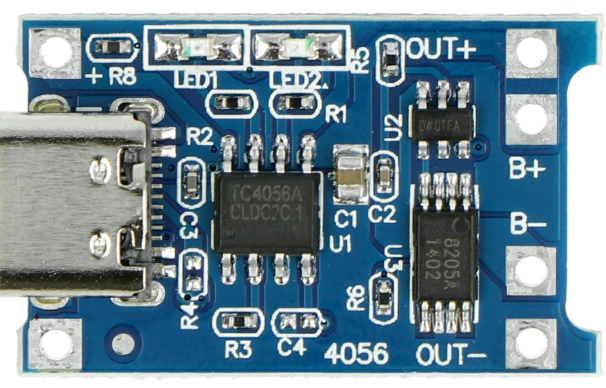
 Design with TP4056 in Cirkit Designer
Design with TP4056 in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
The TP4056 is a lithium-ion battery charger IC manufactured by Makers, with the part ID TP4036. It is designed to provide a constant current/constant voltage (CC/CV) charging profile, making it ideal for charging single-cell lithium-ion batteries. The IC integrates advanced features such as over-voltage protection, under-voltage lockout, and thermal regulation, ensuring safe and efficient charging.
Explore Projects Built with TP4056

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer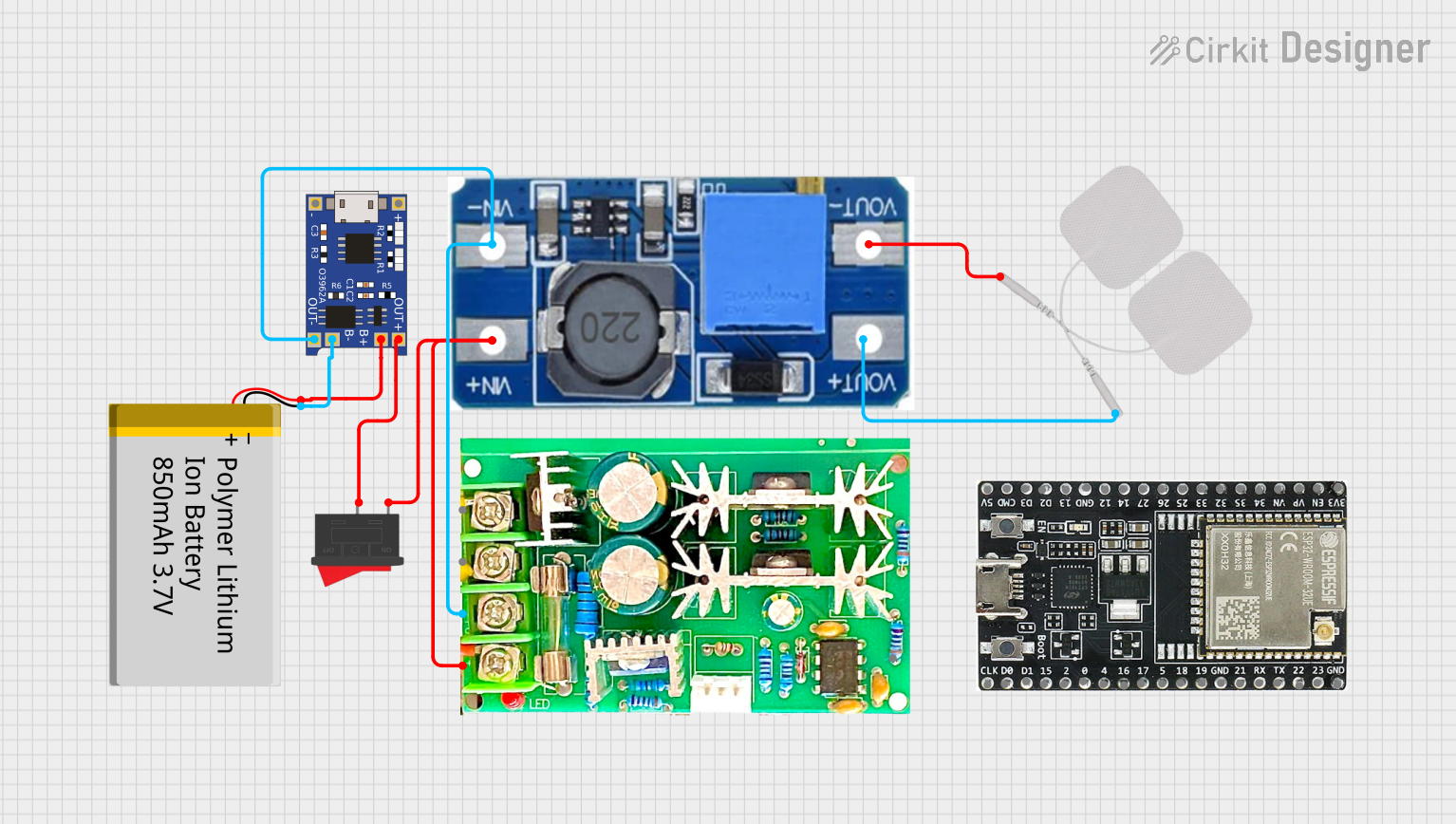
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with TP4056

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications and Use Cases
- Charging single-cell lithium-ion or lithium-polymer batteries
- Power banks and portable battery packs
- USB-powered charging circuits
- Wearable devices and IoT applications
- DIY electronics projects
Technical Specifications
The TP4056 is a highly efficient and compact charging IC. Below are its key technical specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 4.0V to 8.0V |
| Charging Voltage | 4.2V ± 1% |
| Maximum Charging Current | 1A (adjustable via external resistor) |
| Charging Method | Constant Current/Constant Voltage (CC/CV) |
| Operating Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C |
| Standby Current | < 2µA |
| Thermal Regulation | Automatically reduces charge current to prevent overheating |
| Protection Features | Over-voltage, under-voltage lockout, reverse polarity, and thermal shutdown |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The TP4056 IC typically comes in an 8-pin SOP package. Below is the pin configuration and description:
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TEMP | Temperature sense input. Connect to a thermistor for battery temperature monitoring. |
| 2 | PROG | Programs the charging current via an external resistor. |
| 3 | GND | Ground connection. |
| 4 | VCC | Input supply voltage (4.0V to 8.0V). |
| 5 | BAT | Battery connection pin. Connect directly to the positive terminal of the battery. |
| 6 | STDBY | Open-drain status output. Indicates charging status (low = charging, high = standby). |
| 7 | CHRG | Open-drain status output. Indicates charging in progress (low = charging). |
| 8 | CE | Chip enable. Active low. Pull low to enable the IC, or high to disable it. |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the TP4056 in a Circuit
- Power Supply: Connect a regulated DC power supply (4.0V to 8.0V) to the VCC pin. A USB port can also be used as the power source.
- Battery Connection: Connect the positive terminal of the lithium-ion battery to the BAT pin and the negative terminal to GND.
- Programming Charging Current: Use an external resistor (RPROG) connected to the PROG pin to set the desired charging current. The charging current can be calculated using the formula: [ I_{CHG} = \frac{1200}{R_{PROG}} ] where ( R_{PROG} ) is in kΩ and ( I_{CHG} ) is in mA.
- Status Monitoring: Use the CHRG and STDBY pins to monitor the charging status. These pins can be connected to LEDs for visual indication.
- Temperature Monitoring: Connect a thermistor to the TEMP pin for battery temperature monitoring. If not used, connect TEMP to GND.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Ensure the input voltage does not exceed 8.0V to avoid damaging the IC.
- Use a heat sink or proper PCB layout to dissipate heat during high-current charging.
- Place a decoupling capacitor (e.g., 1µF) close to the VCC pin to stabilize the input voltage.
- Use a Schottky diode at the input to prevent reverse polarity damage.
- Avoid using the TP4056 for batteries with a capacity below 500mAh, as the charging current may be too high.
Example: Connecting the TP4056 to an Arduino UNO
The TP4056 can be used with an Arduino UNO to monitor the charging status. Below is an example code snippet:
// TP4056 Charging Status Monitoring with Arduino UNO
// Connect CHRG pin to Arduino pin 2 and STDBY pin to Arduino pin 3
const int chrgPin = 2; // CHRG pin of TP4056
const int stdbyPin = 3; // STDBY pin of TP4056
void setup() {
pinMode(chrgPin, INPUT);
pinMode(stdbyPin, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop() {
int chrgStatus = digitalRead(chrgPin); // Read CHRG pin status
int stdbyStatus = digitalRead(stdbyPin); // Read STDBY pin status
if (chrgStatus == LOW) {
Serial.println("Battery is charging...");
} else if (stdbyStatus == HIGH) {
Serial.println("Battery is fully charged or in standby mode.");
} else {
Serial.println("No battery connected or error.");
}
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before checking again
}
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
The battery is not charging.
- Solution: Check the input voltage at the VCC pin. Ensure it is within the 4.0V to 8.0V range.
- Verify the battery connection to the BAT and GND pins.
- Ensure the CE pin is pulled low to enable the IC.
The IC overheats during charging.
- Solution: Reduce the charging current by increasing the value of the RPROG resistor.
- Improve heat dissipation by adding a heat sink or using a PCB with good thermal management.
The CHRG and STDBY LEDs do not light up.
- Solution: Check the connections to the CHRG and STDBY pins.
- Verify that the LEDs are connected with the correct polarity and have appropriate current-limiting resistors.
The charging current is too high or too low.
- Solution: Recalculate and adjust the RPROG resistor value using the formula provided.
FAQs
Q: Can the TP4056 charge multiple batteries in series?
A: No, the TP4056 is designed for single-cell lithium-ion batteries only. Charging multiple cells in series requires a specialized multi-cell charger.
Q: What happens if the input voltage exceeds 8.0V?
A: The IC may be damaged. Always ensure the input voltage is within the specified range.
Q: Can I use the TP4056 without a thermistor?
A: Yes, if temperature monitoring is not required, connect the TEMP pin to GND.
Q: How do I adjust the charging voltage?
A: The charging voltage is fixed at 4.2V and cannot be adjusted. For other voltages, consider using a different IC.
This concludes the documentation for the TP4056.