
How to Use Sensor Tegangan DC: Examples, Pinouts, and Specs
 Design with Sensor Tegangan DC in Cirkit Designer
Design with Sensor Tegangan DC in Cirkit DesignerIntroduction
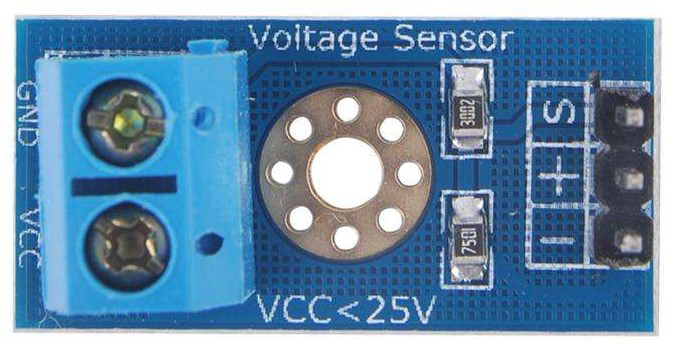
A DC voltage sensor is a device used to measure the voltage level of a direct current (DC) circuit. It provides an output signal that corresponds to the voltage level, enabling monitoring and control in various electronic applications. These sensors are widely used in battery monitoring systems, power supply testing, renewable energy systems, and other applications where accurate voltage measurement is critical.
Explore Projects Built with Sensor Tegangan DC
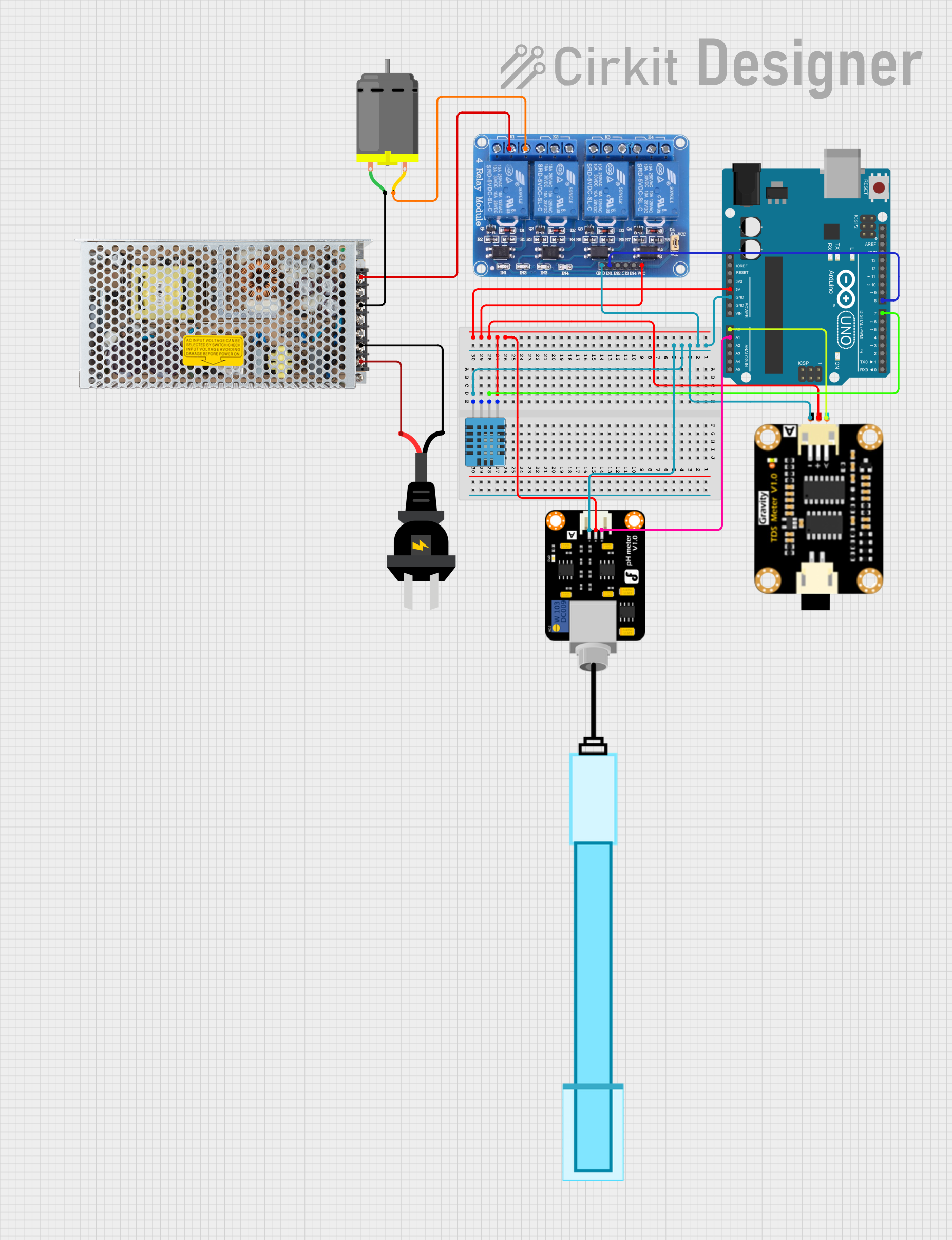
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer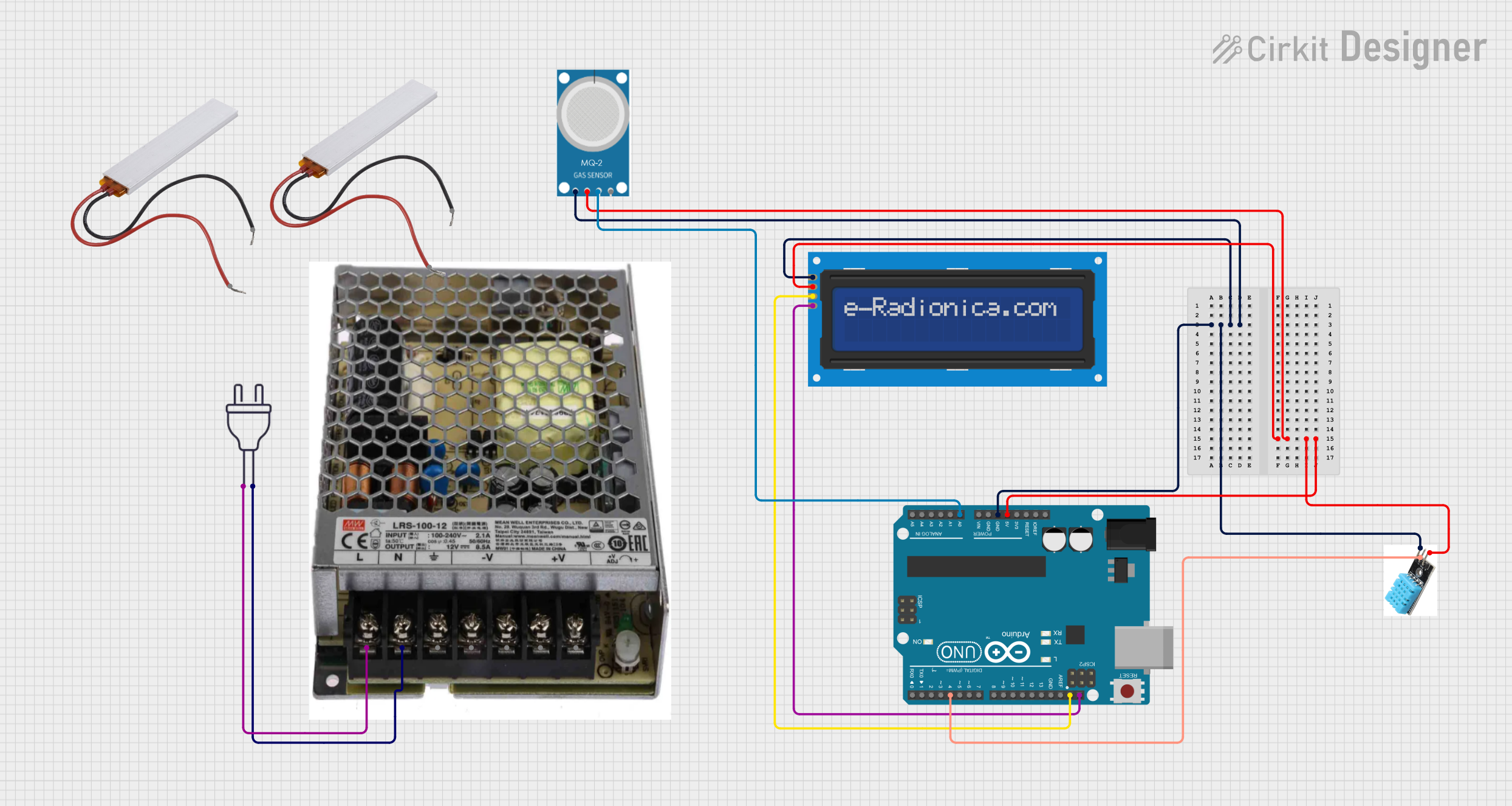
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer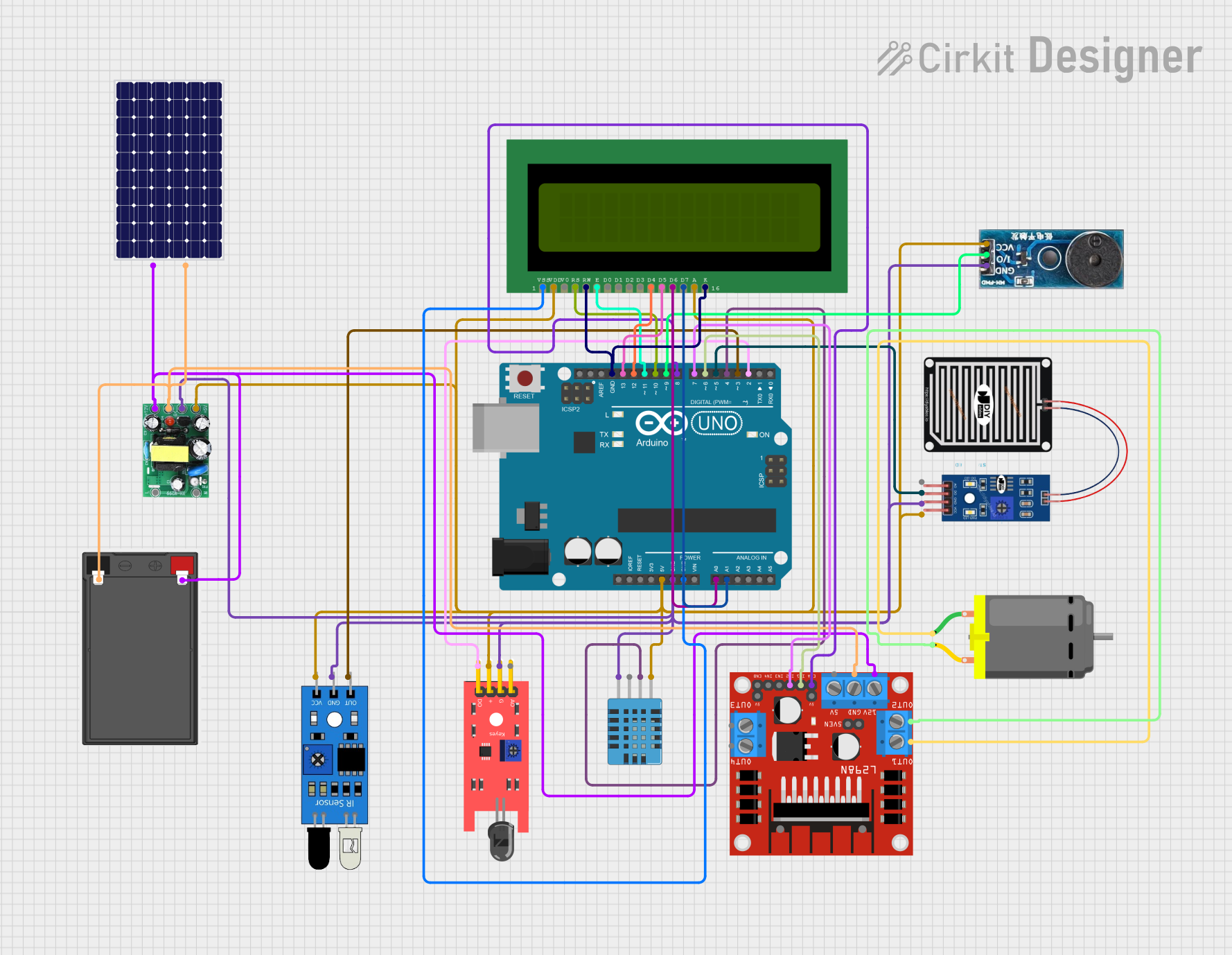
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerExplore Projects Built with Sensor Tegangan DC

 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit Designer
 Open Project in Cirkit Designer
Open Project in Cirkit DesignerCommon Applications:
- Battery voltage monitoring in electric vehicles or backup systems
- Power supply testing and regulation
- Renewable energy systems (e.g., solar panels)
- Industrial automation and control systems
- Microcontroller-based projects (e.g., Arduino, Raspberry Pi)
Technical Specifications
Below are the key technical details for a typical DC voltage sensor:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input Voltage Range | 0V to 25V DC |
| Output Voltage Range | 0V to 5V DC (analog signal) |
| Accuracy | ±1% |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V or 5V DC |
| Operating Current | <10mA |
| Dimensions | 30mm x 20mm x 15mm |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to 85°C |
Pin Configuration and Descriptions
The DC voltage sensor typically has a 4-pin interface. Below is the pinout description:
| Pin | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Power supply input (3.3V or 5V DC) |
| 2 | GND | Ground connection |
| 3 | VOUT | Analog output voltage proportional to input voltage |
| 4 | VIN+ | Positive terminal for the DC voltage to be measured |
Usage Instructions
How to Use the Sensor in a Circuit
- Power the Sensor: Connect the
VCCpin to a 3.3V or 5V DC power source and theGNDpin to the ground of your circuit. - Connect the Voltage Source: Attach the positive terminal of the DC voltage source to the
VIN+pin. Ensure the input voltage does not exceed the sensor's maximum input range (e.g., 25V). - Read the Output: The
VOUTpin provides an analog voltage proportional to the input voltage. This output can be connected to an analog input pin of a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) for further processing.
Important Considerations and Best Practices
- Voltage Divider Circuit: The sensor uses an internal voltage divider to scale down the input voltage. Ensure the input voltage does not exceed the sensor's rated range to avoid damage.
- Calibration: For precise measurements, calibrate the sensor by comparing its output with a known reference voltage.
- Noise Filtering: Use capacitors or software filtering techniques to reduce noise in the output signal.
- Safety: Always disconnect the power supply before making any connections to avoid short circuits or damage.
Example: Using the Sensor with an Arduino UNO
Below is an example code to read the voltage from the sensor using an Arduino UNO:
// Define the analog pin connected to the sensor's VOUT pin
const int sensorPin = A0;
// Define the maximum input voltage of the sensor (e.g., 25V)
const float maxInputVoltage = 25.0;
// Define the maximum output voltage of the sensor (e.g., 5V)
const float maxOutputVoltage = 5.0;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // Initialize serial communication at 9600 baud
}
void loop() {
// Read the analog value from the sensor (0-1023 for 10-bit ADC)
int sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
// Convert the analog value to the corresponding input voltage
float inputVoltage = (sensorValue / 1023.0) * maxInputVoltage;
// Print the measured voltage to the Serial Monitor
Serial.print("Measured Voltage: ");
Serial.print(inputVoltage);
Serial.println(" V");
delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second before the next reading
}
Notes:
- Ensure the Arduino is powered with a compatible voltage (e.g., 5V).
- Use the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE to view the measured voltage.
Troubleshooting and FAQs
Common Issues and Solutions
No Output Signal:
- Cause: Incorrect wiring or no power supply.
- Solution: Double-check all connections and ensure the sensor is powered.
Inaccurate Voltage Readings:
- Cause: Calibration error or noise in the circuit.
- Solution: Calibrate the sensor using a reference voltage and add filtering capacitors if needed.
Output Voltage Exceeds Expected Range:
- Cause: Input voltage exceeds the sensor's maximum range.
- Solution: Ensure the input voltage is within the specified range (e.g., 0-25V).
Arduino Reads Incorrect Values:
- Cause: Incorrect analog reference voltage or scaling factor.
- Solution: Verify the Arduino's analog reference voltage and adjust the scaling factor in the code.
FAQs
Q1: Can this sensor measure AC voltage?
A1: No, this sensor is designed specifically for DC voltage measurement. For AC voltage, use an appropriate AC voltage sensor.
Q2: What happens if the input voltage exceeds 25V?
A2: Exceeding the maximum input voltage can damage the sensor. Use a voltage divider or other protection circuit if higher voltages need to be measured.
Q3: Can I use this sensor with a 3.3V microcontroller?
A3: Yes, the sensor is compatible with 3.3V systems. Ensure the VCC pin is connected to a 3.3V power source.
Q4: How do I improve measurement accuracy?
A4: Calibrate the sensor, use shielded cables to reduce noise, and ensure a stable power supply.
By following this documentation, you can effectively integrate the Sensor Tegangan DC into your projects for accurate and reliable voltage measurement.